Toledo, Ohio facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Toledo
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Downtown Toledo
Lucas County Courthouse
Anthony Wayne Bridge
|
|||||
|
|||||
| Nickname(s):
The Glass City
|
|||||
| Motto(s):
"Laborare est Orare" (To Work is to Pray)
|
|||||
| Country | |||||
| State | |||||
| County | Lucas | ||||
| Founded | 1837 | ||||
| Government | |||||
| • Body | Toledo City Council | ||||
| Area | |||||
| • City | 83.83 sq mi (217.12 km2) | ||||
| • Land | 80.49 sq mi (208.46 km2) | ||||
| • Water | 3.34 sq mi (8.66 km2) | ||||
| Elevation | 604 ft (184 m) | ||||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||||
| • City | 270,871 | ||||
| • Estimate
(2024)
|
265,638 |
||||
| • Rank | US: 86th | ||||
| • Density | 3,365.36/sq mi (1,299.38/km2) | ||||
| • Urban | 497,952 (US: 85th) | ||||
| • Urban density | 2,068.6/sq mi (798.7/km2) | ||||
| • Metro | 606,240 (US: 93rd) | ||||
| Demonym(s) | Toledoan | ||||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) | ||||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | ||||
| ZIP Codes |
Zip codes
|
||||
| Area codes | 419, 567 | ||||
| FIPS code | 39-77000 | ||||
| GNIS ID | 1086537 | ||||
Toledo is a city in Ohio, United States. It is the main city in Lucas County, Ohio. Toledo is located at the western end of Lake Erie, along the Maumee River. It is the fourth-largest city in Ohio. In 2020, about 270,871 people lived there. The larger Toledo area has around 601,000 residents. Toledo is also a big trade center for the Midwest. Its port is the fifth busiest on the Great Lakes.
The city started in 1833 on the Maumee River. It was first part of the Michigan Territory. In 1837, after a disagreement called the Toledo War, it became part of Ohio. Toledo grew quickly after the Miami and Erie Canal was finished in 1845. It also benefited from being on a railway line between New York City and Chicago. Many glass factories came to Toledo in the 1880s. This is how Toledo got its nickname, "The Glass City." Today, Downtown Toledo is being improved with new entertainment areas. The University of Toledo is also located here.
Contents
- Toledo's Past: A Look at History
- Toledo's Location and Surroundings
- Who Lives in Toledo: Population and People
- Toledo's Economy: How People Make a Living
- Arts and Culture in Toledo
- Sports and Recreation in Toledo
- Parks and Fun Places
- Learning in Toledo: Schools and Libraries
- Media: News and Entertainment
- City Services and Travel
- Famous People from Toledo
- Toledo's Sister Cities
- More to Explore
- See also
Toledo's Past: A Look at History
The land where Toledo is now was once home to Native American tribes. These included the Wyandot and the Council of Three Fires (Ojibwe, Potawatomi, and Odawa). French traders came to the area around 1680 for the fur trade. The Odawa tribe moved to this area and lived along the Maumee River. They helped trade between the French and other tribes.
Early American settlers arrived, but many left during the War of 1812. After the war, new settlements began. Two towns, Port Lawrence and Vistula, merged in 1833. They chose the name Toledo. One story says the name was chosen because it was "easy to pronounce" and "pleasant in sound."
The Canal Era and the Toledo War
In 1824, Ohio decided to build the Miami and Erie Canal. This canal would connect Cincinnati to Lake Erie. Many towns wanted to be the end point of the canal. Toledo hoped to be chosen because it would bring a lot of business. The canal was finished in 1843. It helped Toledo grow by connecting it to larger markets.
A small conflict called the Toledo War happened between Ohio and the Michigan Territory from 1835 to 1836. They were fighting over a strip of land that included Toledo. Militias from both sides were sent, but there was almost no fighting. Ohio eventually got the land, and Michigan received a larger part of the Upper Peninsula instead.
As the 1800s continued, railroads became more important than canals. Toledo became a major railroad center. This helped industries like furniture making, carriage building, and glass manufacturing grow. Many immigrant families also moved to Toledo during this time.
Toledo in the 1900s and Beyond
In the 1920s, Toledo's industries grew very fast. However, the city was hit hard by the Great Depression in the 1930s. To help people find jobs, many large projects were built. These included parts of the Toledo Zoo and the Toledo Museum of Art.
After World War II, many African Americans moved to Toledo for factory jobs. They built strong communities. Later, some of these communities faced challenges due to city changes and new highways. As American manufacturing changed, Toledo lost many jobs.
