South East England facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
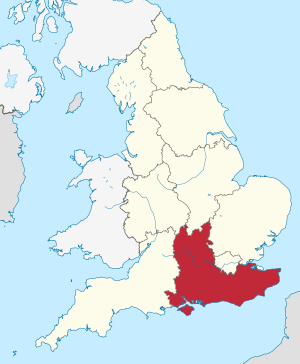
South East England
|
|
|---|---|
|
From top, left to right: Brighton; Oxford; Southampton; Canterbury; Windsor Castle; Blenheim Palace; White Cliffs of Dover
|
|
South East England, highlighted in red on a beige political map of England
|
|
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Country | England |
| Districts |
|
| Counties | |
| Government | |
| • Type | Local authority leaders' board |
| • Body | South East England Councils |
| Area | |
| • Total | 7,500 sq mi (19,400 km2) |
| • Land | 7,364 sq mi (19,072 km2) |
| • Water | 6 sq mi (16 km2) |
| Area rank | 3rd |
| Population
(2021)
|
|
| • Total | 9,294,023 |
| • Rank | 1st |
| • Density | 1,260/sq mi (487/km2) |
| Ethnicity (2021) | |
| • Ethnic groups |
List
|
| Religion (2021) | |
| • Religion |
List
46.5% Christianity
40.2% no religion 3.3% Islam 1.7% Hinduism 0.8% Sikhism 0.6% Buddhism 0.2% Judaism 0.6% other 6.1% not stated |
| GSS code | E12000008 |
| ITL code | TLJ |
| GVA | 2021 estimate |
| • Total | £301.5 billion |
| • Rank | 2nd |
| • Per capita | £32,443 |
| • Rank | 2nd |
| GDP (nominal) | 2021 estimate |
| • Total | £336.2 billion |
| • Rank | 2nd |
| • Per capita | £36,174 |
| • Rank | 2nd |
South East England is one of the nine official regions in England, United Kingdom. It is used for statistical purposes. This region includes nine counties: Buckinghamshire, East Sussex, Hampshire, the Isle of Wight, Kent, Oxfordshire, Berkshire, Surrey and West Sussex. Important towns and cities here are Brighton and Hove, Canterbury, Milton Keynes, Southampton, Portsmouth, Slough, Reading and Oxford.
South East England is the third-largest region in England by land area, covering 19,072 square kilometres (7,364 sq mi). It is also the most populated, with over nine million people. The region has eight official cities: Brighton and Hove, Canterbury, Chichester, Milton Keynes, Oxford, Portsmouth, Southampton and Winchester. Because it is close to London, South East England is a very successful economic area. It has the biggest economy of any UK region, apart from London.
The region is home to Gatwick Airport, the UK's second-busiest airport. Heathrow Airport (the UK's busiest) is right next to the region's border with Greater London. The coastline along the English Channel offers many ferry trips to mainland Europe.
The South East is famous for its beautiful countryside. This includes two national parks: the New Forest and the South Downs. You can also find the North Downs, the Chiltern Hills and part of the Cotswolds here. The River Thames flows through the region, and its valley is called the Thames Valley.
Many famous places are in this region. These include HMS Victory in Portsmouth, Blenheim Palace in Oxfordshire, and Windsor Castle in Berkshire. Other well-known spots are Leeds Castle, the White Cliffs of Dover, and Canterbury Cathedral in Kent. You can also visit Brighton Palace Pier and Thorpe Park in Surrey. The region has many universities, including the University of Oxford, which is one of the oldest and best in the world.
South East England hosts many sports events. These include the Henley Royal Regatta, Royal Ascot (horse racing), and The Derby. Famous sports venues include Wentworth Golf Club and Brands Hatch (motor racing). Some events of the 2012 Summer Olympics were held here. This included rowing at Eton Dorney and part of the cycling road race in the Surrey Hills.
In medieval times, South East England was a big part of the Kingdom of Wessex. This kingdom was the start of modern England. Winchester was the capital of England after different kingdoms joined together. These included the kingdoms of Kent, Sussex and Mercia. Winchester stopped being the capital in the 13th century as City of London became more important for trade.
Contents
History of South East England
The Meonhill Vineyard, near Old Winchester Hill in Hampshire, shows that Roman-British people grew grapes here.
Second World War Events
Many battles of the Battle of Britain were fought in this region, especially in Kent. RAF Bomber Command was based at High Wycombe. RAF Medmenham in Buckinghamshire was important for aerial reconnaissance (spying from the air). Operation Corona helped confuse German night fighters.
