Chancellor of the Exchequer facts for kids
Quick facts for kids United KingdomChancellor of the Exchequer Second Lord of the Treasury |
|
|---|---|

Royal Arms of His Majesty's Government
|
|
| His Majesty's Treasury | |
| Style | The Chancellor (informal) The Right Honourable (within the UK and Commonwealth) |
| Member of |
|
| Reports to | First Lord of the Treasury (Prime Minister of the United Kingdom) |
| Residence | 11 Downing Street |
| Seat | Westminster |
| Nominator | The Prime Minister |
| Appointer | The Monarch
(on the advice of the Prime Minister)
|
| Term length | At His Majesty's pleasure |
| Formation | 22 June 1316 |
| First holder | Hervey de Stanton (in the Kingdom of England only) |
| Deputy | Chief Secretary to the Treasury |
| Salary | £159,038 per annum (2022) (including £86,584 MP salary) |
The Chancellor of the Exchequer is a very important government minister in the United Kingdom. This person leads His Majesty's Treasury, which is the government department in charge of the UK's money. The Chancellor is one of the four most powerful jobs in the British Cabinet.
This role is similar to a finance minister in other countries. The Chancellor handles all money and economic matters for the country. They are also known as the Second Lord of the Treasury. This means they help manage the government's finances. Historically, the Chancellor's job was to collect and check the King's money. The first records of this job go back to 1129.
The Chancellor is the third oldest major government job in British history. Today, it is one of the most powerful jobs in British politics, second only to the Prime Minister. The current Chancellor is Rachel Reeves. She became the first woman to hold this position in July 2024.
Contents
What Does the Chancellor Do?
The Chancellor has a big job managing the UK's money. They decide how the government collects money and how it spends it.
Managing Government Money
The Chancellor has a lot of control over other government departments. This is because the Treasury sets limits on how much money each department can spend. The Chancellor's power depends on their personality and their relationship with the Prime Minister. For example, Gordon Brown was Chancellor for ten years. He was a very strong figure in the government. This made the Chancellor's job even more important.
One of the main tasks is creating the yearly government budget. This is called the Autumn Budget. It predicts how much the government will spend in the next year. It also announces new financial plans. The budget is a big secret until the Chancellor announces it in Parliament. If details are leaked early, it can cause big problems.
Controlling Money Supply
The Bank of England sets interest rates in the UK. However, the Chancellor still plays a key role in how money is managed. The Chancellor sets the inflation target. This is the goal for how much prices should rise each year. The Bank of England then sets interest rates to try and meet this target. The Chancellor also helps choose some members of the Bank's Monetary Policy Committee.
Working with Other Ministers
The Chancellor works with other ministers in the Treasury. The most important is the Chief Secretary to the Treasury. This person helps decide how government money is spent across different departments. There are also other ministers like the Paymaster General and the Financial Secretary to the Treasury. The Chancellor must be a member of the Privy Council. This means they are called "The Right Honourable."
Special Things About the Job
The Chancellor of the Exchequer has some unique traditions and perks.
Official Homes
The Chancellor lives at 11 Downing Street in London. This house is right next door to 10 Downing Street, where the Prime Minister lives. Both houses are now used as offices. The people who live there have apartments in the attic. In 1997, Prime Minister Tony Blair and Chancellor Gordon Brown swapped apartments. This was because the Chancellor's apartment was bigger and suited Blair's family better.
The Chancellor also traditionally gets to use Dorneywood. This is a country house with a large park. It is a summer residence. However, the Prime Minister decides who gets to use it.
The Budget Box
The Chancellor carries their budget speech to Parliament in a special red box. This box is called the 'Budget Box'. It looks like other boxes used by government ministers. But it's famous because the Chancellor shows it to the press before going to Parliament.
