Physics facts for kids
Physics is a super important part of science. It helps us understand how everything around us works, from the tiniest atoms to the biggest galaxies. Physics looks at matter (which is anything that takes up space) and all the forces that make things move or change. It also explores big ideas like energy, momentum, and how things stay balanced in the universe. The word "physics" comes from an old Greek word meaning "nature."
Physics is one of the oldest sciences, and its main goal is to figure out the rules that make the universe tick.
Contents
History of Physics
People have been studying physics for thousands of years! They wanted to understand the world around them.
Early Astronomy
Astronomy, the study of stars and planets, is the oldest natural science. Long ago, before 3000 BC, people like the Sumerians, Ancient Egyptians, and Indus Valley Civilization watched the sky and understood how the stars and planets moved. Many of the names for the groups of stars we call constellations came from Greek astronomers.
Natural Philosophy
Around 650 BC in Greece, some thinkers started to wonder if things happened for a reason, not just because of superstition. They began to think about "natural philosophy." Two of these thinkers, Leucippus and his student Democritus, even came up with the idea of the atom – that everything is made of tiny, unseen particles!
Physics in the Medieval Islamic World
During the Islamic Golden Age, Islamic scholars kept studying the ideas of Aristotelian physics. They also helped create an early version of the scientific method, which is how scientists test their ideas.
Scientists like Ibn al-Haytham studied optics, which is about light and how we see. In his book, Book of Optics, he shared new ideas about vision that were different from what the Greeks believed.
Classical Physics
Physics became its own separate field of study after the scientific revolution.
Galileo's experiments were very important for classical physics. He used a telescope to see that the stars and planets weren't perfectly smooth, and he also studied gravity.
Later, Isaac Newton used Galileo's ideas to create his famous three laws of motion, which explain how things move.
Modern Physics
As scientists learned more, they found things that classical physics couldn't explain.
For example, classical physics thought the speed of light could change, but experiments showed it always stayed the same. Albert Einstein explained this with his theory of special relativity. He said that the speed of light in empty space is always constant. His ideas also changed how we think about space-time, showing that space and time are connected, not separate.
Max Planck started the idea of quantum mechanics to explain why metals release electrons when light shines on them and why hot objects give off light. Quantum mechanics is used for very, very small things, like the tiny parts that make up an atom (electrons, protons, and neutrons). Scientists like Werner Heisenberg, Erwin Schrödinger, and Paul Dirac continued this work, leading to what we now call the Standard Model of particle physics.
What Physics Studies
Physics is the study of energy and matter in space and time, and how they are connected. Physicists use basic measurements like mass, length, time, and electric current to describe everything else.
In the International System of Units (called SI), we use:
There are also three other important units:
- The mole for the amount of matter.
- The candela for how bright a light is.
- The kelvin for temperature.
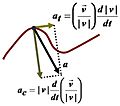
Physics helps us understand how things move, using ideas like velocity (how fast something is going) and acceleration (how quickly its speed changes). Physicists also study forces like gravity, electricity, magnetism, and the forces that hold things together inside atoms.
Physics explores both very large things, like stars, planets, and galaxies, and very small things, like atoms and electrons. It also studies sound, light, and other waves, as well as energy, heat, and radioactivity. Physics helps us understand not just how objects move, but also how they change, make noise, get hot or cold, and what they are made of at the smallest level.
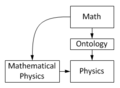
Physics and Math
Physics is a quantitative science, which means it relies on measuring things with numbers. Scientists use mathematics to create models that try to predict what will happen in nature. They then compare these predictions to what actually happens in the real world. Physicists are always working to make their models better and more accurate.
How Physics Works
Physics is all about discovering the basic rules that control matter, movement, forces, space, and time. It tries to find the simplest, most general, and most accurate rules for how the physical universe behaves.
Using the Scientific Method
Physics uses the scientific method. This means:
- Scientists collect information from experiments and observations.
- They create theories to explain this information.
- They use these theories to describe what's happening and to predict how things will behave.
- Finally, they compare their predictions to new observations or experiments to see if the theory is correct.
Theories that are strongly supported by data and are simple and general are sometimes called scientific laws. But even these laws can be changed or replaced if new information shows they aren't completely accurate.
Physics is About Numbers
Physics uses numbers a lot more than many other sciences. Most observations in physics are measured with numbers, and most theories use mathematics to explain their ideas. The predictions from these theories are usually numbers too. This is because the areas physics studies often work best with numbers. Also, physics is one of the oldest sciences, and sciences tend to use more numbers as they develop.
Different Areas of Physics
Physics can be divided into different areas:
- Classical physics includes things like mechanics (how things move), optics (light), electricity, magnetism, acoustics (sound), and thermodynamics (heat).
- Modern physics includes areas that use quantum theory, like quantum mechanics, atomic physics, nuclear physics, particle physics, and condensed matter physics. It also includes general and special relativity. Even in classical areas, we now know that quantum effects can be important.
How Physicists Study Things
There are two main ways physicists work:
- Collecting data: Some physicists do experiments in labs, like in condensed matter physics or nuclear physics. They explore nature and gather information to test theories.
- Developing theories: Other physicists use mathematics to create theories that explain the data. They make predictions and compare them to what is observed. Sometimes, they even create models before any data is available to test them.
These two ways of working use many different skills. For example, theoretical physicists use mathematics, statistics, and computer software. Experimental physicists create new tools and techniques for collecting data, often using engineering and computer technology.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Ibn al-Haytham (c. 965–c. 1040), whose Book of Optics described his camera obscura experiments.
-
Galileo Galilei understood how to combine math, theory, and experiments in physics.
-
Sir Isaac Newton (1643–1727), whose laws of motion and universal gravitation were huge steps in classical physics.
-
Albert Einstein (1879–1955), whose work on the photoelectric effect and relativity changed 20th-century physics.
-
The Solvay Conference of 1927, with famous physicists like Albert Einstein, Werner Heisenberg, Max Planck, Niels Bohr, Marie Curie, and Paul Dirac.
-
The Archimedes' screw, a simple machine for lifting water.
-
An experiment using a laser.
-
Lightning is an electric current.
-
A simulated event in the CMS detector of the Large Hadron Collider, showing a possible Higgs boson.
-
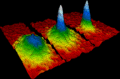
Data showing the speed of rubidium atoms, which helped discover a new phase of matter called the Bose–Einstein condensate.
-
The deepest visible-light image of the universe, called the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field.
-
A Feynman diagram signed by Richard Feynman.
-
A typical phenomenon physics describes: a magnet floating above a superconductor because of the Meissner effect.
See also
 In Spanish: Física para niños
In Spanish: Física para niños