Atlantic City, New Jersey facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Atlantic City, New Jersey
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
City
|
|||||
|
Sunset on the beach at Atlantic City
Ocean Casino Resort
Hard Rock Hotel & Casino Atlantic City
Bally's Atlantic City
Nightlife on the Atlantic City Boardwalk
|
|||||
|
|||||
| Nicknames: | |||||
| Motto(s):
Consilio et Prudentia (Latin)
"By Counsel and Wisdom" |
|||||
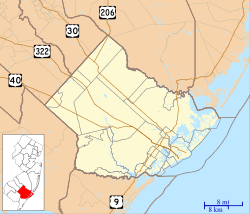
Location of Atlantic City in Atlantic County highlighted in red (left). Inset map: Location of Atlantic County in New Jersey highlighted in orange (right).
|
|||||
| Country | |||||
| State | |||||
| County | Atlantic | ||||
| Incorporated | May 1, 1854 | ||||
| Government | |||||
| • Type | Faulkner Act (mayor–council) | ||||
| • Body | City Council | ||||
| Area | |||||
| • City | 17.21 sq mi (44.59 km2) | ||||
| • Land | 10.76 sq mi (27.87 km2) | ||||
| • Water | 6.45 sq mi (16.72 km2) 37.50% | ||||
| Area rank | 165th of 565 in state 8th of 23 in county |
||||
| Elevation | 7 ft (2 m) | ||||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||||
| • City | 38,497 | ||||
| • Estimate
(2023)
|
38,464 | ||||
| • Rank | 61st of 565 in state 2nd of 23 in county |
||||
| • Density | 3,577.8/sq mi (1,381.4/km2) | ||||
| • Density rank | 188th of 565 in state 4th of 23 in county |
||||
| • Urban | 294,921 (US: 138th) | ||||
| • Urban density | 1,810.7/sq mi (699.1/km2) | ||||
| • Metro | 274,534 (US: 179th) | ||||
| Time zone | UTC−05:00 (EST) | ||||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 (Eastern (EDT)) | ||||
| ZIP Codes |
08401–08406
|
||||
| Area code(s) | 609 | ||||
| FIPS code | 3400102080 | ||||
| GNIS feature ID | 0885142 | ||||
Atlantic City, also known as A.C., is a fun seaside resort city in Atlantic County, New Jersey. It's famous for its casinos, exciting nightlife, the Boardwalk, and beautiful Atlantic Ocean beaches. Many people call it the "Las Vegas of the East Coast."
Atlantic City was the inspiration for the U.S. version of the board game Monopoly. The game uses many street names and places from Atlantic City. In 1976, people in New Jersey voted to allow casinos in Atlantic City. The first casino opened two years later. From 1921 to 2004, and again from 2013 to 2018, Atlantic City hosted the Miss America pageant.
In 2020, about 38,497 people lived in Atlantic City. The city was officially formed on May 1, 1854. It is located on Absecon Island and is surrounded by other towns and the Atlantic Ocean.
Contents
- Exploring Atlantic City's Past
- Where is Atlantic City?
- Who Lives in Atlantic City?
- Atlantic City's Economy
- Arts and Culture in Atlantic City
- Sports in Atlantic City
- Parks and Outdoor Fun
- How Atlantic City is Governed
- Fire Department Services
- Police Department Services
- Learning in Atlantic City
- Media and News
- City Infrastructure
- Famous People from Atlantic City
- See also
Exploring Atlantic City's Past

Before Atlantic City was founded, the Lenape Native American tribe used the area as a summer home. European settlers likely arrived around 1783.
How Atlantic City Grew in the 1800s
In 1850, the area that is now Atlantic City began to be developed as a resort town. It was named Atlantic City in 1853. Because of its location between marshlands and islands, developers saw it as a great spot for a resort. The first hotel, the Belloe House, was built in 1853.
In 1854, Atlantic City became an official city. That same year, train service started, connecting the city to Philadelphia. This made it much easier for people to visit. The Absecon Lighthouse also began construction in 1855.
By 1874, nearly 500,000 passengers were coming to Atlantic City by train each year. Jonathan Pitney, known as the "Father of Atlantic City," helped make the railroad happen. He wanted Atlantic City to be a health resort. The United States Hotel, one of the first and largest hotels, opened around this time.
The first boardwalk was built in 1870. It helped keep sand out of hotel lobbies. At first, it was taken down each year. But it became so popular that it was made longer and wider over time. Before a big hurricane in 1944, the boardwalk was about 7 miles long.
In 1870, the first road connecting the city to the mainland was finished. By 1878, another railroad line was built because so many people wanted to visit. Large, luxurious hotels with modern features were built all over town.
In 1883, salt water taffy was invented in Atlantic City. The story says a storm flooded a taffy shop with ocean water. The owner sold the "salt water taffy," and the name stuck!
Atlantic City in the 1900s

The early 1900s saw a huge building boom in Atlantic City. Many small boarding houses were replaced by grand hotels like the Marlborough-Blenheim and the Traymore Hotel. These hotels were known for their unique designs and modern features.
More large hotels, such as the Brighton, Chelsea, and Ritz Carlton, were built along the boardwalk. By 1930, the Claridge, a 24-story building known as the "Skyscraper by the Sea," also opened.
The 1920s are often called Atlantic City's "golden age" for tourism. During Prohibition (1919-1933), when alcohol was illegal across the U.S., Atlantic City became famous as "The World's Playground." Alcohol was easy to find, and this made the city even more popular.
Mayor Edward L. Bader helped build the city's airport and high school. He also started the idea for the Convention Center, now known as Boardwalk Hall, and helped create the Miss America competition.
In May 1929, a famous meeting of powerful figures from across America took place in Atlantic City.
From the 1930s to the 1960s, Atlantic City was a hub for nightclub entertainment. Famous venues like the 500 Club and Club Harlem drew many visitors.
After World War II, Atlantic City faced challenges. More people had cars, so they didn't stay as long. Air conditioning and swimming pools at home made beach resorts less appealing. Also, cheaper flights allowed people to travel to places like Miami Beach. Many grand hotels closed or were torn down.
Casinos Bring New Life
To help the city recover, New Jersey voters approved casino gambling for Atlantic City in 1976. The first casino, Resorts International, opened on May 26, 1978. It was the first legal casino in the eastern United States.
More casinos were built along the Boardwalk and in the marina area. While gambling brought new visitors, it didn't solve all the city's problems right away. Famous boxer Mike Tyson fought many of his matches in Atlantic City in the 1980s, which helped bring national attention to the city. By the end of the 1980s, Atlantic City was a very popular tourist spot.
Atlantic City in the 2000s

In 2018, the U.S. Supreme Court made a big decision that allowed states to legalize sports betting. New Jersey quickly passed a law, and Atlantic City casinos opened sportsbooks.
However, new casinos in nearby states caused Atlantic City's tourism to decline. In 1999, a new road called the Atlantic City-Brigantine Connector was built to help visitors get to the city's marina district. This led to the opening of the Borgata casino in 2003, which brought new excitement.
Despite new developments, some planned mega-casinos were never built due to economic challenges. Several casinos closed in 2014, including the Atlantic Club, Showboat, Revel, and Trump Plaza. The Trump Taj Mahal also closed in 2016. Many of these properties have since reopened under new names or with new purposes. For example, Revel reopened as Ocean Casino Resort in 2018, and the Trump Taj Mahal became the Hard Rock Hotel & Casino Atlantic City.
In October 2012, "Superstorm Sandy" hit Atlantic City. It caused some flooding and power outages but did not severely damage the main tourist areas.
Helping the Community with Food
Atlantic City has faced challenges with access to fresh food. For a long time, the closest full-service supermarket was about 3 miles away in Ventnor City. Efforts to build a new supermarket have been ongoing. As of late 2023, there was only one main supermarket in the city. A new ShopRite supermarket was planned, with groundbreaking in October 2021, but construction faced delays.
Where is Atlantic City?
Atlantic City covers about 17.21 square miles (44.59 square kilometers). About 10.76 square miles (27.87 square kilometers) is land, and 6.45 square miles (16.72 square kilometers) is water.
The city is located on Absecon Island, which is about 8.1 miles (13 kilometers) long. Other towns like Ventnor City, Margate City, and Longport are also on this island. Atlantic City is about 60 miles (97 kilometers) southeast of Philadelphia and 125 miles (201 kilometers) south of New York City.
Atlantic City's Weather
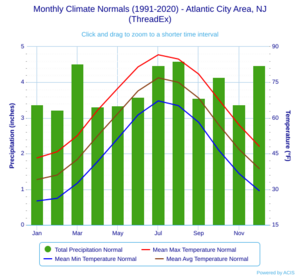
Atlantic City has a humid subtropical climate. This means it has warm, somewhat humid summers and cool winters. It rains throughout the year. In summer, a cool sea breeze often blows, but sometimes it can get very hot. In winter, it can get very cold and windy. The area usually gets 12 to 18 inches of snow each winter. February is often the snowiest month.
