Manufacturing facts for kids
Manufacturing is all about making things! It's the process of turning raw materials into finished products that people can use or buy. This can be done by hand, with machines, tools, or even special chemical processes.
When we talk about manufacturing, we usually mean making things on a large scale in factories. Think about how raw materials like metal or plastic are changed into useful items. These finished items might be sold to other companies to make even more complex products, like aircraft or cars. Or, they might go to stores where you can buy them directly.
The manufacturing process involves many steps. It starts with designing the product and choosing the right materials. Then, these materials are changed using different methods to become the final product. Today, manufacturing includes all the steps needed to create and put together a product's parts. Some industries, like those making computer chips or steel, call this process fabrication.
Manufacturing is closely linked to engineering and industrial design. Big manufacturing companies around the world include General Motors, Toyota, Samsung, and Volkswagen Group.
Contents
The History of Making Things
People have been making things for a very long time!
Early Human Manufacturing
Even our ancient ancestors made stone tools millions of years ago. They would hit a hard stone, like flint, with another stone to create sharp edges. These sharp tools helped them hunt and gather food. Later, they learned to make even finer tools using a method called pressure flaking. During the Neolithic period, people started polishing stone tools, like axes, to make them smoother and stronger.
Later, people discovered how to get metal from rocks. This was a huge step!
- Copper was one of the first metals used. People learned to heat copper ore in special ovens (kilns) to get the metal out.
- Bronze came next. It's a mix of copper and tin. Bronze was much stronger than stone and could be poured into molds to make detailed objects. This helped improve things like shipbuilding.
- The Iron Age began when people learned to make tools and weapons from iron and steel. Iron was harder to work with than bronze, but it was even stronger.
Ancient civilizations also made big advances. The wheel, for example, was invented in Mesopotamia (modern Iraq) around 5,000 BC. The Egyptians mass-produced papyrus paper and pottery, selling them across the Mediterranean.
Manufacturing in the Middle Ages
The Middle Ages brought new ideas and ways of making things.
- Papermaking, which started in China, came to the Middle East and then to Europe. Paper was made from old cloth rags. This led to cheaper paper, which helped the development of printing.
- Blast furnaces became common in France in the 1400s. These furnaces could melt iron at very high temperatures, allowing for the casting of cannons.
- The stocking frame, invented in 1598, was a machine that could knit stockings much faster than by hand.
The Industrial Revolutions
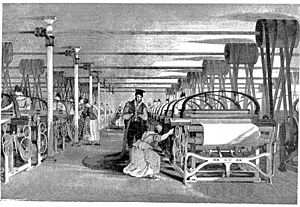
The Industrial Revolution was a huge change in how things were made, starting in Europe and the United States around the late 1700s.
- People stopped making things by hand and started using machine tools in factories.
- New ways of making chemicals and iron were developed.
- Steam power and water power became very important.
- The textile industry (making cloth) was one of the first to use these new methods.
Later, the Second Industrial Revolution (after 1870) brought even more changes:
- New ways to make steel were invented.
- Mass production and assembly lines became common. This meant making many identical products quickly.
- Electricity started to be used in factories.
- The light bulb allowed factories to work day and night.
Modern Manufacturing
The early 1900s saw factories become electrified. Electric motors were easier to use and maintain than old steam engines. This made factories much more efficient and productive.
Mass production really took off in the 1910s and 1920s, thanks to Henry Ford and his Ford Motor Company. He used electric motors with the idea of a continuous production line. Ford also used special machines that could do many tasks at once, making cars like the Ford Model T very quickly and cheaply.
In the 1930s, a new way of manufacturing called lean manufacturing (also known as just-in-time manufacturing) was developed in Japan. This method focuses on reducing waste and making things only when they are needed. It helps companies make products faster and respond quickly to customer needs. This idea spread around the world and is still used today.
Countries That Make the Most Goods
Here are the top countries that produce the most manufactured goods, based on their value in US dollars:
| Rank | Country or region | Millions of $US | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| World | 16,350,207 | 2021 | |
| 1 | 4,975,614 | 2022 | |
| 2 | 2,497,132 | 2021 | |
| 3 | 1,025,092 | 2021 | |
| 4 | 752,742 | 2022 | |
| 5 | 456,064 | 2022 | |
| 6 | 429,058 | 2022 | |
| 7 | 314,701 | 2022 | |
| 8 | 306,009 | 2022 | |
| 9 | 287,713 | 2022 | |
| 10 | 265,231 | 2022 | |
| 11 | 259,314 | 2022 | |
| 12 | 241,873 | 2022 | |
| 13 | 213,557 | 2022 | |
| 14 | 202,566 | 2022 | |
| 15 | 200,552 | 2022 | |
| 16 | 162,160 | 2019 | |
| 17 | 161,698 | 2022 | |
| 18 | 160,032 | 2022 | |
| 19 | 150,631 | 2022 | |
| 20 | 133,867 | 2022 | |
| 21 | 120,308 | 2022 | |
| 22 | 115,189 | 2022 | |
| 23 | 101,318 | 2022 | |
| 24 | 101,217 | 2022 | |
| 25 | 100,162 | 2022 | |
| 26 | 95,696 | 2022 | |
| 27 | 95,218 | 2022 | |
| 28 | 91,299 | 2022 | |
| 29 | 82,660 | 2022 | |
| 30 | 79,351 | 2022 | |
| 31 | 76,139 | 2022 | |
| 32 | 74,920 | 2022 | |
| 33 | 73,788 | 2022 | |
| 34 | 69,696 | 2022 | |
| 35 | 67,996 | 2022 | |
| 36 | 67,938 | 2022 | |
| 37 | 64,246 | 2022 | |
| 38 | 60,989 | 2022 | |
| 39 | 58,237 | 2014 | |
| 40 | 51,622 | 2022 | |
| 41 | 49,714 | 2022 | |
| 42 | 49,658 | 2021 | |
| 43 | 49,317 | 2022 | |
| 44 | 48,796 | 2022 | |
| 45 | 46,654 | 2022 | |
| 46 | 44,716 | 2022 | |
| 47 | 39,865 | 2020 | |
| 48 | 39,582 | 2022 | |
| 49 | 31,254 | 2022 | |
| 50 | 30,514 | 2022 |
Images for kids
- Manufacturing Engineering
- Agile manufacturing
- American system of manufacturing
- British factory system of manufacturing
- Craft or guild system
- Fabrication
- Flexible manufacturing
- Just-in-time manufacturing
- Lean manufacturing
- Mass customization (2000s) – 3D printing, design-your-own web sites for sneakers, fast fashion
- Mass production
- Ownership
- Packaging and labeling
- Prefabrication
- Putting-out system
- Rapid manufacturing
- Reconfigurable manufacturing system
- Soviet collectivism in manufacturing
- History of numerical control
See also
 In Spanish: Manufactura para niños
In Spanish: Manufactura para niños