In the 2000s, Toledo began to improve its downtown area. Old buildings were fixed up and turned into restaurants, homes, and art galleries. Local artists also added murals and public art.
In August 2014, Toledo faced a water crisis. A bloom of toxic blue-green algae in Lake Erie made the city's water unsafe. The Ohio National Guard helped deliver bottled water to residents. The water warning lasted for nearly three days.
More recently, in 2018, a company invested $700 million in East Toledo for a new steel plant. This plant was completed in 2020 and created many jobs.
Toledo's Location and Surroundings

Toledo is located where the Maumee River meets Maumee Bay, which is part of Lake Erie. The city is built on what was once a large wetland called the Great Black Swamp. This is why Toledo is sometimes called "Frog Town." Toledo is also part of a special natural area called the Oak Openings Region.
Toledo is within a 250-mile drive of many large cities. These include Detroit, Cleveland, Columbus, Cincinnati, Pittsburgh, Indianapolis, and Chicago. It is also close to Toronto, Ontario in Canada.
City Areas and Nearby Towns

Toledo has many different neighborhoods. The Old West End is famous for its beautiful old houses.
- Beverly
- Birmingham
- Downtown
- East Toledo
- Old Orchard
- Old West End
- Point Place
- Warehouse District
In 1936, the first building completely covered in glass was built in Toledo. It was for the Owens-Illinois Glass Company. This building was a big step in modern building design.
The Toledo area includes several nearby towns. Some of these are Maumee, Perrysburg, and Sylvania. There are also suburbs in Michigan, like Lambertville.
Toledo's Weather and Climate
Toledo has four clear seasons. Summers are warm and humid, with temperatures often reaching 90°F (32°C) or higher. Winters are cold and snowy. January is usually the coldest month, with temperatures sometimes dropping below 0°F (-18°C). Spring is often the wettest time of year. Toledo gets about 37 inches (94 cm) of snow each year.
Understanding Algae Blooms in Lake Erie
Since the late 1990s, harmful blooms of cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, have returned to Lake Erie. These blooms can harm fish and make the water look and smell bad. They can also create "dead zones" where there isn't enough oxygen for life. Sometimes, the algae blooms are so thick they can slow down boats.
These large blooms happen because of agricultural runoff (water from farms) that flows into the lake. This runoff contains phosphorus, which acts like a fertilizer for the algae. Warmer weather in the summer and fall also helps the algae grow faster. Because Toledo is so close to Lake Erie, its citizens are affected every year. Algae blooms can cause water bills to go up and hurt local businesses like tourism and fishing.
Who Lives in Toledo: Population and People
Toledo's population has changed over the years. In 1870, many people from Germany and Ireland lived in Toledo.
| Historical racial composition | 2020 | 2010 | 2000 | 1990 | 1970 | 1940 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 62.6% | 64.8% | 70.2% | 77.0% | 85.7% | 94.8% |
| —Non-Hispanic | 58.7% | 61.4% | Unk | 75.1% | 84.0% | n/a |
| Black or African American | 27.4% | 27.2% | 23.5% | 19.7% | 13.8% | 5.2% |
| Hispanic or Latino (of any race) | 8.6% | 7.4% | 5.5% | 4.0% | 1.9% | n/a |
| Asian | 1.3% | 1.1% | 1.0% | 1.0% | 0.2% | − |
In 2010, Toledo had 287,128 people. It is the main city in the Toledo Metropolitan Area, which had 651,429 people. This made it the sixth-largest metropolitan area in Ohio.
By the 2020 census, Toledo's population was 270,871. About 60.6% of the people were White, and 28.1% were African American. About 8.8% of the population was Hispanic or Latino. The average household had 2.27 people.
In 2021, the average household income in Toledo was $41,671. About 24.5% of the population lived in poverty. For education, 87.1% of people 25 or older had finished high school.
Crime Trends in Toledo
In the early 2010s, Toledo saw a rise in serious crime. In 2020, the number of homicides (murders) reached 61, the highest in 39 years. In 2021, there were 70 homicides, setting another record. Toledo was one of 12 major U.S. cities that had record high homicides in 2021.
Toledo's Economy: How People Make a Living

Before cars became popular, Toledo was an important port city on the Great Lakes. Later, it became known for making things, especially cars. Companies like General Motors and Chrysler had factories here. Jeep was the biggest employer in Toledo for many years.