| Climate data for Atlantic City, New Jersey (downtown), 1981–2010 normals, extremes 1874–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 72 (22) |
77 (25) |
84 (29) |
91 (33) |
95 (35) |
99 (37) |
102 (39) |
104 (40) |
94 (34) |
91 (33) |
80 (27) |
74 (23) |
104 (40) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 59.3 (15.2) |
59.9 (15.5) |
68.4 (20.2) |
77.3 (25.2) |
83.7 (28.7) |
89.7 (32.1) |
93.5 (34.2) |
91.8 (33.2) |
86.3 (30.2) |
78.9 (26.1) |
70.1 (21.2) |
62.4 (16.9) |
95.3 (35.2) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 41.8 (5.4) |
43.5 (6.4) |
49.6 (9.8) |
57.6 (14.2) |
66.6 (19.2) |
75.7 (24.3) |
81.3 (27.4) |
80.2 (26.8) |
74.8 (23.8) |
65.0 (18.3) |
55.8 (13.2) |
46.3 (7.9) |
61.6 (16.4) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 29.2 (−1.6) |
30.9 (−0.6) |
36.9 (2.7) |
45.5 (7.5) |
54.5 (12.5) |
64.3 (17.9) |
70.0 (21.1) |
69.7 (20.9) |
63.5 (17.5) |
52.5 (11.4) |
42.9 (6.1) |
33.5 (0.8) |
49.5 (9.7) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 11.3 (−11.5) |
16.3 (−8.7) |
22.4 (−5.3) |
33.8 (1.0) |
44.3 (6.8) |
53.7 (12.1) |
61.4 (16.3) |
60.1 (15.6) |
50.5 (10.3) |
39.2 (4.0) |
29.0 (−1.7) |
19.0 (−7.2) |
10.1 (−12.2) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −4 (−20) |
−9 (−23) |
8 (−13) |
15 (−9) |
33 (1) |
45 (7) |
52 (11) |
48 (9) |
37 (3) |
27 (−3) |
10 (−12) |
−7 (−22) |
−9 (−23) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.08 (78) |
2.87 (73) |
4.02 (102) |
3.39 (86) |
3.22 (82) |
2.68 (68) |
3.31 (84) |
3.92 (100) |
3.08 (78) |
3.47 (88) |
3.35 (85) |
3.62 (92) |
40.01 (1,016) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 4.5 (11) |
6.7 (17) |
1.1 (2.8) |
0.3 (0.76) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0.2 (0.51) |
3.7 (9.4) |
16.5 (42) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 9.3 | 9.0 | 10.5 | 10.9 | 10.4 | 8.7 | 8.4 | 8.0 | 7.7 | 7.6 | 8.9 | 10.4 | 109.8 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 2.9 | 2.8 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 1.7 | 8.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 69.5 | 69.0 | 66.9 | 66.4 | 70.7 | 72.9 | 73.9 | 75.7 | 76.4 | 74.8 | 72.8 | 70.6 | 71.6 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 150.8 | 157.9 | 204.5 | 218.9 | 243.9 | 266.2 | 276.3 | 271.3 | 227.6 | 200.5 | 147.4 | 133.8 | 2,499.1 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 50 | 53 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 60 | 61 | 64 | 61 | 58 | 49 | 46 | 56 |
| Source: NOAA (relative humidity and sun 1961–1990 and snow at Atlantic City Int'l) | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Atlantic City Marina, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1873–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 72 (22) |
77 (25) |
86 (30) |
91 (33) |
95 (35) |
99 (37) |
102 (39) |
104 (40) |
94 (34) |
91 (33) |
80 (27) |
74 (23) |
104 (40) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 60.0 (15.6) |
60.3 (15.7) |
67.8 (19.9) |
77.0 (25.0) |
83.8 (28.8) |
90.2 (32.3) |
93.0 (33.9) |
90.8 (32.7) |
86.2 (30.1) |
79.2 (26.2) |
69.3 (20.7) |
62.2 (16.8) |
95.0 (35.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 41.6 (5.3) |
43.1 (6.2) |
48.4 (9.1) |
57.1 (13.9) |
65.7 (18.7) |
75.0 (23.9) |
80.3 (26.8) |
79.2 (26.2) |
74.0 (23.3) |
64.9 (18.3) |
54.9 (12.7) |
46.6 (8.1) |
60.9 (16.1) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 35.8 (2.1) |
37.2 (2.9) |
42.6 (5.9) |
51.4 (10.8) |
60.3 (15.7) |
69.9 (21.1) |
75.4 (24.1) |
74.8 (23.8) |
69.3 (20.7) |
59.3 (15.2) |
49.0 (9.4) |
40.9 (4.9) |
55.5 (13.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 29.9 (−1.2) |
31.3 (−0.4) |
36.9 (2.7) |
45.6 (7.6) |
54.9 (12.7) |
64.8 (18.2) |
70.5 (21.4) |
70.3 (21.3) |
64.6 (18.1) |
53.6 (12.0) |
43.1 (6.2) |
35.1 (1.7) |
50.1 (10.1) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 12.7 (−10.7) |
16.2 (−8.8) |
22.9 (−5.1) |
34.8 (1.6) |
44.9 (7.2) |
54.5 (12.5) |
63.4 (17.4) |
62.4 (16.9) |
52.4 (11.3) |
40.0 (4.4) |
29.4 (−1.4) |
21.4 (−5.9) |
11.0 (−11.7) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −4 (−20) |
−9 (−23) |
8 (−13) |
15 (−9) |
33 (1) |
45 (7) |
52 (11) |
48 (9) |
37 (3) |
27 (−3) |
10 (−12) |
−7 (−22) |
−9 (−23) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.09 (78) |
3.27 (83) |
4.27 (108) |
3.36 (85) |
3.10 (79) |
3.23 (82) |
3.75 (95) |
4.13 (105) |
3.56 (90) |
4.25 (108) |
3.44 (87) |
4.17 (106) |
43.62 (1,108) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 9.9 | 9.5 | 10.9 | 10.6 | 10.6 | 9.3 | 9.0 | 7.9 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 8.8 | 10.9 | 114.1 |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Atlantic City, NJ Ocean Water Temperature, 1911–present normals | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 39.7 (4.3) |
38.5 (3.6) |
41.9 (5.5) |
48.7 (9.3) |
56.4 (13.6) |
64.7 (18.2) |
68.9 (20.5) |
73.1 (22.8) |
72.2 (22.3) |
64.1 (17.8) |
53.6 (12.0) |
45.2 (7.3) |
55.7 (13.2) |
| Source: NCEI | |||||||||||||
Local Plants and Nature
Atlantic City's natural plant life would mostly be Cordgrass and Coastal Prairie. This means you'd find tough grasses that can grow near the ocean.
