Personal computer facts for kids
A personal computer (often called a PC) is a type of computer that people use in their homes and offices. The very first PC, named "IBM PC", was created by the company IBM in 1981. However, other personal computers like the Commodore PET existed before that. Even Smartphones and tablet computers are personal computers, but we usually don't call them "PCs".
Most PCs today come with a main program called an operating system. This system helps you use the computer and makes everything work. The most popular operating system is Windows, made by Microsoft Corporation. Computers from Apple Inc. use a different system called Mac OS.
There are also many free operating systems available, known as Linux operating systems. There are over 300 different kinds of Linux, each for a different purpose. Ubuntu-Linux is one of the easiest and most used Linux systems.
A modern PC needs a few main parts to work. The "Base unit" or "Tower" is the main box that holds the computer's brain. You use a mouse and keyboard to give the computer instructions (this is called input). A monitor shows you what the computer is doing (this is called output). In a laptop computer, all these parts are built together.
Inside the tower, you'll find many electronic parts. The most important ones are the motherboard, the CPU, the hard drive, and the memory.
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is like the computer's brain. It follows all the instructions from the operating system and other programs. The memory, also called RAM, helps the CPU move information very quickly. The hard drive stores all your programs and files even when the computer is turned off. Older computers used floppy drives and CD-ROM drives to store information on removable disks.
Computers often have a modem to send and receive information over phone lines or cable. Computers can also connect to a computer network to share information with other computers.
Modern PCs have different connection points called ports. The most common ones are USB ports.
People use computers for many things. You can use them for work, like doing research on the internet, keeping records, or writing documents. You can also use them to talk to people around the world using Instant messaging, e-mail, or Skype. And of course, many people love playing computer games!
Contents
How Personal Computers Started
In the early days of computers, machines like the ENIAC (from 1946) were huge and needed a highly trained person to operate them. These were not "personal" at all! Over time, computers became smaller and easier for one person to use. For example, the Programma 101 was introduced in 1964, and the Soviet MIR computers came out in the late 1960s.
By the early 1970s, people at universities could use a computer by themselves for a long time. But these computers were still too expensive for most people to own.
In 1968, a researcher named Douglas Engelbart showed off amazing new ideas that we use every day now. These included e-mail, links that take you to other pages (like on the internet), word processing, video calls, and the computer mouse. But his demonstration needed very expensive equipment and a large computer, so it wasn't something a single person could have at home yet.
The invention of the microprocessor in the mid-1970s changed everything. It made computers much cheaper, so small businesses and even individuals could finally afford them.
Early personal computers were often called microcomputers. They were sometimes sold as kits that people had to build themselves. These were mostly for hobbyists who loved electronics. To use them, you had to add parts like keyboards, monitors, and disk drives.
The Micral N, built in 1972, was one of the first ready-made microcomputers. It used the Intel 8008 chip.
In 1973, IBM created a portable computer called SCAMP. It was based on the IBM PALM processor and had a small screen and keyboard. It was considered "the world's first personal computer" by PC Magazine because it was the first portable computer that one person could use. This led to the IBM 5100 in 1975, which was also portable and could be programmed in different languages.
Another important step was the Xerox Alto in 1973. It had a graphical user interface (GUI), which means you could see pictures and icons on the screen instead of just text. This idea later inspired Apple's Macintosh and Microsoft's Windows operating systems. However, the Alto was too expensive to sell widely.
Many people consider the Altair 8800, introduced in 1974, to be the first true "personal computer." It used the Intel 8080 Microprocessor and started the "microcomputer revolution." The way it was built became a standard for other computers, and the first programming language for it was Altair BASIC, which was the start of Microsoft.
In 1976, Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak sold the Apple I computer circuit board. It was different because it came already put together and tested, not as a kit. This made it easier for more people to use.
The first widely sold personal computer was the Commodore PET, shown in January 1977. Soon after, the Apple II was released in June 1977, followed by the TRS-80 in August 1977. These three computers were known as the "1977 trinity." They were ready to use right out of the box, which meant more people could focus on using software instead of building the computer itself.
In the early 1980s, home computers became even more popular for families. They had software for everyday tasks, programming, and games. They often connected to a home television as a screen. Famous examples include the ZX Spectrum (which sold 8 million units) and the Commodore 64 (which sold 17 million units).
IBM's first PC, the IBM 5150, was released on August 12, 1981. In 1982, Time magazine even named "The Computer" their "Machine of the Year."
In 1991, the World Wide Web became available to everyone. This, combined with powerful PCs and easy-to-use Web browsers, created the internet world we know today.
Different Kinds of Personal Computers
Personal computers come in many shapes and sizes.
Stationary Computers
These computers are usually meant to stay in one place, like on a desk.
Desktop Computer
A desktop computer is a common type of PC. It usually has a tall case (called a "tower") that holds all the main parts like the motherboard and processor. The monitor, keyboard, and mouse are separate and plug into the back of the tower. Desktop computers are popular for homes and businesses because they are powerful and you can easily add more screens.
A gaming computer is a special desktop computer with very powerful parts, like a strong video card, processor, and lots of memory. This makes video games run super fast and look amazing.
An all-in-one computer combines the monitor and the computer's main parts into a single unit. The keyboard and mouse are still separate. These are popular because they save space, but they can be harder to upgrade than regular desktops.
A nettop is a small, low-cost computer designed mainly for using the internet and web applications.
