Economy of the United Kingdom facts for kids

London is the heart of the United Kingdom's economy and the second-largest financial centre in the world behind New York City.
|
|
| Currency | Pound sterling (GBP, £) |
|---|---|
| 1 April to 31 March | |
|
Trade organisations
|
WTO, G-20, G7 and OECD |
| Statistics | |
| Population | 67,026,292 (2021) |
| GDP | |
| GDP rank | |
|
GDP growth
|
|
|
GDP per capita
|
|
|
GDP per capita rank
|
|
|
Base borrowing rate
|
|
|
Population below poverty line
|
▼ 18.6% (2017 est.) |
| ▼ 35.4 medium (2021) | |
|
|
|
Labour force
|
33,174,000 / 75.0% in employment (Oct–Dec 2023) |
|
Labour force by occupation
|
List
27.0% Professional
14.8% Associate professional 10.5% Managers, directors and senior officials 9.6% Administrative and secretarial 9.5% Elementary occupations 8.8% Skilled trades 8.0% Caring, leisure and other service 6.2% Sales and customer service 5.4% Process plant and machine operatives (Oct 2022 – Sep 2023) |
| Unemployment | 1,320,000 / 3.8% (Oct–Dec 2023) |
|
Average gross salary
|
£681.70 per week (2023) |
|
Main industries
|
List
Machine tools
electric power equipment automation equipment railway equipment shipbuilding aircraft motor vehicles and parts electronics and communications equipment metals chemicals coal petroleum paper and paper products food processing textiles clothing other consumer goods |
| External | |
| Exports | |
|
Export goods
|
List
£35.9bn Cars
£34.0bn Power generators £26.2bn Medicinal and pharmaceutical products £22.1bn Unspecified goods £20.8bn Crude oil £12.7bn Beverages and tobacco £12.1bn Refined oil £11.8bn Scientific instruments £11.6bn Aircraft £11.4bn Non-ferrous metals £398.7bn Total (12 months to Nov 2023) |
|
Main export partners
|
List
£188.5bn (21.2%) United States
£61.1bn (6.9%) Germany £57.7bn (6.5%) Ireland £57.2bn (6.4%) Netherlands £45.7bn (5.1%) France £41.3bn (4.6%) China £41.1bn (4.6%) Switzerland £25.5bn (2.9%) Belgium £20.2bn (2.3%) Hong Kong £19.4bn (2.2%) Spain £17.6bn (2.0%) Italy £16.1bn (1.8%) United Arab Emirates £16.1bn (1.8%) Canada £16.0bn (1.8%) India £14.6bn (1.6%) Singapore £14.2bn (1.6%) Japan £13.9bn (1.6%) Sweden £13.7bn (1.5%) Australia £12.2bn (1.4%) Luxembourg £11.7bn (1.3%) Saudi Arabia (4 quarters to June 2023) |
| Imports | |
|
Import goods
|
List
£40.3bn Cars
£28.5bn Refined oil £27.3bn Crude oil £26.3bn Gas £26.2bn Power generators £25.6bn Medicinal and pharmaceutical products £21.6bn Miscellaneous electrical goods £17.8bn Telecoms and sound equipment £16.3bn Clothing £14.4bn Other manufactures (consumer) £584.8bn Total (12 months to Nov 2023) |
|
Main import partners
|
List
£121.5bn (13.3%) United States
£85.8bn (9.4%) Germany £68.4bn (7.5%) Netherlands £67.5bn (7.4%) China £56.9bn (6.2%) France £41.1bn (4.5%) Spain £40.7bn (4.5%) Norway £32.3bn (3.5%) Belgium £32.3bn (3.5%) Italy £30.6bn (3.4%) Ireland £22.3bn (2.4%) India £19.4bn (2.1%) Switzerland £19.3bn (2.1%) Poland £16.1bn (1.8%) Turkey £14.4bn (1.6%) Japan £12.7bn (1.4%) Sweden £9.8bn (1.1%) Canada £9.7bn (1.1%) Hong Kong £9.3bn (1.0%) United Arab Emirates £8.9bn (1.0%) Denmark (4 quarters to June 2023) |
|
FDI stock
|
|
| £–78.3 billion (2022) | |
|
Gross external debt
|
£7.286 trillion (2022) (2nd) |
|
Net international investment position
|
£–244.4 billion (2022) |
| Public finances | |
|
Public debt
|
£2.540 trillion / 96% of GDP (2022/23) |
| Revenues | £1.027 trillion (2022/23) |
| Expenses | £1.157 trillion (2022/23) |
| Economic aid | $15.8 billion (2022) |
|
Credit rating
|
List
S&P Global Ratings:
