Baja California facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Baja California
|
||
|---|---|---|
| Free and Sovereign State of Baja California Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California (Spanish) |
||

Constitution 1857 National Park
|
||
|
||
| Anthem: "Canto a Baja California" | ||
State of Baja California within Mexico
|
||
| Country | Mexico | |
| Capital | Mexicali | |
| Largest city | Tijuana | |
| Largest metro | Greater Tijuana | |
| Before statehood | North Territory of Baja California | |
| Admission | 16 January 1952 (29th) | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 71,450 km2 (27,590 sq mi) | |
| Area rank | 12th | |
| Population
(2020)
|
||
| • Total | 3,769,020 | |
| • Rank | 14th | |
| • Density | 52.750/km2 (136.623/sq mi) | |
| • Density rank | 19th | |
| Demonym(s) | Bajacaliforniano(a) | |
| GDP | ||
| • Total | MXN 1.082 trillion (US$53.9 billion) (2022) |
|
| • Per capita | (US$14,185) (2022) | |
| Time zone | UTC-8 (PST) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-7 (PDT) | |
| Postal code |
21, 22
|
|
| Area code |
Area codes
|
|
| ISO 3166 code | MX-BCN | |
| HDI | ||
| a. 2010 and later. Baja California is the only state to use the U.S. DST schedule state-wide, while the rest of Mexico (except for small portions of other northern states) observes standard time year-round. b. The state's GDP was 294.8 billion pesos in 2008, an amount corresponding to 23.03 billion United States dollars, with US$1 valued at 12.80 pesos (value of 3 June 2010). | ||
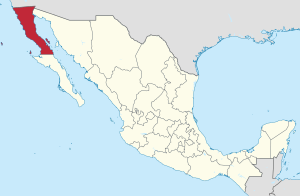
Baja California (which means 'Lower California') is a state in Mexico. It is officially called the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California. This state is the northernmost and westernmost part of Mexico. Before 1952, it was known as the North Territory of Baja California.
The state covers about 70,113 square kilometers (3.57% of Mexico's land). It forms the northern half of the Baja California Peninsula. This includes Guadalupe Island in the ocean. To the west, it borders the Pacific Ocean. To the east, it meets Sonora, the U.S. state of Arizona, and the Gulf of California. To the north, it borders the U.S. state of California. To the south, it borders Baja California Sur.
In 2020, about 3,769,020 people lived here. This is much more than the southern state of Baja California Sur. Most people (over 75%) live in Mexicali (the capital), Ensenada, or Tijuana (the largest city). Other important cities are San Felipe, Rosarito, and Tecate. Many people here are Mestizos, who are people of mixed European and Indigenous ancestry. Many have moved from other parts of Mexico. There are also people of Spanish, East Asian, Middle Eastern, and Indigenous backgrounds. Many immigrants from the United States live here because it's close to San Diego and less expensive. People also come from Central America for a better life and more jobs.
Baja California is the 12th largest state in Mexico by area. Its land changes a lot, from beaches to forests and deserts. The Sierra de Baja California mountains run through the state. Picacho del Diablo, the highest point on the peninsula, is in these mountains. These mountains divide the state's weather. The northwest has a semi-dry, Mediterranean climate. The middle part is more humid because of its height. Here, you can find valleys like the Valle de Guadalupe, which is Mexico's main wine-making area. East of the mountains, the Sonoran Desert takes over. In the south, the weather gets drier, leading to the Vizcaíno Desert. The state also has many islands off its coasts. Guadalupe Island is the westernmost point of Mexico.
Contents
Discovering Baja California's Past
Who Lived Here First?
The first people arrived in Baja California at least 11,000 years ago. Two main groups lived on the peninsula. The Cochimí lived in the south. Several groups speaking the Yuman language family lived in the north. These included the Kiliwa, Paipai, Kumeyaay, Cocopa, and Quechan.