The first Budget Box was used by William Ewart Gladstone in 1853. It was used until 1965. Then, James Callaghan used a new one. In 1997, Gordon Brown also used a new box. This new box was made in Scotland. It was covered in red leather with the Royal crest. Later, Alistair Darling and George Osborne went back to using the original box. But it was very old and fragile. The key to the original box is now lost!
Robe of Office
The Chancellor also has a special robe. It is similar to the one worn by the Lord Chancellor. In modern times, it is mostly worn at coronations. Some Chancellors used to wear it for other special events. The robe that belonged to William Ewart Gladstone and was worn by famous Chancellors like David Lloyd George and Winston Churchill is now missing.
Who Has Been Chancellor?
Here is a list of some of the people who have held this important job.
Chancellors of England (around 1221 – 1708)
| Chancellor of the Exchequer | Term of office | Monarch (Reign) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Eustace of Fauconberg Bishop of London |
c. 1221 | N/A | Henry III (1216–1272) |
|
 |
John Maunsell Secretary of State |
c. 1234 | N/A | ||
| Ralph de Leicester | before 1248 | ||||
| Edward of Westminster | 1248 | N/A | |||
| Albric de Fiscamp | before 1263 | ||||
 |
John Chishull Lord Chancellor |
1263 | 1265 | ||
 |
Walter Giffard Bishop of Bath and Wells |
1265 | 1266 | ||
 |
Godfrey Giffard Lord Chancellor |
1266 | 1268 | ||
 |
John Chishull Lord Chancellor |
1268 | 1269 | ||
 |
Richard of Middleton Archdeacon of Northumberland |
1269 | 1272 | ||
| Roger de la Leye | before 1283 | ||||
| Geoffrey de Neuband | Edward I (1272–1307) |
||||
| Philip de Willoughby | 1283 | 1305 | |||
 |
John Benstead Secretary of State |
1305 | 1306 | ||
 |
John Sandale Bishop of Winchester |
c. July 1307 |
1308 | Edward II (1307–1327) |
|
| John of Markenfield | 1309 | 1312 | |||
 |
John Hotham Bishop of Ely |
1312 | 1316 | ||
 |
Hervey de Stanton | 1316 | c. 1323 | ||
 |
Walter Stapledon Lord High Treasurer |
1323 | c. 1324 | ||
 |
Hervey de Stanton Chief Justice of the Common Pleas |
1324 | c. January 1327 |
||
 |
Adam de Harvington | c. January 1327 |
1330 | Edward III (1327–1377) |
|
 |
Robert Wodehouse | 1330 | 1331 | ||
 |
Robert de Stratford Bishop of Chichester |
1331 | 1334 | ||
| John Hildesle | c. 1338 | N/A | |||
| William de Everdon | 1341 | N/A | |||
| William Askeby Archdeacon of Northampton |
1363 | N/A | |||
 |
Robert de Ashton | 1375 | c. June 1377 |
||
| Sir Walter Barnham | c. June 1377 |
c. September 1399 |
Richard II (1377–1399) |
||
 |
Henry Somer MP for Middlesex |
1410 | 1437 | Henry IV (1399–1413) |
|
| Henry V (1413–1422) |
|||||
| | Henry VI (1422–1461) |
||||
 |
John Somerset | 1441 | 1447 | ||
 |
Thomas Browne MP for Dover |
1440? | 1450? | ||
 |
Thomas Witham | 1454 | N/A | ||
 |
Thomas Thwaites | c. March 1461 |
N/A | Edward IV (1461–1470) |
|
 |
Thomas Witham | 1465 | 1469 | ||
| | Richard Fowler | 1469 | c. April 1471 |
||
| Henry VI (1470–1471) |
|||||
 |
Thomas Thwaites Chancellor of the Duchy of Lancaster |
c. April 1471 |
c. April 1483 |
Edward IV (1471–1483) |
|
 |
William Catesby Speaker of the House of Commons |
c. April 1483 |
c. 1484 | Edward V (1483) |
|
| Richard III (1483–1485) |
|||||
 |
Thomas Lovell Speaker of the House of Commons |
c. August 1485 |
1524 | Henry VII (1485–1509) |
|
| | Henry VIII (1509–1547) |
||||
 |
John Bourchier 2nd Baron Berners |
1524 | 1533? | ||
 |
Thomas Cromwell 1st Earl of Essex Secretary of State |
12 April 1533 |
10 June 1540 |
||
| | John Baker MP for Kent |
1545 | c. November 1558 |
||
 |
|||||
Edward VI (1547–1553) |
|||||
Mary I< (1553–1558) |
|||||
- Died in office.
