Kolkata facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
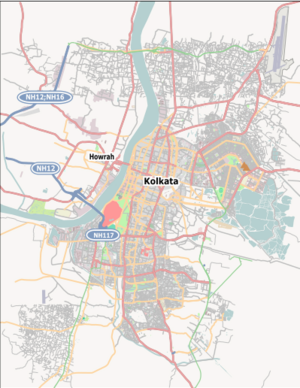
Kolkata
Calcutta
|
|
|---|---|
|
Kolkata skyline
Durga Puja in Kolkata
Park Street flyover with Kolkata CBD on left and Kolkata maidan on right
Vintage trams
Science City Kolkata
Jorasanko Thakur Bari
Birla Planetarium
and The 42 Eden Gardens during a match
Howrah Bridge
|
|
| Nickname(s):
City of Joy, City of Castles, Gateway of Eastern India, Cultural Capital of India
|
|
| Country | |
| State | |
| Division | Presidency |
| District | Kolkata |
| Named for | Kalighat Kali Temple |
| Government | |
| • Type | Municipal Corporation |
| • Body | Kolkata Municipal Corporation |
| Area | |
| • Megacity | 206.08 km2 (79.151 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,886.67 km2 (728.45 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 9 m (30 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Megacity | 2,011 census: 2,023 estimate: |
| • Density | 30,000/km2 (80,000/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 2,011 census: 2,023 estimate: |
| • City rank | 7th in India |
| • Metro rank | 3rd in India; 2nd in Bengal Region; 13th in Asia; 16th in the world |
| Demonyms | Kolkatan Calcuttan |
| Languages | |
| • Official | Bengali • English |
| Time zone | UTC+05:30 (IST) |
| PIN |
700 xxx
|
| Telephone code | +91 33 |
| Vehicle registration | WB-01 to WB-10 |
| UN/LOCODE | IN CCU |
| Metro GDP (PPP) | |
| HDI (2004) | 0.780 (High) |
| International airports | Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose International Airport (CCU) |
| Transit | Rapid Transit: Kolkata Metro Commuter rail: Kolkata Suburban Railway Other(s): Kolkata Tram |
| Metropolitan Planning Authority | Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority |
| Other names | Calcutta, Kolikata, Tilottama |
| Official name: Durga Puja in Kolkata | |
| Type: | Cultural |
| Designated: | 2021 (16th Committee of UNESCO for safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage) |
| Reference #: | [1] |
| Region: | Southern Asia |
| Notability: | First in Asia under "Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity" category |
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta, is a very important city in India. It is the capital and largest city of the state of West Bengal. The city sits on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River. It is about 80 kilometers (50 miles) west of the border with Bangladesh. Kolkata is a major center for money and business in eastern and northeastern India.
It is the seventh most populated city in India. About 4.5 million people live in the city itself. Its larger metropolitan area has over 15 million people. Many people consider Kolkata to be the cultural capital of India. It is a city with a rich history and culture in the region of Bengal. Kolkata is the second-largest city in the world where people speak Bengali. It also has the most Nobel winners of any city in India.
Before the British arrived, Kolkata was made up of three villages. These villages were ruled by the Nawab of Bengal under the Mughal Empire. In 1690, the East India Company got permission to trade there. They built a fort called Fort William. In 1756, Nawab Siraj ud-Daulah took over the fort. But he was defeated in the Battle of Plassey in 1757. After this, Kolkata became the capital of India under British rule until 1911. It was the second-largest city in the British Empire after London. Kolkata was a key center for government, law, education, science, and art in India. It was also important for the Indian nationalist movement.
The division of Bengal in 1947 changed the city's future. After India became independent in 1947, Kolkata faced many years of political violence and slow economic growth. But it later recovered. In the late 20th century, the city helped the government of Bangladesh during the Bangladesh Liberation War in 1971. Many Hindu refugees from East Bengal (now Bangladesh) also came to Kolkata after 1947. This changed the city and its politics. Later, Mumbai became India's largest city.
Kolkata is a city with many different kinds of people and cultures. It has special features like very close-knit neighborhoods called paras. People also enjoy addas, which are relaxed, free-flowing conversations. Kolkata's buildings include many famous landmarks from the British Empire. These include the Victoria Memorial, Howrah Bridge, and the Grand Hotel. The city also has India's only Chinatown. It has signs of Jewish, Armenian, Greek, and Anglo-Indian communities. Kolkata is often called India's cultural capital.
The city is home to important national places. These include the Academy of Fine Arts, the Asiatic Society, the Indian Museum, and the National Library of India. The University of Calcutta, the first modern university in South Asia, has produced many important people. Kolkata is the center of the Bengali film industry, known as Tollywood. It also has many science institutions. The Port of Kolkata is India's oldest working port. Kolkata is famous for its big celebrations of the Hindu festival Durga Puja. UNESCO recognizes this festival for its importance to world heritage. Kolkata is also known as the City of Joy.
Contents
- Understanding Kolkata's Name
- Kolkata's Past: A Historical Journey
- Kolkata's Location and Environment
- Kolkata's City Layout
- Kolkata's Economy
- People and Languages of Kolkata
- Getting Around Kolkata: Transport
- Healthcare in Kolkata
- Education in Kolkata
- Kolkata's Rich Culture
- Media in Kolkata
- Sports in Kolkata
- International Connections
- Images for kids
- See also
Understanding Kolkata's Name
The name Kolkata comes from Kôlikata. This was the Bengali name of one of three villages that existed before the British arrived. The other two villages were Sutanuti and Govindapur.
There are a few ideas about where the name comes from:
- Some think Kolikata is a different way of saying Kalikkhetrô. This means 'Field of [the goddess] Kali'.
- Another idea is that the name comes from Kalighat.
- It might also come from the Bengali word kilkila, meaning 'flat area'.
- The name could also be from khal (meaning 'canal') and kaṭa (meaning 'dug').
- One more idea is that the area made koli chun (quicklime) and kata (coir). So, it was called Kolikata.
Even though people always said Kolkata or Kôlikata in Bengali, the official English name was Calcutta until 2001. Then, it was changed to Kolkata to match the Bengali pronunciation.
Kolkata's Past: A Historical Journey
Evidence shows that people have lived in the Kolkata area for over 2,000 years. Kolkata, or Kalikata, was known as a port, a business center, and a Hindu pilgrimage site. This was because of the Kalighat Temple. The village of Kalikata was first mentioned in a book from 1495. It described how traders would stop there to worship Goddess Kali. Kalikata was seen as a safe place for business people.
Kolkata's written history began in 1690. This is when the English East India Company came to set up their trade in Bengal. Some people thought Job Charnock founded the city. However, a court ruled in 2003 that the city does not have one founder. The city we see today was built on three villages: Kalikata, Gobindapur, and Sutanuti. These villages were sold to the East India Company in 1698.
In 1712, the British finished building Fort William. It was on the east bank of the Hooghly River. Its purpose was to protect their trading post. The British started making their defenses stronger in 1756. This was because of fights with French forces. The Nawab of Bengal, Siraj-ud-Daulah, did not like the company's military actions and tax evasion. He attacked and captured Fort William. This led to the deaths of some East India Company officials.
A year later, Company soldiers and British troops led by Robert Clive took the city back. In 1765, the East India Company became the tax collector for the Mughal emperor in Bengal. By 1773, Calcutta was the main office of the East India Company.
In 1793, the Nawabs lost their power. The East India Company took full control of the city. In the early 1800s, the swampy areas around the city were drained. The government area was built along the Hooghly River. Richard Wellesley, who was in charge from 1797 to 1805, helped develop the city and its buildings. By 1837, the city had about 229,700 people. Only 3,138 of them were British.
In 1864, a big storm hit the city. About 60,000 people died in Kolkata.
By the 1850s, Calcutta had two main parts. "White Town" was mostly British. "Black Town" was mostly Indian. The city grew quickly in industry starting in the 1850s. This was especially true for textile and jute factories. British companies invested a lot in new projects like telegraph lines. British and Indian cultures mixed, creating a new group called the babu class. These were educated Indians who often worked in government or as professionals. In the 19th century, the Bengal Renaissance brought more cultural growth to the city. In 1883, Calcutta hosted the first national meeting of the Indian National Association. This was India's first nationalist group.
The division of Bengal in 1905 caused huge protests. This made Calcutta a less friendly place for the British. So, the capital was moved to New Delhi in 1911. Calcutta remained a center for groups fighting for Indian independence. During World War II, the city and its port were bombed by the Japanese. Millions of people died during the Bengal famine of 1943. This was due to war, poor management, and natural problems. The partition of India in 1947 led to more conflicts and changes in population. Many Muslims moved to East Bengal (now Bangladesh). Hundreds of thousands of Hindus fled into Kolkata.
In the 1960s and 1970s, Kolkata faced many problems. There were power shortages, strikes, and a violent movement by groups called Naxalites. This damaged the city's systems and slowed its economy. During the Bangladesh Liberation War in 1971, Kolkata hosted the government of Bangladesh in exile. Refugees from the war also flooded into the city. In the mid-1980s, Mumbai became India's most populated city. In 1985, Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi called Kolkata a "dying city."
Kolkata's economy started to get better after the 1990s. This was when India began to make its economy more open. Since 2000, the information technology (IT) sector has greatly helped Kolkata's economy. The city is also seeing growth in its manufacturing industries.
Kolkata's Location and Environment
Kolkata is located along the east bank of the Hooghly River. It is part of the lower Ganges Delta in eastern India. The city is about 75 kilometers (47 miles) west of the border with Bangladesh. Kolkata is not very high above sea level, ranging from 1.5 to 9 meters (5 to 30 feet). Much of the city was once a wetland. Over time, it was filled in to make space for the growing population. The remaining wetlands, called the East Kolkata Wetlands, are very important. They are recognized as a "wetland of international importance."
Like most of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, the soil and water in Kolkata are mostly alluvial. This means they are made of rich soil deposited by rivers. Kolkata is in an area called the "Bengal basin." The city is located over a part of this basin that is about 25 kilometers (16 miles) wide. The ground beneath Kolkata is made of layers of clay, silt, sand, and gravel.
The Bureau of Indian Standards places Kolkata in seismic zone III. This means the city has a moderate risk of earthquakes.
Kolkata's Weather and Seasons
Kolkata has a tropical savanna climate. This means it has hot, humid summers and mild winters. A United Nations Development Programme report says the city has a "very high damage risk" from wind and cyclones.
| Climate data for Kolkata (Alipore) 1991–2020, extremes 1901–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 32.8 (91.0) |
38.4 (101.1) |
41.1 (106.0) |
43.3 (109.9) |
43.7 (110.7) |
43.9 (111.0) |
39.9 (103.8) |
38.4 (101.1) |
38.9 (102.0) |
39.0 (102.2) |
34.9 (94.8) |
32.5 (90.5) |
43.9 (111.0) |
| Mean maximum °C (°F) | 29.8 (85.6) |
33.9 (93.0) |
37.5 (99.5) |
38.8 (101.8) |
39.0 (102.2) |
37.8 (100.0) |
36.0 (96.8) |
35.3 (95.5) |
35.5 (95.9) |
35.3 (95.5) |
33.1 (91.6) |
30.0 (86.0) |
39.8 (103.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 25.5 (77.9) |
29.4 (84.9) |
33.7 (92.7) |
35.4 (95.7) |
35.5 (95.9) |
34.1 (93.4) |
32.5 (90.5) |
32.3 (90.1) |
32.6 (90.7) |
32.3 (90.1) |
30.2 (86.4) |
26.7 (80.1) |
31.7 (89.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 19.9 (67.8) |
23.8 (74.8) |
28.2 (82.8) |
30.6 (87.1) |
31.2 (88.2) |
30.6 (87.1) |
29.5 (85.1) |
29.4 (84.9) |
29.4 (84.9) |
28.3 (82.9) |
25.1 (77.2) |
21.1 (70.0) |
27.3 (81.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 14.3 (57.7) |
18.1 (64.6) |
22.9 (73.2) |
25.7 (78.3) |
26.8 (80.2) |
27.1 (80.8) |
26.7 (80.1) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.3 (79.3) |
24.4 (75.9) |
20.1 (68.2) |
15.5 (59.9) |
22.9 (73.2) |
| Mean minimum °C (°F) | 10.9 (51.6) |
12.4 (54.3) |
18.2 (64.8) |
21.1 (70.0) |
21.8 (71.2) |
23.9 (75.0) |
24.3 (75.7) |
24.6 (76.3) |
23.9 (75.0) |
20.9 (69.6) |
16.9 (62.4) |
11.9 (53.4) |
10.0 (50.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 6.7 (44.1) |
7.2 (45.0) |
10.0 (50.0) |
16.1 (61.0) |
17.9 (64.2) |
20.4 (68.7) |
20.6 (69.1) |
22.6 (72.7) |
20.6 (69.1) |
17.2 (63.0) |
10.6 (51.1) |
7.2 (45.0) |
6.7 (44.1) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 15.4 (0.61) |
24.6 (0.97) |
36.8 (1.45) |
55.0 (2.17) |
118.5 (4.67) |
276.7 (10.89) |
371.6 (14.63) |
372.1 (14.65) |
325.0 (12.80) |
179.6 (7.07) |
32.6 (1.28) |
5.6 (0.22) |
1,813.3 (71.39) |
| Average rainy days | 1.1 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 3.2 | 6.2 | 12.6 | 17.5 | 16.8 | 13.6 | 7.4 | 1.4 | 0.7 | 84.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) (at 17:30 IST) | 62 | 55 | 51 | 61 | 68 | 77 | 82 | 83 | 82 | 76 | 68 | 65 | 69 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 213.9 | 211.9 | 229.4 | 240.0 | 232.5 | 135.0 | 105.4 | 117.8 | 126.0 | 201.5 | 216.0 | 204.6 | 2,234 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 6.9 | 7.5 | 7.4 | 8.0 | 7.5 | 4.5 | 3.4 | 3.8 | 4.2 | 6.5 | 7.2 | 6.6 | 6.1 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 7 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 10 |
| Source 1: India Meteorological Department (sun 1971–2000) Weather Atlas | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Tokyo Climate Center (mean temperatures 1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Kolkata (Dumdum Airport) 1991–2020, extremes 1939–2012 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 32.5 (90.5) |
37.3 (99.1) |
40.6 (105.1) |
42.8 (109.0) |
43.1 (109.6) |
43.7 (110.7) |
39.2 (102.6) |
37.7 (99.9) |
37.5 (99.5) |
36.8 (98.2) |
36.0 (96.8) |
33.0 (91.4) |
43.7 (110.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 25.3 (77.5) |
29.2 (84.6) |
33.6 (92.5) |
35.9 (96.6) |
36.1 (97.0) |
34.8 (94.6) |
33.2 (91.8) |
33.0 (91.4) |
33.3 (91.9) |
32.5 (90.5) |
30.1 (86.2) |
26.6 (79.9) |
32.0 (89.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 19.1 (66.4) |
23.0 (73.4) |
27.6 (81.7) |
30.3 (86.5) |
30.9 (87.6) |
30.6 (87.1) |
29.8 (85.6) |
29.7 (85.5) |
29.7 (85.5) |
28.3 (82.9) |
24.5 (76.1) |
20.3 (68.5) |
26.8 (80.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 12.9 (55.2) |
16.9 (62.4) |
21.9 (71.4) |
25.2 (77.4) |
26.2 (79.2) |
26.8 (80.2) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.5 (79.7) |
26.2 (79.2) |
24.1 (75.4) |
19.3 (66.7) |
14.3 (57.7) |
22.2 (72.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 5.0 (41.0) |
6.1 (43.0) |
12.1 (53.8) |
16.6 (61.9) |
17.6 (63.7) |
19.2 (66.6) |
20.1 (68.2) |
21.1 (70.0) |
21.7 (71.1) |
15.7 (60.3) |
11.7 (53.1) |
6.1 (43.0) |
5.0 (41.0) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 15.8 (0.62) |
20.2 (0.80) |
31.9 (1.26) |
53.4 (2.10) |
140.5 (5.53) |
247.5 (9.74) |
366.5 (14.43) |
355.4 (13.99) |
282.1 (11.11) |
170.2 (6.70) |
21.3 (0.84) |
6.8 (0.27) |
1,711.5 (67.38) |
| Average rainy days | 1.1 | 1.4 | 2.3 | 3.5 | 6.6 | 12.4 | 17.6 | 17.1 | 13.0 | 7.1 | 1.1 | 0.7 | 83.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) (at 08:30 IST) | 61 | 53 | 49 | 58 | 66 | 76 | 81 | 82 | 81 | 75 | 67 | 66 | 68 |
| Source 1: India Meteorological Department | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Météo Climat (mean temperature 1991-2020) | |||||||||||||
Temperatures in Kolkata
The average yearly temperature is about 26.8°C (80.2°F). Monthly average temperatures range from 19°C to 30°C (66°F to 86°F). Summers, from March to June, are hot and humid. Temperatures are usually in the low 30s Celsius (80s Fahrenheit). Sometimes, in May and June, temperatures can go above 40°C (104°F). Winter lasts for about two and a half months. Low temperatures can drop to 9–11°C (48–52°F) in December and January. May is the hottest month, and January is the coldest. The highest temperature ever recorded was 43.9°C (111.0°F). The lowest was 5°C (41°F). Winters are pleasant and comfortable.
From April to June, heavy rains or dusty storms often hit the city. These are followed by thunderstorms or hailstorms. They bring a welcome relief from the humidity. These storms are known locally as kal bôishakhi, or "Nor'westers."
Rainfall in Kolkata
The south-west summer monsoon brings most of Kolkata's rain. It rains heavily from June to September. The city gets about 1850 mm (73 inches) of rain each year. July and August have the most rainfall. During these months, continuous rain can sometimes stop daily life in the city. Kolkata gets 2,107 hours of sunshine each year. April has the most sunlight.
Kolkata has been hit by several cyclones. Cyclones in 1737 and 1864 killed thousands of people. More recently, Cyclone Aila in 2009 and Cyclone Amphan in 2020 caused a lot of damage. They brought very strong winds and heavy rain.
Air Quality and Pollution
Pollution is a big problem in Kolkata. In 2008, levels of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide were within national safety limits. However, levels of tiny particles in the air were high. They had been increasing for five years in a row. This causes smog and haze. Bad air pollution has led to more lung problems, like lung cancer, in the city.
Kolkata's City Layout

Kolkata is managed by the Kolkata Municipal Corporation (KMC). It covers an area of 206.08 square kilometers (79.57 square miles). The city is narrow from east to west. It stretches from the Hooghly River to the Eastern Metropolitan Bypass. This is a distance of about 9–10 kilometers (5.6–6.2 miles). The city is longer from north to south. This allows it to be divided into North, Central, South, and East Kolkata.
North Kolkata is the oldest part of the city. It has 19th-century buildings and narrow streets. Areas like Jorasanko, Rajabazar, and Bagbazar are here. Suburban areas like Dum Dum and Baranagar are also part of the greater Kolkata metropolitan area.
Central Kolkata is where the main business district is located. It includes B. B. D. Bagh and the Esplanade. Many government and private offices are here. Another business area is south of Park Street. This area has important roads like Jawahar Lal Nehru Road.
South Kolkata grew after India became independent in 1947. It has nicer neighborhoods like Bhowanipore and Alipore. Suburban areas like Maheshtala are also part of the metropolitan area. The Maidan is a large open field in the city center. It is called the "lungs of Kolkata." It hosts sports events and public gatherings. The Victoria Memorial is at the south end of the Maidan. Other parks include Central Park and Millennium Park.
Metropolitan Area and Nearby Cities
The Kolkata metropolitan area covers 1886.67 square kilometers (728.45 square miles). It includes 4 city corporations, 37 local municipalities, and 24 village councils. In 2011, this urban area had 72 cities and 527 towns and villages. Suburban areas are in districts like North 24 Parganas and Howrah.
Two planned towns near Kolkata are Bidhannagar (Salt Lake City) and Rajarhat (New Town). Salt Lake City's Sector 5 has become a business hub for IT and telecom companies. Both Bidhannagar and New Town are outside the Kolkata Municipal Corporation limits. They have their own city governments.
Kolkata's Economy

Kolkata is the business and financial center of East and Northeast India. It is home to the Calcutta Stock Exchange. It is also a major port for trade and military. Kolkata is one of five cities in eastern India with an international airport.
After India's independence, Kolkata's economy slowed down. This was due to a large increase in population and many strikes. Many factories closed, and businesses moved away. This led to the city being called the "dying city." However, things improved after India's economy became more open in the 1990s. Kolkata's metropolitan area is now one of the most productive in India. Its economy is estimated to be between $150 and $250 billion.
Kolkata has a large informal sector. This means many people work in jobs that are not officially registered. For example, roadside hawkers made a lot of money in 2005. In 2001, most of the city's workers were in service industries. About one-third of the population lives in slums. Many people in slums work in the informal sector.
Major manufacturing companies in Kolkata include Alstom and Larsen & Toubro. The information technology (IT) sector has grown very fast since the late 1990s. Investments in real estate, infrastructure, and retail have also increased. Many large shopping malls and hotels have opened. Companies like ITC Limited and Tata Steel have offices or headquarters in Kolkata. The city is also home to the headquarters of two major banks: UCO Bank and Bandhan Bank. The India Government Mint, Kolkata is one of four mints in India. Many old public sector companies are also based here.
People and Languages of Kolkata
The people who live in Kolkata are called Calcuttan or Kolkatan. In 2011, Kolkata district had a population of 4,486,679 people. The population density was 24,252 people per square kilometer (62,810 per square mile). The number of people decreased slightly from 2001 to 2011. There are 899 females for every 1000 males. This is lower than the national average. Many working men come from rural areas and leave their families behind. Kolkata's literacy rate is 87.14%, which is higher than the national average. The total population of the city in 2011 was 4,496,694. The larger urban area had 14,112,536 people.
|
||||||||||||||||||
In 2003, about one-third of the population lived in slums. These slums can be registered or unregistered. Registered slums have basic services like water and trash removal. Unregistered slums do not have these services. They are built by people living on illegally occupied land. In 2005, about 14% of households in Kolkata were poor. However, 33% lived in slums, showing that some slum households were better off. Mother Teresa won the Nobel Peace Prize for her work with the Missionaries of Charity in Kolkata. This organization helped people who had nowhere else to go.
Languages Spoken in Kolkata
Bengali is the main official language in Kolkata. English is also widely used, especially by people in office jobs. Many people also speak Hindi and Urdu. Bengali Hindus make up most of Kolkata's population. There are also large groups of Marwaris, Biharis, and Urdu-speaking Muslims.
Kolkata has smaller communities too. These include Chinese, Tamils, Nepalis, Pathans, Odias, Telugus, Gujaratis, Anglo-Indians, Armenians, Greeks, Tibetans, Maharashtrians, Punjabis, and Parsis. The number of Armenians, Greeks, and Jews has decreased over time. India's only Chinatown is in eastern Kolkata. Its population has also dropped. The Chinese community traditionally worked in leather tanning and ran Chinese restaurants.
Religions in Kolkata
Others include Sikhism, Buddhism & Other religions (0.03%)
| Religion in Kolkata City (2011) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Religion | Percent | |||
| Hinduism | 76.51% | |||
| Islam | 20.60% | |||
| Christianity | 0.88% | |||
| Jainism | 0.47% | |||
| Others | 1.54% | |||
| Religious group |
1872 | 1881 | 1891 | 1901 | 1911 | 1921 | 1931 | 1941 | 2011 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | |
| Hinduism |
443,970 | 62.84% | 429,180 | 62.69% | 488,532 | 65.92% | 617,303 | 65.04% | 695,052 | 66.62% | 751,619 | 69.77% | 822,293 | 68.71% | 1,531,512 | 72.62% | 3,440,290 | 76.51% |
| Islam |
234,850 | 33.24% | 221,013 | 32.28% | 218,158 | 29.44% | 286,576 | 30.19% | 298,986 | 28.66% | 269,749 | 25.04% | 311,155 | 26% | 497,535 | 23.59% | 926,414 | 20.6% |
| Christianity |
25,352 | 3.59% | 30,478 | 4.45% | 29,904 | 4.03% | 38,515 | 4.06% | 40,511 | 3.88% | 40,376 | 3.75% | 47,484 | 3.97% | 51,991 | 2.47% | 39,758 | 0.88% |
| Buddhism |
1,012 | 0.14% | 1,705 | 0.25% | 2,200 | 0.3% | 2,968 | 0.31% | 2,461 | 0.24% | 3,468 | 0.32% | 3,021 | 0.25% | 3,339 | 0.16% | 4,771 | 0.11% |
| Judaism |
N/A | N/A | 986 | 0.14% | 1,399 | 0.19% | 1,889 | 0.2% | 1,920 | 0.18% | 1,820 | 0.17% | 1,829 | 0.15% | 2,585 | 0.12% | N/A | N/A |
| Sikhism |
N/A | N/A | 284 | 0.04% | 287 | 0.04% | 162 | 0.02% | 1,134 | 0.11% | 1,484 | 0.14% | 4,705 | 0.39% | 8,456 | 0.4% | 13,849 | 0.31% |
| Jainism |
N/A | N/A | 143 | 0.02% | 497 | 0.07% | 1,241 | 0.13% | 1,813 | 0.17% | 5,670 | 0.53% | 3,185 | 0.27% | 6,689 | 0.32% | 21,178 | 0.47% |
| Zoroastrianism |
N/A | N/A | 142 | 0.02% | 167 | 0.02% | 295 | 0.03% | 470 | 0.05% | 620 | 0.06% | 1,199 | 0.1% | 1,430 | 0.07% | N/A | N/A |
| Tribal | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 0 | 0% | 17 | 0% | 67 | 0.01% | 767 | 0.07% | 426 | 0.04% | 1,688 | 0.08% | N/A | N/A |
| Confucian | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 178 | 0.02% | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Others | 1,327 | 0.19% | 727 | 0.11% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 2,607 | 0.25% | 1,597 | 0.15% | 1,437 | 0.12% | 3,766 | 0.18% | 50,434 | 1.12% |
| Total population | 706,511 | 100% | 684,658 | 100% | 741,144 | 100% | 949,144 | 100% | 1,043,307 | 100% | 1,077,264 | 100% | 1,196,734 | 100% | 2,108,891 | 100% | 4,496,694 | 100% |
Getting Around Kolkata: Transport
Kolkata has many ways to get around. Public transport includes the Kolkata Suburban Railway, the Kolkata Metro, trams, rickshaws, taxis, and buses. The suburban rail network connects the city to its far-off areas.
Rail Travel in Kolkata
Kolkata's Metro System
The Kolkata Metro is the city's fast public transport system. It has been running since 1984. It is the oldest underground mass transit system in India. The Blue Line runs north to south through the city center. In 2020, part of the Green Line opened. This line connects Salt Lake City and Howrah, two satellite cities. Other lines like the Purple and Orange lines are also open.
Commuter Trains
The Kolkata Suburban Railway is one of the largest and busiest suburban rail networks in India. Kolkata has five major train stations for long-distance travel. These include Howrah and Sealdah. These stations connect Kolkata to most cities in West Bengal and other major cities in India. Kolkata is also the headquarters for three railway zones of Indian Railways. Kolkata has international train connections to Dhaka, the capital of Bangladesh.
Trams in Kolkata

Kolkata is the only city in India with a tram network. The Calcutta Tramways Company used to run it. Now, the West Bengal Transport Corporation manages it. There are three tram routes still running. Trams are good for the environment. However, they are slow and can cause traffic jams. Heavy rains during the monsoon can also stop tram services.
Roads and Highways
Kolkata and its metropolitan area have the third-largest road network in India. In 2022, the total road network was 4018 kilometers (2497 miles). The city itself has 1850 kilometers (1150 miles) of roads. The number of registered vehicles has increased steadily. Kolkata has the highest car density in India. This causes a lot of traffic. The Kolkata Metro and new roads have helped ease traffic.
Bus services are run by the West Bengal Transport Corporation and private companies. The main bus stations are at Esplanade and Howrah. Major national highways start from the city's outskirts.
Kolkata has international road links. It connects to Dhaka, Bangladesh, via Jessore Road. It also connects to Bangkok, Thailand, and Myanmar through the Kolkata-Thailand-Bangkok Trilateral Highway. Roads also link to Nepal and Bhutan.
Other public transport includes auto rickshaws and yellow metered taxis. Most taxis are old Hindustan Ambassador cars. Newer air-conditioned taxis are also available. In some parts of the city, people use cycle rickshaws and hand-pulled rickshaws for short trips.
Air Travel
The Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose International Airport is located in Dum Dum. It is about 16 kilometers (10 miles) northeast of the city center. This airport handles both domestic and international flights. It was updated in 2013 to handle more air traffic.
Water Transport
The Port of Kolkata was established in 1870. It is India's oldest and only major river port. The Kolkata Port Trust manages the docks in Kolkata and Haldia. The port offers passenger services to Port Blair. It also has cargo services to ports around India and the world. Ferry services connect Kolkata with its twin city of Howrah across the Hooghly River.
Healthcare in Kolkata
In 2011, Kolkata's healthcare system had 48 government hospitals and 366 private medical places. These places had 27,687 hospital beds. For every 10,000 people, there are 61.7 hospital beds. This is higher than the national average. Ten medical and dental colleges are in the Kolkata area. They serve as major hospitals for the state. The Calcutta Medical College, founded in 1835, was the first place in Asia to teach modern medicine. However, these facilities are not enough for everyone in the city.
More than 78% of people in Kolkata prefer private medical care. This is because public hospitals are often too busy. They also have long waiting times.
In 2005, only a small number of Kolkata households had health insurance. The birth rate in Kolkata was 1.4, which was the lowest among eight cities surveyed. The infant death rate was 41 per 1,000 live births. The death rate for children under five was 49 per 1,000 live births.
Kolkata ranked second for children who had not received any vaccinations in 2005. It also ranked second for access to child development centers. The number of malnourished and underweight children in Kolkata was lower than in other cities.
About 18% of men and 30% of women in Kolkata are overweight. Most of them are from richer parts of society. In 2005, Kolkata had the highest percentage of women (55%) with anemia. Also, 20% of men in Kolkata had anemia. Diseases like diabetes, asthma, and goitre are common. Tropical diseases like malaria and dengue are also present, but their numbers are decreasing. Kolkata is a district with a high number of people with HIV/AIDS. In 2014, due to air pollution, people born in the city lived four years less than those in the suburbs.
Education in Kolkata
Schools in Kolkata are run by the state government or private groups. Many private schools are religious. Bengali and English are the main languages used for teaching. Urdu and Hindi are also used, especially in central Kolkata. Schools follow the "10+2+3" system. After high school, students usually go to schools linked with the West Bengal Council of Higher Secondary Education or national boards. They can choose to study arts, business, or science. Job-focused programs are also available. Some Kolkata schools are ranked among the best in India.
In 2010, the Kolkata urban area had 14 state-run universities. Colleges are linked to a university or institution in Kolkata or elsewhere. Aliah University, founded in 1780, is the city's oldest higher education place. The University of Calcutta, founded in 1857, was the first modern university in South Asia. Presidency College, Kolkata, founded in 1855, was one of India's oldest colleges. It became Presidency University, Kolkata in 2010. Bengal Engineering and Science University (BESU) is the second oldest engineering school in the country. It became India's first IIEST. Jadavpur University is known for its arts, science, and engineering programs. The Indian Institute of Management Calcutta was the first of its kind. Kolkata also has the Indian Institute of Foreign Trade.
The West Bengal National University of Juridical Sciences is an independent law school. The Indian Statistical Institute is a public research university. The Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology is the largest technology university in terms of students. Private schools include the Ramakrishna Mission Vivekananda Educational and Research Institute.
Famous Scholars from Kolkata
Many famous scholars were born, worked, or studied in Kolkata. These include physicists Satyendra Nath Bose, Meghnad Saha, and Jagadish Chandra Bose. Chemist Prafulla Chandra Ray and statisticians Prasanta Chandra Mahalanobis and Anil Kumar Gain are also from here. Physician Upendranath Brahmachari and educator Ashutosh Mukherjee are notable. Nobel winners Rabindranath Tagore, C. V. Raman, and Amartya Sen are also connected to the city.
Research Centers
Kolkata has many research institutes, such as:
- All India Institute of Hygiene and Public Health
- Bose Institute
- Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS)
- Nobel winner Sir C. V. Raman did his important work on the Raman effect at IACS.
- Indian Institute of Chemical Biology (IICB)
- Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER)
- Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics (SINP)
- S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBNCBS)
Kolkata's Rich Culture
Kolkata is famous for its literature, art, and history of change. As the former capital of India, it was where modern Indian art and writing began. Kolkata has been called the "City of Furious, Creative Energy" and the "cultural capital of India." The city is known for its paras, which are neighborhoods with a strong community feeling. Each para usually has its own club and a playing field. People enjoy addas, which are relaxed, intellectual conversations. The city also has a tradition of political graffiti.
Kolkata has many buildings with Indo-Islamic and Indo-Saracenic designs. Many old buildings from the colonial period are now "heritage structures." The Indian Museum, founded in 1814, is the oldest museum in India. It has large collections of Indian natural history and art. The Marble Palace is a beautiful European-style mansion. The Victoria Memorial has a museum about the city's history. The National Library of India is the country's main public library. Science City is the largest science center in the Indian subcontinent.
The popularity of commercial theaters has decreased since the 1980s. Group theatres of Kolkata are different. They started in the 1940s and focus on social messages. The Chitpur area has many companies that produce jatra, a folk drama popular in rural Bengal. Kolkata is also the home of the Bengali film industry, called "Tollywood." It has a long history of art films. Famous directors like Satyajit Ray are from here.
In the 19th and 20th centuries, Bengali literature became modern. This was thanks to writers like Rabindranath Tagore and Kazi Nazrul Islam. This, along with social changes, was a big part of the Bengal Renaissance. Later, new literary movements appeared. Most publishers in the city are found around College Street. It is known for its many bookshops.

Kalighat painting started in Kolkata in the 19th century. It showed myths and daily life. The Government College of Art & Craft, founded in 1864, has been home to famous artists. This art college was where the Bengal school of art began. This was a new art movement that reacted against older styles. The Academy of Fine Arts holds regular art shows. The city loves Rabindra Sangeet (songs by Rabindranath Tagore) and Indian classical music. There are many concerts and recitals throughout the year. Bengali popular music, including baul folk songs, is also popular. New music styles have also appeared since the 1990s.
Key parts of Kolkata's food include rice and a fish curry called machher jhol. Desserts include roshogolla, sandesh, and sweet yogurt called mishti dohi. Kolkata has many seafood dishes. Ilish fish is a favorite. Street foods like beguni (fried eggplant), kati roll (flatbread with filling), and phuchka (fried crepe with tamarind sauce) are popular. Indian Chinese cuisine from Chinatown is also well-liked.
Bengali women traditionally wear the sari. However, the shalwar kameez and Western clothes are becoming popular among younger women. Men wear Western clothes more often. But traditional dhoti and kurta are seen during festivals. Durga Puja, in September–October, is Kolkata's biggest festival. It is a time for grand celebrations and artistic decorations. The Bengali New Year, Poila Boishak, is also celebrated. Other festivals include Kali Puja, Diwali, Christmas, and Eid. Cultural events include the Kolkata Book Fair and the Kolkata International Film Festival.
Media in Kolkata
The first newspaper in India, the Bengal Gazette, started in Kolkata in 1780. Popular Bengali newspapers include Anandabazar Patrika and Bartaman. Major English newspapers are The Statesman and The Telegraph. Other English newspapers like The Times of India are also sold. Financial newspapers are widely read. Newspapers in Hindi, Urdu, Gujarati, and Chinese are also available for minority groups.
All India Radio (AIR) broadcasts several radio stations. Kolkata also has 10 local FM radio stations. India's state-owned TV broadcaster, Doordarshan, offers two free channels. Many other channels are available through cable or satellite. Bengali-language 24-hour news channels include ABP Ananda and Zee 24 Ghanta.
Sports in Kolkata
The most popular sports in Kolkata are football and cricket. Unlike most of India, people in Kolkata are very passionate about football. The Indian Football Association, the oldest football association in India, is based here. Kolkata is home to top football clubs like Mohun Bagan AC and East Bengal Club. The Calcutta Football League, Asia's oldest football league, started in 1898. Mohun Bagan AC is the only club called the "National Club of India." Matches between Mohun Bagan and East Bengal, known as the Kolkata Derby, attract huge crowds.
The Salt Lake Stadium, also called Vivekananda Yuba Bharati Krirangan, is India's second-largest stadium. Most matches of the 2017 FIFA U-17 World Cup were played here. Kolkata had 45% of all attendees for that World Cup. The Calcutta Cricket and Football Club is the second-oldest cricket club in the world.
Cricket is also very popular. Kolkata is home to the Indian Premier League (IPL) team Kolkata Knight Riders. The Cricket Association of Bengal manages cricket in West Bengal. Tournaments for cricket, football, badminton, and carrom are held regularly. The Maidan, a large park, hosts many small football and cricket clubs. Eden Gardens, which holds 80,000 people, hosted the final match of the 1987 Cricket World Cup.
The Netaji Indoor Stadium hosted the 1981 Asian Basketball Championship. The city has three 18-hole golf courses. The oldest is at the Royal Calcutta Golf Club, the first golf club outside the UK. The Royal Calcutta Turf Club hosts horse racing and polo. The Calcutta Polo Club is thought to be the oldest polo club in the world. The Calcutta Racket Club is one of the oldest racket clubs in the world. The Calcutta South Club hosts national and international tennis tournaments.
The Calcutta Rowing Club hosts rowing events. Kolkata is a leading center for rugby union in India. The oldest international rugby tournament, the Calcutta Cup, is named after the city. The Beighton Cup, India's oldest field hockey tournament, is usually held at the Mohun Bagan Ground. Famous athletes from Kolkata include Sourav Ganguly and Leander Paes.
International Connections
Foreign Offices
Kolkata has 70 diplomatic offices. These include consulates and honorary consulates. The U.S. Consulate in Kolkata, opened in 1792, is the second oldest U.S. consulate in the world. The Foreigners Regional Registration Office (FRRO) handles immigration and registration for foreigners.
Sister Cities
Kolkata has sister city relationships with these cities around the world:
 Dhaka, Bangladesh
Dhaka, Bangladesh Kunming, China (since October 2013)
Kunming, China (since October 2013) Thessaloniki, Greece (since January 2005)
Thessaloniki, Greece (since January 2005) Naples, Italy
Naples, Italy Karachi, Pakistan
Karachi, Pakistan Incheon, South Korea
Incheon, South Korea Odesa, Ukraine
Odesa, Ukraine Jersey City, New Jersey, United States
Jersey City, New Jersey, United States Long Beach, California, United States
Long Beach, California, United States Dallas, Texas, United States
Dallas, Texas, United States
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Calcuta para niños
In Spanish: Calcuta para niños