Detroit facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Detroit
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||
| Etymology: French: détroit (strait) | |||||
| Nicknames:
The Motor City, Motown, and others
|
|||||
| Motto(s):
Speramus Meliora; Resurget Cineribus
(Latin: We Hope For Better Things; It Shall Rise From the Ashes) |
|||||
| Country | United States | ||||
| State | Michigan | ||||
| County | Wayne | ||||
| Founded (Fort Detroit) |
July 24, 1701 | ||||
| Incorporated | September 13, 1806 | ||||
| Founded by | Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac (1658–1730) & Alphonse de Tonty (1659–1727) | ||||
| Named for | Detroit River | ||||
| Government | |||||
| • Type | Strong Mayor | ||||
| • Body | Detroit City Council | ||||
| Area | |||||
| • City | 142.89 sq mi (370.09 km2) | ||||
| • Land | 138.73 sq mi (359.31 km2) | ||||
| • Water | 4.16 sq mi (10.78 km2) | ||||
| • Urban | 1,284.8 sq mi (3,327.7 km2) | ||||
| • Metro | 3,888.4 sq mi (10,071 km2) | ||||
| Elevation | 656 ft (200 m) | ||||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||||
| • City | 639,111 | ||||
| • Estimate
(2024)
|
645,705 |
||||
| • Rank | 73rd in North America 26th in the United States 1st in Michigan |
||||
| • Density | 4,606.84/sq mi (1,778.71/km2) | ||||
| • Urban | 3,776,890 (US: 12th) | ||||
| • Urban density | 2,939.6/sq mi (1,135.0/km2) | ||||
| • Metro | 4,400,578 (US: 14th) | ||||
| Demonym(s) | Detroiter | ||||
| GDP | |||||
| • Metro | $331.333 billion (2023) | ||||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) | ||||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | ||||
| ZIP Codes |
482XX
|
||||
| Area code(s) | 313 | ||||
| FIPS code | 26-22000 | ||||
| GNIS feature ID | 1617959 | ||||
| Major airports | Detroit Metropolitan Airport, Coleman A. Young International Airport | ||||
| Mass transit | Detroit Department of Transportation, Detroit People Mover, QLine | ||||
Detroit (pronounced dih-TROYT) is the largest city in the state of Michigan. It sits on the Detroit River, right across from Windsor, Ontario, Canada. With a population of over 639,000 people in 2020, it is a major city in the United States. The larger Metro Detroit area is home to more than 4.4 million people. Detroit is famous for its important role in music, art, architecture, and especially its history with cars and factories.
French explorers founded Detroit in 1701. It grew into a big industrial city, especially known for making cars in the early 1900s. The city's population grew a lot during this time. Over the years, Detroit faced some challenges, including changes in its industries and many people moving to the suburbs. In 2013, the city had to reorganize its finances, but it successfully recovered in 2014. Recently, Detroit's population has started to grow again, showing a new period of development.
Detroit is a busy port on the Detroit River, which connects the Great Lakes to the St. Lawrence Seaway. It has one of the biggest economies in the Midwest. The city is known as the heart of the U.S. car industry. Major car companies like General Motors, Ford, and Stellantis North America (which includes Chrysler) have their main offices in the Metro Detroit area. The Detroit Metropolitan Airport is also a very important travel hub. The border crossing between Detroit and Windsor is one of the busiest in North America.
Detroit's culture is rich and diverse, with influences from many places. It is the birthplace of Motown and techno music. It also played a big part in developing jazz, hip-hop, rock, and punk music. Because of its fast growth in the past, Detroit has many unique buildings and historic sites. In recent years, many efforts have helped restore old buildings and create new projects, like renovated theaters, sports stadiums, and a beautiful riverfront. Detroit is becoming a popular place for tourists, welcoming about 16 million visitors each year. In 2015, UNESCO named Detroit a "City of Design," the only U.S. city to receive this honor.
Contents
- Exploring Detroit's Past: A Journey Through History
- Detroit's Landscape: Geography and Nature
- People of Detroit: Demographics and Diversity
- Detroit's Vibrant Arts and Culture Scene
- Detroit's Exciting Sports Scene
- How Detroit is Governed
- Learning in Detroit: Education Opportunities
- Detroit in the News: Media Outlets
- Connecting Detroit: Infrastructure and Transportation
- Famous People from Detroit
- Detroit's Sister Cities
- Images for kids
- See also
Exploring Detroit's Past: A Journey Through History
How Detroit Got Its Name

Detroit is named after the Detroit River. This river connects Lake St. Clair with Lake Erie. The name comes from the French word "détroit," which means "strait." A strait is a narrow passage of water. The city was built on this narrow waterway that links the two lakes.
Early Inhabitants: Indigenous Peoples
Long ago, about 11,000 years ago, Paleo-Indians lived near Detroit. Later, by the 1600s, groups like the Huron, Odawa, Potawatomi, and Iroquois peoples lived in the region. The Anishinaabe people called this area Waawiiyaataanong, meaning 'where the water curves around'.
French Beginnings: Founding Fort Pontchartrain
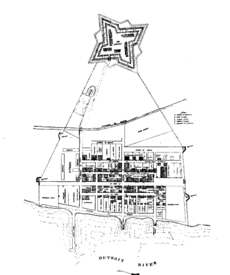
On July 24, 1701, French explorer Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac and his team started building a small fort on the north bank of the Detroit River. They named it Fort Pontchartrain du Détroit. France encouraged families to move to Detroit by offering free land. By 1765, it was the largest European settlement between Montreal and New Orleans. The economy back then was mostly based on the fur trade, where Native American peoples played a big part.
British Control and American Independence
During the French and Indian War (1753–1763), British troops took control of Detroit in 1760. They shortened its name to Detroit. After the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), Great Britain gave Detroit and other lands to the newly independent United States in 1783. British forces finally left in 1796. By the early 1800s, many American settlers began moving west into the area.
Detroit's Enduring Heritage
The municipal flag of Detroit shows its French and English history. Descendants of early French settlers, sometimes called Muskrat French, still form a unique community in the region today.
Growth in the 1800s: Fire, War, and Progress
A big fire in 1805 destroyed most of Detroit's buildings. Amazingly, no one died. After the fire, Father Gabriel Richard created the city's motto: "Speramus Meliora; Resurget Cineribus" (We Hope For Better Things; It Shall Rise From the Ashes). This motto is on the city's seal and flag.
Detroit was the capital of the Michigan Territory from 1805 to 1847. It became Michigan's first state capital in 1837. During the War of 1812, Detroit was a key battleground. The city was officially made a city in 1815. Its design, with wide avenues, was inspired by Washington, D.C.
Before the American Civil War, Detroit was an important stop on the Underground Railroad. Thousands of enslaved African Americans found freedom by escaping to Canada through the city. Detroit also played a big part in supporting the Union during the Civil War.
In the late 1800s, Detroit became a center for shipping and manufacturing. The city grew wealthy, and beautiful mansions were built. In 1896, Henry Ford built his first car in Detroit. The city expanded, becoming a major player in the growing automobile industry.
The Motor City Rises: Early 1900s and World War II
In 1903, Henry Ford started the Ford Motor Company. Along with other car pioneers, they made Detroit the world's car capital. The car industry led to many new businesses and jobs. By 1920, Detroit was the fourth-largest city in the U.S. The Detroit River became one of the busiest commercial waterways in the world.
During World War II, Detroit's car factories switched to making war supplies, earning it the nickname "Arsenal of Democracy." Many people moved to Detroit for these jobs, leading to a huge increase in population.
Modern Detroit: Challenges and Rebirth
After reaching its largest population in 1950, Detroit faced changes in its industries and many people moved to the suburbs. This led to a decrease in population over several decades. However, the city has been working hard to rebuild and create new opportunities.

In 1963, Martin Luther King Jr. gave a famous speech in Detroit, sharing his dream for equality. This event was a powerful moment in the civil rights movement. The city has continued to strive for a fair and inclusive community.
In 2013, Detroit faced financial challenges and had to reorganize its finances. However, it successfully recovered in 2014. Since then, the city has seen many positive changes. Old buildings have been restored, and new developments have brought fresh energy. For example, the historic Michigan Central Station, once empty, was bought by Ford Motor Company and reopened in 2024, bringing new life to the area.

Today, Detroit is experiencing a rebirth. New shops, restaurants, and homes are appearing, especially downtown. This has attracted many young professionals and families. Detroit's population has even started to grow again, showing a bright future for the city.
Detroit's Landscape: Geography and Nature
Detroit is the main city in the Metro Detroit area, located in the Midwestern United States and the Great Lakes region. The city covers about 143 square miles (370 square kilometers), with most of it being land.
The Detroit River International Wildlife Refuge is a special place. It is the only international wildlife preserve in North America located in a major city. It protects islands, wetlands, and shorelines along the Detroit River and Lake Erie.
Detroit's highest point is about 675-680 feet (206-207 meters) above sea level, and its lowest point is along the Detroit River at 572 feet (174 meters).
Belle Isle Park is a large island park in the Detroit River, covering 982 acres (397 hectares). It has attractions like the James Scott Memorial Fountain, the Belle Isle Conservatory, a beach, a golf course, and nature trails. You can see both the Detroit and Windsor skylines from Sunset Point on the island.
Detroit has unique road systems, including avenues that spread out from the waterfront. It is also the only major city on the Canada–U.S. border where you travel south to cross into Canada. There are four border crossings: the Ambassador Bridge, the Detroit–Windsor tunnel, the Michigan Central Railway Tunnel for trains, and the Detroit–Windsor Truck Ferry.
City Views: Architecture and Neighborhoods
Amazing Architecture

Detroit's waterfront features many different building styles. The Ally Detroit Center has tall, pointed spires, while the Renaissance Center is a group of modern skyscrapers. Other famous buildings, like the Guardian Building and Penobscot Building, show off the Art Deco style. Important cultural places include the Fox Theatre and the Detroit Institute of Arts.
While downtown has tall buildings, much of Detroit has smaller homes. Many historic buildings from the late 1800s and early 1900s still stand. Neighborhoods like Indian Village and Boston-Edison have large, beautiful mansions. Efforts to preserve these historic places are helping to bring new life to the city.
Diverse Neighborhoods

Detroit has many types of neighborhoods. Downtown, Midtown, and New Center have many historic buildings and are busy areas. Other neighborhoods are being revitalized with new homes and businesses. For example, Southwest Detroit has a growing economy, especially in areas like Mexicantown.
The city is working on plans to improve neighborhoods and create new green spaces. This includes projects like Hantz Woodlands, which turns unused land into urban farms.
Green Spaces: Parks and Recreation
Detroit Parks & Recreation manages 308 public parks, covering about 5.6% of the city. Belle Isle Park, the largest city-owned island park in the U.S., is a favorite spot.
In the early 1800s, Chief Justice Augustus Woodward planned Detroit's park system. Grand Circus Park was the city's first official park in 1847.
The Detroit International Riverfront has a 3.5-mile (5.6 km) walkway with parks and businesses. This area includes Tri-Centennial State Park and Harbor, Michigan's first urban state park. Other major parks include River Rouge and Palmer Park.
Detroit's Weather: Climate Overview
| Weather chart for Detroit, Michigan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2
32
19
|
2
35
21
|
2.3
46
29
|
2.9
59
39
|
3.4
70
49
|
3.5
79
60
|
3.4
83
64
|
3
81
63
|
3.3
74
55
|
2.5
62
43
|
2.8
49
34
|
2.5
36
24
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| temperatures in °F precipitation totals in inches |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Metric conversion
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Detroit has a climate with warm summers and cold winters. Summers are usually warm, with temperatures sometimes going above 90°F (32°C). Winters are cold, with snow and temperatures often below freezing. The city gets a moderate amount of rain and snow throughout the year. Thunderstorms are common in spring and summer.
| Climate data for Detroit (DTW), 1981–2010 normals, extremes 1874–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 67 (19) |
70 (21) |
86 (30) |
89 (32) |
95 (35) |
104 (40) |
105 (41) |
104 (40) |
100 (38) |
92 (33) |
81 (27) |
69 (21) |
105 (41) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 51.2 (10.7) |
54.6 (12.6) |
70.4 (21.3) |
80.1 (26.7) |
85.8 (29.9) |
92.2 (33.4) |
93.4 (34.1) |
92.0 (33.3) |
88.3 (31.3) |
79.7 (26.5) |
67.2 (19.6) |
54.4 (12.4) |
95.1 (35.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 32.0 (0.0) |
35.2 (1.8) |
45.8 (7.7) |
59.1 (15.1) |
69.9 (21.1) |
79.3 (26.3) |
83.4 (28.6) |
81.4 (27.4) |
74.0 (23.3) |
61.6 (16.4) |
48.8 (9.3) |
36.1 (2.3) |
59.0 (15.0) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 25.6 (−3.6) |
28.1 (−2.2) |
37.2 (2.9) |
49.2 (9.6) |
59.7 (15.4) |
69.4 (20.8) |
73.6 (23.1) |
72.0 (22.2) |
64.4 (18.0) |
52.4 (11.3) |
41.5 (5.3) |
30.1 (−1.1) |
50.4 (10.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 19.1 (−7.2) |
21.0 (−6.1) |
28.6 (−1.9) |
39.4 (4.1) |
49.4 (9.7) |
59.5 (15.3) |
63.9 (17.7) |
62.6 (17.0) |
54.7 (12.6) |
43.3 (6.3) |
34.3 (1.3) |
24.1 (−4.4) |
41.8 (5.4) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | −1.2 (−18.4) |
2.9 (−16.2) |
10.9 (−11.7) |
24.5 (−4.2) |
35.7 (2.1) |
45.8 (7.7) |
52.2 (11.2) |
51.2 (10.7) |
39.8 (4.3) |
29.7 (−1.3) |
19.7 (−6.8) |
5.4 (−14.8) |
−5.1 (−20.6) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −21 (−29) |
−20 (−29) |
−4 (−20) |
8 (−13) |
25 (−4) |
36 (2) |
42 (6) |
38 (3) |
29 (−2) |
17 (−8) |
0 (−18) |
−11 (−24) |
−21 (−29) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 1.96 (50) |
2.02 (51) |
2.28 (58) |
2.90 (74) |
3.38 (86) |
3.52 (89) |
3.37 (86) |
3.00 (76) |
3.27 (83) |
2.52 (64) |
2.79 (71) |
2.46 (62) |
33.47 (850) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 12.5 (32) |
10.2 (26) |
6.9 (18) |
1.7 (4.3) |
trace | 0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0.1 (0.25) |
1.5 (3.8) |
9.6 (24) |
42.5 (108) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 13.1 | 10.6 | 11.7 | 12.2 | 12.1 | 10.2 | 10.4 | 9.6 | 9.5 | 9.8 | 11.6 | 13.7 | 134.5 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 10.4 | 8.3 | 5.4 | 1.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 2.3 | 8.5 | 36.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 74.7 | 72.5 | 70.0 | 66.0 | 65.3 | 67.3 | 68.5 | 71.5 | 73.4 | 71.6 | 74.6 | 76.7 | 71.0 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 119.9 | 138.3 | 184.9 | 217.0 | 275.9 | 301.8 | 317.0 | 283.5 | 227.6 | 176.0 | 106.3 | 87.7 | 2,435.9 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 41 | 47 | 50 | 54 | 61 | 66 | 69 | 66 | 61 | 51 | 36 | 31 | 55 |
| Source: NOAA (relative humidity and sun 1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Detroit | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean No. of days with Maximum temperature => 90.0 °F (32.2 °C) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 |
| Mean No. of days with Minimum temperature => 68.0 °F (20.0 °C) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 10 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 |
| Mean No. of days with Minimum temperature <= 32.0 °F (0.0 °C) | 27 | 25 | 21 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 14 | 24 | 120 |
| Mean No. of days with Maximum temperature <= 32.0 °F (0.0 °C) | 16 | 12 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 10 | 42 |
| Mean No. of days with snow depth => 0.1 in (0.25 cm) | 17 | 14 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 48 |
| Average sea temperature °F (°C) | 33.6 (0.9) |
32.7 (0.4) |
33.4 (0.8) |
39.7 (4.3) |
48.9 (9.4) |
63.9 (17.7) |
74.7 (23.7) |
75.4 (24.1) |
70.5 (21.4) |
60.3 (15.7) |
48.6 (9.2) |
38.1 (3.4) |
51.7 (10.9) |
| Mean daily daylight hours | 9.0 | 11.0 | 12.0 | 13.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 14.0 | 12.0 | 11.0 | 10.0 | 9.0 | 12.2 |
| Average Ultraviolet index | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 4.8 |
| Source 1: NWS (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
| Source 2 : Weather Atlas (daylight-UV-water temperature) | |||||||||||||
People of Detroit: Demographics and Diversity
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1820 | 1,422 | — | |
| 1830 | 2,222 | 56.3% | |
| 1840 | 9,102 | 309.6% | |
| 1850 | 21,019 | 130.9% | |
| 1860 | 45,619 | 117.0% | |
| 1870 | 79,577 | 74.4% | |
| 1880 | 116,340 | 46.2% | |
| 1890 | 205,876 | 77.0% | |
| 1900 | 285,704 | 38.8% | |
| 1910 | 465,766 | 63.0% | |
| 1920 | 993,678 | 113.3% | |
| 1930 | 1,568,662 | 57.9% | |
| 1940 | 1,623,452 | 3.5% | |
| 1950 | 1,849,568 | 13.9% | |
| 1960 | 1,670,144 | −9.7% | |
| 1970 | 1,511,482 | −9.5% | |
| 1980 | 1,203,368 | −20.4% | |
| 1990 | 1,027,974 | −14.6% | |
| 2000 | 951,270 | −7.5% | |
| 2010 | 713,777 | −25.0% | |
| 2020 | 639,111 | −10.5% | |
| 2024 (est.) | 645,705 | −9.5% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 2010–2020 |
|||
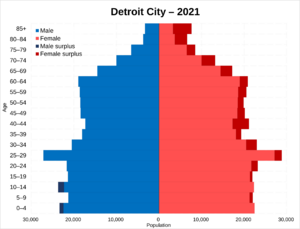
In 2020, Detroit had 639,111 residents. The city has seen its population change over the years. However, recent reports show that Detroit's population has grown for the second year in a row, leading population growth in Michigan.
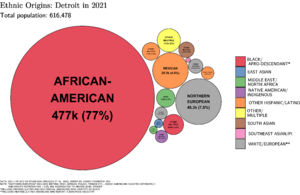
Detroit is a diverse city with many different backgrounds. In 2020, about 77.7% of the population was Black or African American. Non-Hispanic whites made up about 10.1%, and Hispanic or Latino people made up about 8.0%.
Thousands of people from Mexico came to Detroit in the early 1900s to work in factories and farms. Today, Detroit has a large Mexican-American community, especially in Mexicantown. Many people from Jalisco, Mexico, have moved to Detroit, adding to its vibrant Latino culture.
After World War II, many people from the Appalachian region of the U.S. also settled in Detroit. The city also has communities of Lithuanian Americans.
Detroit is home to various Asian communities. Northeast Detroit has a large population of Hmong people. An area near Hamtramck includes Bangladeshi Americans, Indian Americans, and Pakistani Americans. There are also many university students and hospital workers from China, India, and other Asian countries.
Jobs and Opportunities in Detroit
| Rank | Company or organization | # |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Detroit Medical Center | 11,497 |
| 2 | City of Detroit | 9,591 |
| 3 | Rocket Mortgage | 9,192 |
| 4 | Henry Ford Health System | 8,807 |
| 5 | Detroit Public Schools | 6,586 |
| 6 | U.S. Government | 6,308 |
| 7 | Wayne State University | 6,023 |
| 8 | Chrysler (now Stellantis) | 5,426 |
| 9 | Blue Cross Blue Shield | 5,415 |
| 10 | General Motors | 4,327 |
Detroit is a hub for many big companies, especially in car manufacturing, finance, technology, and health care. Some major companies based here include General Motors, Rocket Mortgage, and Little Caesars.
Many people work in downtown Detroit, which is a growing business area. Companies like Comerica and Ally Financial have large offices there. Ford Motor Company is located in the nearby city of Dearborn.
Midtown Detroit is also a busy area with major employers like the Detroit Medical Center and Wayne State University. New businesses and research centers are also growing in this area.
The city has been working hard to create new jobs and improve neighborhoods. This includes building new homes and restoring historic buildings. Since 2006, billions of dollars have been invested in downtown Detroit and its surrounding areas, leading to many new construction jobs.

Many companies have moved their offices to downtown Detroit, bringing more jobs and people. For example, Quicken Loans moved its main office and 4,000 employees to downtown Detroit in 2010. The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office also opened a satellite office here.
New stores like Meijer have opened in Detroit, providing more shopping options for residents. These investments show a strong belief in Detroit's future.
Detroit's Vibrant Arts and Culture Scene
Detroit's downtown and Midtown areas are attracting many young professionals and artists. This has led to new shops and restaurants, making the city an exciting place to live and visit. Many people from the suburbs also come to Detroit to enjoy its cultural events and sports games.
Detroit's Famous Nicknames
Detroit is known as the world's car center, so it's often called the Motor City. It's also famous for its music, earning it the nickname Motown. Other nicknames include City of Champions (for its sports teams), The D, Hockeytown, Rock City, and The 313 (its telephone area code).
The Sound of Detroit: Music History

Detroit has a rich music history and is known for its lively nightlife. The city has many famous music venues and hosts Broadway shows.
Detroit has contributed to many music styles. It hosts important music events like the Detroit International Jazz Festival and the Detroit Electronic Music Festival.
In the 1940s, Detroit blues artists like John Lee Hooker made Detroit a blues center. In the 1950s, it became a hub for jazz music.
Berry Gordy, Jr. founded Motown Records, which became famous in the 1960s and 1970s. Motown artists like Stevie Wonder, the Temptations, Diana Ross & the Supremes, and the Jackson 5 created a unique sound. Motown was the first record label owned by an African American to feature mostly African-American artists.
In the 1960s and 70s, rock artists like Bob Seger and Alice Cooper became popular. The band Kiss even sang about the city in their song "Detroit Rock City." In the 1980s, Detroit was important for hardcore punk rock.
More recently, Detroit has produced famous hip hop artists like Eminem and Kid Rock. The city is also known as the birthplace of techno music in the early 1980s. The Detroit Electronic Music Festival, now called Movement, happens every year.
Performing Arts: Theaters and Shows

Detroit has many grand theaters, including the Fox Theatre, Music Hall Center for the Performing Arts, and the Detroit Opera House. These venues host a variety of performances, from Broadway shows to concerts by the Detroit Symphony Orchestra.
Visiting Detroit: Tourism and Attractions
Detroit has become a popular place for tourists because of its unique culture, beautiful buildings, and new developments. The New York Times and Lonely Planet have both listed Detroit as a top travel destination.
Many of Detroit's famous museums are in the historic cultural center. These include the Detroit Institute of Arts, the Detroit Historical Museum, and the Charles H. Wright Museum of African American History. Other popular spots are the Motown Historical Museum, The Henry Ford museum in Dearborn, and the Detroit Zoo in Royal Oak.
Greektown and three downtown casino hotels offer entertainment. The Eastern Market is a huge outdoor market with over 150 food and specialty businesses. Annual events like the Detroit Festival of the Arts and the North American International Auto Show draw large crowds.

Summer festivals include the Electronic Music Festival and the International Jazz Festival. The Windsor–Detroit International Freedom Festival fireworks are a huge event, attracting millions of people.
Important sculptures in the city include The Spirit of Detroit and a memorial to boxing champion Joe Louis.
Detroit's Exciting Sports Scene
Detroit is one of only four U.S. cities with teams in all four major North American sports leagues. All four teams play in venues located right in the downtown area!
- The Detroit Tigers (baseball) play at Comerica Park. They have won four World Series titles.
- The Detroit Lions (football) play at Ford Field. They have won four NFL titles.
- The Detroit Red Wings (hockey) play at Little Caesars Arena. They have won 11 Stanley Cups, which is the most by any American NHL team.
- The Detroit Pistons (basketball) also play at Little Caesars Arena. They have won three NBA titles.
In the 1930s, Detroit was called the "City of Champions" because its teams won so many championships.
Detroit City FC, a professional soccer club, plays in the USL Championship at Keyworth Stadium in Hamtramck.
Detroit has hosted many big sports events, including the 2005 MLB All-Star Game, Super Bowl XL in 2006, and the NCAA Final Four in 2009. The Detroit Indy Grand Prix is held at Belle Isle Park. In 2024, Detroit hosted the NFL draft, which was the most attended draft ever!
How Detroit is Governed

Detroit is run by a mayor and a nine-member Detroit City Council. There is also an eleven-member Board of Police Commissioners and a city clerk. All these officials are elected by the people. The mayor leads the city, and the council approves budgets and laws. The city clerk manages elections and records.
Detroit's courts are managed by the state. The city has its own police and fire departments to keep everyone safe.
Detroit's Political Landscape
Detroit has had 74 mayors since it became a city in 1802. The city has been a strong supporter of the Democratic Party. In 2025, Detroit elected its first woman as mayor, Mary Sheffield.
Learning in Detroit: Education Opportunities
Colleges and Universities

Detroit is home to several colleges and universities. These include Wayne State University and the University of Detroit Mercy. Grand Valley State University also has a center in Detroit. Sacred Heart Major Seminary offers religious and academic degrees. Other schools are the College for Creative Studies and Wayne County Community College. In 2009, the Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine opened a campus at the Detroit Medical Center.
Schools for Kids: Primary and Secondary Education
The Detroit Public Schools (DPS) district is the largest school district in Michigan, serving about 66,000 students. Detroit also has many charter schools, which are public schools run independently. Some Detroit students also attend schools in nearby towns.
The city is working to improve its schools and provide good education for all children. Many efforts are underway to support students and help them succeed.
Detroit in the News: Media Outlets
The Detroit Free Press and The Detroit News are the main daily newspapers in Detroit. The Metro Times is a weekly paper covering news and entertainment. The Michigan Chronicle, founded in 1935, is one of the oldest African-American weekly newspapers in the U.S.
Detroit is a major market for television and radio. Many people in nearby Ontario, Canada, also watch and listen to Detroit's stations.
Connecting Detroit: Infrastructure and Transportation

Staying Healthy: Health Systems
Detroit has many major hospitals, including the Detroit Medical Center (DMC), Henry Ford Health System, and St. John Health System. The DMC is a large medical center with several hospitals, including Children's Hospital of Michigan. It is a major employer in the city.
In recent years, DMC and Henry Ford Health System have invested a lot in new medical research facilities and hospitals, especially in Midtown and New Center.
Getting Around: Transportation in Detroit

Detroit is an important transportation hub because of its location near Canada, its ports, highways, and airports. The city has three international border crossings connecting it to Windsor, Canada. The Ambassador Bridge is the busiest border crossing in North America.
Canada has invested in building a new bridge, the Gordie Howe International Bridge, which is expected to open in early 2026. This bridge will further improve connections between Detroit and Canada.
Public Transit Systems
Bus services are provided by the Detroit Department of Transportation within the city and by the Suburban Mobility Authority for Regional Transportation (SMART) for trips to the suburbs. SMART also has a FAST service with limited stops on major roads. You can also take the Tunnel Bus to Windsor, Canada.
Downtown Detroit has an elevated train system called the People Mover, which circles the downtown area. The QLine is a streetcar that connects the People Mover to the Amtrak station along Woodward Avenue. There are also plans for a regional rail line connecting Detroit to Ann Arbor.

Amtrak provides train service from Detroit to Chicago and Pontiac. Intercity bus services like Greyhound Lines also connect Detroit to other cities.
Airports Serving Detroit

The main airport for Detroit is Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport (DTW), located in Romulus. It is a major hub for Delta Air Lines. Coleman A. Young International Airport (DET) on Detroit's northeast side handles charter and general aviation flights.
Roads and Freeways
Metro Detroit has a large network of freeways. Four major Interstate Highways surround the city: I-75, I-94, I-96, and I-696. These freeways connect Detroit to other cities in Michigan and beyond.
Unique Services: Floating Post Office
Detroit has a very special floating post office called the J.W. Westcott II. It delivers mail to large ships on the Detroit River! Its ZIP Code is 48222, making it the only floating ZIP Code in the United States.
Famous People from Detroit
Detroit's Sister Cities
Detroit has sister cities around the world, which helps build friendships and understanding between different cultures:
 Chongqing, China
Chongqing, China Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Dubai, United Arab Emirates Huế, Vietnam
Huế, Vietnam Kitwe, Zambia
Kitwe, Zambia Minsk, Belarus
Minsk, Belarus Nassau, Bahamas
Nassau, Bahamas Toyota, Japan
Toyota, Japan Turin, Italy
Turin, Italy
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Detroit para niños
In Spanish: Detroit para niños
 | William Lucy |
 | Charles Hayes |
 | Cleveland Robinson |