| Chancellor of the Exchequer | Term of office | Monarch (Reign) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Richard Sackville MP for Sussex |
February 1559 |
21 April 1566 |
Elizabeth I (1558–1603) |
||
 |
Walter Mildmay MP for Northamptonshire |
1566 | 31 May 1589 |
|||
 |
John Fortescue MP for Buckinghamshire →Middlesex
|
1589 | 1603 | |||
 |
George Home 1st Earl of Dunbar |
24 May 1603 |
April 1606 |
James I (1603–1625) |
||
 |
Julius Caesar MP for Middlesex |
11 April 1606 |
1614 | |||
 |
Fulke Greville MP for Warwickshire |
15 October 1614 |
1621 | |||
 |
Richard Weston MP for 7 constituencies successively |
29 January 1621 |
15 July 1628 |
|||
Charles I (1625–1649) |
||||||
 |
Edward Barrett 1st Lord Barrett of Newburgh |
14 August 1628 |
1629 | |||
 |
Francis Cottington 1st Baron Cottington |
18 April 1629 |
6 January 1642 |
|||
 |
John Colepeper MP for Kent |
6 January 1642 |
22 February 1643 |
|||
 |
Edward Hyde | February 1643 |
1646 | |||
| Vacancy during the Interregnum (1649–1660) | ||||||
| Chancellor of the Exchequer | Term of office | Ministry | Monarch (Reign) |
|||
 |
Edward Hyde 1st Baron Hyde |
1660 | 13 May 1661 |
Clarendon | Charles II (1660–1685) |
|
 |
Anthony Ashley Cooper 1st Baron Ashley |
13 May 1661 |
22 November 1672 |
|||
| Cabal | ||||||
 |
John Duncombe MP for Bury St Edmunds |
22 November 1672 |
2 May 1676 |
|||
| Danby I | ||||||
| | John Ernle MP for 4 constituencies successively |
2 May 1676 |
9 April 1689 |
|||
| Privy Council | ||||||
| | Chits | |||||
James II (1685–1688) |
||||||
| | William III & Mary II  (1689–1694) |
|||||
 |
Henry Booth 2nd Baron Delamer |
9 April 1689 |
18 March 1690 |
Carmarthen–Halifax | ||
 |
Richard Hampden MP for Buckinghamshire |
18 March 1690 |
10 May 1694 |
Carmarthen | ||
 |
Charles Montagu MP for Maldon → Westminster
|
10 May 1694 |
31 May 1699 |
Whig Junto I | ||
William III (1694–1702) |
||||||
 |
John Smith MP for Andover |
31 May 1699 |
23 March 1701 |
Pembroke | ||
| | Henry Boyle MP for Cambridge University → Westminster
|
27 March 1701 |
22 April 1708 |
|||
 |
Godolphin–Marlborough (Tory–Whig) |
Anne (1702–1714) |
||||
Chancellors of Great Britain (1708–1817)
| Chancellor of the Exchequer | Term of office | Party | Ministry | Monarch (Reign) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
John Smith MP for Andover |
22 April 1708 |
11 August 1710 |
Whig | Godolphin–Marlborough (Tory–Whig) |
Anne (1702–1714) |
|
 |
Robert Harley MP for Radnor |
11 August 1710 |
4 June 1711 |
Tory | Oxford–Bolingbroke | ||
 |
Robert Benson MP for York |
4 June 1711 |
21 August 1713 |
Tory | |||
 |
William Wyndham MP for Somerset |
21 August 1713 |
13 October 1714 |
Tory | |||
George I (1714–1727) |
|||||||
 |
Richard Onslow MP for Surrey |
13 October 1714 |
12 October 1715 |
Whig | Townshend | ||
 |
Robert Walpole MP for King's Lynn |
12 October 1715 |
15 April 1717 |
Whig | |||
 |
James Stanhope 1st Earl Stanhope |
15 April 1717 |
20 March 1718 |
Whig | Stanhope–Sunderland I | ||
 |
John Aislabie MP for Ripon |
20 March 1718 |
23 January 1721 |
Whig | Stanhope–Sunderland II | ||
 |
John Pratt Lord Chief Justice (interim) |
2 February 1721 |
3 April 1721 |
Whig | |||
 |
Robert Walpole 1st Earl of Orford MP for King's Lynn |
3 April 1721 |
12 February 1742 |
Whig | Walpole–Townshend | ||
George II (1727–1760) |
|||||||
| Walpole | |||||||
 |
Samuel Sandys MP for Worcester |
12 February 1742 |
12 December 1743 |
Whig | Carteret | ||
| |  |
Henry Pelham MP for Sussex |
12 December 1743 |
8 March 1754 |
Whig | ||
| Broad Bottom (I & II) |
|||||||
 |
William Lee Lord Chief Justice (interim) |
8 March 1754 |
6 April 1754 |
Whig | Newcastle I | ||
 |
Henry Bilson-Legge MP for Orford |
6 April 1754 |
25 November 1755 |
Whig | |||
 |
George Lyttelton MP for Okehampton |
25 November 1755 |
16 November 1756 |
Whig | |||
 |
Henry Bilson-Legge MP for Orford |
16 November 1756 |
13 April 1757 |
Whig | Pitt–Devonshire | ||
 |
William Murray 1st Earl of Mansfield Lord Chief Justice (interim) |
13 April 1757 |
2 July 1757 |
Whig | |||
| 1757 Caretaker | |||||||
 |
Henry Bilson-Legge MP for Orford → Hampshire
|
2 July 1757 |
19 March 1761 |
Whig | Pitt–Newcastle | ||
George III (1760–1820) |
|||||||
 |
William Barrington 2nd Viscount Barrington MP for Plymouth |
19 March 1761 |
29 May 1762 |
Whig | |||
 |
Francis Dashwood MP for Weymouth and Melcombe Regis |
29 May 1762 |
16 April 1763 |
Tory | Bute (Tory–Whig) |
||
 |
George Grenville MP for Buckingham |
16 April 1763 |
16 July 1765 |
Whig | Grenville (Whig–Tory) |
||
 |
William Dowdeswell MP for Worcestershire |
16 July 1765 |
2 August 1766 |
Whig | Rockingham I | ||
 |
Charles Townshend MP for Harwich |
2 August 1766 |
4 September 1767 |
Whig | Chatham (Whig–Tory) |
||
| |  |
Frederick North Lord North MP for Banbury |
11 September 1767 |
27 March 1782 |
Tory | ||
| Grafton | |||||||
| North | |||||||
 |
Lord John Cavendish MP for York |
27 March 1782 |
10 July 1782 |
Whig | Rockingham II | ||
 |
William Pitt the Younger MP for Appleby |
10 July 1782 |
31 March 1783 |
Whig | Shelburne (Whig–Tory) |
||
 |
Lord John Cavendish MP for York |
2 April 1783 |
19 December 1783 |
Whig | Fox–North | ||
 |
William Pitt the Younger MP for Appleby → Cambridge University
|
19 December 1783 |
14 March 1801 |
Tory | Pitt I | ||
 |
Henry Addington MP for Devizes |
14 March 1801 |
10 May 1804 |
Tory | Addington | ||
 |
William Pitt the Younger MP for Cambridge University |
10 May 1804 |
23 January 1806 |
Tory | Pitt II | ||
 |
Edward Law 1st Baron Ellenborough Lord Chief Justice (interim) |
23 January 1806 |
5 February 1806 |
Tory | All the Talents (Whig–Tory) |
||
 |
Lord Henry Petty-Fitzmaurice MP for Cambridge University |
5 February 1806 |
26 March 1807 |
Whig | |||
 |
Spencer Perceval MP for Northampton |
26 March 1807 |
11 May 1812 |
Tory | Portland II | ||
| Perceval | |||||||
 |
Nicholas Vansittart MP for East Grinstead → Harwich
|
9 June 1812 |
12 July 1817 |
Tory | Liverpool | ||
Chancellors of the United Kingdom (1817–present)
The governments of Great Britain and Ireland joined together in 1801. But their money departments didn't combine until 1817.