These groups lived in different ways. The Cochimí in the Central Desert were hunter-gatherers who moved often. But the Cochimí on Cedros Island became skilled at living by the sea. The Kiliwa, Paipai, and Kumeyaay in the wetter northwest also hunted and gathered. This area had more people and a more settled lifestyle. The Cocopa and Quechan in northeastern Baja California grew crops near the lower Colorado River.
Another group, the Guachimis, came from the north. They created the famous Sierra de Guadalupe cave paintings. These paintings are now a UNESCO World Heritage site. We don't know much about them, but they lived there between 100 BC and 1300 AD.
When Europeans Arrived
Europeans first reached Baja California in 1539. Francisco de Ulloa explored its east coast and the west coast up to Cedros Island. Hernando de Alarcón explored the east coast and the lower Colorado River in 1540. Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo finished exploring the west coast in 1542. Sebastián Vizcaíno surveyed the west coast again in 1602. After that, few outsiders visited for a century.
The Jesuits started the first lasting mission colony in Loreto in 1697. Over time, they spread their influence throughout what is now Baja California Sur. From 1751 to 1753, Jesuit explorer Ferdinand Konščak explored northward into Baja California. Jesuit missions were then built for the Cochimí people. These included Santa Gertrudis (1752), San Borja (1762), and Santa María (1767).
After the expulsion of the Jesuits in 1768, the Franciscans took over for a short time (1768–1773). They built one new mission at San Fernando Velicatá. More importantly, an expedition in 1769 led by Gaspar de Portolà and Junípero Serra explored the northwestern part of the state. This expedition aimed to settle Alta California.
The Dominicans took over the missions from the Franciscans in 1773. They built new missions for the northern Cochimí and western Yumans. These missions stretched from El Rosario (1774) to Descanso (1817), just south of Tijuana.
In 1804, Spain divided California into Upper and Lower California. This line separated the Franciscan missions in the north from the Dominican missions in the south.
Baja California After Mexico's Independence
After Mexico became independent in 1821, some leaders wanted to reduce the power of the Roman Catholic Church. They ordered missions to become secular in 1833.
After the Mexican American War (1846–1848) and the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, the United States gained control of much land. Alta California became part of the U.S. and quickly became a state. Baja California kept control of areas like Tijuana, Mexicali, and Tecate.
In 1853, an American soldier named William Walker captured La Paz. He tried to declare himself president of the Republic of Baja California. But the Mexican government forced him to leave after a few months.
Modern Times in Baja California
When General Porfirio Díaz became president in 1876, he worked to develop and modernize Mexico.
- 1884: Luis Huller and George H. Sisson got permission to develop much of the state.
- 1905: The Magonista revolution, an anarchist movement, began.
- 1911: Mexicali and Tijuana were captured by the Mexican Liberal Party. They soon surrendered to government forces.
After the Mexican Revolution:
- 1931: Baja California was divided into Northern and Southern territories.
- 1952: The North Territory of Baja California became the 29th state of Mexico. It was named Baja California. The southern part remained a federal territory.
- 1974: The South Territory of Baja California became the 31st state, Baja California Sur.
- 1989: Ernesto Ruffo Appel became the first governor from an opposition party (PAN). This was the first time since the Mexican Revolution. Baja California became known as a strong area for the PAN party.
Exploring Baja California's Geography
Baja California has many different types of land, even though it's not a huge area. The Peninsular ranges of mountains run through the middle of the state. The most important ranges are the Sierra de Juárez and the Sierra de San Pedro Mártir. These mountains have forests that look like those in Southern California. Picacho del Diablo is the highest point on the peninsula.
Valleys between the mountains have a climate good for farming. These include the Valle de Guadalupe and the Valle de Ojos Negros. These areas grow citrus fruits and grapes. The mountains continue south to the Gulf of California. There, the land widens, forming the Llanos del Berrendo near the border with Baja California Sur. Other mountain ranges in the center and south include the Sierra de La Asamblea, Sierra de Calamajué, Sierra de San Luis, and the Sierra de San Borja.

Cool winds from the Pacific Ocean and the cold California Current make the climate along the northwestern coast nice all year. Because of the California Current, rain from the north doesn't reach the southern areas much, making them drier. South of the El Rosario River, the land changes from Mediterranean to desert. This desert has many types of succulent plants that grow well because of the coastal fog.
To the east, the Sonoran Desert stretches into the state from California and Sonora. Some of Mexico's highest temperatures are recorded near the Mexicali Valley. But with water from the Colorado River, this area has become a big farming center. The Cerro Prieto geothermal area is also near Mexicali. It produces about 80% of the state's electricity and even sends power to California. Laguna Salada, a salty lake below sea level, is also near Mexicali. The state government is thinking about bringing the lake back to life. The highest mountain in the Sierra de los Cucapah is Cerro del Centinela. The Cucapah are the main Indigenous people from these mountains.
Many islands are off the Pacific coast. Guadalupe Island is far to the west and has large groups of sea lions. Cedros Island is in the southwest. The Todos Santos islands and Coronado Islands are off the coasts of Ensenada and Tijuana. All the islands in the Gulf of California on the Baja California side belong to the Mexicali municipality.
Baja California gets much of its water from the Colorado River. In the past, the river flowed into the Colorado River Delta and then into the Gulf of California. But because of high demand for water in the American Southwest, less water reaches the Gulf now. The Tijuana metropolitan area also uses the Tijuana River for water. Much of rural Baja California relies on wells, a few dams, and even oases. Tijuana also buys water from San Diego County. Getting enough clean water is the state's biggest natural resource challenge.
Baja California's Climate Zones

Baja California's climate ranges from Mediterranean to arid (very dry). The Mediterranean climate is in the northwestern part of the state. Here, summers are dry and mild, and winters are cool and rainy. This climate is found from Tijuana to San Quintín and in nearby inland valleys. The cold California Current often creates a low fog near the coast. This fog can be seen along any part of the state's Pacific coast.
As you go higher into the Sierra de Baja California mountains, the climate becomes alpine. Summers are cool, and winters can be cold with temperatures below freezing at night. It often snows in the Sierra de Juárez, Sierra de San Pedro Mártir, and the valleys between them from December to April. Because of how the mountains are shaped, there is much more rain in the northern Baja California mountains than on the coast or in the eastern desert. Pine, cedar, and fir forests grow in these mountains.
The east side of the mountains creates a rain shadow, making the area very dry. The Sonoran Desert part of Baja California has hot summers and mild winters with almost no frost. The Mexicali Valley (which is below sea level) has the highest temperatures in Mexico. It often goes above 47°C (117°F) in mid-summer and can even go over 50°C (122°F) sometimes.
Further south along the Pacific coast, the Mediterranean climate changes into a desert climate. But it is milder and not as hot as the Gulf coast. These changing climates can be found from San Quintín to El Rosario. Further inland and along the Gulf of California, there are few plants, and temperatures are very high in summer. The islands in the Gulf of California also have a desert climate. Some oases (watered areas) can be found in the desert, where a few towns like Catavina, San Borja, and Santa Gertrudis are located.
Animals and Plants of Baja California
In the main wildlife areas, Constitution 1857 National Park and Sierra de San Pedro Mártir National Park, you can find several types of cone-bearing trees. The most common are Jeffrey pine, Pinus ponderosa, Pinus cembroides, Pinus quadrifolia, Pinus monophylla, Juniperus, Arctostaphylos pringlei, Artemisia ludoviciana, and Adenostoma sparsifolium. Baja California shares many plant species with the Laguna Mountains and San Jacinto Mountains in southwest California. The lower parts of the Sierra de Juárez have chaparral (dense shrubs) and desert shrub. Guadalupe Island and its waters, about 250 kilometers (155 miles) off the Pacific coast, are a protected area. This Guadalupe Island Biosphere Reserve helps save endangered marine and land animals and plants.
