Environment of Australia facts for kids
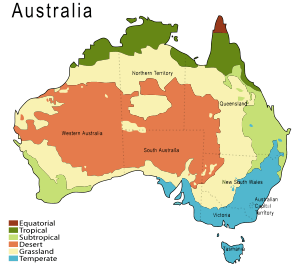
The Australian environment is super interesting because it has everything from icy Antarctica-like places and thick rainforests to busy cities with factories. Scientists have found 40 different natural areas, called ecoregions, across Australia's mainland and islands.
Central Australia is very dry, with many deserts. But most people live along the coasts. Northern Australia gets strong storms called tropical cyclones, and much of the country often has droughts. Because it's so dry and warm, and gets cyclones, Australia is really affected by climate change. Some areas are already seeing more wildfires and delicate natural places are struggling.
Because Australia is an island, it has many unique plants and animals found nowhere else. These include famous marsupials like the kangaroo and koala. Farming (agriculture) and digging for minerals (mining) are big activities that can harm many natural areas. Protecting places like the Great Barrier Reef, forests, and native animals from mining and other activities is a big part of conservation efforts.
Australia's protected areas are great for ecotourism, which means visiting natural places without harming them. Famous spots like the Great Barrier Reef and World Heritage sites such as the Tasmanian Wilderness World Heritage Area or Uluṟu-Kata Tjuṯa National Park attract many visitors from Australia and around the world. Clean Up Australia Day started in 1989 as a way for communities to work together to clean up their local areas. It happens every year on the first Sunday of autumn (in March).
Contents
Protected Areas in Australia
Australia has many special places set aside to protect nature. These protected areas cover about 895,288 square kilometres of land. That's about 11.5% of the country! Most of these areas are strictly protected, meaning they are kept as wild as possible. There are also 200 protected areas in the ocean, covering a huge 64.8 million hectares. Since the 1990s, Indigenous Protected Areas have also been created, managed by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people. The biggest one is in the Tanami Desert.
Some of Australia's most famous natural protected areas are also World Heritage Sites. These include:
- Australian Fossil Mammal Sites (like Riversleigh and Naracoorte)
- Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves
- Fraser Island
- Great Barrier Reef
- Greater Blue Mountains Area
- Heard and McDonald Islands
- Lord Howe Island
- Macquarie Island
- Purnululu National Park
- Shark Bay
- Wet Tropics of Queensland
Other World Heritage Sites that protect both nature and culture include the Tasmanian Wilderness, Uluṟu-Kata Tjuṯa National Park, Willandra Lakes Region, and Kakadu National Park. Places like Ningaloo Reef and Cape Range peninsula are also being considered for World Heritage listing.
Protecting Australia's Nature
Even though much of Australia is dry or desert, it has many different types of natural homes for plants and animals, from cold mountain areas to hot, wet rainforests. This is why Australia is called a megadiverse country, meaning it has a huge variety of life.
Australia's plants and animals are very special because the continent is very old, has changing weather, and has been separated from other land for a long time. This means that much of Australia's wildlife is unique and diverse. For example, about 85% of its flowering plants, 84% of its mammals, over 45% of its birds, and 89% of its fish near the coast are found only in Australia.
Many of Australia's natural areas and the species living in them are in danger. This is often due to human activities and introduced plants and animals that don't belong there. To help protect these species, Australia has a law called the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999. Many protected areas have been set up to save unique ecosystems. Also, 65 wetlands are protected under the Ramsar Convention (an international agreement), and 16 World Heritage Sites have been created.
Most Australian woody plants stay green all year and are good at surviving fires and droughts. This includes many types of eucalyptus and acacia trees. Australia also has many unique legume plants that grow well in poor soil because they work together with tiny bacteria and fungi.
Well-known Australian animals include monotremes (like the platypus and echidna, which lay eggs), many marsupials (like the kangaroo, koala, and wombat), and birds such as the emu and kookaburra. The dingo was brought to Australia by people trading with Indigenous Australians about 3000 years ago. Sadly, many plant and animal species, including the giant Australian megafauna, disappeared after the first humans arrived. Others, like the thylacine, have become extinct since Europeans settled in Australia.
Water in Australia
Australia is the second driest continent on Earth, after Antarctica. Because of frequent droughts, many parts of Australia have rules about how much water people can use. This makes people, farmers, and governments worried about having enough water for the future.
Taking water from rivers for farming has greatly changed how water flows, especially in the Murray–Darling basin. A big project called the Snowy Mountains Scheme even moved most of the water from the Snowy River to other areas.
Cities in Australia use special plants to clean wastewater. Both rainwater runoff (stormwater) and treated wastewater flow into rivers, coastal areas, and beaches.
Water Supply
Environmental Challenges

Australia's environment is facing many challenges and is getting worse due to growing threats. Some big environmental issues in Australia include:
- Whaling (hunting whales)
- Cutting down very old forests
- The impact of irrigation on important rivers like the Murray River, Darling River, and Macquarie Marshes
- Problems with acid sulfate soils and salty soil
- Clearing land and soil erosion
- Uranium mining and dealing with nuclear waste
- Creating marine reserves (protected ocean areas)
- The air quality in cities and near polluting factories
- The effects of pesticides and herbicides
- Growing genetically modified food
There's also a huge grassland area called the Great Australian Savanna.
More coal mining in Australia is a big debate because of its link to global warming. Burning coal releases pollution into the air. Mining also creates dust, causes land to sink, affects rivers like the Hunter River, and can harm other water users. It's also hard to fully fix mined areas, and many worry about whether it's sustainable for the future.
Climate change and global warming are major concerns for Australia. They could affect farming, the Great Barrier Reef and tourism, and even human health. Sea level rise could also cause big problems for low-lying areas and coastal towns.
In cities, loud noises and bad smells are common complaints to environmental protection groups.
Climate Change in Australia
Climate change is a big problem for Australia in the 21st century. Australia is getting hotter. It also faces more extreme heat, bushfires, droughts, floods, and longer fire seasons. Other climate issues include heatwaves, cyclones, rising sea levels, and erosion.
Since the early 1900s, Australia's average yearly temperature has gone up by more than 1.4°C. This warming has happened twice as fast in the last 50 years. Recent very hot temperatures and widespread droughts have made people and the government pay more attention to climate change in Australia. Rainfall in southwestern Australia has dropped by 10–20% since the 1970s. Southeastern Australia has also seen less rain since the 1990s.
Scientists expect Australia's average temperatures to rise by 0.4–2.0°C by 2030. They could go up by 1–6°C by 2070. Rainfall might become heavier but happen less often. It could also be more common in summer than in winter.
Climate change is changing Australia's environment and natural places. Australia is easily affected by global warming. This is because it has large dry areas, an already warm climate, and very changeable rainfall. The high risk of fires makes it even more sensitive to temperature changes. Australia's coastlines will also see erosion and flooding. This is due to an expected 8–88 cm rise in global sea levels. Australia's special places like the Great Barrier Reef and many animal species are also in danger.
Climate change also affects Australia's economy, farming, and people's health. We might see more severe floods, droughts, and cyclones. Many Australians live near the coast. These areas are at risk from rising sea levels. Also, problems with water supply will get worse. Indigenous Australians are especially affected. This is because of existing social and economic challenges. These challenges are linked to how they have been treated in the past. Communities in the North are most affected. Here, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people make up 30% of the population. These communities rely on their traditional land for food, culture, and health. This makes them very vulnerable.
Australia also adds to climate change. Its greenhouse gas emissions per person are higher than the world average. The country uses a lot of coal and other fossil fuels. However, renewable energy is growing. Australia has promised to reach net zero emissions by 2050. This is part of the Paris Agreement. But Australia often ranks low in international climate change reports. Adapting to changes is also important.
Climate change has been a hot topic in Australian politics since the 2000s. This has led to governments putting in place and then removing policies like carbon pricing. Some Australian news outlets have spread wrong information about climate change. The issue has also caused many protests. Some of these have been the biggest in Australia's history.Environmental Reports
The Australian government creates reports called Australia: State of the Environment. These reports come out every five years and give a full picture of how Australia's environment is doing. They use the best information available and are important for people who make laws, businesses, schools, scientists, and the public.
There's also a program called Essential Environmental Measures (EEM). This program helps track changes in Australia's environment by identifying key things to measure. It also makes sure that environmental data is easy to find, use, and share. This information helps with the State of the Environment reports and other environmental planning.
Environment in Western Australia
The southwest coast of Western Australia has a climate like the Mediterranean, with warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters. This area used to have thick forests, including tall karri trees. This farming region is one of the top nine places in the world for land biodiversity, with many unique species. The ocean nearby is also rich in marine life, thanks to the Leeuwin Current, and has the most southerly coral reefs in the world.
Rainfall in this area varies, but it's generally very dry from November to March. Plants here have to be tough to survive the dry periods and poor soil. Winter rainfall has dropped a lot since the mid-1970s, but there are more heavy rain events in summer.
Most of Western Australia (about four-fifths) is semi-desert or desert. Not many people live here, and the main activity is mining. This area gets little rain, mostly from big storms called cyclones in the summer.
The northern tropical regions, like the Kimberley, have a very hot monsoon climate with heavy rain in the wet season (December to March) and a long dry season (April to November). Most of the state's river runoff happens here, but it comes in strong floods, and the soil is generally poor.
The black swan is the state bird of Western Australia, and the red-and-green kangaroo paw is its floral emblem.
Snow is rare in Western Australia, usually only falling in the Stirling Range, which is far enough south and high enough. Snow outside these areas is a very unusual event. Even in the Stirling Range, snow doesn't usually last more than a day.
The hottest temperature ever recorded in Western Australia was 50.5 °C (122.9 °F) at Mardie Station in 1998. The coldest was −7.2 °C (19.0 °F) at Eyre Bird Observatory in 2008.
Environment in Tasmania
Tasmania has a mild climate.
Environment in Northern Territory
The Northern Territory has low humidity and wind. Its climate ranges from hot and dry in the middle of the territory to milder and wetter climates in the south.
Environmental Organizations
Many groups work to protect Australia's environment:
- Australian Conservation Foundation
- Australian Network of Environmental Defenders Offices (ANEDO)
- Greenpeace Australia Pacific
- Sustainable Population Australia
- Trees for Life (in Brooklyn Park)
Images for kids