| Chancellor of the Exchequer | Term of office | Party | Ministry | Monarch (Reign) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Nicholas Vansittart MP for Harwich |
12 July 1817 | 31 January 1823 | Tory | Liverpool | George III (1760–1820) |
|
George IV (1820–1830) |
|||||||
 |
Frederick John Robinson MP for Ripon |
31 January 1823 | 27 April 1827 | Tory | |||
 |
George Canning MP for Seaford |
27 April 1827 | 8 August 1827 | Tory | Canning (Canningite–Whig) |
||
 |
Charles Abbott 1st Baron Tenterden Lord Chief Justice (interim) |
8 August 1827 | 5 September 1827 | Tory | Goderich | ||
 |
John Charles Herries MP for Harwich |
5 September 1827 | 26 January 1828 | Tory | |||
 |
Henry Goulburn MP for Armagh |
26 January 1828 | 22 November 1830 | Tory | Wellington–Peel | ||
William IV (1830–1837) |
|||||||
 |
John Spencer Viscount Althorp MP for Northamptonshire →
South Northamptonshire |
22 November 1830 | 14 November 1834 | Whig | Grey | ||
| Melbourne I | |||||||
 |
Thomas Denman 1st Baron Denman Lord Chief Justice (interim) |
14 November 1834 | 15 December 1834 | Whig | Wellington Caretaker | ||
 |
Robert Peel MP for Tamworth |
15 December 1834 | 8 April 1835 | Conservative | Peel I | ||
 |
Thomas Spring Rice MP for Cambridge |
18 April 1835 | 26 August 1839 | Whig | Melbourne II | ||
Victoria (1837–1901) |
|||||||
 |
Francis Baring MP for Portsmouth |
26 August 1839 | 30 August 1841 | Whig | |||
 |
Henry Goulburn MP for Cambridge University |
3 September 1841 | 27 June 1846 | Conservative | Peel II | ||
 |
Charles Wood MP for Halifax |
6 July 1846 | 21 February 1852 | Whig | Russell I | ||
 |
Benjamin Disraeli MP for Buckinghamshire |
27 February 1852 | 17 December 1852 | Conservative | Who? Who? | ||
 |
William Ewart Gladstone MP for Oxford University |
28 December 1852 | 28 February 1855 | Peelite | Aberdeen (Peelite–Whig) |
||
 |
George Cornewall Lewis MP for Radnor |
28 February 1855 | 21 February 1858 | Whig | Palmerston I | ||
 |
Benjamin Disraeli MP for Buckinghamshire |
26 February 1858 | 11 June 1859 | Conservative | Derby–Disraeli II | ||
 |
William Ewart Gladstone MP for Oxford University →
South Lancashire |
18 June 1859 | 26 June 1866 | Liberal | Palmerston II | ||
| Russell II | |||||||
 |
Benjamin Disraeli MP for Buckinghamshire |
6 July 1866 | 29 February 1868 | Conservative | Derby–Disraeli III | ||
 |
George Ward Hunt MP for North Northamptonshire |
29 February 1868 | 1 December 1868 | Conservative | |||
 |
Robert Lowe MP for London University |
9 December 1868 | 11 August 1873 | Liberal | Gladstone I | ||
 |
William Ewart Gladstone MP for Greenwich |
11 August 1873 | 17 February 1874 | Liberal | |||
 |
Stafford Northcote MP for North Devonshire |
21 February 1874 | 21 April 1880 | Conservative | Disraeli II | ||
 |
William Ewart Gladstone MP for Midlothian |
28 April 1880 | 16 December 1882 | Liberal | Gladstone II | ||
 |
Hugh Childers MP for Pontefract |
16 December 1882 | 9 June 1885 | Liberal | |||
 |
Michael Hicks Beach MP for Bristol West |
24 June 1885 | 28 January 1886 | Conservative | Salisbury I | ||
 |
William Harcourt MP for Derby |
6 February 1886 | 20 July 1886 | Liberal | Gladstone III | ||
 |
Lord Randolph Churchill MP for Paddington South |
3 August 1886 | 22 December 1886 | Conservative | Salisbury II | ||
 |
George Goschen MP for St George Hanover Square |
14 January 1887 | 11 August 1892 | Liberal Unionist | |||
 |
William Harcourt MP for Derby |
18 August 1892 | 21 June 1895 | Liberal | Gladstone IV | ||
| Rosebery | |||||||
 |
Michael Hicks Beach MP for Bristol West |
29 June 1895 | 11 August 1902 | Conservative | Salisbury (III & IV) (Con.–Lib.U.) |
||
Edward VII (1901–1910) |
|||||||
 |
Charles Ritchie MP for Croydon |
11 August 1902 | 9 October 1903 | Conservative | Balfour | ||
 |
Austen Chamberlain MP for East Worcestershire |
9 October 1903 | 4 December 1905 | Liberal Unionist | |||
 |
Herbert Henry Asquith MP for East Fife |
10 December 1905 | 16 April 1908 | Liberal | Campbell-Bannerman | ||
 |
David Lloyd George MP for Caernarvon Boroughs |
16 April 1908 | 25 May 1915 | Liberal | Asquith (I–III) |
||
George V (1910–1936) |
|||||||
 |
Reginald McKenna MP for North Monmouthshire |
25 May 1915 | 10 December 1916 | Liberal | Asquith Coalition (Lib.–Con.–et al.) |
||
 |
Bonar Law MP for Bootle →
Glasgow Central |
10 December 1916 | 10 January 1919 | Conservative | Lloyd George (I & II) |
||
 |
Austen Chamberlain MP for Birmingham West |
10 January 1919 | 1 April 1921 | Conservative | |||
 |
Robert Horne MP for Glasgow Hillhead |
1 April 1921 | 19 October 1922 | Conservative | |||
 |
Stanley Baldwin MP for Bewdley |
27 October 1922 | 27 August 1923 | Conservative | Law | ||
| | Baldwin I | ||||||
 |
Neville Chamberlain MP for Birmingham Ladywood |
27 August 1923 | 22 January 1924 | Conservative | |||
 |
Philip Snowden MP for Colne Valley |
22 January 1924 | 3 November 1924 | Labour | MacDonald I | ||
 |
Winston Churchill MP for Epping |
6 November 1924 | 4 June 1929 | Conservative | Baldwin II | ||
 |
Philip Snowden MP for Colne Valley |
7 June 1929 | 5 November 1931 | Labour | MacDonald II | ||
| National Labour | National I (N.Lab.–Con.–et al.) |
||||||
 |
Neville Chamberlain MP for Birmingham Edgbaston |
5 November 1931 | 28 May 1937 | Conservative | National II | ||
| | National III (Con.–N.Lab.–et al.) |
||||||
Edward VIII (1936) |
|||||||
| | George VI (1936–1952) |
||||||
 |
John Simon MP for Spen Valley |
28 May 1937 | 12 May 1940 | Liberal National | National IV | ||
| Chamberlain War | |||||||
 |
Kingsley Wood MP for Woolwich West |
12 May 1940 | 21 September 1943 | Conservative | Churchill War (All parties) |
||
| |  |
John Anderson MP for Combined Scottish Universities |
24 September 1943 | 26 July 1945 | Independent (National) |
||
| Churchill Caretaker (Con.–Lib.N.) |
|||||||
 |
Hugh Dalton MP for Bishop Auckland |
27 July 1945 | 13 November 1947 | Labour | Attlee (I & II) |
||
 |
Stafford Cripps MP for Bristol East →
Bristol South East |
13 November 1947 | 19 October 1950 | Labour | |||
 |
Hugh Gaitskell MP for Leeds South |
19 October 1950 | 26 October 1951 | Labour | |||
 |
Richard Austen Butler MP for Saffron Walden |
26 October 1951 | 20 December 1955 | Conservative | Churchill III | ||
| Elizabeth II (1952–2022) |
|||||||
| Eden | |||||||
 |
Harold Macmillan MP for Bromley |
20 December 1955 | 13 January 1957 | Conservative | |||
 |
Peter Thorneycroft MP for Monmouth |
13 January 1957 | 6 January 1958 | Conservative | Macmillan (I & II) |
||
 |
Derick Heathcoat-Amory MP for Tiverton |
6 January 1958 | 27 July 1960 | Conservative | |||
 |
Selwyn Lloyd MP for Wirral |
27 July 1960 | 13 July 1962 | Conservative | |||
| | Reginald Maudling MP for Barnet |
16 July 1962 | 16 October 1964 | Conservative | |||
| Douglas-Home | |||||||
 |
James Callaghan MP for Cardiff South East |
17 October 1964 | 29 November 1967 | Labour | Wilson (I & II) |
||
 |
Roy Jenkins MP for Birmingham Stechford |
29 November 1967 | 19 June 1970 | Labour | |||
 |
Iain Macleod MP for Enfield West |
20 June 1970 | 20 July 1970 | Conservative | Heath | ||
| Anthony Barber MP for Altrincham and Sale |
25 July 1970 | 4 March 1974 | Conservative | ||||
 |
Denis Healey MP for Leeds East |
5 March 1974 | 4 May 1979 | Labour | Wilson (III & IV) |
||
| Callaghan | |||||||
 |
Geoffrey Howe MP for East Surrey |
4 May 1979 | 11 June 1983 | Conservative | Thatcher I | ||
 |
Nigel Lawson MP for Blaby |
11 June 1983 | 26 October 1989 | Conservative | Thatcher II | ||
| | Thatcher III | ||||||
 |
John Major MP for Huntingdon |
26 October 1989 | 28 November 1990 | Conservative | |||
 |
Norman Lamont MP for Kingston-upon-Thames |
28 November 1990 | 27 May 1993 | Conservative | Major I | ||
| | Major II | ||||||
 |
Kenneth Clarke MP for Rushcliffe |
27 May 1993 | 2 May 1997 | Conservative | |||
 |
Gordon Brown MP for Dunfermline East →
Kirkcaldy and Cowdenbeath |
2 May 1997 | 27 June 2007 | Labour | Blair (I, II & III) |
||
 |
Alistair Darling MP for Edinburgh South West |
28 June 2007 | 11 May 2010 | Labour | Brown | ||
 |
George Osborne MP for Tatton |
11 May 2010 | 13 July 2016 | Conservative | Cameron–Clegg (Con.–L.D.) |
||
| Cameron II | |||||||
 |
Philip Hammond MP for Runnymede and Weybridge |
13 July 2016 | 24 July 2019 | Conservative | May I | ||
| May II | |||||||
 |
Sajid Javid MP for Bromsgrove |
24 July 2019 | 13 February 2020 | Conservative | Johnson I | ||
| | Johnson II | ||||||
 |
Rishi Sunak MP for Richmond (Yorks) |
13 February 2020 | 5 July 2022 | Conservative | |||
 |
Nadhim Zahawi MP for Stratford-on-Avon |
5 July 2022 | 6 September 2022 | Conservative | |||
| |  |
Kwasi Kwarteng MP for Spelthorne |
6 September 2022 | 14 October 2022 | Conservative | Truss | |
Charles III (2022–present) |
|||||||
 |
Jeremy Hunt MP for South West Surrey |
14 October 2022 | 5 July 2024 | Conservative | |||
| | Sunak | ||||||
 |
Rachel Reeves MP for Leeds West |
5 July 2024 | Incumbent | Labour | Starmer | ||
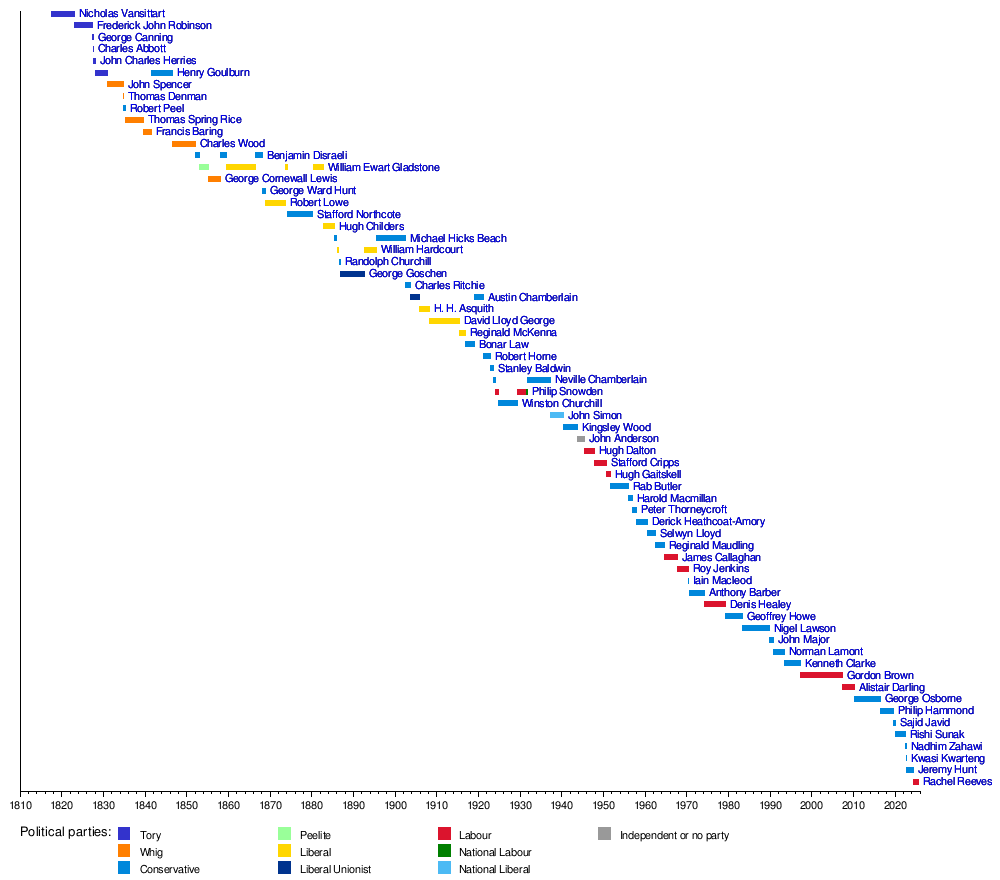
Timeline of Chancellors
This timeline shows who has been Chancellor of the Exchequer since 1817.
See also
 In Spanish: Canciller de la Hacienda del Reino Unido para niños
In Spanish: Canciller de la Hacienda del Reino Unido para niños
- Shadow Chancellor of the Exchequer
- List of lord high treasurers of England and Great Britain
|



