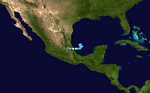
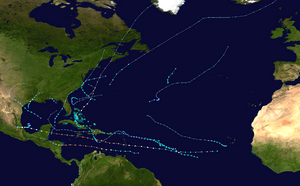
The 2007 Atlantic hurricane season was a period when many tropical cyclones formed in the Atlantic Ocean. This season officially ran from June 1, 2007, to November 30, 2007. Most storms in the Atlantic usually form between these dates. However, Subtropical Storm Andrea started early on May 9, 2007. The last storm, Tropical Storm Olga, didn't end until December 12, 2007. This was the second time in five years that a storm formed before the official season start.
Storms of the 2007 Hurricane Season
Subtropical Storm Andrea: An Early Start
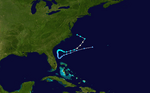
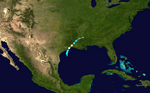
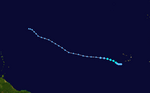
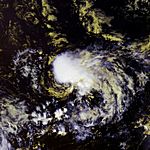
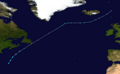
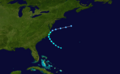
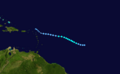
On May 9, a storm that was not fully tropical, called an extratropical cyclone, became Subtropical Storm Andrea. It formed near Savannah, Georgia. Warnings were given for parts of the coast in Georgia and Florida. Andrea was the first named storm to form in May since 1981.
The storm brought rough waves to the coast from Florida to North Carolina. This caused sand to be washed away from beaches. One surfer in Florida sadly drowned because of the strong waves. Andrea's strong winds also made wildfires in northern Florida and southern Georgia much worse. The winds acted like a "chimney," making the fires spread quickly. Smoke from these fires reached as far as Tampa Bay and Miami.
- You can find more details about Subtropical Storm Andrea in the advisory archive from the National Hurricane Center.
Tropical Storm Barry: Bringing Needed Rain
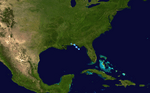
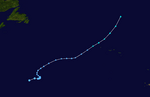
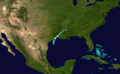
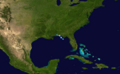
On May 30, a large area of low pressure formed in the Gulf of Honduras. It slowly got stronger as it moved into the Gulf of Mexico. On June 1, the first day of the hurricane season, this system became Tropical Storm Barry. Warnings were quickly issued for the western Florida coast.
Barry brought much-needed rain to parts of Florida and Georgia. These areas had been very dry for months. Barry made landfall near Tampa Bay, Florida, on June 2 as a weak tropical storm. It then weakened into a tropical depression. By June 5, it had moved into Eastern Canada.
- See the National Hurricane Center's advisory archive on Tropical Storm Barry.
Tropical Storm Chantal: Flooding in Canada
An area of low pressure formed near The Bahamas on July 28. It slowly became more organized as it moved north. On July 31, it became Tropical Storm Chantal south of Nova Scotia. This was the first storm in almost two months. The storm quickly changed into an extratropical storm later that day as it moved over cooler waters towards Newfoundland.
On August 1, heavy flooding was reported in Newfoundland. About 100 mm (4 inches) of rain fell in St. John's. Up to 150 mm (6 inches) of rain fell in the Whitbourne area. Many roads were washed out, and houses were flooded. Several communities were cut off. The damage was estimated to be millions of dollars.
- See the National Hurricane Center's advisory archive on Tropical Storm Chantal.
Hurricane Dean: A Powerful Category 5
A strong tropical wave moved off the coast of Africa in early August. It quickly became a low-pressure system on August 12. Tropical Depression Four formed on August 13 in the eastern Atlantic. It was expected to get much stronger because of warm ocean waters.
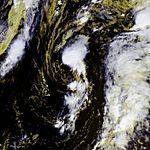
The depression moved west very fast. It became Tropical Storm Dean on August 14. It then quickly strengthened into a Category 1, then Category 2 hurricane on August 16. By August 17, it was a Category 3, then Category 4 hurricane. On August 20, it became a powerful Category 5 hurricane. Dean made landfall in the Yucatán Peninsula as a Category 5 storm. It hit Mexico again on August 22 and then faded away the next day.
Tropical Storm Erin: Impacting Texas
On August 9, an area of thunderstorms formed south of Jamaica. This system moved west-northwest. By August 12, a tropical wave and another weather system started to combine. This created a large area of thunderstorms from the western Caribbean Sea to The Bahamas.
On August 13, a large low pressure area formed north of Cancún, Quintana Roo. On August 15, it was named Tropical Depression Five. Later that day, it was upgraded to Tropical Storm Erin. Erin weakened to a tropical depression as it made landfall near Lamar, Texas, on August 16.
Sadly, two people were killed when a warehouse collapsed in Texas. In total, 17 people were affected by Erin.
- See the National Hurricane Center's advisory archive on Tropical Storm Erin.
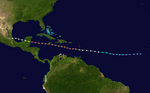
Hurricane Felix: Another Category 5
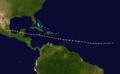
On August 31, a weather system east of the Windward Islands became Tropical Depression Six. Early on September 1, it was named Tropical Storm Felix. Later that day, Felix became a hurricane. On September 2, Felix strengthened into a major hurricane.
Felix made landfall as a Category 5 hurricane in northeastern Nicaragua. This made it the second Category 5 hurricane of 2007. At least 133 people were killed by Hurricane Felix.
Tropical Storm Gabrielle: Minimal Damage
An extratropical storm off the eastern United States coast was named Subtropical Storm Gabrielle on September 7. It was later reclassified as a tropical storm on September 8. After passing over the Outer Banks of North Carolina, it weakened to a depression on September 10.
Gabrielle brought 4-6 inches of rain to the area where it made landfall. However, there was very little damage reported, and no one was killed.
- See the National Hurricane Center's advisory archive on Tropical Storm Gabrielle.
Tropical Storm Ingrid: No Threat to Land
Tropical Depression Eight formed from a tropical wave east of the Lesser Antilles on September 12. It slowly developed and became Tropical Storm Ingrid on September 14. Strong winds from above soon weakened the storm. It became a depression again on September 15.
Ingrid was the first storm of the 2007 season that did not threaten any land. There were no reports of damage or injuries from this storm.
- See the National Hurricane Center's advisory archive on Tropical Storm Ingrid.
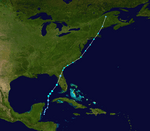
Hurricane Humberto: Rapid Strengthening
Tropical Depression Nine formed from a non-tropical low in the northwestern Gulf of Mexico on September 12. Just three hours later, it had strengthened enough to be named Tropical Storm Humberto. It quickly became a hurricane before fading away over North Carolina. The damage from Humberto was estimated to be about half a billion dollars.
Tropical Depression Ten: Tornadoes in Florida
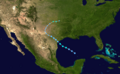
An extratropical low formed off the east coast of Florida on September 18. It slowly moved west and entered the Gulf of Mexico on September 20. It became a subtropical depression on September 21 south of the Florida Panhandle. Three hours later, it was reclassified as a fully tropical depression. Tropical Depression Ten moved onto land later that day and never reached tropical storm strength.
Damage from the storm before it became a depression was reported in Eustis, Florida. One or more tornadoes damaged or destroyed about 50 houses. Luckily, no one was seriously hurt.
- See the National Hurricane Center's advisory archive on Tropical Depression Ten.
Tropical Storm Jerry: Far Out at Sea
Early on September 23, a subtropical depression formed far west of the Azores. It quickly strengthened into Subtropical Storm Jerry later that morning. It stayed far from land. It became a fully tropical storm on September 24 but weakened the same day as it moved over cooler waters. Jerry was later absorbed into a larger weather system.
- See the latest forecast/advisory on Tropical Depression Jerry.
Hurricane Karen: Strengthening in the Atlantic
In the fourth week of September, a very large tropical wave moved off the coast of Africa. It slowly became organized. By early on September 25, it became a tropical depression. Six hours later, it was upgraded to Tropical Storm Karen. Karen quickly became stronger on September 26 and was made a hurricane early that day. However, strong winds from above stopped it from getting even stronger and slowly weakened the storm.
- See the National Hurricane Center's archive history on Tropical Storm Karen.
Hurricane Lorenzo: Hitting Mexico
On September 21, an area of thunderstorms formed in the western Caribbean Sea. A large area of low pressure developed on September 22. By September 25, conditions became better for a tropical cyclone to form. A tropical depression was forming east of Tampico, Mexico.
On the evening of September 25, a Hurricane Hunter aircraft found that the low-pressure area had become a tropical depression. It moved slowly south into the Bay of Campeche. On September 26, the depression got closer to being a tropical storm. On September 27, it rapidly strengthened and became Tropical Storm Lorenzo around midday. Less than 7 hours later, it was upgraded to Hurricane Lorenzo. It hit land in Mexico a little while after.
- See the National Hurricane Center's advisory archive on Hurricane Lorenzo.
Tropical Storm Melissa: Tying a Record
An area of low pressure near the Cape Verde islands became a tropical depression on September 28. Early the next day, it strengthened to become Tropical Storm Melissa. This was the eighth named storm to form in September, which tied a record for the most storms in one month. It soon weakened due to strong winds from above.
- See the National Hurricane Center's archive history on Tropical Storm Melissa.
Tropical Depression Fifteen: Fading Away
On October 11, a tropical depression formed in the central Atlantic east of Bermuda. It came from a low-pressure system that was not tropical before. It faded away without getting any stronger.
- See the National Hurricane Center's advisory archive on Tropical Depression Fifteen.
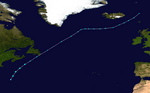
Hurricane Noel: Deadly Rains in the Caribbean
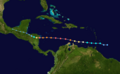
On the evening of October 27, a low-pressure system in the eastern Caribbean became Tropical Depression Sixteen. It steadily got stronger and became a tropical storm on October 28. It made landfall in Haiti on October 29. For the next three days, it moved slowly near Cuba.
Noel brought very heavy rain to the region. This caused at least 120 people to lose their lives. It then sped up northeast, passing through The Bahamas before becoming a hurricane on November 1. Noel started to change into an extratropical storm on November 2.
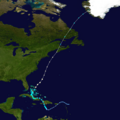
Tropical Storm Olga: After the Season Ends
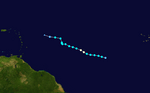
In the second week of December, after the official hurricane season ended, a low-pressure system formed east of the northern Lesser Antilles. On December 10, it became Subtropical Storm Olga north of Puerto Rico. This was the first storm after the season ended since 2005.
The storm made landfall on December 11 on the eastern tip of the Dominican Republic. Olga then changed into a tropical storm. It weakened further and became a leftover low-pressure system on December 12. Flooding and mudslides caused at least 22 deaths. One person was killed in Puerto Rico, two in Haiti, and at least 19 in the Dominican Republic.
- See the National Hurricane Center's advisory archive on Tropical Storm Olga.
Naming the Storms
The names below were used for storms that formed in the Atlantic basin in 2007. Because of the serious damage caused by Hurricanes Dean, Felix, and Noel, their names were retired. This means these names will not be used again for hurricanes. The names that were not retired will be used again in the 2013 season. Andrea was a new name used for the first time in 2007.
|
|
|
- Olga
- Pablo (unused)
- Rebekah (unused)
- Sebastien (unused)
- Tanya (unused)
- Van (unused)
- Wendy (unused)
|
How We Measure Storm Power: Accumulated Cyclone Energy
The table on the right shows the Accumulated Cyclone Energy (ACE) for each storm. ACE is a way to measure how much power a hurricane or tropical storm had. It combines how strong the storm was with how long it lasted. So, storms that were very strong or lasted a long time will have a high ACE value. ACE is only counted for tropical storms and hurricanes. Subtropical storms, like Andrea, are not officially included in the total ACE for the season.
|
Tropical cyclones of the 2007 Atlantic hurricane season
|
|
|
|
|
|
Images for kids
-
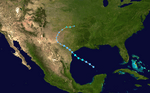
Subtropical Storm Andrea on May 9, 2007.
-
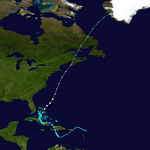
Track of Subtropical Storm Andrea.
-
Tropical Storm Barry on June 1, 2007.
-
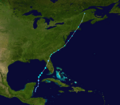
Track of Tropical Storm Barry.
-
Tropical Storm Chantal on July 31, 2007.
-
Track of Tropical Storm Chantal.
-
Hurricane Dean on August 20, 2007.
-
-
Tropical Storm Erin on August 15, 2007.
-
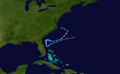
Track of Tropical Storm Erin.
-
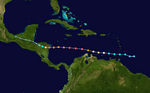
Hurricane Felix on September 2, 2007.
-
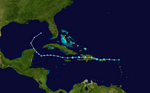
Track of Hurricane Felix.
-
Tropical Storm Gabrielle on September 9, 2007.
-
Track of Tropical Storm Gabrielle.
-
Tropical Storm Ingrid on September 14, 2007.
-
Track of Tropical Storm Ingrid.
-
Hurricane Humberto on September 12, 2007.
-
Track of Hurricane Humberto.
-
Tropical Depression Ten on September 21, 2007.
-
Track of Tropical Depression Ten.
-
Tropical Storm Jerry on September 24, 2007.
-
Track of Tropical Storm Jerry.
-
Hurricane Karen on September 26, 2007.
-
Track of Hurricane Karen.
-
Hurricane Lorenzo on September 27, 2007.
-
Track of Hurricane Lorenzo.
-
Tropical Depression Fourteen (Melissa) on September 28, 2007.
-
Track of Tropical Storm Melissa.
-
Tropical Depression Fifteen on October 11, 2007.
-
Track of Tropical Depression Fifteen.
-
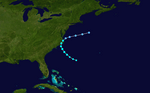
Hurricane Noel on October 28, 2007.
-
-
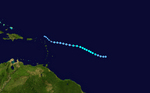
Tropical Storm Olga on December 11, 2007.
-
Track of Tropical Storm Olga.
See also
 In Spanish: Temporada de huracanes en el Atlántico de 2007 para niños
In Spanish: Temporada de huracanes en el Atlántico de 2007 para niños
 In Spanish: Temporada de huracanes en el Atlántico de 2007 para niños
In Spanish: Temporada de huracanes en el Atlántico de 2007 para niños