AA (Domestic) AA (Foreign) AAA (T&C Assessment) Outlook: Stable 20 Oct 2023 Moody's: Aa3 Outlook: Stable 20 Oct 2023 Fitch Ratings: AA- Outlook: Negative 1 Dec 2023 Scope Ratings: AA Outlook: Stable 3 Nov 2023 |
|
Foreign reserves
|
List
Gross reserves (Jan 2024):
UK Government: $185.5 billion Bank of England: $24.6 billion Net reserves (Jan 2024): UK Government: $85.2 billion Bank of England: $0.016 billion |
The economy of the United Kingdom is a very advanced economy. It's the sixth-largest economy in the world when measured by its total value of goods and services (called GDP). It's also the ninth-largest when you consider what people can actually buy with their money (called PPP).
The UK's economy is very connected to the rest of the world. It includes England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. In 2022, the UK was the fourth-largest exporter and importer globally. It also had the fourth-largest amount of money invested abroad.
Most of the UK's economy comes from the service sector, which makes up 82% of its GDP. The financial services industry is super important. London is the second-largest financial hub in the world. Edinburgh is also a big financial centre in Europe. The UK's technology sector is worth a huge amount, ranking third globally. The aerospace industry in the United Kingdom is the second-largest in the world. The pharmaceutical industry is also very important.
The UK's economy also gets a boost from oil and gas production. However, it has bought more oil than it produced since 2005. Some areas, like South East England and North East Scotland, are much richer than others. London's economy makes it the wealthiest city in Europe by GDP per person.
In the 1700s, Britain was the first country to start using machines for manufacturing (this was the Industrial Revolution). By the 1800s, with its large empire and new technology, Britain was a major player in the world economy. But other countries like the United States and Germany started to catch up. The cost of fighting the First and Second World Wars also made the UK's position weaker. Even so, the UK still has a lot of influence around the world today.
The government's role in the economy is mainly handled by His Majesty's Treasury. This department is led by the Chancellor of the Exchequer. Since 1979, the UK has generally let the economy run with less government control. The Bank of England is the UK's central bank. Since 1997, its Monetary Policy Committee has been in charge of setting interest rates.
Contents
- History of the UK Economy
- Economic Charts
- How the Government Manages the Economy
- Economic Sectors
- UK Currency
- Economy by Region
- Trade with Other Countries
- Investments
- Company Mergers and Acquisitions
- Leaving the European Union
- Poverty in the UK
- See also
History of the UK Economy
After World War II (1945-1979)
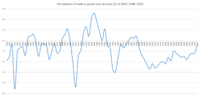
After World War II, Britain had lost a lot of its wealth. A new government took control of major industries like the Bank of England, railways, and coal mines. After the war, the UK had a long period of economic growth. People became more prosperous in the 1950s and 1960s. Unemployment stayed low, usually below 3.5%. The economy grew by about 2.9% each year between 1960 and 1973. However, this was slower than some other European countries.
Many old industries like mining and heavy manufacturing started to close down. This meant many well-paying jobs were lost. The UK's share of global manufacturing dropped a lot over the years. This problem became very serious in the 1970s. The world faced an energy crisis, prices went up quickly (inflation), and cheap goods from Asia flooded the market.
In 1976, the UK had to borrow money from the International Monetary Fund. To get the loan, the government had to cut public spending. The economy improved for a while. By the end of the 1970s, the UK found a lot of oil in the North Sea. This made the British pound stronger, which made UK exports more expensive and imports cheaper. After a period of many public sector strikes, Margaret Thatcher's Conservative Party won the election in 1979.
Modern Changes (1979-1997)
With Margaret Thatcher as Prime Minister, the UK started a new economic approach. Many state-owned industries were sold off to private companies. Taxes were cut, and rules for businesses were relaxed. At first, the economy shrank, but then it grew quickly. By 1988, it was growing at 5% a year.
However, these changes were not easy. To control high inflation, unemployment rose sharply. It went from 5.3% in 1979 to almost 11.9% in 1984. Many old factories and coal mines closed down. Manufacturing jobs decreased, but new industries and the service sector grew. By 1989, unemployment had fallen to 1.6 million.
Britain faced another economic slowdown in late 1990. The economy shrank, and unemployment went up again. However, inflation dropped a lot. The economy then recovered strongly. Unemployment fell to 7.2% by 1997.
Growth and Challenges (1997-2009)
In 1997, the Labour Party, led by Tony Blair, won the election. The new government kept many of the previous economic policies. Four days after the election, the Bank of England was given the power to control monetary policy (like setting interest rates).
During Blair's time in office, the economy grew for 40 quarters in a row. This was one of the best growth periods for any developed country. However, people's household debt also grew a lot.
This long period of growth ended in 2008. The UK entered a recession because of the global financial crisis. The UK's financial sector was very exposed to this crisis. Some banks had to be partly taken over by the government. Unemployment rose from 1.6 million to nearly 2.5 million.
Recovery and New Issues (2009-2020)
In 2009, the Bank of England cut interest rates to a very low 0.5%. It also started a program called quantitative easing (QE) to help the economy. The UK came out of the recession in late 2009. It was the longest and deepest recession since World War II.
After the 2010 election, a new government was formed. They made cuts to government spending to reduce debt. This led to job losses in the public sector, but the private sector created many new jobs.
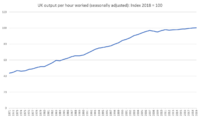
The years after the recession had mixed results. In 2015, more people were employed than ever before. GDP growth was fast compared to other major economies. However, workforce productivity (how much each worker produces) was very low. Real wages (what people could buy with their pay) also fell.
In 2016, the UK voted to leave the European Union. This decision caused some economic uncertainty. The Bank of England cut interest rates again.
Recent Times (2020-Present)
In March 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic hit. Many businesses closed, and the Bank of England cut interest rates even lower. The UK economy shrank by 22.6% in the first half of 2020. This was the deepest recession in UK history. Overall, GDP fell by 9.9% in 2020.
In 2021, prices started to rise quickly (inflation). This was due to higher energy and transport costs. By October 2022, inflation was at 11.1%, the highest in 41 years. Food prices, gas, and electricity all went up a lot. This led to a cost of living crisis.
However, in August 2023, new information showed that the UK's economy had recovered from the pandemic faster than first thought. It was actually larger than its pre-COVID-19 size by the end of 2021.
Economic Charts
How the Government Manages the Economy
The government's main role in the economy is through HM Treasury. This department is led by the Chancellor of the Exchequer. The UK economy is generally managed with less government control. It focuses on low taxes and fewer rules for businesses.
Since 1997, the Bank of England's Monetary Policy Committee sets interest rates. They do this to meet the inflation target set by the Chancellor each year.
Government spending in the UK has usually been around 40% of the total economy (GDP). After the financial crisis in 2007-2010, government spending went up. This was partly because the government had to help out banks. By June 2014, the government's debt was about 77.3% of the GDP.
Taxation in the United Kingdom involves payments to local and central governments. Local governments get money from central government grants and local taxes. The central government gets most of its money from income tax, VAT, and company taxes.
Economic Sectors
Farming and Food

Farming in the UK uses modern methods and machines. It's very efficient compared to other European countries. The UK produces about 65% of the food it needs. In the 1950s, it produced less than 50%, but this rose to 80% in the 1980s.
In 2018, farming added £12.18 billion to the economy. About 467,000 people worked in farming, hunting, and fishing. This sector makes up about 0.5% of the UK's total GDP. Most of what is produced is livestock (like cows and sheep). The rest is crops. The whole food industry, including farming, manufacturing, and retail, is worth £120 billion. It provides 4 million jobs in the UK.
Building and Construction
The construction industry in the UK employed about 2.3 million people in 2019. It added £123.2 billion to the economy.
One of the biggest construction projects was Crossrail. This new railway line runs through London. It cost about £19 billion and opened in 2022. Another big project is the High Speed 2 (HS2) railway line. This line will connect London and the West Midlands.
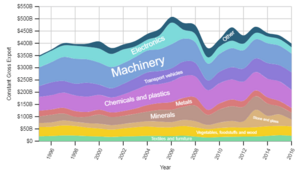
Manufacturing Industries
Electricity, Gas, and Water
This sector added £51.4 billion to the economy in 2018. The UK plans to build new nuclear power plants. This will help replace old generators and increase the UK's energy supply.
Factories and Production
In the 1970s, manufacturing made up 25% of the economy. By 2016, it was only 10%. The number of people working in manufacturing also fell a lot.
However, manufacturing output has actually increased in most years over the last 50 years. In 2011, the manufacturing sector added about £140.5 billion to the economy. It employed around 2.6 million people. The UK was the sixth-largest manufacturer in the world in 2008.
The car manufacturing sector employed about 180,000 people in 2008. It made £52.5 billion and exported £26.6 billion worth of goods. The UK also makes a lot of car engines.
The aerospace industry in the UK is the second largest in the world, after the United States. It employs about 113,000 people directly. Big British companies like BAE Systems and Rolls-Royce (which makes aircraft engines) are part of this industry.
The pharmaceutical industry employs about 67,000 people. It added £8.4 billion to the UK's GDP in 2007. The UK exports more pharmaceutical products than it imports. Major global companies like GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca are based in the UK.
Mining and Oil
This sector added £31.4 billion to the UK economy in 2011. The UK produces oil, natural gas, and coal. However, it has been importing more oil since 2005 and more natural gas since 2004.
The UK has large reserves of coal. It's estimated that there are enough coal reserves to last the UK for 200 to 400 years. The UK is home to major energy companies like BP and Royal Dutch Shell. It also has other natural resources like tin, limestone, and iron ore.
Service Industries
The service sector is the biggest part of the UK economy. It made up 82% of the GDP in 2023.
Creative Businesses
The creative industries include things like advertising, fashion, and design. They grew quickly between 1997 and 2005. London and the North West of England are major hubs for creative industries in Europe. The fashion industry alone contributed £26 billion to the UK economy in 2014. The world's largest advertising company, WPP, is based in the UK.
Education, Health, and Social Work

In 2011, the education sector added £84.6 billion to the economy. Health and social work activities added £104.0 billion.
Most healthcare in the UK is provided by the state-funded National Health Service (NHS). The NHS accounts for over 80% of all healthcare spending. It employs about 1.7 million people, making it the largest employer in Europe.
In 2007/08, higher education institutions (universities) in the UK had a total income of £23 billion. They employed almost 170,000 staff. There were over 2.3 million university students in the UK that year.
Financial and Business Services
The UK financial services industry added £116.4 billion to the economy in 2011. The UK exports a lot of financial and business services. This helps the country's balance of payments.
London is a huge global centre for business and finance. It's one of the top three "command centres" for the world economy. Over 500 banks have offices in London. It's a leading place for banking, insurance, and currency trading. London's financial industry is mainly in the City of London and Canary Wharf. The City is home to the London Stock Exchange and the Bank of England.
Other UK cities also have big financial sectors. Edinburgh is one of Europe's largest financial centres. Leeds is the biggest centre for business and financial services outside London.
Hotels and Restaurants
This industry added £36.6 billion to the UK economy in 2011. InterContinental Hotels Group (IHG), based in the UK, is currently the world's largest hotel company. It owns brands like Holiday Inn.
Public Services
Public administration and defence added £70.4 billion to the UK economy in 2011.
Property and Renting

The UK property market grew a lot for seven years until 2008. In some areas, property values tripled. This was due to low interest rates, economic growth, and foreign investment.
Between 1997 and 2016, average house prices in England and Wales went up by 259%. But earnings only went up by 68%. An average home cost 3.6 times annual earnings in 1997, but 7.6 times in 2016. Rent has also almost doubled as a share of the economy since 1985.
Tourism

In 2019, over 40 million people visited the UK. Tourism added £28.5 billion to the British economy. More than half of this money was spent in London. London was the third most visited city in the world.
Here are the top 10 countries whose tourists spent the most money in the UK in 2019:
| Rank | Market | Spend | Visitors |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | European Union | £9.33 billion | 22,580,591 |
| 2 | United States | £4.18 billion | 4,498,753 |
| 3 | China | £1.71 billion | 883,072 |
| 4 | Australia | £1.17 billion | 1,063,404 |
| 5 | India | £752 million | 692,082 |
| 6 | Canada | £734 million | 874,060 |
| 7 | Saudi Arabia | £627 million | 220,780 |
| 8 | Switzerland | £569 million | 925,727 |
| 9 | Norway | £436 million | 647,460 |
| 10 | Japan | £369 million | 388,839 |
Transport, Storage, and Communication

The transport and storage industry added £59.2 billion to the UK economy in 2011. The telecommunication industry added £25.1 billion in the same year.
The UK has a large road network. It also has a railway system with over 19,000 miles of lines. The government is spending £56 billion on a new high-speed railway line called HS2. Crossrail (now called the Elizabeth line) was Europe's largest infrastructure project. It cost £15 billion and opened in 2022.
UK airports handled almost 285 million passengers between February 2017 and January 2018. London Heathrow Airport is the busiest, handling 78 million passengers. London's six airports together form the world's largest city airport system.
Shops and Retail
This sector includes car sales, repairs, and shops selling personal and household goods. It added £151.8 billion to the UK economy in 2011.
In 2016, shopping on high streets made up about 33% of what people spent. Online sales make up 22% of retail spending in the UK. This is the third highest in the world.
Four main companies dominate the UK grocery market: Tesco, Sainsbury's, Asda, and Morrisons. However, discount supermarkets like Aldi and Lidl are becoming very popular.
London is a major shopping destination. In 2010, it had the highest non-food retail sales of any city in the world. Outside London, Manchester and Birmingham are also big shopping areas. The UK also has many large out-of-town shopping centres.
UK Currency
London is the world capital for currency trading. It handles 43.1% of the daily global turnover.
Sterling is the currency of the UK. The main unit is the pound, shown by the symbol "£". The Bank of England issues the currency. Banks in Scotland and Northern Ireland can also issue their own notes. Sterling is also used as a reserve currency by other countries. It is the third-largest reserve currency after the US dollar and the euro.
The UK decided not to join the euro when it was launched. There used to be a debate about whether the UK should adopt the euro. However, public opinion polls showed that most Britons were against joining. This idea has become a non-issue since the UK left the European Union in 2020.
Economy by Region
The UK economy is different in each country and region. England has the highest economic output per person (GVA), and Wales has the lowest.
| Rank | Country | GVA per head, 2020 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | England | £32,866 ($42136) |
| 2 | Scotland | £29,629 ($37986) |
| 3 | Northern Ireland | £25,575 ($32788) |
| 4 | Wales | £23,882 ($30618) |
Within England, GVA per person is highest in London. Here's how the different regions of England compare:
| Rank | Region | GVA per head, 2020 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | London | £55,974 ($71762) |
| 2 | South East England | £34,516 ($44251) |
| 3 | East of England | £29,176 ($37405) |
| 4 | North West England | £28,257 ($36227) |
| 5 | South West England | £28,012 ($35913) |
| 6 | West Midlands | £26,281 ($33694) |
| 7 | East Midlands | £25,956 ($33277) |
| 8 | Yorkshire and the Humber | £25,696 ($32944) |
| 9 | North East England | £23,109 ($29627) |
Trade with Other Countries
The UK's trade deficit (meaning it imports more than it exports) for goods and services got a little smaller in the three months to November 2018. This was because both exports and imports increased.
The total trade deficit grew in the 12 months to November 2018. This was mainly because the UK earned less from selling services abroad.
After the UK left the European Union, trade deals with other countries became very important. The UK is currently negotiating trade deals with the United States and India. It is also joining the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership.
Investments
In 2013, the UK was the top country in Europe for money invested into it by foreign companies (called FDI). It received $26.51 billion. The UK was also second in Europe for its own companies investing money abroad.
In October 2017, the UK's financial position with the rest of the world was updated. It showed that the UK had a deficit of £22 billion, meaning other countries owned more UK assets than the UK owned abroad.
According to the Office for National Statistics, the UK is the biggest investor in America. It is also the second biggest investor in China.
Company Mergers and Acquisitions
Since 1985, there have been over 103,000 deals where UK companies were involved in mergers or acquisitions. A merger is when two companies combine. An acquisition is when one company buys another. The years 2000, 2007, and 2017 saw a lot of this activity.
Here are some of the biggest deals involving UK companies:
| Rank | Date | Acquirer | Acquirer nation | Target | Target nation | Value (£ billions) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 14 November 1999 | Vodafone AirTouch PLC | United Kingdom | Mannesmann AG | Germany | 126.95 |
| 2 | 16 September 2015 | Anheuser-Busch Inbev SA/NV | Belgium | SABMiller PLC | United Kingdom | 77.24 |
| 3 | 4 August 2015 | Royal Dutch Shell PLC | Netherlands | BG Group PLC | United Kingdom | 46.70 |
| 4 | 17 January 2000 | Glaxo Wellcome PLC | United Kingdom | SmithKline Beecham PLC | United Kingdom | 46.48 |
| 5 | 28 October 2004 | Royal Dutch Petroleum Co | Netherlands | Shell Transport & Trading Co | United Kingdom | 40.75 |
| 6 | 21 October 2016 | British American Tobacco PLC | United Kingdom | Reynolds American Inc | United States | 40.10 |
| 7 | 15 January 1999 | Vodafone Group PLC | United Kingdom | AirTouch Communications Inc | United States | 36.35 |
| 8 | 30 May 2000 | France Telecom SA | France | Orange PLC | United Kingdom | 31.14 |
| 9 | 8 November 1998 | British Petroleum Co PLC | United Kingdom | Amoco Corp | United States | 29.51 |
| 10 | 31 October 2016 | GE Oil & Gas | United Kingdom | Baker Hughes Inc | United States | 26.63 |
| 11 | 26 February 2009 | HM Treasury | United Kingdom | Royal Bank of Scotland Group | United Kingdom | 25.50 |
- In most cases, the companies involved have shareholders from all over the world, not just in the countries listed.
Leaving the European Union
In June 2016, the UK voted to leave the European Union in a national vote. The UK officially left the EU in January 2020. After this, the UK government said that businesses would continue to trade easily within the UK. Also, powers that used to be handled by the EU would now go directly to the governments in Edinburgh, Cardiff, and Belfast.
Poverty in the UK
The United Kingdom is a developed country with systems to help people in need. So, when we talk about poverty here, it means having a lower income compared to other people in the country. The UK has a lower poverty rate than some other developed countries like France and the US.
The poverty line in the UK is usually set at 60% of the average household income. In 2007–2008, about 13.5 million people (22% of the population) lived below this line. This included 4 million children. The welfare state in the UK helps to fight poverty.
See also
 In Spanish: Economía del Reino Unido para niños
In Spanish: Economía del Reino Unido para niños
- Economy of England
- Economy of Scotland
- Economy of Wales
- Economy of Northern Ireland
- UK Infrastructure Bank