Bletchley Park in Buckinghamshire was the main Allied centre for code-breaking. The Colossus computer, one of the world's first, started working there in 1944. The Harwell computer (Dekatron), built in 1949, is believed to be the oldest working digital computer in the world. It is now at the National Museum of Computing at Bletchley.
Scientific Discoveries
John Wallis from Kent introduced the symbol for infinity in 1656. Thomas Bayes from Tunbridge Wells developed his theorem for probability theory. This is used today for things like spam filters and Google's search.
Sir David N. Payne at the University of Southampton invented the erbium-doped fibre amplifier in the 1980s. This invention was very important for the internet. Henry Moseley at Oxford discovered his Moseley's law in 1913. This helped assign the correct atomic number to elements in the periodic table. Carbon fibre was invented in 1963 at the RAE in Farnborough. The cooling system for the Apollo space-suit also came from work done at RAE Farnborough.
Donald Watts Davies invented packet switching in the 1960s at the National Physical Laboratory in Teddington. Packet-switching was used to create the ARPANET, which was the start of the Internet.
Surrey's Alec Reeves invented pulse-code modulation (PCM) in 1937. This is now the standard for digital audio recordings.
Sir John Herschel from Kent invented the term photography in 1839. He also discovered the first photographic fixer, sodium thiosulphate.
GLEEP was Britain's first nuclear reactor. It started in August 1947 at the Atomic Energy Research Establishment (AERE) at Harwell. It worked until 1990.
William Harvey from Folkestone, Kent, discovered how blood circulates in the body. The Lilly Research Centre in Windlesham, Berkshire, developed Olanzapine in 1996. This medicine is used for bipolar disorder. Beecham Research Laboratories discovered meticillin in 1959. This was the first semi-synthetic penicillin.
Industrial Heritage
Transport and Communication Inventions
Sir Francis Pettit Smith from Kent invented the screw propeller.
On May 3, 1830, the world's first passenger train service began. It was the Canterbury and Whitstable Railway (10 kilometres (6.2 mi) long). It was built by George Stephenson. This railway also introduced the world's first railway season ticket in 1834.
The Maidenhead Railway Bridge, famous for its flat arch, was built in 1839.
The Military Vehicles and Engineering Establishment in Chertsey developed Chobham armour.
On April 12, 1903, the world's first bus service started. It was by Eastbourne Buses from Eastbourne railway station to Meads.
The world's first submarine telephone cable was laid between England and France in 1891. This allowed London-Paris calls from April 1891. On December 3, 1992, Neil Papworth of Reading sent the world's first text message. He sent it from his computer to a mobile phone.
The first public automatic telephone exchange in the UK was at Epsom in 1912. It was used across the UK from 1922 for about 70 years.
UK-Belgium 5, laid in 1986 from Kent, was the world's first optical fibre submarine cable. It is 36 miles (58 km) long.
ThrustSSC, the fastest car in the world in 1997, was built in Aldingbourne, West Sussex.
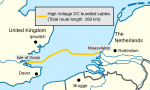
The BritNed power cable from Isle of Grain to Rotterdam was built in 2009. The HVDC Cross-Channel submarine cable (2000MW) was built in 1986. This is the world's highest-capacity submarine HVDC cable.
- Aviation
On October 16, 1908, the British Army Aeroplane No 1 was the first aircraft flown in the UK. It was flown by Samuel Franklin Cody at Farnborough. On May 14, 1909, he flew it for more than a mile. His wife was the first woman to fly in a plane in the UK on August 13, 1909.
The first human airborne ejection seat firing happened on July 24, 1946. It took place over Chalgrove Airfield, Oxfordshire. The Miles M.52, designed in Woodley Aerodrome, had the new flying tail design. This helped with aircraft control at supersonic speeds. Its design was used in the American Bell X-1, the first supersonic aircraft.
The first Harrier aircraft flew on December 28, 1967. This was the first RAF aircraft with a head-up display system. Royston Instruments developed the world's first multi-channel flight data recorders in 1965.
The first jet airliner ever built (an individual plane) was a Nene-powered Vickers VC.1 Viking. It flew on April 6, 1948, from Wisley Airfield. The world's first turboprop airliner also flew from there on July 16, 1948. In 1939, John Godeck invented the plan position indicator method of radar display at Cowes. Sperry Gyroscope in Bracknell made the guidance systems for Britain's 1960s space rockets.
Other Industries
The Wealden iron industry was the site of Britain's first blast furnace in 1491. It produced much of Britain's cast iron until the 1770s.
Portsmouth Block Mills had the world's first metal machine tools. These were built to make wooden pulleys. This was also the site of the world's first industrial assembly line in 1803.
South Foreland Lighthouse was the world's first lighthouse with electric light. This happened on December 8, 1858. The first industrial electrical generator was made by Frederick Hale Holmes. From this lighthouse in 1899, the first international radio broadcast to France was made.
Portland cement was developed in Northfleet, Kent, by William Aspdin. He heated the ingredients to a very high temperature (around 1450 °C). This created clinker, which made the cement much stronger.
The tallest freestanding structure in the region is the chimney of Grain Power Station at 801 feet (244 m).
George Albert Smith developed the first colour film process, called Kinemacolor, in 1906. George E. Davis from Slough is known as the father of chemical engineering. Bentalls in Bracknell had the first point of sale terminal in Europe in 1973.
The National Fruit Collection at Brogdale is the world's largest collection of fruit trees. Scalextric was invented by Fred Francis in 1956 in Havant. The world's first Mars Bar was made in Slough in 1932. The Ford GT40 car was developed by Ford Advanced Vehicles in Slough in the mid-1960s.
Geography of South East England
The highest point in the region is Walbury Hill in Berkshire at 297 m (974 ft).
Britain's tallest native tree is a 144 feet (44 m) beech at Devil's Dyke in West Sussex.
Historical Boundaries
Before 1999, the South East region included Bedfordshire, Greater London, Essex and Hertfordshire. The current official region covers a similar area to the former South East Civil Defence Region.
Historic Counties
Historic counties were used for administration until 1899. However, they are still important to some people, especially for county cricket.
Alternative Definitions
Sometimes, "South East" can mean a smaller area, like only London, Kent, East Sussex, West Sussex, and Surrey. Other times, it can refer to the older, larger statistical region. The term is also sometimes used to mean the home counties.
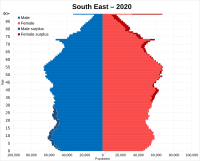
Population of South East England
In 2011, the population of the region was 8,634,750. This makes it the most populated English region. Large urban areas include South Hampshire (855,000 people) and Brighton/Worthing/Littlehampton (474,000 people). Areas closer to London are part of the Greater London Urban Area.
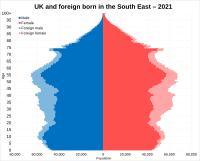
The South East has the second highest percentage of people born outside Britain, after London. The 2021 census showed that 78.8% of residents were White British.
| Census | Population | Change |
|---|---|---|
| 1801 | 962,350 | |
| 1811 | 1,072,563 | |
| 1821 | 1,239,883 | |
| 1831 | 1,378,755 | |
| 1841 | 1,561,792 | |
| 1851 | 1,687,558 | |
| 1861 | 1,957,208 | |
| 1871 | 2,226,880 | |
| 1881 | 2,496,534 | |
| 1891 | 2,776,842 | |
| 1901 | 3,093,606 | |
| 1911 | 3,472,091 | |
| 1921 | 3,718,228 | |
| 1931 | 3,995,122 | |
| 1941a | 4,443,002 | |
| 1951 | 4,976,340 | |
| 1961 | 5,738,844 | |
| 1971 | 6,718,771 | |
| 1981 | 7,025,593 | |
| 1991 | 7,677,641 | |
| 2001 | 8,000,550 | |
| 2011 | 8,634,750 | |
| 2021 | 9,278,063 |
a There was no census in 1941.
Cities and Towns by Population
| City/town | Ceremonial county | Population | |
|---|---|---|---|
| City/town (2019) |
Conurbation (2011) |
||
| Brighton and Hove | East Sussex | 290,885 | 474,485 |
| Milton Keynes | Buckinghamshire | 269,457 | 229,941 |
| Southampton | Hampshire | 252,520 | 855,569 |
| Portsmouth | Hampshire | 214,905 | |
| Slough | Berkshire | 164,455 | 163,777 |
| Reading | Berkshire | 161,780 | 318,014 |
| Oxford | Oxfordshire | 152,457 | 171,380 |
| High Wycombe | Buckinghamshire | 125,257 | 133,204 |
| Basingstoke | Hampshire | 113,776 | 107,642 |
| Maidstone | Kent | 113,137 | 107,627 |
| Crawley | West Sussex | 112,409 | 180,508 |
| Worthing | West Sussex | 110,570 | |
| Gillingham | Kent | 104,157 | 243,931 |
| Eastbourne | East Sussex | 103,745 | 118,219 |
Ethnic Groups in the South East
| Ethnic group | 1981 estimates | 1991 | 2001 | 2011 | 2021 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| White: Total | 6,691,186 | 97.2% | 7,271,256 | 96.9% | 7,608,989 | 95.10% | 7,827,820 | 90.65% | 8,009,380 | 86.2% |
| White: British | – | – | – | – | 7,304,678 | 91.3% | 7,358,998 | 85.22% | 7,315,058 | 78.8% |
| White: Irish | – | – | – | – | 82,405 | 1.02% | 73,571 | 0.9% | 78,219 | 0.8% |
| White: Irish Traveller/Gypsy | – | – | – | – | – | – | 14,542 | 0.2% | 16,748 | 0.2% |
| White: Roma | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 12,786 | 0.1% |
| White: Other | – | – | – | – | 221,906 | 2.77% | 380,709 | 4.4% | 586,569 | 6.3% |
| Asian or Asian British: Total | – | – | 149,198 | 2% | 219,704 | 2.74% | 452,042 | 5.23% | 650,545 | 7% |
| Asian or Asian British: Indian | – | – | 64,888 | 0.9% | 89,219 | 1.1% | 152,132 | 1.76% | 241,537 | 2.6% |
| Asian or Asian British: Pakistani | – | – | 35,946 | 0.5% | 58,520 | 99,246 | 145,311 | 1.6% | ||
| Asian or Asian British: Bangladeshi | – | – | 8,546 | 0.1% | 15,358 | 27,951 | 39,881 | 0.4% | ||
| Asian or Asian British: Chinese | – | – | 18,226 | 0.2% | 33,089 | 53,061 | 64,329 | 0.7% | ||
| Asian or Asian British: Asian Other | – | – | 21,592 | 0.3% | 23,518 | 119,652 | 1.38% | 159,487 | 1.7% | |
| Black or Black British: Total | – | – | 46,636 | 0.6% | 56,914 | 0.71% | 136,013 | 1.57% | 221,584 | 2.4% |
| Black or Black British: African | – | – | 9,588 | 0.1% | 24,582 | 87,345 | 150,540 | 1.6% | ||
| Black or Black British: Caribbean | – | – | 23,633 | 0.3% | 27,452 | 34,225 | 43,523 | 0.5% | ||
| Black or Black British: Other | – | – | 13,415 | 0.2% | 4,880 | 14,443 | 27,521 | 0.3% | ||
| Mixed: Total | – | – | – | – | 85,779 | 1.07% | 167,764 | 1.94% | 260,871 | 2.8% |
| Mixed: White and Caribbean | – | – | – | – | 23,742 | 0.3% | 45,980 | 62,087 | 0.7% | |
| Mixed: White and African | – | – | – | – | 9,493 | 0.1% | 22,825 | 38,633 | 0.4% | |
| Mixed: White and Asian | – | – | – | – | 29,977 | 0.4% | 58,764 | 88,106 | 0.9% | |
| Mixed: Other Mixed | – | – | – | – | 22,567 | 0.3% | 40,195 | 72,045 | 0.8% | |
| Other: Total | – | – | 32,964 | 0.4% | 29,259 | 0.36% | 51,111 | 0.59% | 135,683 | 1.4% |
| Other: Arab | – | – | – | – | – | – | 19,363 | 29,574 | 0.3% | |
| Other: Any other ethnic group | – | – | 32,964 | 0.4% | 29,259 | 0.36% | 31,748 | 0.36% | 106,109 | 1.1% |
| Ethnic minority: Total | 191,229 | 2.8% | 228,798 | 3.1% | 391,656 | 4.9% | 806,930 | 9.4% | 1,268,683 | 13.8% |
| Total | 6,882,415 | 100% | 7,500,054 | 100% | 8,000,645 | 100% | 8,634,750 | 100% | 9,278,063 | 100% |
Religion in the South East
| Religion | 2021 | 2011 | 2001 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| Christianity | 4,313,319 | 46.5% | 5,160,128 | 59.8% | 5,823,025 | 72.8% |
| Islam | 309,067 | 3.3% | 201,651 | 2.3% | 108,725 | 1.4% |
| Hinduism | 154,748 | 1.7% | 92,499 | 1.1% | 44,575 | 0.6% |
| Sikhism | 74,348 | 0.8% | 54,941 | 0.6% | 37,735 | 0.5% |
| Buddhism | 54,433 | 0.6% | 43,946 | 0.5% | 22,005 | 0.3% |
| Judaism | 18,682 | 0.2% | 17,761 | 0.2% | 19,037 | 0.2% |
| Other religion | 54,098 | 0.6% | 39,672 | 0.5% | 28,668 | 0.4% |
| No religion | 3,733,094 | 40.2% | 2,388,286 | 27.7% | 1,319,979 | 16.5% |
| Religion not stated | 566,279 | 6.1% | 635,866 | 7.4% | 596,896 | 7.5% |
| Total population | 9,278,068 | 100% | 8,634,750 | 100% | 8,000,645 | 100% |
Education in the South East
Schools in the Region
Some areas like Buckinghamshire, Medway, Kent, and Slough have a selective education system. This means students take exams to get into grammar schools. Kent has 33 grammar schools, Buckinghamshire has 13, Medway has 6, and Slough has 4. Other areas use a comprehensive system.
The oldest school in England, The King's School, Canterbury, dates back to 597 AD. Reading School, a grammar school, often sends the highest percentage of its students to Oxford or Cambridge universities (Oxbridge) among state schools.
The South East has the most students in state secondary schools in England (508,000). Kent has the highest number for a county (101,000). The region also has the highest percentage of students attending grammar schools (12%).
For GCSE results, Buckinghamshire consistently has the highest scores in the South East and England. Schools in Surrey and Hampshire also do very well. Some areas, like Portsmouth and the Isle of Wight, have lower average results.
There are 49 colleges for further education (FE) in the region.
Universities in the South East

The most famous university here is the University of Oxford. It is known for its excellent academics and beautiful colleges. In 2013, it was ranked the fourth best university in the world.
Other universities in the region include:
- University of Brighton, Brighton and Eastbourne
- University of Buckingham, Buckingham
- Buckinghamshire New University, High Wycombe, Aylesbury, Uxbridge and Great Missenden
- Canterbury Christ Church University, Canterbury, Medway towns and Tunbridge Wells
- University of Chichester, Chichester and Bognor Regis
- University of Kent, Canterbury
- The University of Law, Guildford
- University of Reading, Reading, Henley-on-Thames
- The Open University, Milton Keynes
- Oxford Brookes University, Oxford
- University of Portsmouth, Portsmouth
- Royal Holloway, University of London, Egham
- Solent University, Southampton
- University of Southampton, Southampton
- University of Surrey, Guildford
- University of Sussex, Brighton
- University of Winchester, Winchester
The Open University and University of Oxford receive the most funding. The University of Southampton also gets a large amount of funding for research. Many students from the South East stay in the region for university. After graduating, most (over 50%) also choose to stay in the South East.
Economy of South East England
The South East of England is a very wealthy area. It has the second largest regional economy in the UK, after London. In 2006, its economy was worth £177 billion. In 2007, the average income per person was £22,624. This made it the second richest region per person, after London. However, wealth can vary a lot within the region. Some areas are much richer than others.
Many high-tech companies are located near the M3 motorway in Surrey and the M4 motorway in Berkshire. Companies like Microsoft and Oracle have their UK headquarters in Reading. The Gatwick Diamond area, around Gatwick Airport, is also a hub for high-tech industries. The largest company in the South East, by how much money it makes, is Vodafone.
| South-East Region | GDP € | GDP per capita € (2013) |
|---|---|---|
| Berkshire | €45.2 bn | €51,500 (includes Borough of Reading) |
| Buckinghamshire | €18.6 bn | €36,100 (excludes City of Milton Keynes UA) |
| Oxfordshire | €25.3 bn | €38,000 |
| Milton Keynes | €12.8 bn | €50,300 |
| Brighton & Hove | €8.4 bn | €30,400 |
| East Sussex CC | €11.1 bn | €20,800 |
| Surrey | €46.6 bn | €40,500 |
| West Sussex | €24.6 bn | €32,000 |
| Portsmouth | €6.8 bn | €33,000 |
| Southampton | €7.4 bn | €30,700 |
| Hampshire CC | €44.6 bn | €33,400 (excludes Portsmouth and Southampton) |
| Isle of Wight | €2.8 bn | €20,300 |
| Medway | €5.6 bn | €20,900 |
| Kent CC | €38.6 bn | €25,900 |
| TOTAL | €300.5 bn | €34.200 |
Transport in the South East

The main roads include the M1, M40, M4, M2, M20, M23, and M3. All these roads connect to the M25, which runs around London.
The A34 connects north to south through Oxfordshire, Berkshire, and Hampshire. The A27 and M27 provide an east-west route in the south.
The main international airport is Gatwick Airport. Smaller regional airports are at Kent International Airport (Ramsgate), Shoreham Airport and Southampton Airport. Heathrow Airport is in Greater London but is also used by people from the South East.
Major railway lines pass through the region, connecting it to London and other parts of the UK. The Port of Dover and the port at Folkestone offer many ferry services to France.
Culture of South East England
The culture of South East England is shaped by its beautiful countryside, which has inspired the "idealised English identity." It also acts as a commuting area for Greater London. Recently, the region has become a hub for the UK's creative industries.
Literature, TV, Film, Music, and Food
Ashdown Forest in East Sussex was the inspiration for the Hundred Acre Wood in the Winnie-the-Pooh stories. The author, A.A. Milne, lived nearby. Alice Liddell, who inspired Alice in Lewis Carroll's Alice's Adventures in Wonderland, spent much of her childhood in Oxford.
Roger Hargreaves wrote his Mr. Men books while living in Sunbury. Mary Tourtel from Canterbury created Rupert Bear. Gerry Anderson's company filmed Thunderbirds on the Slough Trading Estate.
The first multiplex cinema in the UK opened in Milton Keynes in the mid-1980s.
Elgar wrote his Cello Concerto in Fittleworth, West Sussex, in 1919. Isaac Watts, a hymn writer from Southampton, wrote famous hymns like When I Survey the Wondrous Cross. At Chalfont St Giles, Milton finished Paradise Lost. Olney in Buckinghamshire is known for the Olney Hymns, including Amazing Grace.
Pimm's was invented by James Pimm of Kent in the 1820s. Banoffee pie was invented in 1972 in Jevington, East Sussex. The Granny Smith apple was created by Maria Ann Smith from Sussex, who moved to Australia. Horticulturist Richard Cox bred his popular Cox's Orange Pippin apple in Colnbrook.
Media in the South East
Television Channels
The BBC broadcasts South Today from Southampton and South East Today from Tunbridge Wells, Kent. ITV News Meridian has offices in Whiteley, near Fareham.
- Television coverage for Buckinghamshire is split. The western part gets BBC South and ITV Meridian. Much of Milton Keynes is covered by BBC East and ITV Anglia. The south of the county is covered by BBC London News and ITV London News.
- That's Solent TV covers Portsmouth, Isle of Wight, Southampton, and Winchester.
Radio Stations
- BBC Local Radio services include Berkshire, Surrey, Sussex, Solent, Oxford, and Kent. Buckinghamshire and Milton Keynes are served by BBC Three Counties Radio.
- Commercial radio stations include:
- Wave 105, a regional music station from Fareham.
- Heart South covers much of the region. Milton Keynes is served by Heart East.
- Capital South
- Greatest Hits Radio South
- Nation Broadcasting operates Nation Radio South Coast and Easy Radio South Coast from Southampton.
- More Radio broadcasts on four frequencies in Sussex.
- Isle of Wight Radio
- KMFM, a network of seven stations in Kent.
- Milton Keynes is served by BBC Three Counties Radio, Heart FM, and MKFM.
Newspapers
Newspapers in the region include the Southern Daily Echo (Southampton), Portsmouth News, Hampshire Chronicle, Oxford Times, Oxford Mail, Argus (Brighton), Reading Evening Post, KM Group titles (Kent), Surrey Advertiser, Reading Chronicle, Medway News, KOS Media titles (Kent), Basingstoke Gazette (Basingstoke), and the Milton Keynes Citizen.
Sport in the South East
Badminton England is in Milton Keynes. The Royal Yachting Association (RYA) is in Hamble, Hampshire. The World Squash Federation is in Hastings. England Hockey is in Bisham Abbey. The first World Transplant Games were held in Portsmouth in 1978.
The All England Jumping Course at Hickstead hosts the Royal International Horse Show. There are many horse-racing stables on the Lambourn Downs. The Epsom Derby is held in early June. In the mid-18th century, the Hambledon Cricket Club in Hampshire was very important for modern cricket.
The BDO World Darts Championship is held in January at Lakeside Leisure Complex.
Wentworth Golf Club in Surrey hosts the BMW PGA Championship.
Charles William Miller, who went to school in Southampton, helped bring football to Brazil.
See also
 In Spanish: Región del Sudeste de Inglaterra para niños
In Spanish: Región del Sudeste de Inglaterra para niños