Megafauna facts for kids


Megafauna means "large animals." This term is often used for the huge land animals that lived during the last ice age, called the Pleistocene epoch. Think of animals like mammoths! It also describes the biggest wild land animals alive today, such as elephants, giraffes, hippopotamus, rhinoceros, and elk.
Many of these giant animals that lived 12,000 years ago are now extinct. Scientists are still discussing why this happened. The two main ideas are hunting by humans and big climate changes. Both of these reasons together could explain why these amazing animals disappeared. For example, Elephant birds on Madagascar and Moas in New Zealand were definitely hunted until they became extinct. The Moas had survived being hunted by the giant Haast's eagle, but they couldn't survive being hunted for food by the Maori people.
For many other megafauna, the changing climate might have been the main reason they died out.
Giant Animals of the Past
Many incredible megafauna once roamed the Earth. Some were huge land animals, while others were giant creatures of the sea or sky.
-
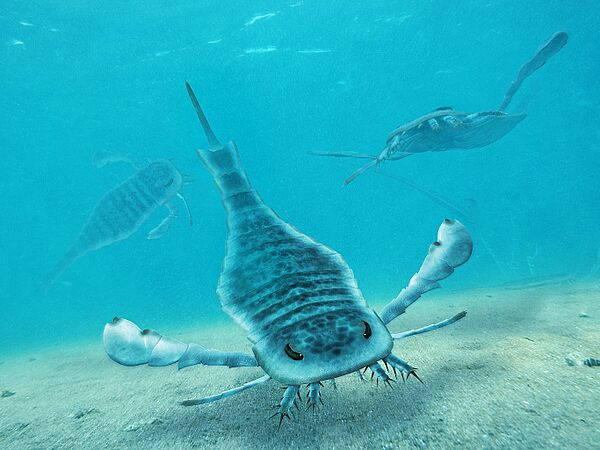
Some ancient Paleozoic sea scorpions, like Eurypterus, were bigger than a human!
-
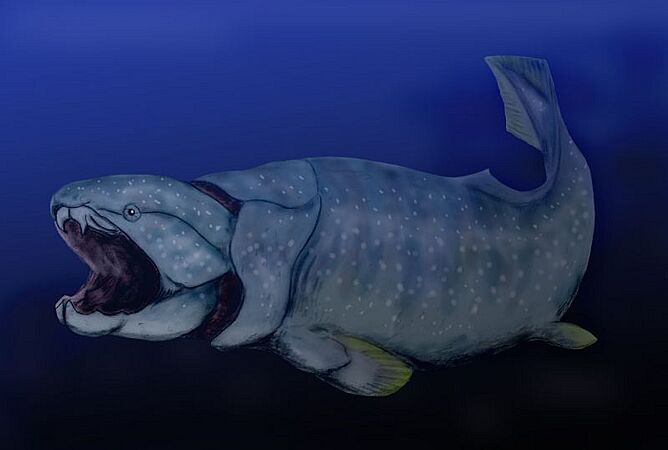
Dunkleosteus was a 10-meter (33-foot) long, armored fish with no teeth. It was a fierce hunter in the Devonian seas.
-
The sail-backed Dimetrodon and the amphibian Eryops lived in North America during the Permian period.
-
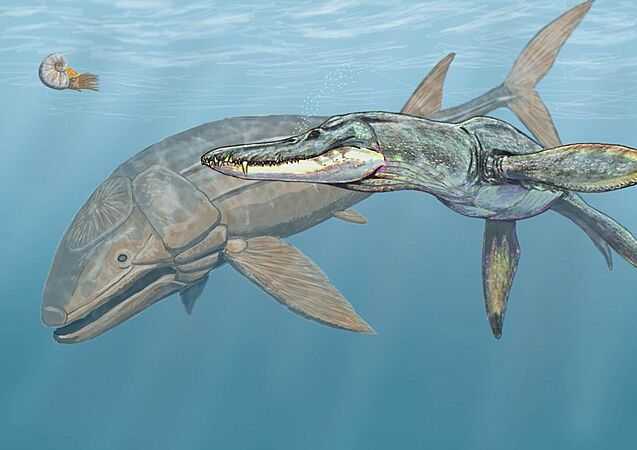
The Pliosaur Pliosaurus (right) hunted the huge filter-feeding fish Leedsichthys during the Jurassic period.
