São Paulo (state) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
State of São Paulo
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Motto(s):
Pro Brasília Fiant Eximia (Latin)
"Let great things be done for Brazil" |
|||
| Anthem: Bandeirantes Anthem | |||
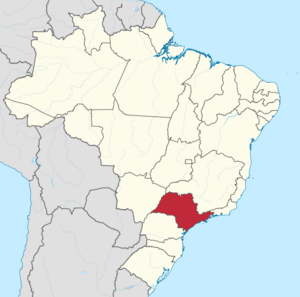
Location of State of São Paulo in Brazil
|
|||
| Country | |||
| Capital and Largest City | São Paulo | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 248,209.4 km2 (95,834.2 sq mi) | ||
| Area rank | 12th | ||
| Population | |||
| • Total | 41,252,160 | ||
| • Rank | 1st | ||
| • Density | 166.19902/km2 (430.45350/sq mi) | ||
| • Density rank | 3rd | ||
| Demonym(s) | Paulista | ||
| GDP | |||
| • Year | 2008 (IBGE) | ||
| • Total | R$ 1,003,016,000,000 (1st) | ||
| • Per capita | R$ 24,456 (2nd) | ||
| HDI | |||
| • Year | 2005 | ||
| • Category | 0.833 – high (3rd) | ||
| Time zone | UTC-3 (BRT) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-2 (BRST) | ||
| Postal Code |
01000-000 to 19990-000
|
||
| ISO 3166 code | BR-SP | ||
| Website | http://www.saopaulo.sp.gov.br/ | ||
São Paulo is one of the 26 states in Brazil. It is named after Saint Paul. São Paulo state has the most developed economy in Brazil.
With over 46 million people in 2019, São Paulo is Brazil's most populated state. It is also the most populated area in the Americas, besides entire countries. Only Brazil and Colombia as countries have more people in South America.
The people living here come from many different backgrounds. Most are descendants of Italians and Portuguese. Italians started arriving in the late 1800s. Portuguese people were the first Europeans to settle the region. There are also many indigenous peoples and Africans. Africans were brought to Brazil as enslaved people long ago. People from other parts of Brazil also moved here. Many Arabs, Germans, Spanish, Japanese, Chinese, and Greeks also live in São Paulo.
The city of São Paulo is the state capital. It is one of the world's largest cities. Its surrounding area, called Greater São Paulo, has 20 million people. This makes it the 9th largest in the world and the biggest in the Americas.
Contents
History of São Paulo State
The land that is now São Paulo state was first home to native groups. They lived here from about 12,000 BC. In the early 1500s, Portuguese and Spanish explorers visited the coast. In 1532, Martim Afonso de Sousa started the first permanent Portuguese settlement. It was a village called São Vicente.
In the 1600s, people from São Paulo called bandeirantes explored deep into the colony. This helped Portugal expand its land in South America. In the 1700s, São Paulo became more important politically.
After Brazil became independent in 1820, São Paulo grew as a big farm producer. It mainly grew coffee. This made some rural families very rich and powerful. They shared control of the Brazilian government with leaders from Minas Gerais in the late 1800s.
Later, during the Vargas Era, São Paulo was one of the first states to start building many factories. Its population also became one of the most urban in Brazil.
Geography of São Paulo

São Paulo is one of Brazil's 27 states. It is in the southwest of the Southeast Region. The state covers about 248,222 square kilometers (95,840 square miles). Most of it is north of the Tropic of Capricorn. It is the 12th largest state in Brazil by area.
The state has many hills and mountains. About 85% of its land is between 300 and 900 meters (980 and 2,950 feet) above sea level. Only 8% is below 300 meters, and 7% is above 900 meters.
The state stretches 611 km (380 mi) from north to south. It is 923 km (574 mi) from east to west. São Paulo uses the Brasilia time zone. This is three hours behind the Greenwich Meridian. São Paulo borders Minas Gerais to the north, Paraná to the south, Rio de Janeiro to the east, and Mato Grosso do Sul to the west. The Atlantic Ocean is to its southeast.
The coast has flat lands below 300 meters (980 feet). These lands are next to the Serra do Mar mountain range. The highest point in the state is Mine Stone, in the Serra da Mantiqueira. It is 2,798 meters (9,180 feet) above sea level. This makes it the fifth highest point in Brazil.
São Paulo has 21 river basins. These are part of three larger river systems. The biggest is the Paraná River basin. It covers most of the state. The Rio Grande starts in Minas Gerais. It joins the Paranaiba to form the Paraná River. The Paraná River separates São Paulo from Mato Grosso do Sul.
Two other important rivers in São Paulo are the Paranapanema and the Tiete River. The Paranapanema is 930 km (578 mi) long. It forms a natural border between São Paulo and Paraná for much of its length. The Tietê River is 1,136 km (706 mi) long. It flows across the state from southeast to northwest. It starts in Salesópolis and ends in Itapura.
Climate in São Paulo
São Paulo state has seven different types of climates. These depend on temperature and rainfall. In the mountain areas, like Serra do Mar and Serra da Mantiqueira, the climate is subtropical. Summers are humid and hot. The average temperature in the coolest month is below 18°C (64°F). There is also an oceanic climate with steady rain all year. Summers are warmer here.
Along the coast, the climate is very humid tropical. It is similar to the equatorial climate in the Amazon. It rains more than 60 millimeters (2.4 inches) every month. There is no dry season.
Most of the state has a tropical climate with high altitude. This means it has a rainy summer and a dry winter. Temperatures are above 22°C (72°F) in the hottest month. Other areas have a tropical savanna climate. Here, rainfall is less than 60 mm (2.4 in) in some months. It is warmer, with average temperatures above 18°C (64°F) all year. Some small areas also have a monsoon climate.
Snow is very rare in São Paulo. But it has been seen in Campos do Jordão. There are also reports of snow in the southern part of the state, except for the Ribeira Valley. Frost is common, especially in areas higher than 800 meters (2,600 feet).
People of São Paulo
In 2014, about 44 million people lived in São Paulo state. The population density was about 177 people per square kilometer (459 per square mile). A study showed that 63.1% of people were White. About 29.3% were Brown (mixed race). Around 6.4% were Black. About 1% were Asian, and 0.1% were Native American.
Many towns, including the capital city, have a lot of people of Italian descent. About 65% of people in the capital have at least one Italian ancestor. Most Italians came from Veneto and Campania regions.
People of Portuguese and Spanish descent are common in most towns. Many Portuguese immigrants came from northern Portugal. Spanish immigrants mostly came from Galicia and Andalusia.

São Paulo also has the largest Asian population in Brazil. It has the biggest Japanese community outside of Japan.
Many people are of Levantine descent, mainly Syrian and Lebanese. Most Brazilian Jews live in the state, especially in the capital city. There are also Jewish communities in other cities like Campinas and Santos.
Main Cities in São Paulo
Some of the most important cities in São Paulo state are: São Paulo, Campinas, Guarulhos, Osasco, Ribeirão Preto, Santo André, Santos, São Bernardo do Campo, São Carlos, São José dos Campos, and Sorocaba.
Economy of São Paulo
In 2009, the service sector made up 69% of the state's GDP. The industrial sector was 31%. Farming made up 2% of the GDP. São Paulo state produces 34% of all goods and services in Brazil.
São Paulo (state) exports many things. These include vehicles (17%), airplanes and helicopters (12%), and food products (10%). It also exports sugar and alcohol fuel (8%), orange juice (5%), and telecommunications (4%).
São Paulo state is a major economic hub in Latin America. Its economy is very diverse. Key industries include metal-mechanics, sugar cane, textiles, and car and aviation manufacturing. Service and financial sectors are also very important. The state also grows a lot of oranges, sugar cane, and coffee beans. This economy makes up 34% of Brazil's total GDP.
Cities like Campinas, Ribeirão Preto, and São José do Rio Preto are important centers. They have universities and focus on engineering, farming, technology, and health sciences. The Instituto Butantan in São Paulo is a science center. It studies snakes and other poisonous animals. It also makes antidotes for venom. The Instituto Pasteur makes medical vaccines.
The state is a leader in making ethanol. It also produces a lot of soybeans. Aircraft are built in São José dos Campos. The state's rivers are important for making electricity using hydroelectric plants.
São Paulo is also a major producer of many foods. These include beans, rice, oranges and other fruit, coffee, sugar cane, alcohol, flowers, and vegetables. It also produces maize, cattle, pigs, milk, cheese, wine, and oil. Shopping areas like Rua José Paulino and 25 de Marco in São Paulo city attract shoppers from all over Brazil. They even attract customers from countries like Cape Verde and Angola in Africa.
Tourism in São Paulo

Tourism is a big part of São Paulo's economy. The state offers many different places to visit:
The city of São Paulo is a major center for business tourism in Brazil. It hosts about 45,000 events each year. São Paulo also has the largest number of hotels in Brazil. The city is also famous for its food. It is known as the "World Capital of Gastronomy". Cultural tourism is also important. There are many museums, theaters, and events like the Biennale of Arts.
The coast of São Paulo state has 622 km (386 miles) of beaches. These are along the South Atlantic Ocean. Cities like Santos, Praia Grande, Ubatuba, and São Sebastião get many tourists in the summer.
Inland, you can find resorts and places for rural tourism. There are also eco-friendly towns with a European-like climate. You can visit waterfalls, caves, rivers, mountains, and spas. There are also historical buildings from the 1500s, 1600s, and 1700s. You can also see old Jesuit and Roman Catholic church buildings and archaeological sites. One example is the Alto Ribeira Tourist State Park (PETAR).
For fun, you can visit Hopi Hari. It is a big theme park in Brazil, near Campinas. This area also has a hotel and the Wet 'n Wild water park. Another popular place is Parque Aquático Thermas dos Laranjais. It is the most visited water park in Latin America. It is located in Olímpia, in the northern part of the state. For nature lovers, Juquitiba has great facilities for ecotourism. In winter, Campos do Jordão is a top tourist spot. It hosts the Winter Festival. Temperatures there can drop below 0 degrees Celsius.
Transportation in São Paulo
São Paulo has the largest and most efficient transportation system in Brazil.
The city of São Paulo has an underground train system and suburban rail lines. City buses also help people get around.
Air traffic in São Paulo is the busiest in all of Brazil.
Harbors along the state's coast handle a large amount of Brazil's exports and imports.
Sports in São Paulo

São Paulo is a very active place for sports. Football (soccer) is the most popular sport. But the state also has many great athletes and facilities for other sports.
The state has many professional soccer clubs. Volleyball is also very popular here.
Auto racing is a big part of life for people in São Paulo. The state has produced many famous racing drivers who are known worldwide.
Images for kids
-
António Raposo Tavares, a colonial bandeirante
-
Coffee Stock Exchange, in Santos
-
Altino Arantes Building in São Paulo, opened in 1947.
-
Tiete River in the dam between the towns of Barra Bonita and Igaraçu do Tietê.
-
Liberdade district is a Little Tokyo of São Paulo city.
-
The Basilica of Our Lady of Aparecida is the second largest Catholic church in the world in interior area after the St. Peter's Basilica in the Vatican City.
-
REPLAN, the largest oil refinery in Brazil, in Paulínia
-
Toyota headquarters in São Bernardo do Campo
-
Aerial view of University of São Paulo in São Paulo.
-
Classroom in University of Campinas in Campinas.
-
Teaching laboratory of Universidade Federal do ABC in Santo André.
-
Viracopos International Airport in Campinas is the third busiest airport in the State of São Paulo
See also
 In Spanish: Estado de São Paulo para niños
In Spanish: Estado de São Paulo para niños
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |