Tampa, Florida facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Tampa
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
University of Tampa
Raymond James Stadium
|
|||
|
|||
| Nicknames:
Cigar City, The Big Guava
|
|||
| Country | |||
| State | |||
| County | |||
| Settled (Fort Brooke) |
1823 | ||
| Incorporated (Village of Tampa) |
January 18, 1849 | ||
| Incorporated (Town of Tampa) |
September 10, 1853 and August 11, 1873 |
||
| Incorporated (City of Tampa) |
December 15, 1855 and July 15, 1887 |
||
| Government | |||
| • Type | Strong mayor–council | ||
| Area | |||
| • City | 175.83 sq mi (455.40 km2) | ||
| • Land | 114.02 sq mi (295.30 km2) | ||
| • Water | 61.82 sq mi (160.10 km2) 35.3% | ||
| • Urban | 968.9 sq mi (2,509.5 km2) | ||
| • Metro | 2,554 sq mi (6,610 km2) | ||
| Elevation | 48 ft (14.6 m) | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • City | 384,959 | ||
| • Estimate
(2023)
|
403,364 | ||
| • Rank | 49th in the US | ||
| • Density | 3,376.4/sq mi (1,303.6/km2) | ||
| • Urban | 2,783,045 (US: 17th) | ||
| • Urban density | 2,872.3/sq mi (1,109.0/km2) | ||
| • Metro | 3,175,275 (US: 18th) | ||
| Demonym(s) | Tampan, Tampanian, Tampeño | ||
| GDP | |||
| • Metro | $219.414 billion (2022) | ||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | ||
| ZIP codes |
33601–33626, 33629–33631, 33633–33635, 33637, 33646, 33647, 33650, 33655, 33660–33664, 33672–33675, 33677, 33679–33682, 33684–33689, 33694
|
||
| Area code(s) | 813, 656 | ||
| FIPS code | 12-71000 | ||
| GNIS feature ID | 0292005 | ||
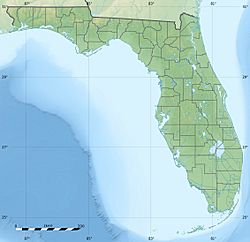
Tampa is a big city on the Gulf Coast of Florida. It sits on the north shore of Tampa Bay. Tampa is the largest city in the Tampa Bay area. It is also the main city of Hillsborough County. In 2023, about 403,364 people lived in Tampa. This makes it the 49th largest city in the U.S. and the third largest in Florida.
Tampa started as a military base called Fort Brooke in the 1800s. The cigar industry grew here thanks to Vincente Martinez Ybor. The area where his factories were is now called Ybor City. Tampa's economy today relies on tourism, healthcare, money, and shipping. The port is the biggest in Florida. It helps the state's economy by over $15 billion.
Tampa is part of a larger area called the Tampa-St. Petersburg-Clearwater, Florida Metropolitan Statistical Area. About 3.1 million people live in this four-county area. It is the second-largest metro area in Florida.
Contents
- What Does the Name "Tampa" Mean?
- Tampa's History: A Journey Through Time
- Tampa's Geography and Climate
- People of Tampa
- Economy: How Tampa Makes Money
- Arts and Culture: Fun Things to Do in Tampa
- Sports: Tampa's Teams and Championships
- Education: Schools and Libraries
- Media: News, TV, and Radio
- Infrastructure: Getting Around and Staying Healthy
- Sister Cities
- See also
What Does the Name "Tampa" Mean?
When the town near the U.S. Army base Fort Brooke became a village in 1849, it was called "Tampa Town." The name was shortened to "Tampa" in 1855. The name "Tampa" might come from the Calusa or Timucua language. Some think it relates to "itimpi" in the Creek language, meaning "close to." But its exact meaning is not known.
People from Tampa are often called "Tampans" or "Tampeños." "Tampeños" is often used for descendants of Cuban, Italian, and Spanish immigrants. These groups came in the late 1800s to work in the cigar factories.
Tampa's History: A Journey Through Time
Early People and European Visitors
The shores of Tampa Bay have been home to people for thousands of years. About 2,000 years ago, people from the Weeden Island culture lived here. They mostly got their food from the sea. When Europeans arrived in the 1500s, the Safety Harbor culture was in charge.
Spanish explorers like Pánfilo de Narváez and Hernando de Soto landed near Tampa. But they did not stay long. Florida had no gold or silver. The native people fought back against Spanish settlements. Many native people died from diseases brought by the Europeans. By 1600, the local cultures had mostly disappeared.
The Seminole people moved into northern Florida in the mid-1700s. They came to central Florida after the U.S. took control in 1821. Before the U.S. arrived, some Cuban and Native American fishermen had small camps here.
How the U.S. Took Control
After buying Florida from Spain in 1821, the U.S. built forts. Fort Brooke was built in 1824 in Downtown Tampa. Tampa was a lonely place at first. Most people left during the Second Seminole War (1835-1842). After the war, many settlers returned.
Florida became the 27th state on March 3, 1845. On January 18, 1849, Tampa became the "Village of Tampa." It had 185 civilians. By 1855, it was called the "Town of Tampa."
Tampa During the Civil War
During the Civil War, Florida joined the Confederate States of America. Confederate soldiers defended Fort Brooke. The city government stopped working during the war.
The Union Navy blocked southern ports. This stopped trade for the Confederacy. Small ships sometimes got past the blockade. They delivered cattle to Cuba for gold. In 1862, a Union ship fired on Fort Brooke. This was called the Battle of Tampa. It caused little damage. In 1863, Union forces destroyed two blockade-running ships. This hurt Tampa's economy.
In 1864, Union troops took Fort Brooke. They destroyed much of the fort. They threw cannons into the Hillsborough River. The Civil War ended in 1865. Federal troops then occupied Tampa until 1869.
After the war, Tampa was a poor fishing village. It had about 1,000 people. Yellow fever outbreaks also made people leave. In 1869, residents voted to end the city government. By 1880, only about 700 people lived in Tampa. Fort Brooke closed in 1883. This opened up the waterfront for new buildings.
Tampa's Economic Boom in the 1880s
In the mid-1880s, Tampa's luck changed. First, phosphate was found in 1883. This mineral is used for fertilizers. Tampa still ships a lot of phosphate today.
The discovery of phosphate, the new railroad, and the founding of Ybor City changed Tampa. The small village became a busy city very quickly. By 1900, it was one of Florida's largest cities.
Plant's Railroad Arrives
Henry B. Plant's railroad reached Tampa in 1883. This connected Tampa to the rest of the country. Before this, roads were sandy and hard to use. The railroad made it easy to move goods. Phosphate and fish could go north. New products came into Tampa. The first tourists also arrived.
Ybor's Cigar Factories

The new railroad helped another industry come to Tampa. In 1885, Vicente Martinez Ybor moved his cigar factories here. It was easy to get tobacco from Cuba by sea. Plant's railroad helped ship finished cigars by land.
Tampa was small, so Ybor built homes for workers. Many Cuban and Spanish cigar workers moved in. Ybor City's factories started making cigars in 1886. Many other cigar makers came to Tampa. Italian and Jewish immigrants also arrived. They opened businesses for the workers. By 1900, over 10,000 immigrants lived in Ybor City. More Cuban immigrants built West Tampa, another cigar area. Tampa became the "Cigar Capital of the World."
Early 1900s: Cigar Capital
In the early 1900s, cigar making was key to Tampa's economy. Factories in Ybor City and West Tampa made huge numbers of cigars. In 1929, they made over 500 million cigars by hand.
In 1904, a group of businessmen started Ye Mystic Krewe of Gasparilla. They staged a fake pirate "invasion" of the city. This led to a parade. The Gasparilla Pirate Festival has been held almost every year since.
Mid to Late 1900s: Growth and Change

Tampa grew a lot because of World War II. Before the U.S. joined the war, MacDill Field was built. It was a main base for the United States Army Air Corps. After the war, MacDill stayed open. Other airfields became Tampa International Airport and St. Pete–Clearwater International Airport.
In the 1950s and 1960s, Tampa's population grew very fast. New highways and bridges were built. This brought more people and tourists to the city. During this time, Busch Gardens and Lowry Park were developed. These became popular tourist spots.
The University of South Florida opened in 1960. This led to new homes and businesses nearby. Tampa kept growing away from the city center. New hospitals, schools, and neighborhoods appeared.
In 1988, Tampa added a large rural area. This area became New Tampa.
Tampa's Geography and Climate
What Does Tampa Look Like?
Tampa has a total area of about 175.83 square miles. About 35.3% of this is water. The highest point in the city is only 48 feet above sea level. Tampa is next to Old Tampa Bay and Hillsborough Bay. These two bays form Tampa Bay, which flows into the Gulf of Mexico.
The Hillsborough River flows into Hillsborough Bay. It passes through Downtown Tampa. This river is Tampa's main source of fresh water. The Palm River flows into McKay Bay. Tampa's geography is shaped by the Interbay Peninsula. This land divides Hillsborough Bay from Old Tampa Bay.
Tampa's Weather: Hot Summers, Mild Winters
Tampa has a humid subtropical climate. This means it has hot, humid summers with many thunderstorms. Winters are usually dry and mild. High temperatures are usually between 71 and 91 degrees Fahrenheit. Lows are between 53 and 77 degrees Fahrenheit.
Tampa is in a warm plant zone. This means plants like coconut palms can grow here. However, a plant disease called Texas phoenix palm decline is hurting palm trees.
Tropical Storms and Hurricanes
Tampa is often threatened by tropical storms. But it rarely gets hit directly by major hurricanes. No hurricane has hit the immediate Tampa Bay area since 1921. That storm caused a lot of damage.
Four major hurricanes were expected to hit Tampa Bay in recent decades. These were Hurricane Donna (1960), Hurricane Charley (2004), Hurricane Irma (2017), and Hurricane Ian (2022). But all of them turned away. They hit other parts of Florida instead. Irma had the biggest effect on Tampa. It caused widespread power outages for days.
Because many people live and build near the coast, Tampa Bay is very vulnerable. A direct hit from a major storm could cause huge damage.
Seasonal Weather Patterns
Summer Weather
Summer weather lasts from late May to early October. This is the rainy season. Days are usually hot and humid. Highs are around 91 degrees Fahrenheit. Lows are in the mid-70s Fahrenheit. Rain often falls in the afternoon. The highest temperature ever recorded in Tampa is 99 degrees Fahrenheit.
Afternoon thunderstorms are common. They are caused by sea breezes from the Gulf and Atlantic. The Tampa Bay area is known as the "Lightning Capital of North America." These storms can bring heavy rain, lightning, and strong winds.
Autumn Weather
Temperatures start to drop in September. Rainfall also decreases. November is usually Tampa's driest month. But tropical storms can bring a lot of rain in the fall.
Winter Weather
Winter is generally dry and cooler. Highs are in the low to mid-70s Fahrenheit. Lows are in the low to mid-50s Fahrenheit. Cold fronts sometimes bring cooler weather. Temperatures can drop to the 50s Fahrenheit during the day. Nighttime lows can be near 40 degrees Fahrenheit.
Frosts happen sometimes. Hard freezes (28 degrees Fahrenheit or below for hours) are rare. The last widespread freeze was in January 2018. The lowest temperature ever recorded was 18 degrees Fahrenheit in 1962. The only time snow was officially recorded was in January 1977.
Spring Weather
Temperatures slowly rise starting in mid-February. Spring brings warm and sunny weather. It is usually dry until June. This means there is a risk of brush fires. Sometimes, a late cold front brings a short period of bad weather.
People of Tampa
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1850 | 974 | — | |
| 1870 | 796 | — | |
| 1880 | 720 | −9.5% | |
| 1890 | 5,532 | 668.3% | |
| 1900 | 15,839 | 186.3% | |
| 1910 | 37,782 | 138.5% | |
| 1920 | 51,608 | 36.6% | |
| 1930 | 101,161 | 96.0% | |
| 1940 | 108,391 | 7.1% | |
| 1950 | 124,681 | 15.0% | |
| 1960 | 274,970 | 120.5% | |
| 1970 | 277,714 | 1.0% | |
| 1980 | 271,523 | −2.2% | |
| 1990 | 280,015 | 3.1% | |
| 2000 | 303,447 | 8.4% | |
| 2010 | 335,709 | 10.6% | |
| 2020 | 384,959 | 14.7% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 403,364 | 20.2% | |
| source: | |||
Tampa first appeared in the 1850 U.S. Census. It had 974 people, including soldiers.
Tampa's Population in 2020
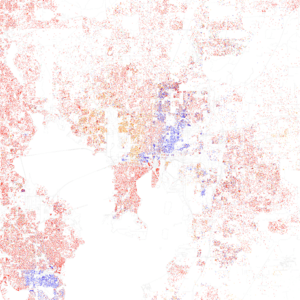
In 2020, Tampa had 384,959 people. There were 156,705 households.
The U.S. Census counts race in different ways. One way includes Hispanic people in racial groups. Another way lists Hispanic people separately.
In 2020, including Hispanic people in racial counts:
- 49.70% were White.
- 21.91% were Black.
- 0.41% were Native American.
- 5.43% were Asian.
- 0.08% were Pacific Islander.
- 7.63% were of another race.
- 14.85% were of two or more races.
When Hispanic people are counted separately:
- 43.32% were White (not Hispanic).
- 20.93% were Black (not Hispanic).
- 0.19% were Native American (not Hispanic).
- 5.35% were Asian (not Hispanic).
- 0.06% were Pacific Islander (not Hispanic).
- 0.71% were of another race (not Hispanic).
- 3.81% were of two or more races (not Hispanic).
- 25.62% were Hispanic or Latino.
Economy: How Tampa Makes Money
Tampa's economy is strong in many areas. These include money and banking, shopping, healthcare, insurance, and shipping. National defense, sports, tourism, and real estate are also very important. Hillsborough County has about 740,000 workers. This number is expected to grow.
Since 2000, Tampa has seen more demand from shoppers. This shows that more wealth is in the area. In 2021, the U.S. Department of Labor gave a grant to help train people for manufacturing jobs. This program helps address a shortage of skilled workers.
Big Companies and Nonprofits in Tampa
Many large companies have offices in Tampa. The biggest credit union in Florida, Suncoast Credit Union, is based here.
Several large companies are headquartered in the Tampa area. These include Bloomin' Brands, WellCare, Jabil, TECO Energy, and Raymond James Financial. Other companies based in Tampa are Odyssey Marine Exploration, Greenway Health, and The Mosaic Company.
| Employer | Employees | Industry |
|---|---|---|
| BayCare Health System | 19,600 | Healthcare |
| Publix Super Market | 13,800 | Retail |
| HCA West Florida | 13,150 | Healthcare |
| Frontier Communications | 9,950 | Telecommunications |
| Tampa General Hospital | 6,600 | Healthcare |
| Wal-Mart | 5,800 | Retail |
| Florida Hospital | 5,100 | Healthcare |
| JPMorgan Chase & Co. | 5,000 | Finance |
| Moffitt Cancer Center | 4,300 | Healthcare |
| Citi | 4,000 | Finance |
Downtown Tampa's Growth
Downtown Tampa is growing a lot. Many new homes, hotels, and mixed-use buildings are being built. This is making downtown a place where people live and work all day. In 2014, Tampa was named the second-best city for real estate investment.
Port Tampa Bay: A Busy Harbor
Port Tampa Bay is the seventh largest port in the U.S. It is Florida's biggest port by weight of goods. It handles almost half of all goods shipped by sea in the state. The port is very important for the economy.
Tampa is also second in Florida for cruise ship travel, after Miami. Several cruise lines use Tampa as a port.
MacDill Air Force Base: A Major Employer
MacDill Air Force Base is a big employer. Over 15,000 military and civilian staff work there. Many retired military personnel work there too.
MacDill is home to important military commands. These include United States Central Command (USCENTCOM) and United States Special Operations Command (USSOCOM).
Arts and Culture: Fun Things to Do in Tampa
Arts and Entertainment
Tampa has many places for stage shows and performances. These include the David A. Straz Jr. Center for the Performing Arts and Tampa Theatre.
Many performing arts groups are based in Tampa. These include the Florida Orchestra and Opera Tampa.
Tampa is also a hub for professional wrestling. Many wrestlers live and train here. The city is also known for death metal music. Many famous bands from this music style are from Tampa. The rock band Underoath is also based here.
Museums: Learning About Tampa
The Tampa area has many museums. They cover different topics.