-
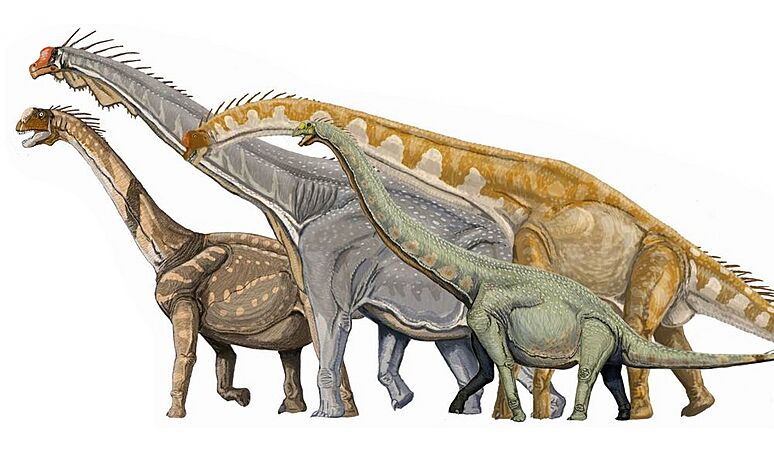
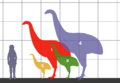
Giant sauropod dinosaurs. From left: Camarasaurus, Brachiosaurus, Giraffatitan, and Euhelopus.
-
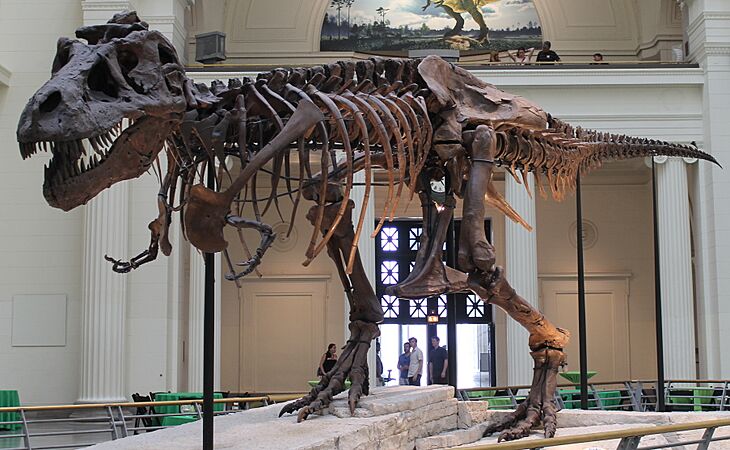
Tyrannosaurus was a 12.3-meter (40-foot) long theropod dinosaur. It was a top predator in western North America.
-
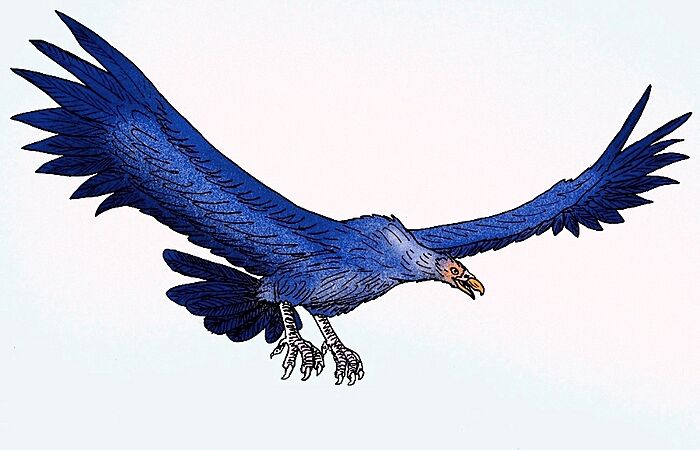
Argentavis was a huge bird from South America. It lived in the Late Miocene and had a wingspan of 7 meters (23 feet)!