Today, healthcare is the biggest employer in Toledo, thanks to the University of Toledo. Several large companies have their main offices in the Toledo area. These include Dana Holding Corporation, Owens Corning, and Libbey Incorporated.
Toledo is called the "Glass City" because of its long history of making glass. This includes windows, bottles, and glass art. The Toledo Museum of Art has a large collection of glass art. Many big glass companies started here.
Toledo is also home to Jeep headquarters and two production plants. During World War II, Toledo's factories made important products for the military, like the Willys Jeep.
In the 2000s, Toledo saw growth in "green jobs" related to solar energy. The University of Toledo received money for solar energy research. Companies like Xunlight and First Solar opened plants in the area.
Arts and Culture in Toledo
Art and Performances

Toledo has many places for classical arts. These include the Toledo Opera, Toledo Symphony Orchestra, and Toledo Ballet. There are also theaters like the Stranahan Theater and the historic Valentine Theatre.
The Toledo Museum of Art is a famous building in the Old West End. It has a concert hall called The Peristyle, where the Toledo Symphony Orchestra performs. The museum also has a special Glass Pavilion, which opened in 2006. Toledo was the first city in Ohio to have a "One Percent for Art" program. This means many public art pieces, like sculptures and murals, can be found around the city.
Music Scene
Toledo has a rich music history, especially in jazz. Famous jazz musicians like Art Tatum and Jon Hendricks came from Toledo. Other well-known singers and musicians with Toledo roots include Teresa Brewer and Anita Baker.
Museums to Explore
The National Museum of the Great Lakes is located near downtown Toledo. You can also visit the Col. James M. Schoonmaker, a former lake freighter that is now a museum.
The Imagination Station is a hands-on science museum downtown. It's a great place to learn through play.
Tony Packo's Cafe is a famous restaurant in the Hungarian neighborhood. It's known for its hot dogs and walls covered with signed hot dog buns from celebrities.
Sports and Recreation in Toledo
| Club | Sport | League | Venue |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toledo Mud Hens | Baseball | International League | Fifth Third Field |
| Toledo Walleye | Ice hockey | ECHL | Huntington Center |
| Glass City Rollers | Roller derby | WFTDA | Glass City Center |
| Toledo Villa FC | Soccer | USL League Two | Paul Hotmer Field |
| Glass City Wranglers | Basketball | BSL | Maumee Valley Country Day School |
| Toledo Rockets | 15 collegiate teams | NCAA Division I Mid-American Conference | Glass Bowl Savage Arena Scott Park Baseball Complex |
Toledo has several sports teams. The Toledo Mud Hens are a baseball team, and the Toledo Walleye play ice hockey. The Toledo Rockets are the college sports teams for the University of Toledo.
Toledo Speedway is a local auto racetrack. It hosts stock car races and concerts. The Automobile Racing Club of America (ARCA) has its main office in Toledo.
The Inverness Club is a famous golf course in Toledo. It has hosted many major golf tournaments, including the 1993 PGA Championship and the 2021 Solheim Cup.
Parks and Fun Places
The Toledo Metroparks system has over 12,000 acres (4,856 hectares) of land. It includes the University/Parks Trail for biking and the Toledo Botanical Garden.
The Toledo Zoo was the first zoo to have a "hippoquarium" exhibit. In 2014, USA Today named it the #1 zoo in the country. The R. A. Stranahan Arboretum is a 47-acre (19-hectare) tree garden run by the University of Toledo.
Hollywood Casino Toledo opened in 2012.
Learning in Toledo: Schools and Libraries
Colleges and Universities

The University of Toledo is a large public research university. It is the biggest college in Toledo. Other colleges with campuses in Toledo include Tiffin University and Owens Community College.
For health studies, there is the University of Toledo College of Medicine and Life Sciences and Mercy College of Ohio, a nursing school.
Schools for Kids
The Toledo City School District runs public schools in most of the city. It is the fourth-largest school district in Ohio. Some high schools in this district include Bowsher High School and Waite High School.
Toledo also has public charter schools and many private schools. The Roman Catholic Diocese of Toledo operates Catholic schools in the area. Notable private high schools include Maumee Valley Country Day School and Central Catholic High School.
Public Libraries
The Toledo Lucas County Public Library was rated as a 4-star library in 2009. It is one of the biggest-spending libraries in the United States.
Media: News and Entertainment
Newspapers and Magazines
The Blade is Toledo's daily newspaper. It started in 1835. The Toledo City Paper is a weekly newspaper about arts and entertainment. Other local weekly papers include the West Toledo Herald and the Toledo Journal.
TV Stations
Toledo has several TV stations. These include:
- WTOL 11 (CBS)
- WTVG 13 (ABC)
- WNWO 24 (NBC)
- WUPW 36 (Fox)
- PBS stations WBGU 27 and WGTE 30
Radio Stations
There are 23 full-power radio stations in Toledo. They play different types of music like Contemporary Christian, Country, and Rock. There are also news/talk and sports radio stations. WGTE-FM is Toledo's NPR station.
City Services and Travel
Getting Around: Roads and Bridges
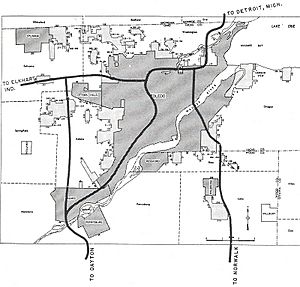

Three major interstate highways pass through Toledo. Interstate 75 (I-75) goes north and south. The Ohio Turnpike carries I-80/I-90, connecting Toledo to Chicago and Cleveland.
There are also two other interstate highways. Interstate 475 is a bypass around the city. Interstate 280 connects the Ohio Turnpike to I-75. The Veterans' Glass City Skyway is part of I-280. This tall bridge has a glass-covered tower that lights up at night. The Anthony Wayne Bridge is another famous bridge in Toledo, known as the "High-Level Bridge."
Public Transportation
Local bus service is provided by the Toledo Area Regional Transit Authority (TARTA). For people with disabilities, there are special services called TARPS. Long-distance bus services are available from Greyhound Lines and Barons Bus Lines.
Airports
Toledo Express Airport is the main airport for the city. It is located in nearby suburbs. Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport is also about 45 miles north. There are also smaller airports for general aviation.
Trains
Amtrak, the national passenger rail system, serves Toledo. Trains like the Lake Shore Limited stop at Martin Luther King, Jr. Plaza. This station was built in 1950. Toledo was the busiest Amtrak station in Ohio in 2011. Freight trains also operate in Toledo.
In the past, Toledo was a very important center for railroads. Many different railroad companies moved goods to and from Toledo's factories. Toledo also used to have streetcars and interurban railways that connected it to other towns.
Healthcare Services
ProMedica is a large healthcare organization that started in Toledo. It has grown to be one of the biggest non-profit healthcare systems in the United States. ProMedica has 13 hospitals in Northwest Ohio and Southeast Michigan, including ProMedica Toledo Hospital.
Mercy Health - St. Vincent Medical Center is Toledo's first hospital. It is a top center for treating high-risk mothers and babies. It is also a Level I Trauma Center for children and adults.
Toledo also has 18 community health centers that provide healthcare services to local neighborhoods.
Water Supply
Toledo gets its drinking water from Lake Erie. The city's Water Treatment Division cleans about 80 million gallons of water every day for about 500,000 people.
In August 2014, a problem with microcystis toxins from algae blooms made Toledo's water unsafe. About 400,000 people were told not to use tap water. The Ohio National Guard helped deliver water. The ban was lifted after three days.
Famous People from Toledo
Many notable people have come from Toledo, Ohio.
Toledo's Sister Cities
Toledo has a special connection with other cities around the world. It was twinned with Toledo, Spain, in 1931. This was the first "sister city" relationship in the United States.
Toledo's sister cities are:
 Beqaa Valley, Lebanon
Beqaa Valley, Lebanon Coburg, Germany
Coburg, Germany Coimbatore, India
Coimbatore, India Delmenhorst, Germany
Delmenhorst, Germany Hyderabad, Pakistan
Hyderabad, Pakistan Londrina, Brazil
Londrina, Brazil Nanchong, China
Nanchong, China Poznań, Poland
Poznań, Poland Qinhuangdao, China
Qinhuangdao, China Szeged, Hungary
Szeged, Hungary Tanga, Tanzania
Tanga, Tanzania Toledo, Spain
Toledo, Spain Toyohashi, Japan
Toyohashi, Japan
More to Explore
- Auto-Lite strike
- Baseball parks of Toledo, Ohio
- Glassmen Drum and Bugle Corps, a famous drum and bugle corps
- Greater Toledo
- Outbreak of green-blue algae in Lake Erie
- Roman Catholic Diocese of Toledo
- Toledo Area Regional Transit Authority, local bus transportation
- Toledo City League, high school sports league
- USS Toledo, three ships named after the city
See also
 In Spanish: Toledo (Ohio) para niños
In Spanish: Toledo (Ohio) para niños
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |