Cuba facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of Cuba
República de Cuba (Spanish)
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Motto: Patria o Muerte, Venceremos
("Homeland or Death, We Shall Overcome!") |
|
Cuba, shown in dark green
|
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Havana 23°8′N 82°23′W / 23.133°N 82.383°W |
| Official languages | Spanish |
| Other spoken languages | Haitian Creole English Lucumí Galician Corsican |
| Ethnic groups
(2012)
|
|
| Religion
(2020)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Cuban |
| Government | Unitary Marxist–Leninist one-party socialist republic |
|
• President and First Secretary
|
Miguel Díaz-Canel |
| Salvador Valdés Mesa | |
| Manuel Marrero Cruz | |
| Legislature | National Assembly of People's Power |
| Independence
from Spain and the United States
|
|
| 10 October 1868 | |
| 24 February 1895 | |
|
• Recognized (Handed over to the United States from Spain)
|
10 December 1898 |
|
• Republic declared (Independence from United States)
|
20 May 1902 |
| 26 July 1953 – 1 January 1959 | |
|
• Current constitution
|
10 April 2019 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
110,860 km2 (42,800 sq mi) (104th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
0.94 |
| Population | |
|
• 2023 estimate
|
|
|
• 2022 census
|
|
|
• Density
|
90.7/km2 (234.9/sq mi) (80th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2015 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$254.865 billion |
|
• Per capita
|
$22,237 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2000) | 38.0 medium |
| HDI (2022) | high · 85th |
| Currency | Cuban peso (CUP) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (CST) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC−4 (CDT) |
| Calling code | +53 |
| ISO 3166 code | CU |
| Internet TLD | .cu |
Cuba (KEW-bə), officially the Republic of Cuba (Spanish: República de Cuba), is an island country. It includes the main island of Cuba, plus Isla de la Juventud and several smaller groups of islands. Cuba is part of Latin America in its culture.
Cuba is a founding member of the United Nations. It also belongs to the G77, the Non-Aligned Movement, and other important groups. Cuba has a planned economy. Its economy mainly relies on tourism and exporting skilled workers, sugar, tobacco, and coffee. Cuba has a good history in areas like reading skills, low infant deaths, and long life expectancy.
Contents
What's in a Name? The Meaning of "Cuba"
Historians think the name Cuba comes from the Taíno language. The exact meaning isn't fully known. It might mean 'where fertile land is abundant' (cubao), or 'great place' (coabana).
Exploring Cuba's Geography
Cuba is located where the northern Caribbean Sea, Gulf of Mexico, and Atlantic Ocean meet. It is east of Mexico's Yucatán Peninsula. Cuba is also south of Florida and the Bahamas. It lies west of Hispaniola (Haiti/Dominican Republic) and north of Jamaica and the Cayman Islands.
The main island of Cuba is about 1,250 km (780 mi) long. It makes up most of the country's land. It is the largest island in the Caribbean. It is also the 17th-largest island in the world by land area. The main island has mostly flat plains. The Sierra Maestra mountains are in the southeast. Their highest point is Pico Turquino, which is 1,974 m or 6,476 ft tall.
The second-largest island is Isla de la Juventud (Isle of Youth). It is in the Canarreos archipelago. Its area is 2,200 km2 (850 sq mi). Cuba has six natural areas called ecoregions. These include moist forests, dry forests, and wetlands.
Area and Population of Cuba
The official land area of Cuba is 109,884 km2 (42,426 sq mi). This does not include its ocean waters. Cuba is the second-most populated country in the Caribbean after Haiti. It has over 11 million people.
Cuba's Largest Cities
|
Largest cities or towns in Cuba
According to the 2018 Estimate |
||
|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Pop. |
| 1 | Havana | 2,131,480 |
| 2 | Santiago de Cuba | 433,581 |
| 3 | Camagüey | 308,902 |
| 4 | Holguín | 297,433 |
| 5 | Santa Clara | 216,854 |
| 6 | Guantánamo | 216,003 |
| 7 | Victoria de Las Tunas | 173,552 |
| 8 | Bayamo | 159,966 |
| 9 | Cienfuegos | 151,838 |
| 10 | Pinar del Río | 145,193 |
A Brief History of Cuba
-
A map of Cuba made in 1680
-
Black Cubans in Havana during the 1800s
-
Workers on a Cuban sugar plantation
-
Cuban revolutionaries in 1958
The land that is now Cuba was first lived in by the Ciboney people. Later, the Guanahatabey and Taíno peoples lived there. This was until Spanish explorers arrived in the 15th century.
From the 15th century, Cuba was a colony of Spain. Slavery was ended in 1886. Cuba stayed a Spanish colony until the Spanish–American War in 1898. After this war, it was briefly managed by the United States. Cuba then gained independence in 1902.
In 1940, Cuba created a new constitution. In 1959, the Cuban Revolution led by Fidel Castro changed the country's government. Cuba then became a socialist state. After 49 years, Fidel Castro stepped down in 2008. His brother, Raúl Castro, took over. In 2018, Miguel Díaz-Canel became president. He is the first leader not from the Castro family since the revolution.
Cuba approved a new constitution in 2019. This new constitution says the Communist Party is the only political party. It also states that health and education are basic rights. It sets limits on how long a president can serve. It also recognizes private property. In 2022, Cuba approved a new Family Code. This made same-sex marriage and same-sex adoption legal.
How Cuba is Governed
President of the National Assembly
The Republic of Cuba is a socialist country. Its government follows the ideas of Marxism–Leninism. The 1992 Constitution says the Communist Party of Cuba is the main force in society and the state. The political system in Cuba is based on democratic centralism.
The First Secretary of the Communist Party of Cuba holds the most important position. This person leads the Politburo and Secretariat. This makes them the most powerful person in the Cuban government. The President of Cuba is elected for five years. They can serve two terms.

The People's Supreme Court is Cuba's highest court. It handles appeals from lower courts.
Cuba's main law-making body is the National Assembly of People's Power. It has 474 members who serve five-year terms. The assembly meets twice a year. Between meetings, a smaller group called the Council of Ministers holds legislative power. All Cuban citizens over 16 can vote if they have not committed a crime. Voting is free, equal, and secret.
Cuba's Military
In 2018, Cuba spent about US$91.8 million on its armed forces. This was 2.9% of its total economy. During the Cold War, Cuba had one of the largest armies in Latin America. After the Soviet Union ended, Cuba made its military smaller. The number of military personnel went from 235,000 in 1994 to about 49,000 in 2021. In 2017, Cuba signed a UN treaty to ban nuclear weapons.
Law Enforcement in Cuba

All police agencies are part of Cuba's Ministry of the Interior. This ministry is overseen by the Revolutionary Armed Forces. People in Cuba can call "106" for police help. The police force is called "Policía Nacional Revolucionaria" or PNR.
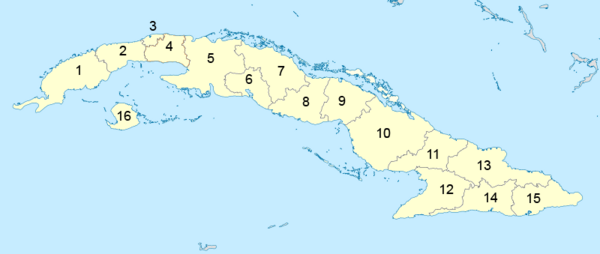
Administrative Divisions of Cuba
Cuba is divided into 15 provinces. It also has one special municipality, Isla de la Juventud. These divisions are similar to old Spanish military areas. The provinces are further divided into smaller areas called municipalities.
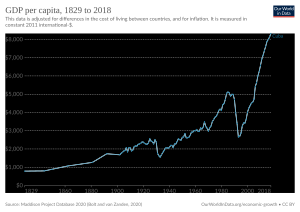
Cuba's Economy
Cuba has a planned economy. This means the government owns and runs most businesses. Most workers are employed by the state.
When a company hires a Cuban, it pays the Cuban government. The government then pays the employee in Cuban pesos. In 2021, the minimum wage became about 2100 CUP (US$17.50). The average wage is about 4000 CUP (US$33).
The recent global health crisis greatly affected Cuba's tourism. This, along with other challenges, has led to more young Cubans leaving the country.
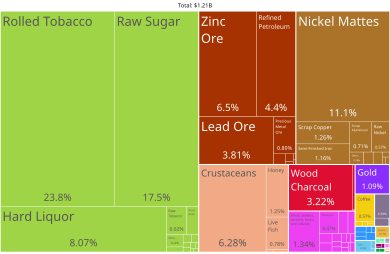
Natural Resources of Cuba
Cuba's natural resources include sugar, tobacco, fish, and citrus fruits. They also grow coffee, beans, rice, and potatoes. Livestock farming is also important. The most important mineral resource is nickel. It made up 21% of all exports in 2011.
Oil exploration in 2005 found that the North Cuba Basin might have a lot of oil. Cuba started testing these areas for oil in 2006.
Tourism in Cuba


In 2003, 1.9 million tourists visited Cuba. Most came from Canada and Europe. This brought in US$2.1 billion. In 2011, Cuba had 2,688,000 international tourists. This was the third-highest number in the Caribbean.
Cuba also has a medical tourism sector. Thousands of people visit each year for medical care. A study shows Cuba has potential for mountaineering. This could help tourism, along with biking, diving, and caving. These activities could help local areas grow.
In 2017, Hurricane Irma damaged some tourist places. The worst damage was on islands north of the main island. The main tourist areas were not as badly hit.
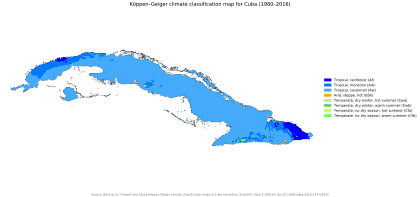
Cuba's Climate
Cuba has a semi-tropical climate. Cool ocean winds keep it from getting too hot. Cuba has a wet season and a dry season. The dry season is from November to April. The wet season is from May to October. August to October is also hurricane season. Because of this, many port cities can flood along the coast.
The average temperature is 21 °C (70 °F) in January. It is 27 °C (81 °F) in July. The warm Caribbean Sea and Cuba's location make it prone to hurricanes. These storms are most common in September and October.
Interesting Facts About Cuba
- In 2012, a study said Cuba was the only country to meet WWF's sustainable development goals.
- The Cuban trogon or tocororo is Cuba's national bird. It is a bird found only in Cuba.
- Hedychium coronarium, called mariposa, is Cuba's national flower.
- The native bee hummingbird or zunzuncito is the world's smallest bird. It is only 55 mm (2+1⁄8 in) long.
- Cuba's literacy rate is 99.8 percent. This is the tenth-highest globally. This is because education is free at all levels.
- Cuba's high school graduation rate is 94 percent.
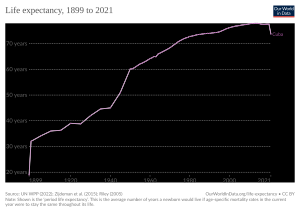
- Life expectancy at birth in Cuba is 79.64 years. This ranks Cuba 59th in the world.
- Cuba has the most doctors per person in the world. It has sent doctors to over 40 countries. The World Health Organization says Cuba is known for training excellent doctors and nurses.
People and Culture of Cuba
| Population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Million | ||
| 1950 | 5.9 | ||
| 2000 | 11.1 | ||
| 2018 | 11.3 | ||
In 2010, Cuba's population was 11,241,161 people. This included 5,628,996 men and 5,612,165 women. Its birth rate is one of the lowest in the Western Hemisphere. The population has grown since 1961, but the growth has slowed. It started to decline in 2006. This is due to a low fertility rate and people moving away.
Most of Cuba's population lives in cities, about 77%. The rural population was about 23% in 2021. Cuba's population has stayed mostly the same since the early 2000s.
Ethnoracial Groups in Cuba
| 2012 Cuban census data | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Race | ||||
| White | 64.1% | |||
| Mulatto | 26.6% | |||
| Black | 9.3% | |||

Religion in Cuba
In 2010, about 59.2% of Cubans were Christian. About 23% said they had no religion. About 17.4% followed folk religions like santería. Cuba is officially a secular state. This means it does not have an official religion. Religious freedom has increased since the 1980s.
Roman Catholicism is the largest religion. It came from Spanish colonization. Popes have visited Cuba several times. Before each visit, the Cuban government has released prisoners.
Languages Spoken in Cuba
The official language of Cuba is Spanish. Most Cubans speak it. The Spanish spoken in Cuba is called Cuban Spanish. Haitian Creole is the second most spoken language. It is spoken by Haitian immigrants and their families. Other languages spoken by immigrants include Galician and Corsican.
Education in Cuba
The University of Havana was founded in 1728. There are many other colleges and universities. Before 1959, almost 80% of Cubans could read. After the revolution, the government created a free public education system. Private schools were not allowed. School is required from age six until about age 15. All students wear uniforms.
Higher education is offered by universities and institutes. The Ministry of Higher Education has programs for distance learning. Education in Cuba also focuses on political and social ideas. Cuba offers free education to some foreign students. This is at the Latin American School of Medicine.
The top universities in Cuba include Universidad de la Habana.
Health Care in Cuba
After the revolution, Cuba started a free public health system. Today, Cuba has universal health care. This means everyone can get medical care. Even with some shortages of supplies, there are many medical workers. Cuba ranks high on health indexes. It is the only developing country to rank so high.
The government made universal health care a top goal. More rural hospitals were built. Medical care faced challenges after 1991. This was due to fewer foreign funds and trade restrictions. Challenges include low doctor salaries and lack of equipment. Cuba developed a lung cancer vaccine called Cimavax. This vaccine has been free for Cubans since 2011.
Media in Cuba
Mass media in Cuba includes television, radio, newspapers, and the Internet. The Cuban government controls the media. Private ownership of broadcast media is not allowed. The government owns all major media outlets.
Internet access in Cuba has been limited. All content can be reviewed by the government. Cuba has an online encyclopedia called EcuRed. It works like a "wiki". The sale of computers is carefully managed.
Since 2018, mobile data is available for Internet access. In 2019, 7.1 million Cubans could access the Internet. The cost of Internet has gone down. This is especially true since 2021. In 2021, 7.7 million Cubans had Internet access. There were 6.14 million mobile connections in January 2021.
Cuban Culture
Cuban culture is a mix of different influences. These mainly come from Spain, Africa, and the native Taínos. After the 1959 revolution, the government started a reading campaign. It offered free education. It also created strong sports, ballet, and music programs.
Cuban Cuisine

Cuban food mixes Spanish and Caribbean cuisines. Cuban recipes use similar spices and cooking methods as Spanish food. They also have Caribbean flavors. Food rationing has been common in Cuba. This limits how often some dishes are available. A traditional Cuban meal is served all at once.
A typical meal might have plantains, black beans and rice. It could also include ropa vieja (shredded beef). Cuban bread, pork with onions, and tropical fruits are also common. Black beans and rice are called moros y cristianos. Plantains are also a main food in Cuba. Many meat dishes are cooked slowly with light sauces. Garlic, cumin, oregano, and bay leaves are common spices.
Cuban Literature
Cuban literature started to grow in the early 1800s. Themes of independence and freedom were important. José Martí was a key writer. Writers like Nicolás Guillén used literature to talk about social issues. The poetry and novels of Dulce María Loynaz and José Lezama Lima have been very important. Miguel Barnet wrote Everyone Dreamed of Cuba. This book shows a more thoughtful side of Cuba.
Alejo Carpentier was important in the magic realism movement. Many Cuban writers have gained international fame. Some have chosen to live outside Cuba to continue their work. However, many writers still live and write in Cuba. These include Miguel Barnet and Nancy Morejón.
Cuban Music
Cuban music is very rich and well-known. The main style is son. Many other music styles came from son. These include "Danzón de nuevo ritmo", mambo, cha-cha-chá, and salsa music. Rumba music came from early Afro-Cuban culture. It mixed with Spanish styles. The Tres instrument was invented in Cuba. It combines parts of the Spanish guitar and lute. Other Cuban instruments are from African or Taíno origins. These include maracas, güiro, and various drums.
Cuban popular music is loved worldwide. Cuban classical music also has strong African and European influences. Composers like Ernesto Lecuona have received international praise. Havana was the center of the rap scene in Cuba in the 1990s.
Reggaetón also became popular. The Cuban government has sometimes criticized reggaetón. Famous Cuban artists include Los Van Van orchestra and pianists Chucho Valdés and Frank Fernández. Omara Portuondo is a member of the Buena Vista Social Club. Many Cuban artists have won Grammy Awards.
Cuban Dance
Cuban culture has many dance forms. Danzón was Cuba's official dance. Mambo music and dance started in Cuba. They were further developed by Cuban musicians in other countries. The cha-cha-cha is another dance from Cuba. The Cuban bolero started in Santiago de Cuba in the late 1800s. The government supports Concert dance. This includes famous groups like the Ballet Nacional de Cuba.
Salsa dancing also started in Cuba. Cuban salsa is danced all over the world.
Sports in Cuba
Because of its history with the United States, many Cubans play sports popular in North America. Baseball is the most popular sport. Other popular sports include volleyball, boxing, athletics, wrestling, basketball, and water sports. Cuba is very strong in amateur boxing. Cuban boxers often win many medals in international events. The government does not allow Cuban boxers to become professional. Cuba also has a national team that competes in the Olympic Games. Jose R. Capablanca was a Cuban world chess champion from 1921 to 1927.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Cuba para niños
In Spanish: Cuba para niños
 | Tommie Smith |
 | Simone Manuel |
 | Shani Davis |
 | Simone Biles |
 | Alice Coachman |