- Museum of Science & Industry (MOSI) has science exhibits. It has Florida's only domed IMAX theater.
- Tampa Museum of Art shows art.
- Tampa Bay History Center teaches about the area's history.
- Henry B. Plant Museum is in the old Tampa Bay Hotel.
- Ybor City Museum State Park tells the story of Ybor City.
- The SS American Victory is a World War II ship. It is now a museum ship in the Channel District.
- Florida Museum of Photographic Arts shows local and international photos.
Glazer Children's Museum
The Children's Museum of Tampa opened in 1986. It was made for young children to learn and explore. In 2010, it moved to a bigger place downtown. It was renamed Glazer Children's Museum.
Food: What to Eat in Tampa
Tampa has many kinds of food. You can find small cafes, bakeries, and fancy restaurants. Tampa's food has influences from Cuban, Spanish, Italian, and Floribbean styles. There are also Colombian, Puerto Rican, and Vietnamese restaurants. Seafood is very popular. Greek food is also common, especially near Tarpon Springs.
Food trucks are popular. Tampa holds the record for the world's largest food truck rally. Seminole Heights and South Tampa are known for their restaurants.
Tampa is where the Florida version of the deviled crab was created. It is also the birthplace of the Cuban sandwich. The city council officially named the Cuban sandwich the "signature sandwich of the city of Tampa." A Tampa Cuban sandwich is special because it includes Genoa salami. This is likely due to Italian immigrants in Ybor City.
Many restaurant chains started in Tampa. These include Outback Steakhouse, The Melting Pot, and Checkers and Rally's.
Tourism and Recreation: Fun for Everyone


Tampa has over 165 parks and beaches. Hillsborough County maintains 42 more parks nearby. These include Hillsborough River State Park. Tampa has many attractions and theme parks.
- Busch Gardens Tampa Bay is a 335-acre Africa-themed park. It has many thrilling roller coasters. You can also see African wildlife.
- Adventure Island is a water park next to Busch Gardens.
- ZooTampa at Lowry Park has over 2,000 animals. It offers interactive exhibits and shows.
- The Florida Aquarium is a 250,000 square foot aquarium. It has over 20,000 types of aquatic plants and animals. It is known for its glass design.
- Big Cat Rescue is a sanctuary for abused and abandoned big cats. It cares for about 80 lions, tigers, and other species.
Popular shopping areas include International Plaza and Bay Street and Hyde Park Village.
The Port of Tampa has three cruise ship terminals. Cruise ships sail from Tampa to the Western Caribbean islands, Honduras, Belize, and Mexico.
Events: Festivals and Fun Times
The most famous event is the Gasparilla Pirate Festival. It is a fake pirate invasion held every year in late January or early February. It is like Tampa's "Mardi Gras." The pirate ship Jose Gasparilla leads a parade. Over 400,000 people attend. This event brings millions of dollars to the city. Many other Gasparilla events happen from January to March. These include the Children's Parade and the Gasparilla Festival of the Arts. The Gasparilla parade is the third largest in the U.S.

Other big events include the Outback Bowl football game. It is held on New Year's Day. The Florida State Fair brings crowds each February. "Fiesta Day" celebrates Tampa's immigrant heritage. Guavaween is a Halloween street party in Ybor City.
Downtown Tampa hosts Metrocon, Florida's largest anime convention. Ybor City also hosts "GaYbor Days," an annual street party. The Tampa International Gay and Lesbian Film Festival is one of the largest gay film festivals in the country.
Tampa hosted the 2012 Republican National Convention. It also hosted the 15th International Indian Film Academy Awards in 2014.
Since 2015, Tampa has hosted the annual Tampa Riverfest. It is held along the Tampa Riverwalk. It features music and local food. In March 2024, Tampa hosted its first International Book Fair.