Who Lives in Atlantic City?
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1860 | 687 | — | |
| 1870 | 1,043 | 51.8% | |
| 1880 | 5,477 | 425.1% | |
| 1890 | 13,055 | 138.4% | |
| 1900 | 27,838 | 113.2% | |
| 1910 | 46,150 | 65.8% | |
| 1920 | 50,707 | 9.9% | |
| 1930 | 66,198 | 30.6% | |
| 1940 | 64,094 | −3.2% | |
| 1950 | 61,657 | −3.8% | |
| 1960 | 59,544 | −3.4% | |
| 1970 | 47,859 | −19.6% | |
| 1980 | 40,199 | −16.0% | |
| 1990 | 37,986 | −5.5% | |
| 2000 | 40,517 | 6.7% | |
| 2010 | 39,558 | −2.4% | |
| 2020 | 38,497 | −2.7% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 38,464 | −2.8% | |
| Population sources: 1860–2000 1860–1920 1870 1880–1890 1890–1910 1860–1930 1940–2000 2000 2010 2020 |
|||
In 2010, Atlantic City had 39,558 people. About 27.3% of households had children under 18. The average household had 2.5 people. The median age was 36.3 years old.
Atlantic City's Economy
The Tourism District
In 2010, New Jersey's Governor announced a plan to help Atlantic City's tourism. In 2011, the Atlantic City Tourism District was created. This state-run area includes the boardwalk casinos, marina casinos, outlet stores, and Bader Field. The goal was to make the area safer and more beautiful to attract new businesses and visitors.
The district includes areas like the Marina District, Ducktown, Chelsea, and Gardner's Basin. It also covers main roads leading into the city.
Casinos and Gaming Fun
The history of gambling in Atlantic City goes back to the 1920s. In 1976, New Jersey voters decided to allow casinos only in Atlantic City. Resorts Atlantic City was the first casino to open in May 1978.
Atlantic City is known as the "Gambling Capital of the East Coast." It currently has nine large casinos. In 2011, the casinos employed about 33,000 people and had 28.5 million visitors. They brought in $3.3 billion in gaming money.
After a tough economic period and new casinos opening in nearby states, several Atlantic City casinos closed in 2014. However, some have reopened under new names. For example, the Trump Taj Mahal became the Hard Rock Hotel & Casino Atlantic City. In 2022, the nine casinos made $2.79 billion, which was a 9% increase from the year before.
Current Casinos in Atlantic City
| Casino | Opening date | Casino Operator | Theme | Hotel rooms | Section of city | Total Gaming Space |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resorts | May 26, 1978 | DGMB Casinos | Roaring Twenties | 942 | Uptown | 100,000 sq ft |
| Caesarsa | June 26, 1979 | Caesars Entertainment | Roman Empire | 1,141 | Midtown | 145,000 sq ft |
| Bally'sa | December 29, 1979 | Bally's Corporation | Modern | 1,214 | Midtown | 225,756 sq ft |
| Harrah's | November 27, 1980 | Caesars Entertainment | Marina Waterfront | 2,587 | Marina | 160,000 sq ft |
| Tropicana | November 26, 1981 | Caesars Entertainment | Old Havana | 2,364 | Downbeach | 125,935 sq ft |
| Golden Nugget | June 19, 1985 | Landry's | Gold Rush Era | 717 | Marina | 74,252 sq ft |
| Borgata | July 2, 2003 | MGM Resorts | Tuscany | 2,767 | Marina | 161,000 sq ft |
| Hard Rock | June 27, 2018 | Hard Rock International | Rock and roll | 2,032 | Uptown | 167,000 sq ft |
| Ocean | June 27, 2018 | AC Beachfront, L.L.C. | Ocean | 1,900 | Uptown | 130,000 sq ft |
| Total | 15,602 | 1,144,943 sq ft |
- a The Wild Wild West Casino, which opened on July 2, 1997, and has an American Old West theme, was part of Bally's Atlantic City until 2020, when it became part of Caesars.
