Darwin, Northern Territory facts for kids
Quick facts for kids DarwinNorthern Territory |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||||||
| Population | 139,902 (2021) (17th) | ||||||||
| • Density | 44.2196/km2 (114.528/sq mi) | ||||||||
| Established | 1869 | ||||||||
| Area | 3,163.8 km2 (1,221.6 sq mi)(2011 urban) | ||||||||
| Time zone | ACST (UTC+9:30) | ||||||||
| Location | |||||||||
| LGA(s) | Darwin, Palmerston, Litchfield | ||||||||
| County | Palmerston County | ||||||||
| Territory electorate(s) | Port Darwin (and 14 others) | ||||||||
| Federal Division(s) | Solomon, Lingiari | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
Darwin is the capital city of the Northern Territory in Australia. Its traditional name in the Larrakia language is Garramilla. About half of the Northern Territory's population, around 139,902 people, live in Darwin. It is the smallest, wettest, and most northern capital city in Australia. Darwin is also the main hub for the region known as the Top End.
Darwin is close to Southeast Asia, making it an important link between Australia and countries like Indonesia and Timor-Leste. The Stuart Highway, a major road, starts in Darwin. It stretches south through central Australia to Port Augusta, South Australia. The city is built on a low cliff overlooking Darwin Harbour. Darwin's suburbs reach from Lee Point in the north to Berrimah in the east. The Stuart Highway also connects to Palmerston, a nearby city.
Like much of the Top End, Darwin has a tropical climate with a wet and a dry season. Before the wet season, there's a period called "the build up" when it gets hotter and more humid. The wet season usually starts in late November or early December. It brings heavy monsoon rains, amazing lightning shows, and more cyclone activity. During the dry season, the city enjoys clear skies and gentle sea breezes.
The Larrakia people are the original inhabitants of the Darwin area. Aboriginal people make up a big part of the population today. In 1839, the ship HMS Beagle sailed into Darwin Harbour. John Clements Wickham named the area "Port Darwin" to honor Charles Darwin. Charles Darwin had sailed with them on the ship's earlier journey. The settlement was first called Palmerston in 1869, but its name changed to Darwin in 1911. The city has been almost completely rebuilt four times. This was due to damage from cyclones in 1897 and 1937, Japanese air raids during World War II, and Cyclone Tracy in 1974.
Contents
Exploring Darwin's Past
Early Days and First People
The Larrakia people are the traditional owners of the Darwin area. They were the first people to live here. They had trading routes with Southeast Asia. They also traded goods from as far away as South and Western Australia. Stories and histories were shared through songlines across the land.
Dutch explorers visited Australia's northern coast in the 1600s. They landed on the Tiwi Islands but were turned away by the Tiwi people. The Dutch made the first European maps of this area. That's why some places have Dutch names, like Arnhem Land and Groote Eylandt. The first British person to see Darwin Harbour was Lieutenant John Lort Stokes in 1839. The ship's captain, Commander John Clements Wickham, named the port after Charles Darwin.
In 1863, the Northern Territory became part of South Australia. In 1869, George Goyder started a small settlement of 135 people at Port Darwin. He named it Palmerston after the British Prime Minister, Lord Palmerston. In 1870, the first poles for the Australian Overland Telegraph Line were put up in Darwin. This line connected Australia to the rest of the world. Gold was found near Pine Creek in the 1880s. This led to a gold rush and helped the young colony grow.
In 1875, Darwin's population grew to about 300 because of the gold rush. Many people left Darwin on the ship Gothenburg in February 1875. The ship was caught in a cyclone and sank. Only 22 men survived, and many Darwin residents were lost. This tragedy greatly affected the small community.
Darwin in the 1900s

In 1911, the town was officially renamed Darwin.
Between 1911 and 1919, there was a lot of unrest, especially with trade unions. This led to the 'Darwin Rebellion' in 1918. About 1000 people marched to Government House. They protested against the Administrator of the Northern Territory, John A. Gilruth, and a company called Vestey's Meatworks. Both Gilruth and Vestey's left Darwin soon after.
When World War II began, about 10,000 Australian and Allied troops came to Darwin. They were there to protect Australia's northern coast. On 19 February 1942, 188 Japanese warplanes attacked Darwin. This attack killed at least 243 people and caused huge damage. It was the most serious attack on Australia during the war. Many more air raids followed.
After the war, Darwin grew further. New roads were built to connect it to Alice Springs and Mount Isa. Manton Dam was built to supply water to the city. On Australia Day in 1959, Darwin officially became a city.
From 1970 to Today
On 25 December 1974, Cyclone Tracy hit Darwin. It killed 71 people and destroyed over 70% of the city's buildings. Many old stone buildings, like the Palmerston Town Hall, were ruined. After the disaster, 30,000 people were evacuated. This was the biggest airlift in Australia's history. The city was rebuilt in the late 1970s using stronger materials and building methods. A new city called Palmerston was built 20 km (12 mi) south of Darwin in the early 1980s.
In 2003, the Adelaide–Darwin railway was completed. This railway connected Darwin to the rest of Australia.
Darwin's Location and Landscape
Darwin is located in the Northern Territory, right on the Timor Sea. The main part of the city sits on a low cliff overlooking Darwin Harbour. It has Frances Bay to the east and Cullen Bay to the west. The rest of the city is mostly flat and low. Coastal areas have parks, long beaches, and great fishing spots.
Darwin is actually closer to the capital cities of five other countries than it is to Australia's capital, Canberra. For example, Dili (East Timor) is only 656 km (408 mi) away. Jakarta (Indonesia) is 2,700 km (1,678 mi) away. This shows how close Darwin is to Asia.
Besides being a gateway to Asia, Darwin is also a starting point for visiting amazing places. These include Kakadu National Park, Arnhem Land, and islands like Groote Eylandt and the Tiwi Islands. As the biggest city in the area, Darwin provides important services for these remote communities.
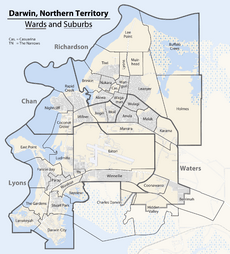
City Layout and Neighborhoods
Darwin and its suburbs form a triangle shape. The older suburbs and the city center are in one corner. Newer northern suburbs are in another, and eastern suburbs stretch towards Palmerston.
The Darwin International Airport and the Royal Australian Air Force Base separate the old part of Darwin from the newer northern suburbs. Palmerston is a city about 20 km (12 mi) south of Darwin. It was built in the 1980s and is one of Australia's fastest-growing areas. Rural areas around Darwin, like Howard Springs and Humpty Doo, are also growing fast.
Darwin's main business area is called the CBD (Central Business District). It has seen many big projects, like the redevelopment of the Stokes Hill wharf waterfront. This area now has a convention center, apartments, shops, and a wave pool. The city's main industrial areas are along the Stuart Highway, near Winnellie. The biggest shopping center is Casuarina Square.
The most expensive homes are along the coast in suburbs like Larrakeyah. Some areas, like Millner and Karama, have more affordable housing.
Darwin's Climate
Darwin has a tropical savanna climate. This means it has clear wet and dry seasons. The average maximum temperature stays pretty much the same all year. The dry season runs from May to September. During this time, almost every day is sunny, and the air is not very humid.
The driest time of year is between May and September. In June and July, the coolest months, the temperature can drop to about 14 °C (57 °F). It rarely gets colder than that in the city center. However, outer suburbs can sometimes get as low as 5 °C (41 °F). Darwin once had no rain for 147 days during the dry season in 2012.
The wet season brings tropical cyclones and monsoon rains. Most rain falls between December and March. Thunderstorms are common, and the air is very humid. It doesn't rain every day, but it's often cloudy. January usually has less than 6 hours of sunshine daily. Darwin's highest daily rainfall was 367.6 millimetres (14.47 in) in February 2011 during Cyclone Carlos. February 2011 was also Darwin's wettest month ever.
November is the hottest month, just before the main rains start. The "feels like" temperature can sometimes go above 45 °C (113 °F) because of the humidity. Darwin gets a lot of sunshine, averaging 8.4 hours per day. This is the second most of any Australian capital city.
Darwin is one of the most lightning-prone areas in Australia. On one day in 2002, there were over 5,000 lightning strikes near Darwin. That's about three times what another city like Perth sees in a whole year!
People and Cultures
Backgrounds and New Arrivals
| Birthplace | Population |
|---|---|
| Australia | 85,832 |
| Philippines | 4,963 |
| England | 4,154 |
| New Zealand | 2,896 |
| India | 2,697 |
| Greece | 1,234 |
| Mainland China | 1,057 |
| East Timor | 1,008 |
| Indonesia | 1,002 |
Darwin's population changed a lot after World War II. Many people from Europe, especially Italians and Greeks, moved to Darwin in the 1960s and 1970s. People from other European countries like the Dutch and Germans also came. Today, a large number of Darwin's residents are recent immigrants from Asia, including people from East Timor.
At the 2016 census, the most common backgrounds people identified with were Australian, English, Irish, and Scottish. About 8.7% of the population identified as Indigenous Australians (Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islanders). This is the highest percentage among Australian capital cities.
Languages Spoken
In 2016, 58% of people in Darwin spoke only English at home. Other languages spoken include Tagalog, Greek, Mandarin, and Nepali. Many other languages are also spoken, showing Darwin's diverse culture.
Age of Residents
In 2011, the average age of people in Darwin was 33 years old. This is younger than the national average of 37. This is partly because of the military presence and because many older people choose to retire elsewhere.
Beliefs and Religions
Christianity is the most common religion in Darwin, with about 49.5% of the population. The largest Christian groups are Roman Catholicism, Anglicanism, and Greek Orthodoxy. Other religions like Buddhism, Islam, and Hinduism are also present. About 23.3% of people said they had no religion.
Darwin's Economy
The two biggest parts of Darwin's economy are mining and tourism. Because of its location, Darwin is a key entry point for Australians traveling to Asia.
Mining and energy production in the area bring in over $2.5 billion each year. Important minerals include gold, zinc, and bauxite. Energy comes mostly from oil and natural gas found off-shore in the Timor Sea. There are also large amounts of uranium near Darwin. Tourism provides jobs for 8% of Darwin residents. It is expected to grow as more people visit throughout the year. Government spending also adds a lot to the local economy.
Darwin's role as a port is expected to grow. This is because of more oil and gas being found in the Timor Sea. Also, the railway link and growing trade with Asia are important. In 2005, many big building projects started in Darwin. One was the redevelopment of the Wharf Precinct. This area now has a large convention center, apartments, shops, and fun places like a wave pool. A "Chinatown" project is also planned with Chinese-themed shops and restaurants.
Visiting Darwin: Tourism
Tourism is one of Darwin's biggest industries. In 2005–2006, 1.38 million people visited the Northern Territory. They spent over $1.5 billion. Tourism directly created over 8,391 jobs in the Territory.
Darwin is a great base for tours to Kakadu National Park, Litchfield National Park, and Katherine Gorge. The year is usually split into wet and dry seasons. However, there are up to six traditional seasons in Darwin. It's warm and sunny from May to September. Humidity rises during the "green season" (October to April). This brings thunderstorms and monsoon rains that make the landscape lush. Most tourists visit during the cooler dry season, from April to September.
Military Presence
The military has a large presence in Darwin and the Northern Territory. This provides many jobs. In 2011, Australia and the United States announced that U.S. troops would be stationed in Darwin. This was the first time since World War II. The plan was for 250 Marines to arrive in 2012. This number would grow to 2,500 troops by 2017. They would stay for six-month periods. The agreement also includes supporting air forces.
Darwin also hosts "Exercise Pitch Black" every two years. This is a large exercise involving military personnel from many countries. In 2014, it included Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, United Arab Emirates, and the United States.
Learning in Darwin
Education in the Northern Territory is managed by the Department of Education and Training. They work to improve learning for all students, especially Indigenous students.
Schools for All Ages
Darwin has many public and private schools. They serve local and international students. Over 16,500 students attend primary and secondary schools in Darwin. Most schools are secular, meaning they are not religious. However, there are some Catholic and Lutheran schools. Students work towards their Northern Territory Certificate of Education or other certificates.
Since 2007, schools have been set up as Primary, Middle, and High schools.
Higher Education
Darwin's largest university is Charles Darwin University. It is the main place for higher education in the Northern Territory. It offers both hands-on training (vocational) and academic courses. It acts as both a university and a TAFE institute. More than 5,500 students are enrolled in these courses.
Buildings and Design
Darwin has been destroyed by cyclones and bombs many times. Because of this, not many old buildings are left. The Administrator's Office, built in 1883, was damaged by bombs but completely destroyed by the 1974 cyclone. It was rebuilt in 1981 and now holds government offices. Nearby, Survivors Lookout offers a view of the marina.
In a park in the south of the CBD, you can see the ruins of the Town Hall. It was built in 1883 and destroyed by the 1974 cyclone. Brown's Mart is a stone building from 1880. It was used for many things, like trade and meetings. Now, it's a theater.
One of Darwin's most famous buildings is the Chinese Temple. It was founded in 1887 and damaged by cyclones and bombs. It was completely destroyed by the 1974 cyclone but rebuilt in 1978.
Darwin also has modern churches. St Mary's Star of the Sea Roman Catholic Cathedral opened in 1962. Christ Church Anglican Cathedral was rebuilt in 1977 after being damaged by bombs and destroyed by Cyclone Tracy.
Fun Events and Festivals
- The annual Darwin Fringe Festival happens for 10 days every July. It's an open festival where anyone can take part.
- The Darwin Festival takes place each August. It includes comedy, dance, theater, music, film, and art. It also features the NT Indigenous Music Awards.
- The Nightcliff Seabreeze Festival started in 2005. It's held in May in the suburb of Nightcliff. It shows off local talent. A popular event is the Saturday family fun along the Nightcliff foreshore.
- The Darwin beer-can regatta is in August. People race boats made from beer cans! Also in August are the Darwin Cup horse race and a rodeo.
- The World Solar Challenge race brings teams from all over the world. They race cars powered by the sun. Many teams are from universities or high schools.
- The Royal Darwin Show is held every July. It features agriculture, livestock, and horse events. There's also entertainment and sideshows for three days.
- The Darwin Street Art Festival is an annual event in September. Street artists from around the world create large outdoor murals.
- A yearly music festival, BASSINTHEGRASS, has been held since 2003. Since 2019, it has been at Mindil Beach.
- On 1 July, people in the Northern Territory celebrate Territory Day. This is the only day, besides Chinese New Year and New Year's Eve, when fireworks are allowed. In Darwin, the main celebration is at Mindil Beach with a big fireworks display.
- Other festivals include the Glenti, which celebrates Darwin's large Greek community. India@Mindil is a similar festival by the city's Indian community. The Chinese New Year is also celebrated with great joy, showing the East Asian influence in Darwin.
Arts and Culture
The Darwin Symphony Orchestra started in 1989 and performs across the Territory. The Darwin Theatre Company is a local professional theater group.
The Darwin Entertainment Centre is the city's main place for concerts, theater, and orchestra shows. The Darwin Convention Centre opened in 2008. It is part of the big Darwin Waterfront project.
The Northern Territory Museum and Art Gallery (MAGNT) in Darwin tells the history of the area. It has exhibits on Cyclone Tracy and boats from the Pacific Islands. The MAGNT also hosts the annual Telstra National Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Art Award. This is Australia's longest-running Indigenous art award. The MAGNT also runs the Defence of Darwin Experience. This exhibit tells the story of the Japanese air raids on Darwin during World War II.
The NT Dance Company is led by choreographer Gary Lang. The company focuses on culture and works with young Indigenous people.
You can hear local and visiting bands at places like the Darwin Entertainment Centre and Happy Yess. Artists like Jessica Mauboy are from Darwin.
Because Darwin has so many different cultures, Southeast Asian noodle broth laksa has become the city's favorite meal!
Other Fun Things to Do
Weekly markets are very popular. These include the Mindil Beach Sunset Market (Thursdays and Sundays during the dry season), Parap Market, Nightcliff Market, and Rapid Creek market.
Darwin's only casino opened in 1979. It is now called Skycity Darwin and is located on Mindil Beach.
Mitchell Street in the city center is full of nightclubs, takeaways, and restaurants. It's the main entertainment area. There are also several smaller theaters and three cinema complexes. The Deckchair Cinema is an open-air cinema that shows independent films during the dry season.
Recreation and Outdoors
Beaches to Enjoy
From October to May, the sea can have dangerous box jellyfish. These are known as stingers. Saltwater crocodiles are common in waterways around Darwin. They are sometimes seen in Darwin Harbour and on beaches. The government has a program to trap crocodiles in the urban area.
The city has many kilometers of beaches. These include Casuarina Beach and the famous Mindil Beach, where the Mindil Beach markets are held.
Bundilla Beach was once called Vesteys Beach. In 2021, it was officially renamed Bundilla Beach. This is the name the Larrakia people, the traditional owners, have always used.
The Darwin Surf Life Saving Club offers events and teaches lifesaving skills. Lake Alexander is a man-made swimming lake at East Point Reserve.
Fishing Adventures
Fishing is a very popular hobby for people in Darwin. Visitors often try to catch the barramundi, a famous fish in the region. This fish is found in rivers like the Daly River and Mary River.
You can also go blue-water fishing off the coast of Darwin. Here you can catch fish like Spanish mackerel and snapper.
Parks and Green Spaces
Darwin has many beautiful parks and gardens. These include the George Brown Darwin Botanic Gardens, East Point Reserve, and Charles Darwin National Park. Other popular spots are Leanyer Recreation Park and the Nightcliff Foreshore.
Amazing Wildlife
Darwin is a great place for bird-watching. You can spot many birds at the George Brown Darwin Botanic Gardens and East Point Reserve. A bit further away, Fogg Dam Conservation Reserve is one of the best birding spots in Australia.
Some native mammals, like the common brushtail possum, are more common in Darwin than in the wild. This is likely because of the gardens, lack of fires, and places to hide in houses.
Darwin is also home to many frogs and reptiles. It has more types of snakes than any other Australian capital city. Luckily, most of these snakes are not highly venomous.
Sports and Games
The Marrara Sports Complex has stadiums for many sports. These include Australian rules, cricket, rugby league, football, basketball, and athletics. Every two years, Darwin hosts the Arafura Games, a big regional sports event. In 2003 and 2004, Darwin hosted its first international test cricket matches.
Australian rules football is played all year. Darwin is home to the Northern Territory's main league, the Northern Territory Football League. Some Australian Football League (AFL) games are played at Marrara Oval. The Darwin-based Indigenous All-Stars team has played in the AFL pre-season.
Rugby League and Rugby Union club competitions are also played in Darwin. The Darwin Hottest Sevens tournament is held every January. Rugby Sevens teams from many countries compete. It's the richest Rugby 7s tournament in the Southern Hemisphere.
Darwin hosts a round of the Supercars Championship every year. This brings thousands of motorsports fans to the Hidden Valley Raceway. Next to it is Northline Speedway, a dirt track racing venue.
The Darwin Cup is a popular horse race event. It happens on the first Monday of August at Fannie Bay Racecourse. This day is a public holiday in the Northern Territory.
In 2022, the Darwin Salties basketball club will start playing in the Queensland-based NBL1 North competition. This makes the NBL1 the first Australian sports league with clubs in every state and territory.
News and Media

Darwin's main newspapers are the Northern Territory News (Monday–Saturday) and The Sunday Territorian (Sunday). The national newspaper, The Australian, is also available. Free weekly community newspapers include Sun Newspapers.
Five free TV channels serve Darwin. These include commercial channels like Seven Darwin and Nine Darwin. The government-owned channels are the ABC and SBS. You can also get subscription TV services like Foxtel.
Darwin has many radio stations on AM, FM, and digital radio. These include ABC Local Radio, ABC Radio National, and Triple J. There are also commercial stations like Hot 100 and Mix 104.9. Other stations include university-based Territory FM and Indigenous community stations like Radio Larrakia.
Getting Around Darwin
Public transport in Darwin is managed by the Department of Lands and Planning. Darwin has a bus network that serves its main suburbs.
Darwin does not have a local train system for daily travel. However, long-distance passenger trains do run from the city. The Alice Springs-Darwin railway line was finished in 2003. It connects Darwin to Adelaide. The Ghan passenger train runs once a week in each direction.
Historically, the North Australia Railway carried people and goods from Darwin inland. It closed in 1976.
Darwin International Airport is Darwin's only airport. It shares its runways with the Royal Australian Air Force's RAAF Base Darwin.
You can reach Darwin by road via the Stuart Highway. This highway runs through the Northern Territory to Adelaide. Other major roads in Darwin include Tiger Brennan Drive and Bagot Road. Bus service in the greater Darwin area is provided by Darwinbus.
Darwin's Port
Ferries leave from Port Darwin to nearby islands, mainly for tourists. A ferry service to the Tiwi Islands operates from Cullen Bay.
Darwin has a deepwater port called East Arm Wharf, which opened in 2000. It can handle large ships.
City Services
Water and Power
Water supply and power for Darwin are managed by PowerWater. They also manage sewage and major water sources. Most of Darwin's water comes from the Darwin River Dam. For many years, Manton Dam was the main water source.
Darwin and its nearby cities, Palmerston and Katherine, get their power from the Channel Island Power Station. This is the Northern Territory's largest power plant.
Connecting with the World
Darwin once had Australia's only international connection through an undersea telegraph cable to Java. The southern part of this cable connected Darwin to Adelaide. In 2022, the Northern Territory Government announced a new international undersea cable system. This will directly connect Darwin to Indonesia, Singapore, the United States, and Timor Leste. This new cable is expected to create a new digital economy for Darwin.
|
| Climate data for Darwin Airport (1941–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 36.1 (97.0) |
36.0 (96.8) |
36.0 (96.8) |
36.7 (98.1) |
36.0 (96.8) |
34.6 (94.3) |
34.8 (94.6) |
37.0 (98.6) |
37.7 (99.9) |
38.9 (102.0) |
37.3 (99.1) |
37.0 (98.6) |
38.9 (102.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 31.8 (89.2) |
31.4 (88.5) |
31.9 (89.4) |
32.7 (90.9) |
32.0 (89.6) |
30.7 (87.3) |
30.6 (87.1) |
31.4 (88.5) |
32.6 (90.7) |
33.3 (91.9) |
33.3 (91.9) |
32.6 (90.7) |
32.0 (89.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 24.8 (76.6) |
24.7 (76.5) |
24.6 (76.3) |
24.0 (75.2) |
22.1 (71.8) |
19.9 (67.8) |
19.3 (66.7) |
20.3 (68.5) |
23.0 (73.4) |
24.9 (76.8) |
25.3 (77.5) |
25.3 (77.5) |
23.2 (73.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 20.2 (68.4) |
17.2 (63.0) |
19.2 (66.6) |
16.0 (60.8) |
13.8 (56.8) |
12.1 (53.8) |
10.4 (50.7) |
13.0 (55.4) |
14.3 (57.7) |
19.0 (66.2) |
19.3 (66.7) |
19.8 (67.6) |
10.4 (50.7) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 423.7 (16.68) |
371.3 (14.62) |
315.2 (12.41) |
100.4 (3.95) |
21.6 (0.85) |
1.8 (0.07) |
1.1 (0.04) |
4.8 (0.19) |
15.8 (0.62) |
70.3 (2.77) |
141.3 (5.56) |
252.4 (9.94) |
1,719.7 (67.7) |
| Average rainy days | 21.3 | 20.4 | 19.5 | 9.2 | 2.3 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 2.4 | 6.9 | 12.4 | 16.9 | 112.9 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 70 | 72 | 67 | 52 | 43 | 38 | 37 | 40 | 47 | 52 | 58 | 65 | 53 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 176.7 | 162.4 | 210.8 | 261 | 297.6 | 297 | 313.1 | 319.3 | 297 | 291.4 | 252 | 213.9 | 3,092.2 |
| Climate data for Darwin PO (City Centre) 1882–1942 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 37.7 (99.9) |
38.3 (100.9) |
37.8 (100.0) |
38.3 (100.9) |
37.4 (99.3) |
35.8 (96.4) |
36.7 (98.1) |
37.1 (98.8) |
38.3 (100.9) |
40.4 (104.7) |
38.8 (101.8) |
38.8 (101.8) |
40.4 (104.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 32.4 (90.3) |
32.2 (90.0) |
32.7 (90.9) |
33.5 (92.3) |
32.6 (90.7) |
31.2 (88.2) |
30.6 (87.1) |
31.7 (89.1) |
33.0 (91.4) |
34.1 (93.4) |
34.2 (93.6) |
33.6 (92.5) |
32.6 (90.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 25.2 (77.4) |
25.0 (77.0) |
24.9 (76.8) |
24.4 (75.9) |
22.6 (72.7) |
20.8 (69.4) |
19.7 (67.5) |
20.9 (69.6) |
23.3 (73.9) |
25.1 (77.2) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.6 (78.1) |
23.6 (74.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 20.2 (68.4) |
20.5 (68.9) |
20.0 (68.0) |
18.9 (66.0) |
15.7 (60.3) |
13.4 (56.1) |
13.7 (56.7) |
14.7 (58.5) |
17.2 (63.0) |
20.4 (68.7) |
16.7 (62.1) |
20.8 (69.4) |
13.4 (56.1) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 393.2 (15.48) |
329.7 (12.98) |
257.0 (10.12) |
102.6 (4.04) |
14.3 (0.56) |
3.0 (0.12) |
1.3 (0.05) |
1.6 (0.06) |
12.8 (0.50) |
51.6 (2.03) |
124.0 (4.88) |
241.8 (9.52) |
1,532.9 (60.34) |
| Average rainy days | 18.4 | 17.8 | 16.0 | 7.3 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 1.7 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 14.3 | 93 |
| Historical Populations of Darwin | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1911 | 1,082 | — |
| 1921 | 1,399 | +29.3% |
| 1933 | 1,566 | +11.9% |
| 1947 | 2,538 | +62.1% |
| 1954 | 8,071 | +218.0% |
| 1961 | 15,477 | +91.8% |
| 1966 | 21,671 | +40.0% |
| 1971 | 37,100 | +71.2% |
| 1976 | 44,200 | +19.1% |
| 1981 | 61,412 | +38.9% |
| 1986 | 75,360 | +22.7% |
| 1991 | 86,415 | +14.7% |
| 1996 | 95,829 | +10.9% |
| 2001 | 106,842 | +11.5% |
| 2006 | 105,991 | −0.8% |
| 2011 | 129,106 | +21.8% |
| 2016 | 145,916 | +13.0% |
- Australian (37.4%)
- English (32.7%)
- Irish (11.1%)
- Scottish (8.8%)
- Indigenous (8.7%)
- German (5%)
- Filipino (4.8%)
- Chinese (4.5%)
- Greek (3.2%)
- Indian (2.8%)
- Italian (2.6%)
- Dutch (1.5%)
- Indonesian (1.1%)
- New Zealander (1.1%)
| Preceding station | Journey Beyond | Following station | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terminus | The Ghan | Katherine
towards Adelaide
|
||
See also
 In Spanish: Darwin (Australia) para niños
In Spanish: Darwin (Australia) para niños