Sports: Tampa's Teams and Championships
| Team | League | Stadium | First season | Championships |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tampa Bay Buccaneers | National Football League (NFL) | Raymond James Stadium | 1976 | 2 (XXXVII, LV) |
| Tampa Bay Lightning | National Hockey League (NHL) | Amalie Arena | 1992 | 3 (2004, 2020, 2021) |
| Tampa Bay Rays | Major League Baseball (MLB) | George M. Steinbrenner Field | 1998 | 0 |
| Tampa Bay Rowdies | United Soccer League (USL) | Al Lang Stadium (St. Petersburg) | 1975 (original club), 2010 (current club) | 3 (1975, 2012, 2020*) |
| Tampa Bay Titans | The Basketball League (TBL) | Pasco–Hernando State College | 2019 | 0 |
| Tampa Bay Sun | USL Super League | Riverfront Stadium | 2024–25 | 0 |
*Co-champions, championship game canceled due to COVID-19 pandemic.
Tampa has teams in three major professional sports leagues. These are the National Football League (NFL), the National Hockey League (NHL), and Major League Baseball (MLB). The NFL's Tampa Bay Buccaneers and the NHL's Tampa Bay Lightning play in Tampa. The Tampa Bay Rays of the MLB play in St. Petersburg. These teams represent the whole Tampa metropolitan area. Tampa Bay teams have won eight championships.
The Tampa Bay area also hosts Major League Baseball spring training. The New York Yankees train in Tampa. Their minor league team, the Tampa Tarpons, also plays here.
At the college level, the University of South Florida Bulls play in NCAA Division I. The University of Tampa Spartans play in NCAA Division II.
Between 2020 and 2021, all three of Tampa Bay's major teams and the Tampa Bay Rowdies made it to their sport's championship. The Lightning won the Stanley Cup twice. The Buccaneers won the Super Bowl. The Rays made it to the World Series. This led to the area being called "Champa Bay."
Football Teams in Tampa
Tampa Bay Buccaneers
The Tampa Bay Buccaneers joined the NFL in 1976. They had a tough start, losing their first 26 games. After some success in the late 1970s, they struggled again. In 2003, they won their first Super Bowl. They won their second Super Bowl in 2021. They were the first NFL team to win a Super Bowl in their home stadium.
Tampa Bay Storm
The Tampa Bay Storm was an Arena Football League (AFL) team. They moved to Tampa in 1991. They won five ArenaBowl championships. This was the most in league history. The team stopped playing after the 2017 season.
Tampa Bay Bandits
Tampa was also home to the Tampa Bay Bandits of the United States Football League. They made the playoffs twice. They had many fans. But the league folded in 1985.
Tampa Bay Vipers
The Tampa Bay Vipers played in the XFL. Their first season was cut short due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The team later moved to Las Vegas.
Tampa Bay Tornadoes
The Tampa Bay Tornadoes started in 2020. They play in the American Arena League.
Baseball in Tampa Bay
Baseball History
The Tampa Bay area has a long history with baseball. It has hosted spring training and minor league teams for over 100 years. Tampa was the first Florida city to host a major league team for spring training in 1913. The Tampa Smokers were the city's first minor league team in 1919.
Tampa Bay Rays
After many years, the Tampa Bay area finally got a Major League Baseball team in 1998. The Tampa Bay Devil Rays started playing in St. Petersburg. In 2008, they shortened their name to just Rays. They then won the American League Pennant. They also won division titles in 2008 and 2010.
The Rays have been looking for a new stadium closer to Tampa. But it has been hard to find a location and money for it. So, they still play in St. Petersburg.
In 2020, the Rays won their division again. They made it to the World Series but lost to the Los Angeles Dodgers.
Minor League Baseball
Several Major League teams have Spring Training in the area. Most also have minor league teams here. The New York Yankees and their minor league team, the Tampa Tarpons, use George M. Steinbrenner Field.
Other minor league teams in the area include the Clearwater Threshers and Dunedin Blue Jays. These teams play in Pinellas County.
Hockey: The Tampa Bay Lightning

The NHL's Tampa Bay Lightning started in 1992. They play their home games at Amalie Arena in downtown Tampa. In 2004, they won their first Stanley Cup. They won two more Stanley Cups in 2020 and 2021.
Tampa hosted the NHL All-Star Game in 2018.
Soccer in Tampa Bay
Tampa Bay Rowdies
The Tampa Bay Rowdies play in the United Soccer League Championship. They started playing in Tampa in 2010. They won their first championship in 2012. In 2020, they made it to the USL Championship Final. The game was canceled due to COVID-19. The Rowdies and the other team were named co-champions.
Tampa also had an earlier team called the Tampa Bay Rowdies. They were the area's first major sports team. They won a championship in 1975.
Tampa Bay Mutiny
Major League Soccer (MLS) started a team in Tampa in 1996. The Tampa Bay Mutiny had early success. But the team folded in 2001. This was because they could not get local owners.
Tampa Bay Sun
Tampa Bay Sun FC was founded in 2023. They are a new women's soccer team. They will play at Riverfront Stadium.
Basketball in Tampa Bay
The Tampa Bay area does not have a professional basketball team. The Orlando Magic are the closest NBA team.
The Tampa Bay Titans played in a minor league from 2019 to 2022. Their games were at Pasco–Hernando State College.
Amalie Arena was home to the NBA's Toronto Raptors for the 2020–2021 season. This was because of Canadian rules during the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada. It was the first time an NBA team played home games in Tampa.
College Sports in Tampa
University of South Florida Bulls
The University of South Florida (USF) has the only NCAA Division I sports program in Tampa. USF started playing sports in 1965. The Bulls have a football team and a basketball team. They have 17 teams in total. USF has won six national championships in softball, swimming, and sailing.
University of Tampa Spartans
The University of Tampa Spartans play in NCAA Division II. They have 20 sports teams. They have won 19 national championships, including eight in baseball.
Hillsborough Community College Hawks
The Hillsborough Community College Hawks are a junior college team. They play in NJCAA Division I.
Major Sports Events Hosted in Tampa Bay
Tampa Bay has hosted many big sports events:
- Super Bowls XVIII, XXV, XXXV, XLIII, and LV
- 2004 Stanley Cup Finals, 2015 Stanley Cup Finals, and 2021 Stanley Cup Finals games
- 2008 World Series games
- 2017 College Football Playoff National Championship Game
- NCAA Division I Men's and Women's Basketball Final Fours
- NCAA Division I Men's Soccer Championship games
- NCAA Division I Men's Hockey Frozen Fours
Education: Schools and Libraries

Primary and Secondary Schools
Public schools in Tampa are run by Hillsborough County Public Schools. This is the eighth-largest school district in the U.S. It has about 189,469 students. The district runs 208 schools. These include elementary, middle, and high schools. Many high schools in the district are on Newsweek's list of America's Best High Schools.
Public Libraries
Tampa's libraries are part of the Tampa-Hillsborough County Public Library System. This system has 25 libraries in Tampa and Hillsborough County. The main library is the John F. Germany Public Library downtown. Tampa's first library opened in the early 1900s. It was built with money from Andrew Carnegie. The libraries are part of a larger network. This network includes libraries in Temple Terrace and Plant City.
Colleges and Universities
Tampa has several colleges and universities.
The main campus of the University of South Florida (USF) is here. It is a large public university. USF is known for its research. It is one of Florida's top research universities. In 2021, USF had over 51,000 students.
The University of Tampa (UT) is a private university. It was founded in 1931. In 1933, it moved into the old Tampa Bay Hotel. UT has grown a lot. In 2018, it had over 9,000 students.
Hillsborough Community College is a two-year college. It has campuses in Tampa. Southern Technical College is a private two-year college in Tampa.
The Stetson University College of Law has a campus in downtown Tampa.
Media: News, TV, and Radio
The main newspaper in Tampa is the Tampa Bay Times. It bought its old rival, The Tampa Tribune, in 2016. Other local newspapers and magazines include the Florida Sentinel Bulletin and Creative Loafing. La Gaceta is special because it is the only newspaper in the U.S. printed in three languages: English, Spanish, and Italian. This is because of its history in Ybor City.
Major TV stations in Tampa include WFLA-TV (NBC), WTSP (CBS), and WTVT (Fox). The area also has many FM and AM radio stations. WDAE was Florida's first radio station. It started in 1922.
Infrastructure: Getting Around and Staying Healthy
Transportation: Roads, Airports, and Trains
Three bridges connect Tampa to Pinellas County. These are the Howard Frankland Bridge, the Courtney Campbell Causeway, and the Gandy Bridge. Part of the old Gandy Bridge was saved for walking and biking. It was called The Friendship Trail.

