Lanzhou facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Lanzhou
兰州市
|
|
|---|---|
|
Prefecture-level city
|
|
|
From top, left to right: Lanzhou skyline, Xiguan Mosque, Chanyuan Temple, Lanzhou city from Five Springs Park, Lanzhou beef noodles, Yellow River Mother sculpture
|
|
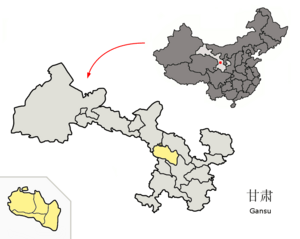
Location of Lanzhou City jurisdiction in Gansu
|
|
| Country | China |
| Province | Gansu |
| County-level divisions | 8 |
| Municipal seat | Chengguan District |
| Government | |
| • Type | Prefecture-level city |
| • Body | Lanzhou Municipal People's Congress |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 13,086.9 km2 (5,052.9 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 2,432.9 km2 (939.3 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,112.9 km2 (429.7 sq mi) |
| Population
(2020 census)
|
|
| • Prefecture-level city | 4,359,446 |
| • Density | 333.1153/km2 (862.765/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 3,474,858 |
| • Urban density | 1,428.278/km2 (3,699.22/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 3,042,863 |
| • Metro density | 2,734.17/km2 (7,081.5/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Prefecture-level city | CN¥ 209.6 billion US$ 33.7 billion |
| • Per capita | CN¥ 56,972 US$ 9,147 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code |
730000
|
| Area code(s) | 931 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-GS-01 |
| License plate prefixes | 甘A |
|
Rugosa Rose |
|
| Lanzhou | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

"Lanzhou" in Simplified (top) and Traditional (bottom) Chinese characters
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 兰州 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 蘭州 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal | Lanchow | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "Orchid [Hills] Prefecture" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lanzhou is a big city and the capital of Gansu province in northwestern China. It sits right by the Yellow River. This city is super important for travel, connecting western China by train to the eastern parts. For a long time, Lanzhou was a key stop on the ancient Northern Silk Road. It is also a major center for factories and making chemicals from oil.
Lanzhou is the third largest city in Northwest China. It's also an important place for science and learning, especially after Xi'an. Many research places are here, like Lanzhou University, which is one of China's top universities.
Contents
History of Lanzhou
Lanzhou was first part of the land of the ancient Western Qiang people. Then, in the 6th century BC, it became part of the Qin State.
Around 81 BC, during the Han dynasty, the city was taken from the Huns. It became known as Jincheng (Golden City). For thousands of years, it was a major stop on the ancient Northern Silk Road. It was also an important place to cross the Yellow River. To keep the city safe, the Great Wall of China was even extended to reach Yumen. You can still see parts of the Great Wall in the city today.
After the Han dynasty ended, Lanzhou became the capital for different groups. In the 4th century, it was the capital of the independent state of Liang for a short time. From the 5th to the 11th century, the Gansu province area became a big center for Buddhist studies. Under the Sui dynasty, the city was first called Lanzhou. It kept this name during the Tang dynasty.
In 763, the Tibetan Empire took over the area. But the Tang dynasty won it back in 843. Later, it was controlled by the Western Xia dynasty and then by the Song dynasty in 1081. The name Lanzhou was used again.
After 1127, the Jin dynasty took control. Then, after 1235, the Mongol Empire ruled it.
During the Ming dynasty, Lanzhou became a county. But in 1477, it was made a political unit again.
The city got its current name in 1656, during the Qing dynasty. When Gansu became its own province in 1666, Lanzhou was made its capital.
In the 1920s and 1930s, Lanzhou became a center for Soviet influence in northwestern China.
Lanzhou During World War II

During the Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945), Lanzhou was a key stop. It was connected to Xi'an by a highway built in 1935. This highway was used to bring supplies from the Soviet Union to China. It was the main road for traffic in northwestern China for many years.
Lanzhou's old airport was a main entry point for warplanes sent to China. The city and its civilian areas were heavily bombed by Japanese air forces. Many air battles happened over Lanzhou from 1937 to 1945. Chinese and Soviet pilots fought bravely against the Japanese planes. For example, in February 1939, Chinese and Soviet pilots shot down many Japanese bombers.
In 1941, Japanese forces were preparing for war in the Pacific. They trained new aircrews in China. On May 22, 1941, a Chinese pilot shot down a Japanese bomber over Lanzhou. On the ground, Chinese Muslim generals protected Lanzhou with their cavalry. They fought so well that the Japanese never captured the city.
Geography and Climate
Lanzhou is about 1600 meters (5,250 feet) above sea level. It is in the middle of China's northwest region. The city area stretches for over 20 square kilometers (7.7 square miles) along the southern banks of the Yellow River. The river flows through the city from west to east. Mountains like the Qilian Ranges are on the south and north sides of Lanzhou.
Lanzhou is located where the Yellow River comes out of the mountains. It has been an important place since ancient times. It was at the southern end of the route that led through the Hexi Corridor to Central Asia. It also controlled the paths to the old capital of Chang'an (now Xi'an).
Lanzhou's Climate
Lanzhou has a semi-arid climate. This means it has hot summers and cold, very dry winters. In the city, the average temperature in January is about -4.1°C (24.6°F). In July, it's about 23.4°C (74.1°F). The average temperature for the whole year is 10.9°C (51.6°F).
The city gets about 309 millimeters (12.2 inches) of rain each year. Most of this rain falls from May to October. Winters are so dry that it rarely snows, except in fall and spring. Lanzhou gets a good amount of sunshine, about 2,350 hours each year.
| Climate data for Lanzhou, elevation 1,517 m (4,977 ft), (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1951–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.1 (62.8) |
21.0 (69.8) |
26.0 (78.8) |
34.6 (94.3) |
35.5 (95.9) |
36.8 (98.2) |
39.8 (103.6) |
37.3 (99.1) |
34.4 (93.9) |
27.4 (81.3) |
20.3 (68.5) |
16.5 (61.7) |
39.8 (103.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 2.3 (36.1) |
7.6 (45.7) |
14.1 (57.4) |
20.7 (69.3) |
24.9 (76.8) |
28.6 (83.5) |
30.2 (86.4) |
28.8 (83.8) |
23.6 (74.5) |
17.5 (63.5) |
10.3 (50.5) |
3.5 (38.3) |
17.7 (63.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −4.1 (24.6) |
0.6 (33.1) |
7.0 (44.6) |
13.2 (55.8) |
17.7 (63.9) |
21.7 (71.1) |
23.4 (74.1) |
22.2 (72.0) |
17.2 (63.0) |
10.7 (51.3) |
3.5 (38.3) |
−2.9 (26.8) |
10.9 (51.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −8.4 (16.9) |
−4.3 (24.3) |
1.6 (34.9) |
7.2 (45.0) |
11.5 (52.7) |
15.8 (60.4) |
17.9 (64.2) |
16.9 (62.4) |
12.6 (54.7) |
6.1 (43.0) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
−7.0 (19.4) |
5.7 (42.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −21.1 (−6.0) |
−17.6 (0.3) |
−11.6 (11.1) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
5.7 (42.3) |
9.8 (49.6) |
8.6 (47.5) |
1.6 (34.9) |
−7.1 (19.2) |
−12.3 (9.9) |
−19.7 (−3.5) |
−21.1 (−6.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 1.7 (0.07) |
3.0 (0.12) |
6.7 (0.26) |
16.3 (0.64) |
39.0 (1.54) |
44.0 (1.73) |
63.5 (2.50) |
66.0 (2.60) |
43.7 (1.72) |
21.7 (0.85) |
2.7 (0.11) |
0.7 (0.03) |
309 (12.17) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 2.4 | 2.4 | 3.7 | 5.8 | 7.8 | 8.9 | 10.7 | 10.1 | 9.9 | 6.5 | 2.1 | 1.0 | 71.3 |
| Average snowy days | 4.9 | 4.4 | 3.3 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.0 | 3.1 | 2.9 | 20.6 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 51 | 46 | 42 | 40 | 44 | 48 | 55 | 58 | 63 | 63 | 58 | 54 | 52 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 149.7 | 173.1 | 210.3 | 226.0 | 245.1 | 234.0 | 239.6 | 226.6 | 173.2 | 173.6 | 155.5 | 143.1 | 2,349.8 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 48 | 56 | 56 | 57 | 56 | 54 | 54 | 55 | 47 | 51 | 51 | 48 | 53 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Administration | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather China | |||||||||||||
Environmental Challenges and Improvements
Lanzhou is in a narrow river valley surrounded by mountains. This can trap air, making air quality a challenge. In 2013, Lanzhou was one of the most air-polluted cities in the world. Sometimes, the air was so thick you couldn't see the nearby Lanshan mountain. Many factories, including oil processing plants, are in Lanzhou. The city also gets big dust storms from the Gobi Desert, especially in winter and spring.
However, Lanzhou has worked hard to improve its air quality. They closed polluting factories and moved others outside the city. In 2015, Lanzhou was recognized for its climate progress. The city has reduced its air pollution faster than many other cities in China. While there are still challenges, the air quality has gotten much better.
The Yellow River in Lanzhou carries a lot of mud, which gives it its famous muddy look. But the water quality in this part of the river is better than further downstream. Recently, some rare Chinese giant salamanders have been found in and near the Yellow River in Lanzhou.
In 2014, there was a temporary issue with tap water quality due to a factory problem. In 2020, a factory accident caused a health issue for some people in Lanzhou.
Earthquakes in Lanzhou
Lanzhou experiences earthquakes regularly, but they are usually not very strong. In 1920, a large earthquake happened in the region, but only a few people were hurt in Lanzhou itself. This was because the wooden buildings in the city were strong and flexible. Lanzhou was also affected by the 2008 Sichuan earthquake.
Population Growth
In 2020, Lanzhou's population went over 4 million people for the first time. The main city area has over 3 million residents. The city has grown a lot recently. Many people are moving to Lanzhou for better education for their children. Also, retired workers are returning to Gansu, and city services have improved.
Sports and Recreation
The Northwest Minzu University Stadium is a main sports place in Lanzhou. It can hold 14,000 people and is mostly used for football games. A new sports complex is being built, which will include a stadium for 60,000 spectators and a swimming hall.
Lanzhou used to have a professional soccer team called Gansu Tianma. They played from 1999 to 2003.
Places to Visit
- The Five Spring Mountain Park (五泉山公园) is famous for its five springs and many old Buddhist temples.
- The Zhongshan Bridge (中山桥) was the first permanent bridge built over the Yellow River.
- Baita Mountain Park (白塔山公园) is on a mountain about 1700 meters (5,577 feet) high. It opened in 1958 and is across the Zhongshan Bridge.
- The Lanzhou Botanical Garden (兰州植物园) in Anning District has many different trees, flowers, and plants.
- Xiguan Mosque (西关清真寺) is one of the biggest mosques in China. It was first built in the Ming dynasty.
- Xinglong Mountain (兴隆山) is covered with thick pine forests and has many colorful temples.
- Lutusi ancient government (鲁土司衙门旧址) is a large group of old government buildings.
Museums to Explore
- Gansu Provincial Museum (甘肃省博物馆) shows old finds like pottery and fossils from Gansu. It also has exhibits on Gansu's history.
- Lanzhou Museum (兰州市博物馆) is an important cultural place on the Silk Road. It has over 13,000 items, including pottery, bronze, and jade.
- Gansu Art Museum (甘肃艺术馆) is a place for artists to show their work and share ideas.
- Lanzhou City Planning Exhibition Hall (兰州市规划展览馆) shows the rich Yellow River culture of Lanzhou. It combines indoor exhibits with city features.
- Lanzhou Painted Pottery Museum (兰州彩陶博物馆) has 250 pieces of painted pottery. It shows the ancient pottery culture of Majiayao.
- Gansu Science and Technology Museum (甘肃科技博物馆) uses cool technology like sound and light. It helps visitors learn about modern science in a fun way.
Economy and Industry
Since 1949, Lanzhou has changed a lot. It went from being the capital of a poor province to a major industrial area. It was one of the first cities in China to build many factories.
Lanzhou's economy has grown steadily. In 2015, its economic output per person was about US$9,182.
Natural Resources
Lanzhou has many natural resources, including:
There are power plants that use coal from nearby areas. Also, there are hydroelectric power stations on the Yellow River, including a large dam called Liujia Gorge.
Main Industries
Lanzhou's main industries include:
- Textile mills (making fabric)
- Rubber processing
- Fertilizer plants
- Oil refineries (processing oil)
- Petrochemicals (chemicals from oil)
- Machinery
- Metal industries
Gansu province has one of the biggest oil refineries in China, and Lanzhou is the center of its petrochemical industry. The refinery is connected to oil fields by pipelines. Lanzhou also makes equipment for the oil industry.
Lanzhou has a large textile industry, especially known for wool and leather products. The city also makes trains and train parts for the northwestern railways. It produces machine tools and mining equipment. Large amounts of aluminum products, industrial chemicals, and fertilizers are made here. Copper is mined in nearby Gaolan.
Since the 1960s, Lanzhou has been an important center for China's nuclear power industry.
Agriculture
Lanzhou is a central place for collecting and selling farm products and animals from the surrounding area.
- Spring wheat
- Vegetables
- Beans
- Oil-boiling crops
- Melons
- Peaches
- Tobacco
- Roses and lilies
Transportation in Lanzhou
Airport
Lanzhou Zhongchuan International Airport is the main airport for Lanzhou. It is about 70 kilometers (43 miles) north of the city. The airport opened in 1970. It has direct flights to over 70 places both in China and other countries.
Railway System
Subway System
Lanzhou was the second city in northwest China to start building a subway. The Lanzhou Metro system will have six lines. The first line, which is completely underground, opened in June 2019. Line 2 opened in June 2023. You can change between Line 1 and Line 2 at Dongfanghong Square Station and Wulipu Station.
Regional Trains
Lanzhou Railway Station is a very important train hub in western China. More than 100 passenger trains start or pass through this station every day. It connects the western provinces with eastern China. Lanzhou West Railway Station is the city's second main train station. It offers high-speed train services.
Lanzhou Railway Station connects to several important railway lines:
- Longhai Railway goes east to cities like Xi'an and Shanghai.
- Lanxin Railway goes west and northwest to Ürümqi and further into Kazakhstan.
- Lanqing Railway goes west and southwest to Xining and Lhasa.
- Chongqing–Lanzhou railway goes southeast to Chongqing.
- A line goes north and northeast to Yinchuan and Baotou.
- The Lanzhou–Zhongchuan Airport Intercity Railway connects the city to the airport.
High-Speed Rail
New high-speed train lines are finished, going both east (the Xuzhou–Lanzhou high-speed railway) and west (the Lanzhou–Xinjiang high-speed railway). These trains only stop at Lanzhou West Railway Station. Other high-speed lines are being built.
Freight Trains
Lanzhou is a key part of the Eurasian Land Bridge, which is a railway route connecting Asia and Europe. It also provides train access to Qinghai, Xinjiang, and Tibet. A large new train freight terminal has been built for more cargo. Lanzhou has China's fourth largest train sorting yard.
Freight trains regularly connect Lanzhou to places like Chongqing, Hamburg, and Kathmandu.
Road Network
In 2016, Lanzhou had some of the worst traffic jams in China. But by 2017, after a new city ring road was built, traffic improved a lot.
Major Highways
- G75 Lanzhou–Haikou Expressway
- G30 Lianyungang–Khorgas Expressway
- G6 Beijing–Lhasa Expressway
- G22 Qingdao–Lanzhou Expressway
- G2201 Lanzhou Ring Expressway
- China National Highway 212
- China National Highway 213
- China National Highway 312
Bus Services
For long-distance buses, Lanzhou has three main bus stations. There are also 132 local city bus lines.
Lanzhou has a good bus rapid transit system that opened in 2013. It helped the city win an award for sustainable transport.
Media and Culture
- Gansu People's Press in Lanzhou publishes Duzhe, which is a very popular magazine in China.
- Lanzhou Radio provides news and music to the Lanzhou area.
- Gansu Daily is a newspaper for Gansu Province. Its offices are in Lanzhou.
Local Culture
Lanzhou is the cultural center of Gansu. Many different groups live here, including the Han, Hui, and Zang. Each group has its own culture.
- Chinese opera: Qinqiang Opera is a traditional art form.
- Food: Lanzhou beef noodles are famous all over China. Lanzhou has over 1,000 beef noodle restaurants! The root of the lily and many kinds of mutton are also important parts of Lanzhou's food culture.
- Islam in China: Xiguan Mosque was built in the Ming dynasty and rebuilt in 1990. It is one of the most important mosques in China. Its design looks a lot like Arab architecture.
Colleges and Universities
Lanzhou is a big center for science and education in Northwestern China, second only to Xi'an. The city is one of the top 60 cities in the world for scientific research. It is home to Lanzhou University, which was founded in 1909. Other important schools include Northwest Normal University and a branch of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
List of Universities
- Lanzhou University, founded 1909
- Gansu Agricultural University, founded 1958
- Gansu University of Chinese Medicine
- College of Politics and Law, Gansu
- Lanzhou University of Arts and Science
- College of Technology, Lanzhou
- Lanzhou City College, founded 1958
- Lanzhou University of Finance and Economics
- Lanzhou Jiaotong University, founded 1958
- Lanzhou University of Technology, founded 1919
- Northwest University for Nationalities
- Northwest Normal University, founded 1902
Healthcare
Lanzhou has many hospitals and healthcare centers, including:
- People's Hospital of Gansu
- Second People's Hospital of Gansu
- Third People's Hospital of Gansu
- First People's Hospital of Lanzhou
- Second People's Hospital of Lanzhou
- Lanzhou University First Hospital
- Lanzhou University Second Hospital
- General Military Hospital
- Lanzhou Military Hospital
- Lanzhou Heavy Ion Cancer Treatment Center
- Gansu Tumor Hospital
Sister Cities
Lanzhou has special partnerships with cities around the world, called sister cities:
- Albuquerque,
 United States
United States - Akita,
 Japan (friendship city)
Japan (friendship city) - Ashkhabad,
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan - Chorley,
 England
England - Penza,
 Russia
Russia - Nouakchott,
 Mauritania
Mauritania - Young Shire,
 Australia
Australia - Hachinohe, Aomori,
 Japan
Japan
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Lanzhou para niños
In Spanish: Lanzhou para niños