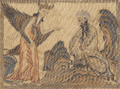Islam facts for kids
Islam ( Arabic: ٱلْإِسْلَام, romanized: al-Islām) is one of the world's largest religions. People who follow Islam are called Muslims. Their holy book is the Quran (also spelled Qur'an or Koran). Muslims believe that the Quran contains the exact words of God (called Allah in Arabic). They believe these words were given to Muhammad by the angel Gabriel.
Muslims see Muhammad as the last prophet and messenger sent by God. They also follow teachings from hadith, which are reports of what Muhammad said and did. Muslims believe that many prophets came before Muhammad. These include Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, and Jesus. They believe all these prophets shared God's message. However, Muslims believe the Quran is the final, unchanged word from God.
Most Muslims belong to one of two main groups. The largest group is Sunni Islam, making up 75–90% of all Muslims. The second group is Shia Islam, which includes 10–20% of Muslims.
Contents
History of Islam
Islamic tradition says that Muhammad was born in Mecca around 570 CE. He became known as the "trusted one" because he was fair and honest. He later married a businesswoman named Khadija.
In 610 CE, Muhammad went to the Cave of Hira near Mecca. There, he is believed to have received his first message from God through the angel Gabriel. This event is very important in Islam. For the next 22 years, Muhammad continued to receive messages from God. Muslims believe he was the last prophet sent to all people.
While in Mecca, Muhammad began to teach people to worship only one God. Many early followers were women, poor people, and slaves. The leaders in Mecca did not like Muhammad's teachings. They felt he was changing their way of life.
After 12 years of challenges, Muhammad and his followers moved in 622 CE. This move, called the Hijra, was to the city of Yathrib (now called Medina). In Medina, Muhammad became a leader for both religious and political matters. He helped create the Constitution of Medina. This agreement allowed different groups in Medina to have religious freedom. It also made them agree to protect Medina together.
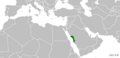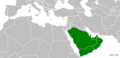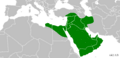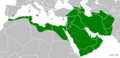
Muslims fought battles against the Meccan forces. They won the Battle of Badr in 624 CE. They also defended Medina successfully in the Battle of the Trench in 627 CE. In 628 CE, a peace treaty was signed, but Mecca broke it two years later. More tribes started to follow Islam. By 629 CE, Muhammad and his followers peacefully took over Mecca. By the time he passed away in 632 CE, Muhammad had united the tribes of Arabia.
What Muslims Believe

Muslims have six main beliefs. They believe in God, His angels, His holy books, His messengers (prophets), the Last Day (Day of Judgment), and divine destiny (God's plan).
God's Oneness
The most important idea in Islam is tawḥīd, which means that God is one and unique. Muslims believe God has no partners. He is not like the Christian Trinity.
Islam teaches that God created everything in the universe by simply saying "Be, and it is." The main goal of life, for Muslims, is to worship God. Muslims believe they can talk to God directly. There are no special people, like clergy, needed to connect with God. The word Allāh is the Arabic word for God. It has no plural or gender. Arabic-speaking Christians and Jews also use this word for God.
Angels in Islam

Angels (malak in Arabic) are beings created by God. Their purpose is to worship God and carry out His commands. Some angels deliver messages from God, like Gabriel. Others record people's actions or take souls when someone dies. Angels are often described as being made of light. They do not need to eat or drink. Important angels mentioned in the Quran include Gabriel (Jibrīl) and Michael (Mika'il).
The Quran
The Quran is the holy book of Islam. Muslims believe its verses were revealed to Muhammad by God, through the archangel Gabriel, between 610 CE and 632 CE.
The Quran has 114 chapters, called sūrahs. These chapters contain 6,236 verses, called āyāt. The Quran also shares stories of ancient civilizations and past prophets.
Besides its religious importance, the Quran is seen as a masterpiece of Arabic literature. It has greatly influenced art and the Arabic language.
Other important Islamic teachings come from the Sunnah. The Sunnah tells about Muhammad's life. The Hadith are collections of his sayings. Islamic scholars use hadith to understand the Quran better and to help with Islamic law. Muslims believe the Quran is a guide for all humanity. Its teachings should be followed and shared.
Prophets in Islam
Prophets (anbiyāʾ in Arabic) are people chosen by God to share His message. Some prophets also bring a new holy book. These are called "messengers." Muslims believe prophets are human, not divine. All prophets are believed to have taught the same basic message: to surrender to God's will. This is why there are similarities among different religions.
The Quran mentions many prophets. These include Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, and Jesus. Muslims believe God sent Muhammad as the final prophet, known as the "Seal of the prophets." Muslims are encouraged to live their lives by following Muhammad's good examples.
Resurrection and Judgment

Belief in the "Day of Resurrection" or Yawm al-Qiyāmah is very important for Muslims.
Muslims believe that all people will be judged by their good and bad actions. They will then go to Jannah (paradise) or Jahannam (hell). The Quran lists actions that can lead to hell. However, it also says that God can forgive those who truly repent. Good deeds, like giving to charity, praying, and being kind to animals, are rewarded with entry to heaven. Muslims see heaven as a place of great joy and blessings.
God's Plan
The idea of divine destiny in Islam (al-qadāʾ wa l-qadar) means that everything, good or bad, is believed to be part of God's plan. Muslims often say "Inshallah" (meaning "if God wills") when talking about future events. This shows their belief in God's control.
The Five Pillars of Islam
Muslims follow five basic practices. These are called "The Five Pillars of Islam":
- Shahadah: This is the declaration of faith. It means believing there is no god but Allah, and that Muhammad is His last messenger.
- Salaat: Muslims pray five times each day at specific times. When they pray, they face the Kaaba. The Kaaba is a large cube-shaped building in the holy city of Mecca.
- Zakat: Muslims who have enough money must give a small part of their savings (2.5% each year) to help those in need.
- Sawm or Siyam: This is fasting during Ramadan. Ramadan is the ninth month of the Islamic year. Muslims do not eat or drink from dawn until sunset for this entire month. After Ramadan, there is a holiday called Eid al-Fitr. On this day, Muslims usually go to the mosque for a special service. Then, they celebrate with family and friends.
- Hajj: This is a pilgrimage to Mecca. It happens during the 12th month of the Islamic Calendar. Muslims who can afford it and are healthy enough are encouraged to go to Mecca.
Note: The "Five Pillars of Islam" is a term used by Sunni Muslims. Shia Muslims have a similar set of beliefs called Osul al-Din (Religion Principles). These include Tawheed (God's oneness), Adl (Justice), Nabovah (Prophethood), Imamah (Leadership), and Maad (Resurrection).
Prayer in Islam

Muslims pray in a place of worship called a mosque. In Arabic, a mosque is called a masjid. Many mosques have a dome and one or more towers, called minarets. However, some mosques are built without them.
Muslims take off their shoes before entering a mosque to pray. Prayer is a very important part of a Muslim's daily life.
Muslims are called to prayer (Salah or solah) five times a day. This call is called the Adhan. A person called a muezzin makes the call to prayer. Often, a loudspeaker carries his voice to people nearby. In Muslim countries, the call to prayer is a normal part of daily life.
Muslims often pray on a special mat. This is called a prayer mat or prayer rug. Common Arabic names for it are sajjāda and namazlık.
When it is time to pray, Muslims face the direction of Qibla. This is the direction towards Mecca. They then unroll their prayer mat and perform their prayers to God.
Showing Respect to Prophets
According to Islamic teachings, Muslims say "Peace be upon him" (PBUH) whenever they hear a prophet's name. This is how they show respect to Muhammad and other prophets.
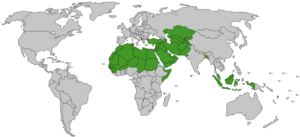
Islam Around the World
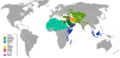
A study in 2009 found that about 23% of the world's population were Muslims. This was about 1.57 billion people. Most of these were Sunni (75-90%), and a smaller part were Shi'a (10-25%). A very small number belong to other Islamic groups.
Most Muslims live in Asia and Africa. About 62% of the world's Muslims live in Asia. Large Muslim populations are found in Indonesia, Pakistan, India, and Bangladesh.
In the Middle East, countries like Turkey and Iran have very large Muslim populations. In Africa, Egypt and Nigeria have the biggest Muslim communities.
Different Groups in Islam
Like other religions, Islam has different groups that have developed over time. These groups have different ways of understanding the holy texts. Here are some of the main groups:
- Non-denominational Muslims: These Muslims do not follow any specific branch. They simply call themselves Muslim.
- Shi'ites: Shi'a Muslims believe that God chose Ali to be the leader after Muhammad. About 10-20% of Muslims are Shi'a. They are the majority in countries like Iran, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Iraq, and Lebanon.
- Sunnism: Sunnis believe that the leaders of Islam should be chosen by the Muslim community. They make up about 75% of all Muslims. After Muhammad, they believe Abu Bakr was the first chosen leader, followed by Omar, Uthman, and then Ali. Sunni beliefs are based on the Quran and collections of Muhammad's sayings called hadiths.
- Sufi: Sufism is a branch of Islam that focuses more on the spiritual and mystical parts of the religion. Sufis often end their prayers with special recitations called dhikr.
Interesting Facts About Islam
- Islam is the second-largest religion in the world. It has about 1.75 billion followers, which is about 24% of the world's population.
- Islam is also the fastest-growing religion in the world.
- Islam has three very holy sites: Jerusalem, Mecca, and Medina.
- Arabs make up about 20% of all Muslims worldwide.
- A Hafeez is a Muslim who has memorized the entire Quran. They can recite every word accurately without looking at the book.
Images for kids
-
Muhammad receiving his first revelation from the angel Gabriel. From the manuscript Jami' al-Tawarikh by Rashid-al-Din Hamadani, 1307.
-
The first chapter of the Quran, Al-Fatiha (The Opening), is seven verses.
-
Silver coin of the Mughal Emperor Akbar, inscribed with the Shahadah.
-
Pilgrims at the Great Mosque of Mecca during the Hajj season.
-
Portrait of the Mughal Emperor Akbar praying to God.
-
Dome of the Rock built by caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan.
-
The eye, according to Hunain ibn Ishaq from a manuscript dated c. 1200.
-
Ghazan Khan, 7th Ilkhanate ruler of the Mongol Empire, converts to Islam.
-
Abdülmecid II was the last Caliph of Islam from the Ottoman dynasty.
-
Ulu mosque in Utrecht, Netherlands.
-
The nine volumes of Sahih Al-Bukhari, one of the six Sunni hadith books.
-
The Imam Hussein Shrine in Iraq is a holy site for Shia Muslims.
-
The Whirling Dervishes, or Mevlevi Order by the tomb of Sufi-mystic Rumi.
-
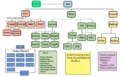
Islamic schools of law in the Muslim world.
-
Crimean Tatar Muslim students (1856).
-
Islamic veils represent modesty.
-
John of Damascus, under the Umayyad Caliphate, viewed Islamic doctrines as a mix from the Bible.
-
Dome in Po-i-Kalyan, Bukhara, Uzbekistan.
See also
 In Spanish: Islam para niños
In Spanish: Islam para niños