Casinos That Changed Names
| Old Casino Name | New Name |
|---|---|
| ACH Casino Resort | Atlantic Club Casino Hotel |
| Atlantic City Hilton (Original) | Trump's Castle |
| Atlantic City Hilton | ACH Casino Resort |
| Bally's Grand | The Grand |
| Bally's Park Place | Bally's Atlantic City |
| Brighton Casino | Sands Atlantic City |
| Del Webb's Claridge | Claridge |
| Golden Nugget (Original) | Bally's Grand |
| Park Place | Bally's Park Place |
| Harrah's at Trump Plaza | Trump Plaza |
| ... Hotel & Casino | Permanent casino license denied; renamed Atlantis Casino |
| The Grand | The Atlantic City Hilton |
| Trump's Castle | Trump Marina |
| Trump Marina | Golden Nugget |
| Revel Atlantic City | Ocean Casino Resort |
| Trump Taj Mahal | Hard Rock Hotel & Casino Atlantic City |
Casinos That Have Closed
| Casino | Opening Date | Closing Date | What Happened to the Property |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trump Taj Mahal | April 2, 1990 | October 10, 2016 | This casino closed after not reaching an agreement with its workers. It reopened in 2018 as the Hard Rock Hotel and Casino Atlantic City. |
| Trump Plaza | May 14, 1984 | September 16, 2014 | This casino was sold for a very low price and was later torn down on February 17, 2021. |
| Revel | April 2, 2012 | September 2, 2014 | This casino closed but was later sold and reopened as the Ocean Resort Casino in June 2018. |
| Showboat | April 2, 1987 | August 31, 2014 | Stockton University bought the property but later sold it. The building reopened in July 2016 as a hotel without a casino. |
| Atlantic Club | December 12, 1980 | January 13, 2014 | The building and its contents were sold. |
| Trump Marina | June 19, 1985 | May 23, 2011 | The building was sold and renamed the Golden Nugget Atlantic City. |
| Sands | August 31, 1980 | November 11, 2006 | The building was torn down in 2007. The site is now an empty lot. |
| Claridge | July 20, 1981 | December 30, 2002 | It now operates as a hotel without a casino. |
| Trump World's Fair | May 15, 1996 | October 3, 1999 | The building was torn down and replaced by new stores. |
| Atlantis Casino | April 14, 1981 | July 4, 1989 | This casino closed and was later sold to become part of the Trump Plaza. |
Casinos That Were Never Built
| Casino | What Happened to the Property |
|---|---|
| Camelot | Cancelled; currently an empty lot |
| Dunes Atlantic City | Never finished; now an empty lot |
| Hilton (Original) | Casino license denied; current site of Golden Nugget Atlantic City |
| Le Jardin | Cancelled; currently Borgata |
| Margaritaville Marina Casino | Cancelled; current site of Golden Nugget Atlantic City |
| Mirage Atlantic City | Cancelled; currently Borgata |
| MGM Grand Atlantic City | Cancelled; currently an empty lot |
| Penthouse Casino | Never built; currently an empty lot |
| Resorts Taj Mahal | Cancelled; current site of Hard Rock Hotel and Casino Atlantic City |
| Sahara Atlantic City | Cancelled; now a parking lot |
The Famous Boardwalk
The Atlantic City Boardwalk opened on June 26, 1870. It was the first boardwalk in the world! At 5.5 miles (8.9 kilometers) long, it's also one of the longest and busiest boardwalks.
The Boardwalk stretches from Absecon Inlet in the north to the city limit, then continues into Ventnor City. Along the Boardwalk, you'll find casinos, hotels, shops, restaurants, and fun attractions. Some famous spots include Boardwalk Hall and the Ripley's Believe It or Not! museum.
In October 2012, Hurricane Sandy damaged the northern part of the boardwalk, but the main section in front of the casinos was mostly fine.
The first pier on the boardwalk, Applegate's Pier, opened in 1884. It later became the Central Pier, which is still open today. The most famous pier was Steel Pier, which opened in 1898. It was known as "The Showplace of the Nation." It closed in 1978 but was rebuilt and is now an amusement pier.
Captain John L. Young opened the "Young's Million Dollar Pier" in 1906. It was once a rival to Steel Pier. After some changes, it became a shopping mall. In 2006, it was renamed "The Pier Shops at Caesars," then "Playground Pier" in 2015. In September 2023, it was renamed "ACX1 Studios" for film and entertainment studios. It plans to reopen in summer 2024 with shops, restaurants, and studios.
Garden Pier, near the Ocean Casino Resort, used to have a movie theater. Now it's home to the Atlantic City Historical Museum.
Shopping Fun
Atlantic City has many places to shop, often inside or next to the casino resorts. Some casinos have smaller themed shopping areas.
Major shopping spots include:
- Playground Pier: An indoor shopping center with an underwater theme. It has high-end stores.
- Tanger Outlets The Walk: An outdoor outlet mall with many different stores. It opened in 2003 and is still growing.
