Taos, New Mexico facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Taos, New Mexico
|
||
|---|---|---|

Taos Plaza and the Hotel La Fonda, within the Taos Downtown Historic District
|
||
|
||
Location of Taos, New Mexico
|
||
U.S. Census map
|
||
| Country | United States | |
| State | New Mexico | |
| County | Taos | |
| Founded | 1795 | |
| Incorporated | 1934 | |
| Named for | Taos Pueblo | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | Mayor-Council-Manager | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 6.04 sq mi (15.64 km2) | |
| • Land | 6.04 sq mi (15.64 km2) | |
| • Water | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km2) | |
| Elevation | 6,969 ft (2,124 m) | |
| Population
(2020)
|
||
| • Total | 6,474 | |
| • Density | 1,072.03/sq mi (413.94/km2) | |
| Time zone | UTC−7 (Mountain (MST)) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−6 (MDT) | |
| ZIP code |
87571
|
|
| Area code(s) | 575 | |
| FIPS code | 35-76200 | |
| GNIS feature ID | 2413366 | |
| Website | www.taosgov.com | |
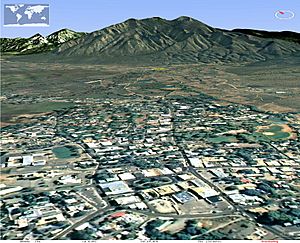
Taos (/taʊs/) is a town in Taos County, located in the north-central part of New Mexico. It sits among the beautiful Sangre de Cristo Mountains. The town was officially started in 1795 by Governor Fernando Chacón of Nuevo México. It was built as a strong trading post and fort.
Taos was a meeting place for the nearby Native American Taos Pueblo people and the Hispano communities. The town gets its name from the Taos Pueblo. Other communities nearby include Ranchos de Taos, Cañon, Taos Canyon, Ranchitos, El Prado, and Arroyo Seco. Taos became an official town in 1934. In 2021, about 6,567 people lived there.
Taos is the main town, or county seat, of Taos County. The name Taos comes from the native Taos language. It means "(place of) red willows."
Contents
Discover the History of Taos
The Ancient Taos Pueblo Community
The Taos Pueblo is a very old community right next to the town of Taos. People have lived there for almost 1,000 years! Experts believe the pueblo was built between the years 1000 and 1450 A.D. It is one of the oldest places in the United States where people have continuously lived.
The pueblo is in a valley that leads to the Rio Grande river. It is the most northern of the New Mexico pueblos. Some parts of the pueblo buildings are five stories high. They are made up of many individual homes that share walls. Over 1,900 Taos Pueblo people live in the wider community. Many have modern homes near their fields for summer. They stay in the main pueblo buildings when the weather is colder. About 150 people live in the main pueblo buildings all year. The Taos Pueblo became a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1992.
Spanish Settlement in Taos
Taos was first settled around 1615. It was called Don Fernando de Taos after the Spanish took over the Indian Pueblo villages. At first, the Spanish settlers and the Taos Pueblo people got along well. But problems started because of missionaries and demands for tribute. This led to a revolt in 1640. Taos Indians killed their priest and some Spanish settlers. They left the pueblo but came back in 1661.
In 1680, Taos Pueblo joined the big Pueblo Revolt. After the Spanish took back control in 1692, Taos Pueblo kept fighting until 1696. Governor Diego de Vargas defeated the Indians at Taos Canyon.
During the 1770s, Comanches from the plains of what is now eastern Colorado often raided Taos. Juan Bautista de Anza, the governor of New Mexico, led a successful mission in 1779 against the Comanches.
Between 1780 and 1800, Don Fernando de Taos (now just Taos) was established. From 1796 to 1797, land was given to 63 Spanish families in the Taos valley. The town was built as a strong plaza with adobe buildings. Today, it is a central plaza surrounded by homes. Mountain men who trapped beaver in the area made Taos their home in the early 1800s.
Becoming a U.S. Territory and State
Mexico gave the region to the U.S. in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848. This happened after the Mexican–American War. After the U.S. took over New Mexico in 1847, Hispanic and Native American people in Taos started a rebellion. It was called the Taos Revolt. During this revolt, the new U.S. Governor, Charles Bent, was killed. New Mexico became a territory of the United States in 1850 and a state in 1912.
For historical reasons, the American flag flies all the time at Taos Plaza, day and night. This tradition started during the American Civil War. People who supported the Confederacy tried to take down the flag. A Union officer named Kit Carson had guards protect the area and keep the flag flying 24 hours a day.
Anton Docher, known as the "Padre of Isleta," was a priest in Taos before moving to Isleta in 1891.
The Famous Taos Art Colony
Artists started moving to Taos in 1899. Six of them formed the Taos Society of Artists in 1915. Over time, the Taos art colony grew. Many paintings showed local scenes, especially the Taos Pueblo and its people. The artists often used Native Americans from the pueblo as models. Some of the artists' studios are still preserved today for visitors to see. These include the Ernest L. Blumenschein House, the Eanger Irving Couse House and Studio—Joseph Henry Sharp Studios, and the Nicolai Fechin house. All of these are listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
Several foundations offer artist residencies in Taos. The famous Helene Wurlitzer Foundation started hosting artists in 1954. They welcome painters, writers, composers, sculptors, poets, and filmmakers at Casa Encantado.
Explore Historic Sites and Tourism in Taos
Taos has more than twenty places listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
Visiting the Pueblos
About 3 miles (4.8 km) north of Taos is Taos Pueblo. Picuris Pueblo is about 25 miles (40 km) south.
Celebrating Taos Fiestas
The Fiestas de Taos is a yearly community celebration held in the Taos Plaza. It honors the two patron saints of Taos, Santa Ana and Santiago. It usually happens on the third weekend of July. A special mass and procession from Our Lady of Guadalupe Church start the event on Friday evening. Then, a Fiestas Queen is crowned. The celebration continues with music and dance performances on the plaza every hour. There are two parades: a children's parade on Saturday and a larger Fiesta Parade on Sunday.
Bent Street: A Historic Location
Bent Street is just north of the Taos Plaza. This was where Governor Charles Bent lived.
Governor Bent was killed by Pueblo warriors during the Taos Revolt on January 19, 1847. During the revolt, Bent's horses were set free from their stable.
Homes and Studios of Famous Artists
Modern Artist Studios
The Helene Wurlitzer Foundation is a non-profit group in Taos. It offers free residencies to eleven artists. Each year is split into three residency sessions, each lasting three months, at Casa Encantado.
Abbie Conant, a former main trombonist for the Munich Philharmonic Orchestra, has a studio three blocks from the plaza. Her studio can seat 60 people and has a two-bedroom living space. She and her husband perform there. The studio also hosts poetry readings, presentations, and performances from local artists and fellows from the Wurlitzer Foundation.
Historic Artist Homes
Many historic sites are homes and studios of artists. These include the Mabel Dodge Luhan House, Eanger Irving Couse House and Studio—Joseph Henry Sharp Studios, the Nicolai Fechin House, the Leon Gaspard House, and the Ernest Martin Hennings House.
Doc Martin's restaurant in the historic Taos Inn used to be the office of Thomas "Doc" Martin. Other parts of the inn were his home. It was also where the Taos Society of Artists was founded. On Ledoux Street, south of the Taos Plaza, you can find the Ernest L. Blumenschein House and Harwood House.
Other Important Historic Sites
The center of the Taos Downtown Historic District is the Taos Plaza. Just west of it is the Our Lady of Guadalupe Church. North of the Taos Plaza are the Governor Charles Bent House and the Taos Inn. Further north in Taos is The Bernard Beimer House. On the southwest edge of the Taos Historic district is La Loma Plaza Historic District. East of the plaza on Kit Carson Road is the Kit Carson House.
North of Taos are the Turley Mill and Distillery Site and the Rio Grande Gorge Bridge. Just outside Taos in Ranchitos is the Martinez Hacienda. This was the home of the late Padre Antonio José Martínez and is now a museum. South of Taos is the Ranchos de Taos Plaza with the San Francisco de Asis Mission Church.
 |
Governor Charles Bent House, Taos Inn, The Bernard Beimer House, Taos Art Museum, the Nicolai Fechin House, Taos Pueblo | Mabel Dodge Luhan House |  |
|
| Our Lady of Guadalupe Church | Kit Carson House, Eanger Irving Couse House and Studio—Joseph Henry Sharp Studios, Ernest Martin Hennings House, the Leon Gaspard House | |||
Taos Downtown Historic District |
||||
| La Loma Plaza Historic District | Ernest L. Blumenschein House, Harwood House |
About 20 miles (32 km) northwest is the D. H. Lawrence Ranch. This was the home of the English novelist D. H. Lawrence in the 1920s. It is now owned by the University of New Mexico. Many believe his ashes are buried there at the D. H. Lawrence Memorial.
Arts and Culture in Taos
Taos has three art museums: Harwood Museum of Art, Taos Art Museum, and Millicent Rogers Museum. They show art from the Pueblo Native Americans, the Taos Society of Artists, and modern artists. The town has over 80 art galleries. You can also visit several homes of the Taos Society of Artists.
Taos has several places for performing arts. The Taos Center for the Arts (TCA) hosts famous and local performers at the Taos Community Auditorium. They also show independent films. Three chamber music groups perform at TCA: Taos School of Music, Taos Chamber Music Group, and Music from Angel Fire. The Harwood Museum of Art also hosts performances and lectures. The Town of Taos Convention Center is another place for local performances.
The Taos Talking Pictures Film Festival was a film festival held in the town from the mid-1990s to 2003. The top prize at the festival was 5 acres (2.0 ha) of land.
Outdoor Recreation in Taos
The Carson National Forest and Rio Grande del Norte National Monument offer many fun outdoor activities. You can go hiking, skiing, fly fishing, horseback riding, golfing, hot air ballooning, llama trekking, rafting, and mountain biking. The South Boundary National Recreation trail, east of town, is known as the best mountain bike trail in New Mexico.
There are also many hot springs along the Rio Grande and in the Taos Mountains. Ojo Caliente offers places where visitors can enjoy mineral springs. They also offer massages and other spa treatments. The Cumbres & Toltec Scenic Railroad offers a ride through the Toltec Gorge and Rocky Mountain passes. It uses an authentic narrow-gauge steam railroad.
In winter, many people come to Taos to ski in the mountains. Nearby Wheeler Peak is 13,161 feet (4,011 m) high. It is the highest peak in New Mexico. The Taos area has four ski areas: Taos Ski Valley, Red River ski area, Sipapu (ski area), and Angel Fire ski area. Other winter activities include hot air ballooning, horseback riding, snow-shoeing, cross-country skiing, ice skating, ice fishing, and snowmobiling.
Understanding Taos Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1940 | 965 | — | |
| 1950 | 1,815 | 88.1% | |
| 1960 | 2,163 | 19.2% | |
| 1970 | 2,475 | 14.4% | |
| 1980 | 3,369 | 36.1% | |
| 1990 | 4,065 | 20.7% | |
| 2000 | 4,700 | 15.6% | |
| 2010 | 5,716 | 21.6% | |
| 2020 | 6,474 | 13.3% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||
Taos is the main town of the Taos, NM, Micropolitan Statistical Area. This area includes all of Taos County.
In 2010, Taos had a population of 5,716 people. The average age was 44 years old. The population was made up of different ethnic and racial groups. About 40.1% were non-Hispanic white, 0.7% African American, 1% Asian, and 5.3% Native American. About 51.9% were Hispanic or Latino.
In 2000, there were 4,700 people living in Taos. There were 2,067 households and 1,157 families. About 27.5% of households had children under 18. The average household had 2.18 people. The average family had 2.87 people.
The median income for a household in Taos in 2000 was $25,016. For a family, it was $33,564. About 23.1% of the population lived below the poverty line. This included 26.8% of those under 18 and 24.4% of those 65 or older.
Geography and Climate of Taos
Taos is located at 36°23′38″N 105°34′36″W / 36.39389°N 105.57667°W. The town covers about 5.4 square miles (14 km2) of land.
Taos is part of two watersheds. Most of the town is in the Outlet Rio Fernando del Taos Watershed. Its two water bodies are considered unhealthy. Local groups are working to improve the watershed's health. The northern part of town is in the Rio Fernando del Taos-Rio Pueblo del Taos Watershed.
Just west of Taos is the Rio Grande Gorge. This deep canyon cuts through old lava flows. The Rio Grande Gorge Bridge, part of U.S. Route 64, crosses it.
The town is 6,969 feet (2,124 m) above sea level. North of Taos is Wheeler Peak, which is 13,161 feet (4,011 m) high. It is the highest point in New Mexico. Taos has a warm-summer humid continental climate (Köppen Dfb). It is almost a semi-arid climate (BSk) because it doesn't get much rain. The town has big changes in temperature between day and night. Even when summer days are very hot, nights cool down a lot.
| Climate data for Taos, New Mexico, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1892–2016 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 66 (19) |
73 (23) |
80 (27) |
82 (28) |
99 (37) |
98 (37) |
101 (38) |
99 (37) |
95 (35) |
89 (32) |
83 (28) |
67 (19) |
101 (38) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 53.8 (12.1) |
59.4 (15.2) |
68.7 (20.4) |
75.6 (24.2) |
83.4 (28.6) |
91.5 (33.1) |
93.2 (34.0) |
90.5 (32.5) |
86.2 (30.1) |
77.8 (25.4) |
66.7 (19.3) |
56.1 (13.4) |
93.9 (34.4) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 42.1 (5.6) |
46.4 (8.0) |
55.2 (12.9) |
63.0 (17.2) |
72.9 (22.7) |
83.7 (28.7) |
86.5 (30.3) |
84.2 (29.0) |
78.1 (25.6) |
67.0 (19.4) |
53.1 (11.7) |
42.4 (5.8) |
64.6 (18.1) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 27.1 (−2.7) |
32.9 (0.5) |
40.2 (4.6) |
46.8 (8.2) |
55.0 (12.8) |
65.5 (18.6) |
69.6 (20.9) |
67.7 (19.8) |
61.4 (16.3) |
49.7 (9.8) |
37.8 (3.2) |
28.0 (−2.2) |
48.5 (9.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 12.2 (−11.0) |
19.4 (−7.0) |
25.3 (−3.7) |
30.5 (−0.8) |
37.1 (2.8) |
47.4 (8.6) |
52.7 (11.5) |
51.3 (10.7) |
44.8 (7.1) |
32.3 (0.2) |
22.4 (−5.3) |
13.6 (−10.2) |
32.4 (0.2) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | −3.3 (−19.6) |
−1.0 (−18.3) |
10.5 (−11.9) |
19.8 (−6.8) |
26.6 (−3.0) |
36.5 (2.5) |
45.3 (7.4) |
44.3 (6.8) |
32.1 (0.1) |
19.0 (−7.2) |
6.4 (−14.2) |
−4.9 (−20.5) |
−9.6 (−23.1) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −27 (−33) |
−27 (−33) |
−11 (−24) |
0 (−18) |
13 (−11) |
28 (−2) |
34 (1) |
36 (2) |
22 (−6) |
0 (−18) |
−21 (−29) |
−27 (−33) |
−27 (−33) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.67 (17) |
0.45 (11) |
0.71 (18) |
0.83 (21) |
1.22 (31) |
0.86 (22) |
1.53 (39) |
1.77 (45) |
1.37 (35) |
1.34 (34) |
0.88 (22) |
1.07 (27) |
12.70 (323) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 6.0 (15) |
3.3 (8.4) |
4.0 (10) |
1.9 (4.8) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
1.4 (3.6) |
2.8 (7.1) |
9.0 (23) |
28.4 (71.9) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 3.7 | 3.5 | 4.4 | 3.8 | 4.9 | 4.8 | 7.2 | 10.2 | 5.8 | 4.6 | 3.9 | 4.2 | 61.0 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 2.6 | 2.4 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 3.1 | 12.0 |
| Source 1: NOAA | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: XMACIS2 (mean maxima/minima, snow depth 1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
Understanding Mud Season
Dirt roads and driveways in Taos can get very muddy. This happens when winter weather is followed by unusually warm temperatures. The soil in the area has a lot of silt. This makes it easily affected by frost heaving, which causes the mud.
Education in Taos Schools and Universities
The public schools in Taos are run by Taos Municipal Schools. They include Arroyos del Norte Elementary School, Enos García Elementary (also Taos Elementary School), Ranchos Elementary School, Taos Middle School, Taos High School, and Taos Cyber Magnet School.
Charter schools in the area are Anansi Charter School, Taos Academy (State Charter), Taos Municipal Charter School, and Vista Grande High School. There are also other alternative and private schools. These include Chrysalis Alternative School, Sped Discipline, Yaxche Private School, Taos Christian Academy, and San Francisco De Asis School. The Bureau of Indian Education runs the Taos Day School in nearby Taos Pueblo.
Dallas-based Southern Methodist University has a 295-acre (119 ha) campus at Fort Burgwin in Taos.
Albuquerque-based University of New Mexico (UNM) has a community campus in Taos. It has eight buildings in Taos. These include the UNM Harwood Museum of Art and Taos High School, where some classes are held.
The Earthship Academy (or Earthship Biotecture Academy) teaches about Earthship design. Earthship is a special type of sustainable architecture. It focuses on using solar power.
Transportation in Taos
Public Transportation Options
The RTD Chile Line is Taos' only public transportation system. It is run by the North Central Regional Transit District (NCRTD). It offers free service within the town. It also provides seasonal service up to Taos Ski Valley. The system also has paratransit service for people with special needs. All buses are equipped for the American Disability Act (ADA).
The RTD Taos Express helps local tourism. It offers weekend express service for a small fee. It goes from the Taos Plaza to the New Mexico Rail Runner, Santa Fe Municipal Airport, and Santa Fe transit.
The North Central Regional Transit District (NCRTD) provides public transportation into Taos from all over Taos County. It also serves Santa Fe, Rio Arriba, and Los Alamos Counties. The Taos region has service to Cerro, Penasco, Questa, Red River, the Rio Grande corridor, and the University of New Mexico – Taos Klaur campus. At the Española Transit Center, you can connect to other routes. These go to Española, Santa Fe, Los Alamos, and the Northern Pueblos area. The Regional Transit District Act was passed in 2003. It allowed for the creation of Regional Transit Districts (RTDs) in New Mexico. In September 2004, the North Central Regional RTD was the first to be certified.
Airports Near Taos
Taos Regional Airport (SKX) is managed by the Town of Taos. The airport is a few miles north of Taos on U.S. Route 64. It is on the way to the Rio Grande Gorge Bridge.
Other airports in New Mexico include the Santa Fe Municipal Airport and Albuquerque International Sunport.
Media and News in Taos
Newspapers in Taos
El Crepusculo de la Libertad was the first newspaper in Taos. It started in 1834 with the first printing press west of the Mississippi River. Its current version, The Taos News, also known as El Crepusculo, is the main printed newspaper in Taos.
- The Taos News, a weekly online and print publication.
- Sangre de Cristo Chronicle (no longer active) served Angel Fire, New Mexico, Red River, Cimarron, Eagle Nest, Taos, Las Vegas, Questa, and Sipapu.
- The Santa Fe New Mexican
- Albuquerque Journal North Edition.
Online News
The Taos News provides weekly online versions of their newspaper.
Television in Taos
There are two local cable television stations: Taos Local Television Public Access Channel 2 and Channel 22. You can also see a List of television stations in New Mexico.
Radio Stations in Taos
Radio stations that serve Taos include:
(Some stations are in the nearby areas of El Prado and Arroyo Seco.)
| Radio station | Frequency | FM/AM | Format |
|---|---|---|---|
| KCEI | 90.1 | FM | Variety. |
| KNCE | 93.5 | FM | "True Taos Radio", variety |
| KKIT | 95.9 | FM | "The Mountain", pop, rock, classic rock. |
| KKTC | 99.9 | FM | "True Country". |
| KLNN | 103.7 | FM | Adult contemporary music. |
| KRRT | 90.9 | FM | Top-40, local transmitter for the University of New Mexico's KUNM. |
| KTAO | 101.9 | FM | Solar radio station with an adult album alternative music format. |
| KVOT | 1340 | AM | Religious (Christian) music. |
| KXMT | 99.1 | FM | Radio Exitos is the local 24-hour Spanish radio station serving Taos, northern New Mexico and Southern Colorado. |
| KYBR | 92.9 | FM | Spanish. Located in Española, but serves Santa Fe and Taos as well. |
Sister Cities of Taos
Taos has one sister city. This is a town that has a special partnership with Taos. It is chosen by Sister Cities International:
 Xalisco, Nayarit, Mexico
Xalisco, Nayarit, Mexico
Notable People from Taos


Artists and Actors
- Lynn Anderson, country/pop singer
- Chiara Aurelia, actress
- Abbie Conant, trombonist and professor
- Oscar E. Berninghaus, artist
- Emil Bisttram, artist
- Larry Bell, sculptor
- Ernest L. Blumenschein, founding member, Taos Society of Artists
- Dorothy Brett, artist and personality
- Joshua Bryant, actor, director, author and speaker former longtime resident and founder of the Taos Talking Pictures Film Festival & Media Forum
- Agnes Chavez, artist
- E. Irving Couse, artist
- Andrew Dasburg, artist
- Ronald Davis, artist
- W. Herbert Dunton, artist
- Nicolai Fechin, artist
- R. C. Gorman, artist
- E. Martin Hennings, artist
- William Victor Higgins, artist
- Dennis Hopper, actor, director, artist
- Gene Kloss, artist
- Agnes Martin, artist
- Robert Mirabal, Native American flute player and maker from Taos Pueblo
- Bror Julius Olsson Nordfeldt, artist
- Bert Geer Phillips, artist
- Suzan Pitt, artist, director
- Kenneth Price, ceramicist
- Christian Ristow, artist
- Julia Roberts, actress
- Dean Stockwell, artist and actor
- Joseph Henry Sharp, artist
- Walter Ufer, artist
- Kristen Vigard, actress and singer
- Harold Joe Waldrum, artist
- Michael Walker, custom knife maker and sculptor
- Julius Rolshoven, artist
Sportspeople
- Ross Anderson, skier
- Kit Carson, frontiersman
- Chris Del Conte, athletic director of the University of Texas at Austin
- Dave Hahn, mountaineer
- Danelle Umstead, Paralympic skier
Professors and Medical Professionals
- Fred Wendorf, Henderson-Morrison Professor of Anthropology at Southern Methodist University
- Thomas "Doc" Martin, physician
Authors, Poets, and Teachers
- Julia Cameron, author of The Artist's Way
- Judson Crews, poet and publisher
- James Doss, author
- Natalie Goldberg, writer
- Margaret Catherine Alice Hyson, missionary and teacher in Ranchos de Taos, New Mexico
- D. H. Lawrence, author
- Anne MacNaughton, poet and cofounder of Taos Poetry Circus
- John Nichols, author of The Milagro Beanfield War
- Olivia Romo, poet, spoken word artist and water rights activist
- Elizabeth Shepley Sergeant, journalist and writer
- John Muir, engineer, mechanic and writer
- Marilyn Gayle Hoff, author and activist
Businesspeople and Architects
- Marcelino Baca, 19th-century fur trader
- Mabel Dodge Luhan, patron of the arts
- Susan Powter, health and fitness entrepreneur
- Mike Reynolds, Earthship architect
- Millicent Rogers, socialite, fashion icon, and art collector
- Maria Rosa Villalpando (1738-1830) A Hispanic woman who became a captive of the Comanche and later a businesswoman in St. Louis.
Politicians and Military Figures
- Daniel R. Barrone, mayor of Taos and member of the New Mexico House of Representatives
- Charles Bent, first Territorial Governor of New Mexico
- Gary Johnson, former two-term governor of New Mexico
- John Márquez, politician in Richmond, California
- Joe P. Martínez, Medal of Honor recipient
- Kristina Ortez, politician
- Rebecca Vigil-Giron, 20th and 22nd New Mexico Secretary of State
Religious Figure
- Antonio José Martínez, priest
Images for kids
-
Mabel Dodge Luhan House, a National Historic Landmark
See also
 In Spanish: Taos (Nuevo México) para niños
In Spanish: Taos (Nuevo México) para niños