The animals in the parks include many mammals. These are mainly mule deer, bighorn sheep, cougars, bobcats, ringtail cats, coyotes, rabbits, squirrels, and over 30 types of bats. The park is also home to many birds. These include bald eagles, golden eagles, falcons, woodpeckers, black vultures, crows, and several types of Sittidae (nuthatches) and ducks.
Earthquakes in Baja California
The 2010 Easter Earthquake
On Easter Sunday, April 4, 2010, at 3:40:41 PM, a strong earthquake hit the Mexicali Valley. It had a magnitude of 7.2. Its center was about 26 kilometers (16 miles) southwest of Guadalupe Victoria, Baja California. People felt the main earthquake as far away as Los Angeles, Las Vegas, Phoenix, Tucson, and Yuma.
At least six smaller earthquakes (aftershocks) with magnitudes between 5.0 and 5.4 happened afterward. One was a 5.1-magnitude quake at 4:14 AM, centered near El Centro. By April 5, 2010, two people were confirmed to have died.
People and Communities in Baja California
|
Largest cities or towns in Baja California
Source: |
||
|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Pop. |
| 1 | Tijuana | 1,810,645 |
| 2 | Mexicali | 854,186 |
| 3 | Ensenada | 330,652 |
| 4 | Rosarito | 100,660 |
| 5 | Tecate | 81,059 |
| 6 | Villa del Campo | 33,360 |
| 7 | Maneadero | 27,969 |
| 8 | Guadalupe Victoria | 19,081 |
| 9 | Lázaro Cárdenas | 18,829 |
| 10 | San Felipe | 17,143 |
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1895 | 42,875 | — |
| 1900 | 7,583 | −82.3% |
| 1910 | 9,760 | +28.7% |
| 1921 | 23,537 | +141.2% |
| 1930 | 48,327 | +105.3% |
| 1940 | 78,907 | +63.3% |
| 1950 | 226,965 | +187.6% |
| 1960 | 520,165 | +129.2% |
| 1970 | 870,421 | +67.3% |
| 1980 | 1,177,886 | +35.3% |
| 1990 | 1,660,855 | +41.0% |
| 1995 | 2,112,140 | +27.2% |
| 2000 | 2,487,367 | +17.8% |
| 2005 | 2,844,469 | +14.4% |
| 2010 | 3,155,070 | +10.9% |
| 2015 | 3,315,766 | +5.1% |
| 2020 | 3,769,020 | +13.7% |
| 2015 data from Encuesta Intercensal 2015. | ||
| Religion in Baja California (2010 census) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roman Catholicism | 72.1% | |||
| Other Christian | 15.1% | |||
| Other religion | 0.1% | |||
| No religion | 10.0% | |||
| Unspecified | 2.7% | |||

Baja California has a mix of people. Many have European roots. It also has a history of people moving here from East and Southeast Asia. Mexicali has a large Chinese community. Many Filipinos also came to the state during the Spanish and American rule in the 19th and 20th centuries. Tijuana and Ensenada were important entry points for East Asians going into the U.S.
In 2020, about 1.71% of Baja California's population identified as Black, Afro-Mexican, or of African descent.
Since 1960, many people from southern Mexican states have moved here. They come to work in farming, especially in the Mexicali Valley, and in factories. Cities like Ensenada, Tijuana, and Mexicali grew because of these migrants. Many hoped to become U.S. citizens. These temporary residents waiting to enter the United States are sometimes called flotillas. This comes from the Spanish word flota, meaning 'fleet'.
There are also many immigrants from Central and South America. A large number of people from the United States and Canada live here too. About 200,000 Americans live in the state. They often choose coastal towns like Ensenada, known for affordable homes for retirees. San Felipe, Rosarito, and Tijuana also have many Americans. They like the cheaper housing and being close to San Diego.
About 60,000 people from Oaxaca live in Baja California. Some of them do not have proper birth certificates.
A study by Conacyt (Mexico's science and technology council) found that almost a million people in the state were considered "poor." This number was higher than in 2008. The study did not explain if these were local people or migrants.