A Home theater PC (HTPC) is a computer that acts like a home entertainment system. It connects to your TV and can play movies, music, show photos, and even record TV shows.
Portable Computers
These computers are designed to be carried around.
Laptop
A laptop computer is made for portability. It has a "clamshell" design, meaning it folds shut. The keyboard and computer parts are on one side, and the screen is on the other. Laptops have a rechargeable battery, so you can use them anywhere. Because they are designed to be small and light, their parts are often less powerful than desktop computers, especially for gaming.
A desktop replacement computer is a large, powerful laptop that can do almost everything a desktop computer can. They usually have bigger screens and stronger parts, but they might not have a long battery life.
Netbooks are smaller, lighter, and less powerful laptops. They were designed mainly for browsing the internet and doing basic tasks. They usually don't have a CD/DVD drive.
Tablet

A tablet uses a touchscreen display that you control with your finger or a stylus pen. Some tablets have a keyboard that can be attached or folded away. Many tablets have USB ports to connect a keyboard or mouse.
Smartphone
Smartphones are very similar to tablets, but they always have phone call features. They are usually smaller than tablets.
Ultra-mobile PC
An ultra-mobile PC (UMPC) is a very small tablet computer. It was developed by companies like Microsoft, Intel, and Samsung.
Pocket PC
A pocket PC is a small, handheld computer (like a personal digital assistant, or PDA) that runs a special version of Microsoft Windows. They have many features similar to a desktop PC.
Computer Parts: Hardware and Software
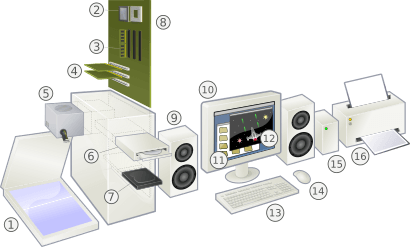
Computer hardware refers to all the physical parts of a computer. This includes everything you can touch, like the screen, keyboard, and the parts inside the computer case.
Most modern computers are easy to set up. You just plug in the power, monitor, and other cables. A typical desktop computer has a case (often called a "tower") that holds the power supply, motherboard, hard disk drive, and sometimes an optical disc drive. Many towers have empty spaces where you can add more parts later.
External devices like a computer monitor, keyboard, and a pointing device (mouse) are usually connected to the computer.
The motherboard is like the main circuit board that connects all the other parts. The RAM, graphics card, and processor are usually plugged directly into the motherboard.
The central processing unit (CPU chip) plugs into a special socket on the motherboard. Memory modules plug into their own sockets. Some motherboards have the video and sound parts built-in, while others use expansion slots for extra cards like graphics cards. Disk drives, which store lots of data, connect to the motherboard and the power supply with cables.
A peripheral is a device that connects to a computer to help it communicate or add extra features. Peripherals usually connect using USB ports. Flash drives are small, portable storage devices that use flash memory. Memory cards are also portable storage, often used in phones and cameras. You can use a memory card reader to access files from them.
Webcams are video cameras that record video in real time. They can be built into your computer or connected via USB. Game controllers can be plugged in via USB to play video games. Headphones and speakers let you listen to audio. Microphones let you record your voice or other sounds.
Computer Programs: Software
Computer software is any kind of program or instructions that tell the computer what to do. It's different from hardware because you can't touch it. Software includes programs like word processors (for writing documents) and system software like operating systems, which help the hardware work.
Common software programs include those for word processing, browsing the Internet, sending e-mail, playing multimedia (like music and videos), playing computer games, and writing new computer programs.
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is the main software that manages all the computer's resources. It helps you use the computer and makes sure all the programs run smoothly. The OS handles basic tasks like managing memory, controlling input and output devices (like your keyboard and printer), connecting to computer networks, and organizing your files.
Popular desktop operating systems today are Microsoft Windows, macOS, and Linux. Windows, macOS, and Linux all have versions for both personal computers and larger servers.
Early personal computers used operating systems where you typed commands to tell the computer what to do. You had to remember many commands. But starting in the 1960s, people began exploring graphical user interfaces (GUIs). These let you click on icons and menus with a mouse, making computers much easier to use. By the early 2000s, almost all personal computers used GUIs.
Applications
Application software (or just "apps") are programs that help you do specific tasks. For example, a word processor helps you write, and a spreadsheet helps you work with numbers. The operating system (system software) helps these applications run by managing memory and connections.
Think of it like this: an electric light bulb (the application) needs electricity from a power plant (the system) to work. The power plant generates electricity, but it's the light bulb that actually helps you by providing light.
Many applications are bundled together in an "application suite." Microsoft Office and LibreOffice are good examples. They include a word processor, a spreadsheet, and other useful programs.
Gaming
PC gaming is very popular, especially among people who buy more expensive, powerful PCs.
Environmental Impact
Personal computers contribute to electronic waste. About 50 million tons of electronic waste are thrown away each year, which is a big problem for the environment.
Images for kids
-
An artist's depiction of a 2000s-era desktop-style personal computer, which includes a metal case with the computing components, a display monitor and a keyboard (mouse not shown)
-
The 8-bit architecture Pravetz 82 computer produced in Bulgaria from 1982, in school class in the Soviet Union
-
Children being taught how to use a laptop computer in 2005. An older (1990s-era) desktop personal computer's CRT monitor is visible in the background.
See also
 In Spanish: Computadora personal para niños
In Spanish: Computadora personal para niños
 | Jewel Prestage |
 | Ella Baker |
 | Fannie Lou Hamer |