- The Quarter at Tropicana: An indoor shopping center at the Tropicana casino. It has an old Havana theme with over 40 stores, restaurants, and nightclubs.
Convention Centers
Boardwalk Hall is a large arena on the boardwalk. It was the main convention center until the Atlantic City Convention Center opened in 1997. The new Convention Center has a huge amount of space for shows and meetings. Both are managed by the Atlantic City Convention & Visitors Authority.
Arts and Culture in Atlantic City
Monopoly Game Connection
Atlantic City is famous for being featured in the U.S. version of the board game Monopoly. The properties on the game board are named after real places in and near Atlantic City. The game's creator, Charles Darrow, copied a homemade board that used Atlantic City street names.
Interestingly, "Marvin Gardens" on the board is a misspelling of the real place, "Marven Gardens." The game company, Parker Brothers, apologized for this mistake in 1995, but the spelling was never changed on the board.
Some of the places on the board have changed over time. Illinois Avenue was renamed Martin Luther King Jr. Boulevard in the 1980s. St. Charles Place no longer exists.
The "Short Line" in the game might refer to an old streetcar line or bus route. The "Electric Company" and "Water Works" are based on the real utility companies in Atlantic City.
Fun Attractions to See
Atlantic City has always had unique attractions. In the early 1900s, the Steel Pier featured horse diving, where horses would dive into a pool! It also had other exciting acts.
Rolling chairs have been a boardwalk tradition since 1876. These wicker chairs on wheels are pushed by attendants, like a rickshaw, along the boardwalk. A tram service also started in 2015.
The Absecon Lighthouse is a tall lighthouse in Atlantic City. It's the tallest in New Jersey and the third tallest made of stone in the U.S. It was first lit in 1857. Even though it's not used for navigation anymore, its light still shines every night. Nearby is Gardner's Basin, with the Atlantic City Aquarium and shops.
Just 2 miles south of Atlantic City, in Margate City, is Lucy the Elephant. Lucy is a six-story building shaped like an elephant! Built in 1882, she was meant to attract tourists. Over the years, Lucy has been a restaurant, office, and even a tavern. She was saved from demolition in 1970 and is now a museum.
The Miss America Pageant
Atlantic City was the original home of the Miss America competition. It hosted the event from 1921 until 2004, and again from 2013 to 2018. The pageant started to extend the tourist season after Labor Day. The first winner, Margaret Gorman, was crowned in 1921. The pageant has been on TV since 1954.
Boardwalk Empire TV Show
The TV show Boardwalk Empire on HBO made Atlantic City's history popular again. The show is set in Atlantic City during the Prohibition era (the 1920s). It's based on a book about a historical figure named Enoch Johnson, who is called "Enoch Thompson" in the show.
Festivals and Events
Atlantic City hosts many exciting events:
- The TidalWave Music Festival happens on the beach in August, featuring country music stars.
- The North to Shore Festival began in June 2023, with music and entertainment across New Jersey, including Atlantic City.
- The Adjacent Music Festival, focused on emo and pop-punk music, had its first event on the Atlantic City beach in May 2023.
- The Frantic City indie and punk festival started in 2022 at the Orange Loop Amphitheater.
- An LGBTQ event called the "Miss'd America Pageant" is held every year. It features drag queens in a similar style to the Miss America pageant.
- Since 2003, Atlantic City has hosted Thunder over the Boardwalk, an annual airshow. This event attracts over 750,000 visitors each year.
Religious Gatherings
- A Ratha Yatra festival is held by the ISKCON of Central Jersey with the local Hindu community.
- The Faith and Law Enforcement March is organized by the Atlantic City Police Department with local religious groups.
The Orange Loop Neighborhood
The Orange Loop is a neighborhood near the beach in Atlantic City. It's known for its live music venues like Anchor Rock Club. The area gets its name from the orange streets on a traditional Monopoly gameboard.
Sports in Atlantic City
| Club | Sport | League | Venue | Year(s) |
| Atlantic City Blackjacks | Arena football | AFL | Boardwalk Hall | 2019 |
| Atlantic City FC | Soccer | NPSL | Silver Eagle Stadium | 2018–present |
| Atlantic City Diablos | Soccer | NPSL | St. Augustine College Preparatory School | 2007–2008 |
| Atlantic City Boardwalk Bullies | Ice hockey | ECHL | Boardwalk Hall | 2001–2005 |
| Atlantic City CardSharks | Indoor football | NIFL | Boardwalk Hall | 2004 |
| Atlantic City Surf | Baseball | Can-Am League | Bernie Robbins Stadium | 1998–2008 |
| Atlantic City Seagulls | Basketball | USBL | Atlantic City High School | 1996–2001 |
The Atlantic City Race Course was a horse racing track that operated from 1946 to 2015. The ShopRite LPGA Classic is a women's golf tournament held near Atlantic City since 1986.
Professional Boxing Matches
Atlantic City has hosted many professional boxing matches since 1887. In the 1980s, it was a major spot for big fights, sometimes even competing with Las Vegas. Famous boxers like Mike Tyson fought many of their matches here.
Parks and Outdoor Fun
Atlantic City is one of only five towns in New Jersey that offers free public access to its ocean beaches, with lifeguards on duty.
How Atlantic City is Governed
Local Government Structure
Atlantic City is run by a Mayor and a City Council. The Mayor and nine Council members are elected for four-year terms. Six Council members represent different areas (wards), and three serve the city as a whole (at-large). The City Council makes laws and decisions for the city.
As of 2024, the Mayor is Democrat Marty Small Sr.. The City Council includes members like Council President Aaron "Sporty" Randolph and Council Vice President Kaleem Shabazz. In 2024, Maria Lacca became one of two Republicans on the City Council.
City and State Agencies
- New Jersey Casino Control Commission: This state agency makes sure casinos operate fairly and honestly.
- New Jersey Division of Gaming Enforcement: This group checks casino money, licenses employees, and handles complaints.
- Casino Reinvestment Development Authority (CRDA): Founded in 1984, the CRDA uses money from casinos to fund projects that help Atlantic City and other parts of New Jersey.
- Atlantic City Convention and Visitors Authority (ACCVA): This group used to promote the city and manage Boardwalk Hall and the Convention Center. In 2011, it became part of the CRDA.
- Atlantic City Special Improvement District (SID): This group worked to improve the city's business areas. In 2011, it also became part of the CRDA.
Fire Department Services
| Operational area | |
|---|---|
| Country | United States |
| State | New Jersey |
| City | Atlantic City |
| Agency overview | |
| Established | April 4, 1904 |
| Staffing | Career |
| Fire chief | Scott Evans |
| EMS level | BLS First Responder |
| IAFF | 198 |
| Facilities and equipment | |
| Divisions | 1 |
| Battalions | 1 |
| Stations | 6 |
| Engines | 7 |
| Ladders | 3 |
| Rescues | 1 |
| HAZMAT | 1 |
| USAR | 1 |
| Fireboats | 2 |
| Light and air | 1 |
The Atlantic City Fire Department (ACFD) helps protect the city from fires and provides emergency medical services. The ACFD has six fire stations located throughout the city.
Fire Station Locations
-
Station 5; Bader Field. Engine 5, Air Cascade Unit 1
Police Department Services
The city is protected by the Atlantic City Police Department. They handle about 150,000 calls each year. The Chief of Police is James A. Sarkos.
Learning in Atlantic City
The Atlantic City School District serves students from pre-kindergarten through high school. In the 2020–21 school year, the district had 11 schools and 6,553 students.
Students from nearby towns like Brigantine, Longport, Margate City, and Ventnor City also attend Atlantic City High School. Students can also choose to attend the Atlantic County Institute of Technology or the Charter-Tech High School for the Performing Arts.
Our Lady Star of the Sea Regional School is a Catholic elementary school in the city. Nearby colleges include Atlantic Cape Community College and Stockton University.
Media and News
Newspapers and Magazines
- The Press of Atlantic City
Radio Stations
- WEHA 88.7 FM – Gospel
- WAYV 95.1 FM – Top 40
- WTTH 96.1 FM – Urban AC
- WFPG 96.9 FM – AC (Lite Rock 96.9)
- WENJ 97.3 FM – Sports
- WTKU 98.3 FM – Classic hits (Kool 98.3)
- WZBZ 99.3 FM – Rhythmic (The Buzz)
- WZXL 100.7 FM – Rock (The Rock Station)
- WLRB 102.7 FM – Contemporary Christian (K-Love)
- WMGM 103.7 FM – Active rock (WMGM Rocks)
- WSJO 104.9 FM – Top 40 (SoJo 104.9)
- WPUR 107.3 FM – Country (Cat Country 107.3)
- WWJZ 640 AM – Religious
- WMID 1340 AM – Oldies
- WOND 1400 AM – News/Talk
- WPGG 1450 AM – Talk
- WBSS 1490 AM – Regional Mexican
Television Stations
Atlantic City is part of the Philadelphia TV market. There are six stations licensed in the area.
- WACP Channel 4 Atlantic City (Independent)
- WMGM-LP Channel 7 Atlantic City (Silent)
- WMGM-TV Channel 40 Wildwood (Justice Network)
- W45CP-D Channel 45 Atlantic City (Daystar)
- W48DP-D Channel 48 Atlantic City (EICB TV)
City Infrastructure
Getting Around Atlantic City
Atlantic City has over 100 miles of roads. Three main roads lead into the city: Black Horse Pike, White Horse Pike, and the Atlantic City Expressway.
Public Transportation Options
NJ Transit trains connect Atlantic City to Philadelphia. The Atlantic City Rail Terminal is located at the Convention Center.
The Atlantic City Bus Terminal is a hub for local and long-distance buses, including NJ Transit and Greyhound. Greyhound offers express service to Atlantic City from cities like New York City and Philadelphia.
Within the city, NJ Transit buses run on 13 different routes. The Atlantic City Jitney Association (ACJA) also offers service on four routes and shuttles.
Flying to Atlantic City
Commercial flights serve Atlantic City International Airport, which is about 9 miles (14 kilometers) northwest of the city. Many travelers also fly into larger airports like Philadelphia International Airport. The historic Bader Field airport in Atlantic City is now closed and will be redeveloped.
Healthcare Services

The AtlantiCare Regional Medical Center is a health system in Atlantic City. It has two hospitals and offers specialized care like a cancer institute and a heart institute.
City Utilities
South Jersey Industries provides natural gas to the city. Marina Energy operates two power plants that serve casinos. Another plant, the Midtown Thermal Control Center, provides chilled water for hotels along the Boardwalk.
Atlantic City Electric provides electricity to Atlantic City.
The Jersey-Atlantic Wind Farm, opened in 2005, is the first onshore coastal wind farm in the United States. It uses wind to create electricity.
Famous People from Atlantic City
Many interesting people have connections to Atlantic City:
- Jack Abramoff (born 1958), a former lobbyist.
- James Avery (1945–2013), actor known as Uncle Phil from The Fresh Prince of Bel-Air.
- Harry Bacharach (1873–1947), served as mayor of Atlantic City multiple times.
- Edward L. Bader (1874–1927), mayor from 1920 to 1927, known for his contributions to the city's development.
- Joseph Carleton Beal (1900–1967), co-writer of the Christmas song Jingle Bell Rock.
- Benjamin Burnley (born 1978), lead singer of the band Breaking Benjamin.
- Greg Buttle (born 1954), a linebacker who played for the New York Jets.
- Carole Byard (1941–2017), a visual artist and illustrator of children's books.
- Harry Carroll (1892–1962), songwriter for "I'm Always Chasing Rainbows".
- Rosalind Cash (1938–1995), an actress.
- Rocky Castellani (1926–2008), a middleweight boxer.
- Jack Collins (born 1943), a long-serving Speaker of the New Jersey General Assembly.
- Stuart Dischell (born 1954), a poet and professor.
- Sidney Drell (1926–2016), a theoretical physicist.
- Robert Ettinger (1918–2011), known as "the father of cryonics".
- Frank S. Farley (1901–1977), a politician who served in the New Jersey Legislature.
- Chris Ford (born 1949), a basketball coach for several NBA teams.
- Helen Forrest (1917–1999), a famous singer from the Swing Era.
- John J. Gardner (1845–1921), a U.S. Representative and former mayor of Atlantic City.
- Patsy Garrett (1921–2015), an actress.
- William Green (born 1979), an NFL running back.
- Marjorie Guthrie (1917–1983), a dancer and wife of folk musician Woody Guthrie.
- Celestine Tate Harrington (1956–1998), a quadriplegic street musician.
- Pete Hunter (born 1980), a cornerback who played in the NFL.
- Candy Jones (1925–1990), a fashion model and radio host.
- Marvin Josephson (1927–2022), a talent agent who founded ICM Partners.
- Allan Kaprow (1927–2006), a painter and pioneer in performance art.
- Amy Kennedy (born 1978), an educator and politician.
- Marie Kibler (1912–1978), an artistic gymnast who competed in the 1936 Summer Olympics.
- Pinky Kravitz (1927–2015), a radio broadcaster and journalist.
- Jacob Lawrence (1917–2000), an artist known for depicting African-American life.
- Bill Libby (1927–1984), a sportswriter and biographer.
- James J. McCullough (born 1942), a politician who served in the New Jersey Senate.
- Don McGahn (born 1968), a former White House Counsel.
- Bob Merrill (1921–1998), a songwriter and screenwriter.
- Arnold Newman (1918–2006), a famous photographer.
- John P. O'Neill (1952–2001), an FBI specialist who died in the September 11th attacks.
- Joshua Ozersky (1967–2015), a food writer and historian.
- Chris Pallies (1957–2019), a professional wrestler.
- Reese Palley (1922–2015), an entrepreneur and art dealer.
- Joseph B. Perskie (1885–1957), a Justice of the New Jersey Supreme Court.
- Monique Samuels, a television personality.
- Jeremy Slate (1926–2006), an actor and songwriter.
- George Smathers (1913–2007), a U.S. Senator from Florida.
- Larry Steele (1913–1980), an impresario known for his shows at Club Harlem.
- Dave Thomas (1932–2002), the founder of Wendy's fast-food restaurant.
- Jean Webster (1935–2011), who ran a soup kitchen in Atlantic City.
- Jim Whelan (1948–2017), a politician who served as Mayor of Atlantic City and in the New Jersey Senate.
- Norman Joseph Woodland (1921–2012), the inventor of the barcode.
See also
 In Spanish: Atlantic City (Nueva Jersey) para niños
In Spanish: Atlantic City (Nueva Jersey) para niños
- Atlantic City Sandpipers
- Chicken Bone Beach
- Kentucky Avenue Renaissance Festival