Learning in Baja California
Baja California has one of the best education systems in Mexico. It ranks high in schooling and student success.
The state government offers education and training to improve job skills. For example, school-enterprise programs help train workers for what industries need.
About 91.60% of children aged six to fourteen go to elementary school. About 61.95% of people over fifteen have attended or graduated from high school. Public schools are available at all levels, from kindergarten to university.
The state has 32 universities. They offer 103 different professional degrees. These universities also have 19 research and development centers. They do research in areas like biotechnology, physics, oceanography, computer science, geothermal technology, astronomy, aerospace, electrical engineering, and clean energy. The number of advanced degrees, including PhD programs, is 121. The state has 53 graduate schools. Baja California wants to be good at new technology and science on its own. It wants to rely less on other countries. Businesses today need new ways to produce things and new technology for starting companies.
Baja California's Economy

In 2005, Baja California's economy made up 3.3% of Mexico's total economic output. This was about US$21.996 billion. The state's economy focuses a lot on manufacturing goods for export without tariffs (taxes). These factories are called maquiladoras. In 2005, 284,255 people worked in manufacturing. Over 900 companies operate under a special federal program in Baja California.
Jobs in Baja California
In 2021, Baja California created 57,550 new jobs. This is about 15.2 jobs for every 1000 people. This made it the 5th highest state in Mexico for new jobs. It was the second highest among border states, after Nuevo León. Most of these new jobs were in and around Tijuana, Mexicali, Ensenada, Playas de Rosarito, and Tecate. The industries that grew the most in 2021 included manufacturing, transport and communication, commerce, and construction.
As of November 2021, Baja California had the highest employment rate of any state in northern Mexico, at 96.7%.
Money Coming into the State
As of September 2021, Baja California receives the third highest amount of foreign direct investment (money from other countries) in Mexico. It gets about 7.7% of the national total. Only Nuevo León (7.7%) and Mexico City (16.5%) receive more. About 81.4% of this foreign money comes from the United States. Of that, 50.3% goes into building natural gas pipelines, and 8.2% goes into making cars and trucks.
Buying Land in Baja California
Mexico's Foreign Investment Law of 1973 allows people from other countries to buy land near the borders and coasts of Mexico. They do this through a special trust managed by a Mexican bank (called a Fideicomiso). This trust gives the buyer all the rights of ownership. The land can be sold, inherited, rented, or transferred at any time. Since 1994, the law says the Fideicomiso must be for a 50-year term. Buyers can ask for another 50-year renewal at any time.
Any Mexican citizen buying a property held in a bank trust can either keep it in the trust or take it out and get the title in their own name (called an escritura).
Mexico's early history included invasions and losing a lot of land. To prevent this from happening again, the Mexican constitution created a "Restricted Zone." In 1973, to attract more tourists and investment, the Fideicomiso bank trust was created. This allowed non-Mexicans to own land without changing the constitution. Since then, the law has been updated many times to make buying land in Mexico safer.
Major Roads
- Mexican Federal Highway 1
- Mexican Federal Highway 2
- Mexican Federal Highway 3
- Mexican Federal Highway 5
- Mexican Federal Highway 12
News and Media
Newspapers in Baja California include El Centinela, El informador de Baja California, El Mexicano (edición Tijuana), El Mexicano Segunda Edición, El Sol de Tijuana, El Vigía, Esto de las Californias, Frontera, La Crónica de Baja California, La Voz de la Frontera, and Semanario Zeta.
Images for kids
-
Crotalus cerastes (Sidewinder rattlesnake)
-
Eschscholzia californica (California poppy)
-
Washingtonia filifera (California fan palm)
-
Coreopsis gigantea (Giant coreopsis)
-
Pinus radiata (Monterey pine)
See also
 In Spanish: Baja California para niños
In Spanish: Baja California para niños
 | Victor J. Glover |
 | Yvonne Cagle |
 | Jeanette Epps |
 | Bernard A. Harris Jr. |