Tampa has several freeways. The Lee Roy Selmon Expressway (SR 618) runs from Brandon to South Tampa. The Veterans Expressway (SR 589) connects Tampa International Airport to the northwest suburbs.
Three interstate highways cross Tampa. Interstate 4 and Interstate 275 meet near downtown. Interstate 75 runs along the east side of town.
Major surface roads include Hillsborough Avenue, Dale Mabry Highway, and Kennedy Boulevard.
Airports
Tampa is served by three airports:
- Tampa International Airport (TPA) is the main airport. It is known for being a favorite among travelers.
- St. Pete–Clearwater International Airport (PIE) is across the bay. It is popular for low-cost airlines. It is also home to a large U.S. Coast Guard air station.
- Sarasota–Bradenton International Airport (SRQ) is in nearby Sarasota.
Rail Travel

Tampa's train service is at Tampa Union Station. This historic station is near downtown. Amtrak's Silver Star train stops here twice a day. It goes south to Miami and north to New York City. Union Station also connects to bus services for other cities.
Uceta Rail Yard handles freight trains for CSX. The city's seaports also have rail facilities for cargo.
Seaports
Port Tampa Bay is Florida's largest port by tonnage. It is one of the busiest commercial ports in North America. Petroleum and phosphate are the main goods shipped. The port also has a Foreign Trade Zone. This helps companies with importing and exporting.
The bay bottom is sandy. The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers constantly digs out the ship channels. This keeps them deep enough for large cargo ships.
Mass Transit
From the early 1900s to the late 1940s, Tampa had a large streetcar system. It carried millions of passengers. The system had at least 13 lines. It ran from early morning until midnight. It was shut down after World War II. Most of the tracks were removed.
Public transportation in Tampa is run by Hillsborough Area Regional Transit Authority (HART). It includes buses and a streetcar line. The HART bus system's main hub is the Marion Transit Center downtown. HART also has a rapid-transit bus system called MetroRapid.
The TECO Line Streetcar offers electric streetcar service. It connects Ybor City, the Channel District, the Tampa Convention Center, and downtown Tampa. The streetcars look like old ones from the past.
Water taxis are available for tours along the downtown waterfront. The Cross-Bay ferry goes from downtown Tampa to St. Pete.
The Tampa Bay Area Regional Transportation Authority (TBARTA) plans future transportation options. These include buses and light rail.
Healthcare: Hospitals and Research
Tampa has over 20 hospitals. It has four trauma centers. There are also many cancer treatment centers. Tampa is home to health research places. Major hospitals include Tampa General Hospital and H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center & Research Institute. Shriners Hospitals for Children is based in Tampa. USF's Byrd Alzheimer's Institute is a research and patient care center.
Utilities: Water and Power
Water in the area is managed by the Southwest Florida Water Management District. The main water source is the Hillsborough River. Power is mostly generated by TECO Energy.
Sustainability Efforts
Tampa was given a Gold Certification for its commitment to sustainability in 2021. The city government offers programs to promote sustainability. These include faster building permits for green projects. They also work to save water and plan for climate change.
Water Street Tampa was the first neighborhood in the world to get a special WELL Design and Operations award. In 2022, Water Street Tampa also got a LEED silver certification. This made it the first neighborhood in Tampa to get this award.
Sister Cities
Tampa has official sister city agreements with these cities:
 Agrigento, Italy (1991)
Agrigento, Italy (1991) Ashdod, Israel (2005)
Ashdod, Israel (2005) Barranquilla, Colombia (2012)
Barranquilla, Colombia (2012) Boca del Río, Mexico (2002)
Boca del Río, Mexico (2002) Le Havre, France (1993)
Le Havre, France (1993) Heraklion, Greece (2019)
Heraklion, Greece (2019) İzmir, Turkey (1993)
İzmir, Turkey (1993) Lanzhou, China (2016)
Lanzhou, China (2016) Oviedo, Spain (1992)
Oviedo, Spain (1992) Porto Alegre, Brazil (2013)
Porto Alegre, Brazil (2013) South Dublin County, Ireland (2015)
South Dublin County, Ireland (2015) Veracruz, Mexico (2002)
Veracruz, Mexico (2002)
See also
 In Spanish: Tampa para niños
In Spanish: Tampa para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |