Prince William County, Virginia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Prince William County
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| County of Prince William | |||
|
|||
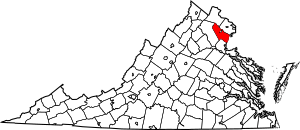
Location within the Commonwealth of Virginia
|
|||
| Country | |||
| State | |||
| Founded | 1731 | ||
| Named for | Prince William, Duke of Cumberland | ||
| County seat | Manassas | ||
| Largest community | Dale City | ||
| Government | |||
| • Body | Board of Supervisors | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 348 sq mi (900 km2) | ||
| • Land | 336 sq mi (870 km2) | ||
| • Water | 12 sq mi (30 km2) 3.5% | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • Total | 482,204 |
||
| • Density | 1,400/sq mi (500/km2) | ||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | ||
| Area code | 703/571 | ||
| FIPS code | 51153 | ||
| GNIS feature ID | 1480161 | ||
| U.S. House | 7th, 10th | ||
| Virginia Senate | 13th, 28th, 29th, 36th, 39th | ||
| Virginia House | 2nd, 13th, 31st, 40th, 51st, 87th | ||
| Website | http://www.pwcgov.org/ | ||
Prince William County is a large county in Virginia, located right next to the Potomac River. It's a busy place, and in 2020, it was the second most populated county in Virginia. The main town, or county seat, is Manassas.
Prince William County is part of Northern Virginia, which is close to Washington, D.C.. This means it's part of a big metropolitan area. In 2020, it was also one of the wealthiest counties in the United States!
Contents
- History of Prince William County
- Geography and Location
- Economy and Jobs
- Education in Prince William County
- Population and People
- Sports and Recreation
- Museums and History
- Libraries for Learning
- Parks and Outdoor Fun
- Transportation and Travel
- Communities in Prince William County
- Notable People from Prince William County
- Other Important Places to Visit
- See also
History of Prince William County
Long ago, before Europeans arrived, the Doeg lived in this area. They were a group of Native Americans who spoke the Algonquian language. In 1608, when English explorers like John Smith explored the Potomac River, they found a Doeg village called Pemacocack. This name meant "plenty of fish." Sadly, by 1700, the Doeg people had left their villages due to European diseases and conflicts.
How the County Was Formed
Prince William County was officially created in 1731 by the Virginia colony. It was formed from parts of Stafford County and King George County. At first, it was much larger! It included areas that are now Arlington, Fairfax, Fauquier, and Loudoun counties. It also included cities like Alexandria and Manassas. Over time, these areas became their own separate places.
The county was named after Prince William, Duke of Cumberland. He was the third son of King George II of Great Britain.
Life in the Early County
In 1790, most people in the county were white, but many Black people were enslaved. The area used to have large tobacco farms. However, the soil became tired, and farming changed to different crops. After the American Revolution, more enslaved people in Virginia became free. This was because some white people believed in the new ideas of freedom.
For many years, Prince William County was mostly rural and agricultural. People lived mainly around Manassas, which had a big railroad junction, and near Occoquan and Woodbridge by the Potomac River.
Growth and Modern Times
Starting in the late 1930s, more people moved to the county as new homes were built. The population grew very fast after 1960. This was because more federal, military, and business jobs came to Northern Virginia. By 2000, it was the third most populated area in Virginia.
Between 2000 and 2010, the population jumped by over 43%! Prince William County became the first county in Virginia where no single racial or ethnic group was the majority. Many people moved here from Central and South America, Africa, and Asia.
Today, the county is home to important places like the Marine Corps Heritage Museum and the Hylton Performing Arts Center. There are also plans for an American Wartime Museum. The county has also hosted events to remember the famous First Battle of Manassas and Second Battle of Manassas from the Civil War.
Geography and Location
Prince William County covers about 348 square miles. Most of this is land, with about 12 square miles of water. It shares borders with several other counties and the Potomac River. Across the Potomac River is Charles County, Maryland.
Neighboring Areas
- Loudoun County, Virginia - North
- Fairfax County, Virginia - Northeast
- Charles County, Maryland - Southeast
- Stafford County, Virginia - South
- Fauquier County, Virginia - West
- Manassas, Virginia - Center (a city completely surrounded by the county)
- Manassas Park, Virginia - Center (another city surrounded by the county)
Protected Natural Areas
Prince William County is home to several important natural and historical sites:
- Featherstone National Wildlife Refuge
- Manassas National Battlefield Park
- Occoquan Bay National Wildlife Refuge
- Prince William Forest Park
Economy and Jobs
Prince William County has a strong economy with many job opportunities.
Top Employers in the County
Here are some of the biggest employers in Prince William County:
| # | Employer | # of Employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Prince William County Public Schools | 1,000 and over |
| 2 | U.S. Department of Defense | 1,000 and over |
| 3 | Prince William County Government | 1,000 and over |
| 4 | Walmart | 1,000 and over |
| 5 | Morale, Welfare and Recreation | 1,000 and over |
| 6 | Sentara Healthcare | 1,000 and over |
| 7 | Wegmans Food Markets | 500 to 999 |
| 8 | Minnieland Private Day School | 500 to 999 |
| 9 | Northern Virginia Community College | 500 to 999 |
| 10 | Target Corporation | 500 to 999 |
The county is also a major hub for data centers, which are buildings that house many computers and servers for the internet.
Education in Prince William County
Prince William County offers many educational options for students of all ages.
Schools for Younger Students
Prince William County Public Schools is the second largest school system in Virginia. It has many elementary, middle, and high schools. There are also special schools for different learning needs. The school system even has its own TV station, PWCS-TV!
Students living on Marine Corps Base Quantico attend schools run by the Department of Defense Education Activity (DoDEA).
Colleges and Universities
For higher education, students can attend:
- George Mason University
- National University
- Northern Virginia Community College
- Strayer University
Catholic Schools
The Diocese of Arlington also runs several schools in the county. These include schools for pre-kindergarten through middle school, and Pope John Paul the Great Catholic High School for grades 9-12.
Population and People
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 11,615 | — | |
| 1800 | 12,733 | 9.6% | |
| 1810 | 11,311 | −11.2% | |
| 1820 | 9,419 | −16.7% | |
| 1830 | 9,330 | −0.9% | |
| 1840 | 8,144 | −12.7% | |
| 1850 | 8,129 | −0.2% | |
| 1860 | 8,565 | 5.4% | |
| 1870 | 7,504 | −12.4% | |
| 1880 | 9,180 | 22.3% | |
| 1890 | 9,805 | 6.8% | |
| 1900 | 11,112 | 13.3% | |
| 1910 | 12,026 | 8.2% | |
| 1920 | 13,660 | 13.6% | |
| 1930 | 13,951 | 2.1% | |
| 1940 | 17,738 | 27.1% | |
| 1950 | 22,612 | 27.5% | |
| 1960 | 50,164 | 121.8% | |
| 1970 | 111,102 | 121.5% | |
| 1980 | 144,636 | 30.2% | |
| 1990 | 215,686 | 49.1% | |
| 2000 | 280,813 | 30.2% | |
| 2010 | 402,002 | 43.2% | |
| 2020 | 482,204 | 20.0% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790–1960 1900–1990 1990–2000 2010 2020 |
|||
Population in 2020
In 2020, Prince William County had a population of 482,204 people. The county is known for its diverse population. Many different racial and ethnic groups live here.
| Group | Population in 2010 | Population in 2020 | Percentage in 2010 | Percentage in 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White (not Hispanic) | 195,656 | 185,048 | 48.67% | 38.38% |
| Black or African American (not Hispanic) | 78,492 | 94,939 | 19.53% | 19.69% |
| Asian (not Hispanic) | 29,986 | 49,836 | 7.46% | 10.34% |
| Mixed Race (not Hispanic) | 13,783 | 26,221 | 3.43% | 5.44% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 81,460 | 121,524 | 20.26% | 25.20% |
| Total Population | 402,002 | 482,204 | 100.00% | 100.00% |
Note: The U.S. Census counts Hispanic/Latino people as an ethnic group, separate from racial categories. People who are Hispanic/Latino can be of any race.
More About the Population
In 2010, there were over 130,000 households in Prince William County. Most of these were families. About 42% of households had parents living with their children under 18.
About 29% of the county's population is under 18 years old. Only about 6.5% are 65 or older. The average age in the county is about 33 years old.
In 2009, the average household income was about $89,785. This shows that Prince William County is a prosperous area. Only a small percentage of the population lives below the poverty line.
Sports and Recreation
Prince William County offers various sports and recreational activities.
Local Sports Teams
Northern Virginia FC is a minor league soccer team based in Woodbridge, Virginia. They are connected to D.C. United, a professional soccer team in Washington, D.C.
Historic Racing Track
The Old Dominion Speedway was a famous race track in Manassas. It opened in 1948 and hosted the first commercial drag race on the East Coast. It was also a stop for NASCAR races in the past. The speedway closed in 2012 due to noise complaints.
Museums and History
Prince William County has several museums where you can learn about history and other interesting topics.

- The National Museum of the Marine Corps in Triangle, Virginia is free to visit.
- The Historic Preservation Division of Prince William County runs five other museums:
- Rippon Lodge Historic Site
- Brentsville Historic Centre
- Bristoe Station Battlefield Heritage Park
- Lucasville Historic Site
- Ben Lomond Historic Site
Libraries for Learning
The Prince William Public Library System serves Prince William County and the cities of Manassas and Manassas Park. It has several full-service branches and smaller neighborhood branches, making books and resources available throughout the area.
Parks and Outdoor Fun
Prince William County is full of beautiful parks and outdoor spaces.
National Parks
Two National Parks are located within the county:
- Prince William Forest Park: This park was created in 1936. It's the largest protected natural area in the Washington, D.C. metropolitan region, covering over 15,000 acres.
- Manassas National Battlefield Park: This park is north of Manassas. It protects the sites of two major Civil War battles: the First Battle of Manassas (July 21, 1861) and the Second Battle of Manassas (August 28-30, 1862). These battles are also known as the first and second battles of Bull Run.
County Parks and Recreation
The Prince William County Department of Parks & Recreation manages many parks and facilities, including:
- Fifty local parks
- Two water parks
- Two recreation centers
- Two community centers
- Six sports complexes
- An ice-skating rink
- Leesylvania State Park: This park was once the home of the famous Lee family. It offers many fun activities and great views of the river.
Transportation and Travel
Prince William County has many major roads and ways to get around.
Major Roads
Some of the main highways and roads include:
 Interstate 66
Interstate 66 Interstate 95
Interstate 95 U.S. Route 1 (Richmond Highway)
U.S. Route 1 (Richmond Highway) U.S. Route 15 (James Madison Highway)
U.S. Route 15 (James Madison Highway) U.S. Route 29 (Lee Highway)
U.S. Route 29 (Lee Highway) State Route 28
State Route 28 State Route 55
State Route 55 State Route 123
State Route 123 State Route 234
State Route 234 State Route 294
State Route 294
Airports
The Manassas Regional Airport is nearby. For bigger flights, people use Dulles Airport and Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport.
Public Transportation
The Potomac and Rappahannock Transportation Commission provides public bus service. This includes OmniRide, OmniLink, and OmniMatch services.
The county also has train service from Virginia Railway Express (VRE). The Manassas line has stations at Manassas Park, Manassas, and Broad Run / Airport. The Fredericksburg line has stations at Woodbridge, Rippon, and Quantico. You can also catch Amtrak trains at the Manassas, Quantico, and Woodbridge stations.
Communities in Prince William County
Prince William County has several towns and many other communities.
Towns
Census-Designated Places
These are areas that are like towns but are not officially incorporated as towns.
- Buckhall
- Bull Run
- Bull Run Mountain Estates
- Cherry Hill
- County Center
- Dale City
- Gainesville
- Independent Hill
- Lake Ridge
- Linton Hall
- Loch Lomond
- Quantico Base
- Marumsco
- Montclair
- Neabsco
- Nokesville
- Potomac Mills
- Sudley
- Triangle
- Woodbridge
- Yorkshire
Other Communities (Unincorporated)
These are smaller communities that are not officially part of a town or city.
- Aden
- Antioch
- Bethel
- Brentsville
- Bristow
- Buckland
- Canova
- Catharpin
- Cornwell
- Featherstone
- Greenwich
- Hoadly
- Quantico Station
- Rixlew
- Southbridge
- Sudley Springs
- Thoroughfare
- Waterfall
- Wellington
- West Gate
Cities Within the County
The cities of Manassas and Manassas Park are independent cities. This means they are not officially part of Prince William County, even though the county surrounds them. Before 1975, they were towns within the county.
Prince William County, Manassas, and Manassas Park share the same court system and some government offices. The main courthouse complex for the county is actually located inside the city of Manassas.
Notable People from Prince William County
- Margaret Kempe Howell, mother-in-law of Jefferson Davis
- Austin Steward, an important person who worked to end slavery
- Tommy Richman, a rapper
Other Important Places to Visit
- Marine Corps Base Quantico: A large military base.
- Hylton Performing Arts Center: A place for concerts and shows.
- Jiffy Lube Live: A big outdoor concert venue.
- Potomac Mills: A huge shopping mall and a popular place for tourists.
- FBI Academy: The training center for the Federal Bureau of Investigation.
- Camp William B. Snyder: One of the largest Cub Scout Camps in the United States.
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Prince William para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Prince William para niños