-
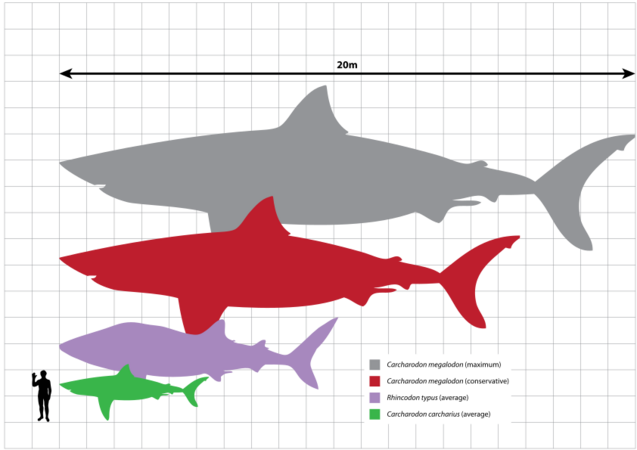
C. megalodon (two possible sizes) compared to a whale shark, great white shark, and a human.
-
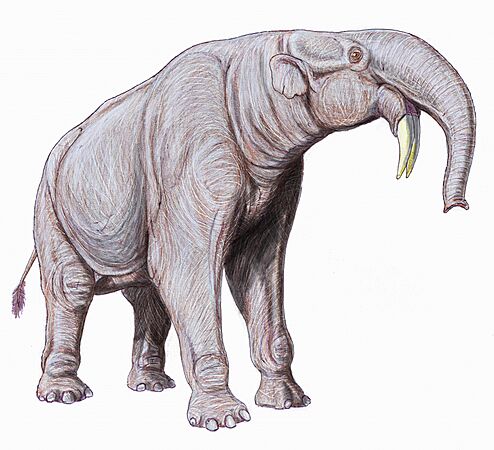
Deinotherium had tusks that curved downwards. These huge animals lived across Africa and Eurasia.
-
Titanis walleri was a 2.5-meter (8-foot) tall terror bird. It was the only one known to have moved into North America.
-
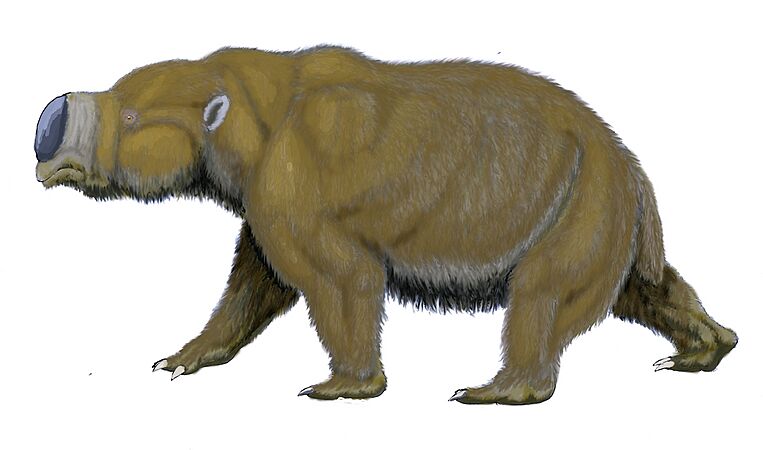
Diprotodon was the largest marsupial ever. It was the size of a hippo and lived in Australia, becoming extinct 40,000 years ago.
-
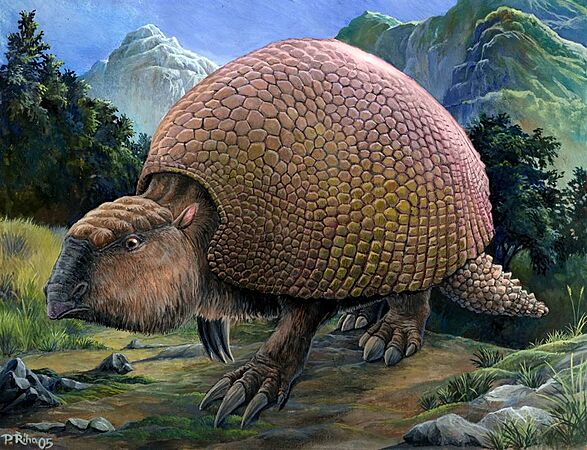
Glyptodon lived in South America during the Pleistocene. It was a relative of armadillos, about the size of a car!
-
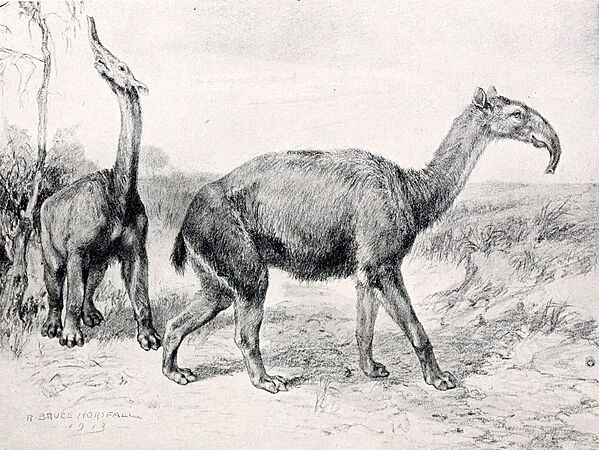
Macrauchenia was the last and largest litoptern from South America. It probably had a short trunk like a saiga.
-
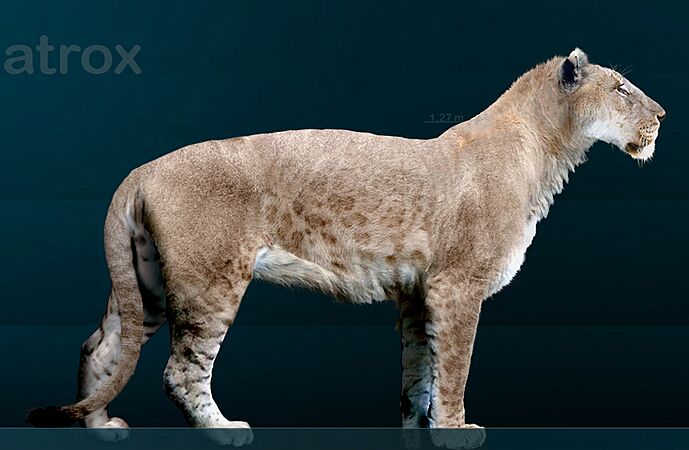
American lions were bigger than today's lions. They lived across much of North America until about 11,000 years ago.
-
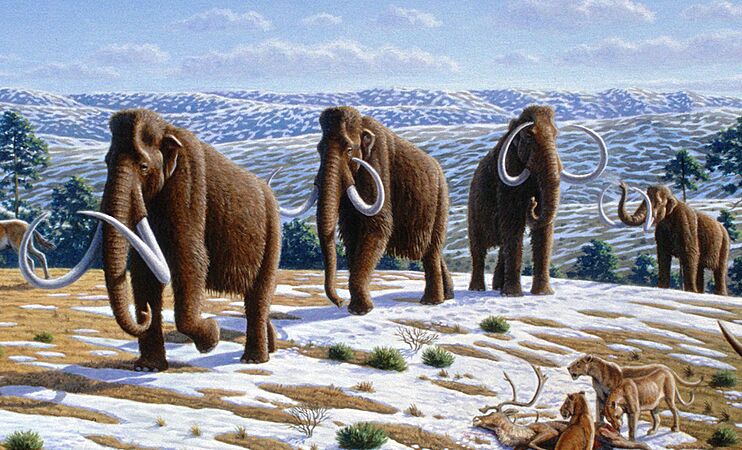
Woolly mammoths disappeared after humans arrived in their homes in Eurasia and North America.
-
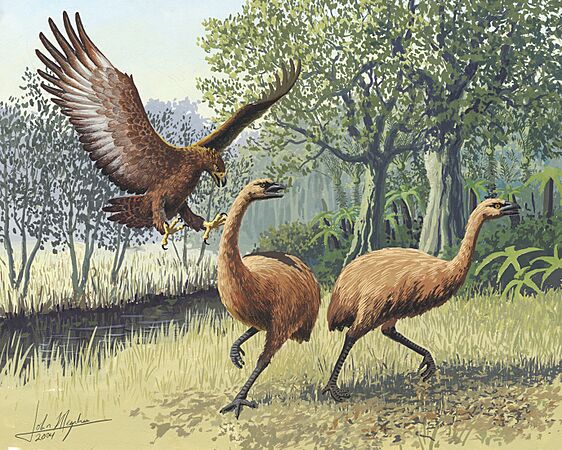
Haast's eagle, the largest eagle known, attacking a moa (which included the tallest bird known).
Giant Animals Alive Today
Even today, our planet is home to many incredible megafauna. These are some of the largest animals currently living.
-
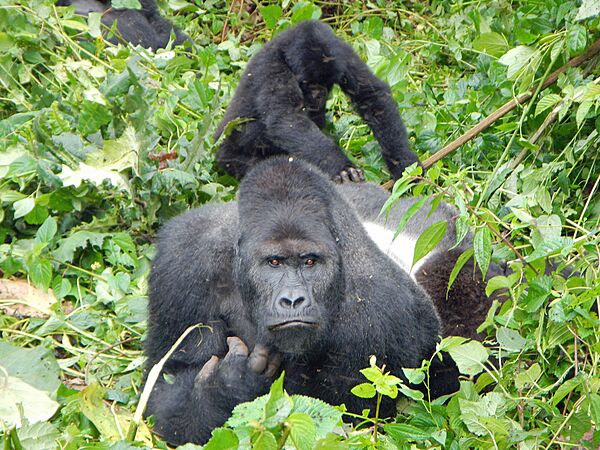
The eastern gorilla is the largest and one of the most endangered primates on Earth.
-
Bengal tigers are the most common tiger subspecies. They are endangered due to poaching and habitat destruction.
-
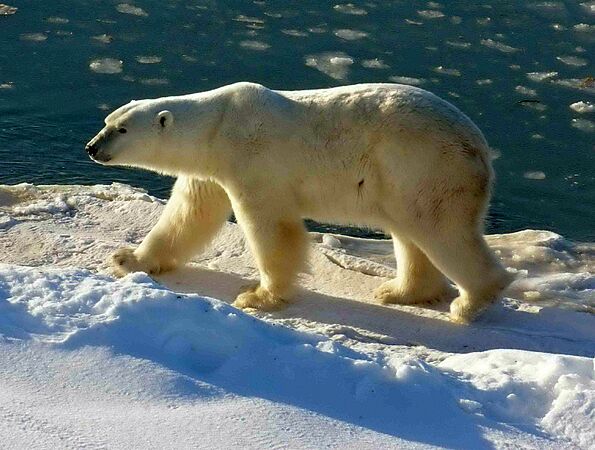
Polar bears are among the largest bears. They are vulnerable to global warming.
-
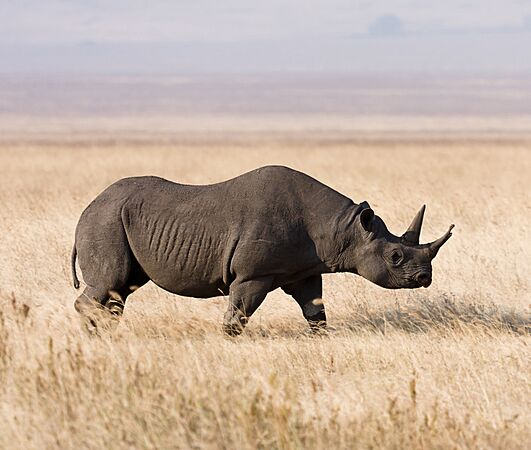
The critically endangered black rhinoceros can be up to 3.75 meters (12 feet) long. It is threatened by poaching.
-
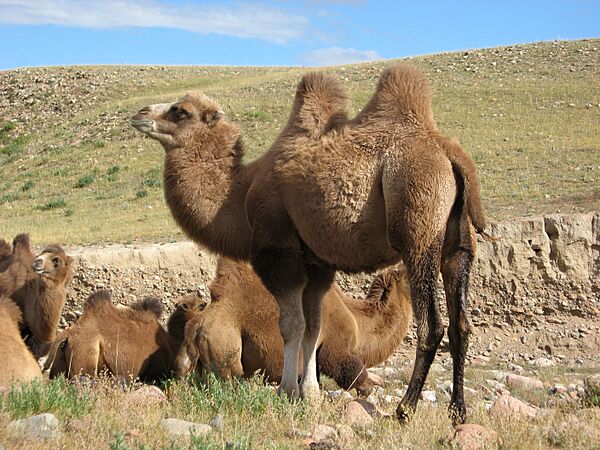
Wild Bactrian camels are critically endangered. Their ancestors came from North America.
-
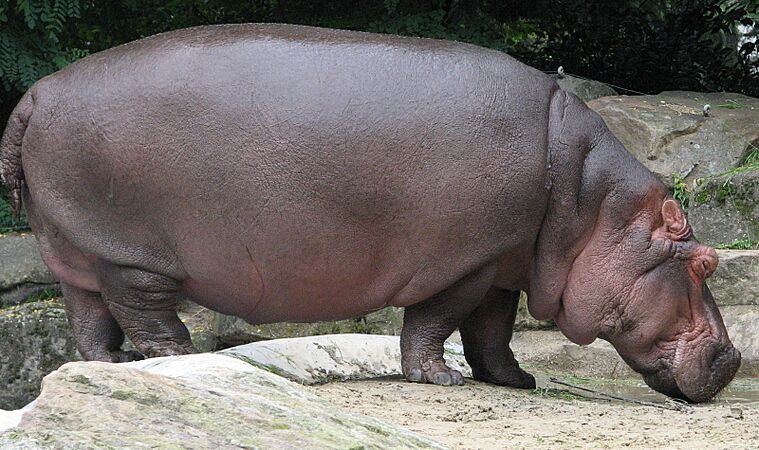
Hippos are the heaviest and most water-loving even-toed ungulates. They are the whales' closest living relatives.
-
The sperm whale is the largest toothed whale and the biggest toothed predator. It also has the biggest brain on Earth.
-
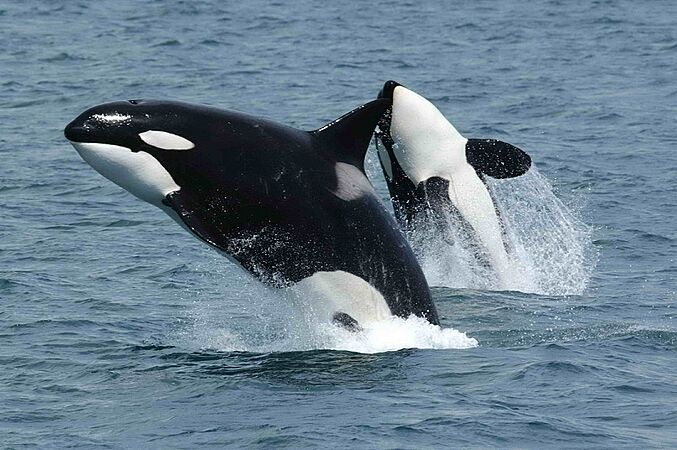
The orca is the largest dolphin and a pack hunter. They are very intelligent and live in complex groups.
-
The cassowary is the heaviest non-African bird. It can run at 50 km/h (31 mph) through thick rainforests.
-
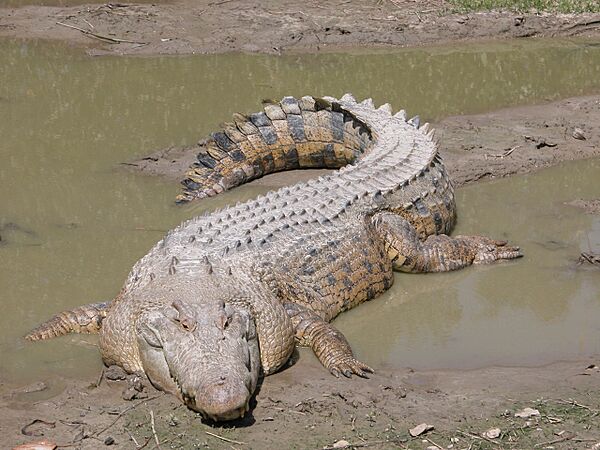
The saltwater crocodile is the largest living reptile. It is also a dangerous predator of humans.
-
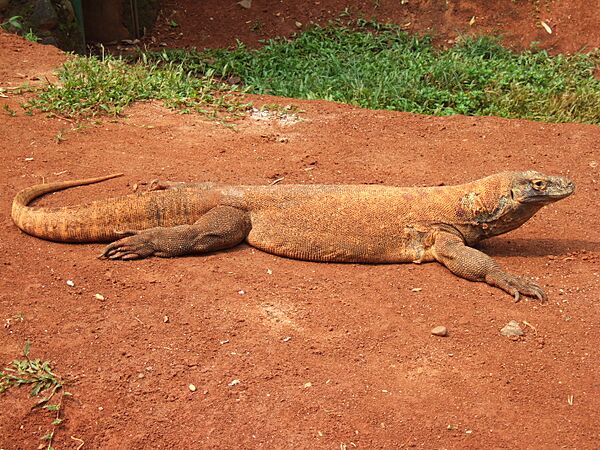
The Komodo dragon is a giant lizard from islands. It has serrated teeth and a venomous bite.
-
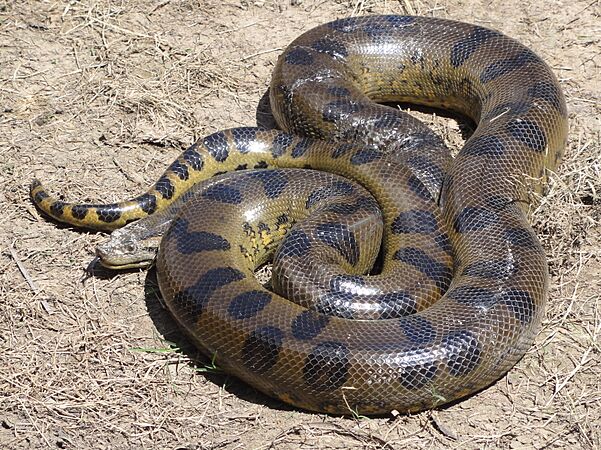
The green anaconda is an aquatic constrictor. It is the heaviest snake, weighing up to 97.5 kg (215 lb) or more.
-
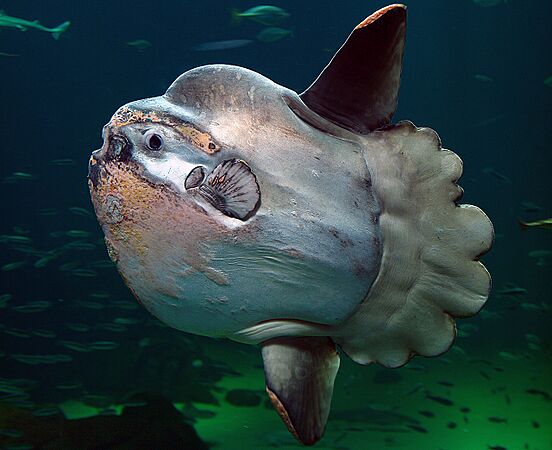
The ocean sunfish is the largest bony fish. It can dive very deep, but its skeleton is mostly cartilage.
-
The Nile perch is one of the largest freshwater fish. It is also a harmful invasive species in some places.
-
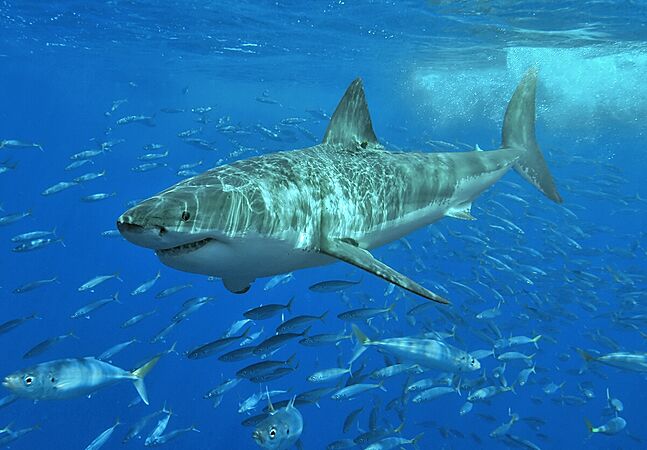
The great white shark is the largest fish that hunts other animals. It is more endangered than the tiger.
-
This image shows a 9-meter (30-foot) giant squid. It is a giant from the deep sea and the second largest cephalopod.
Images for kids
-
The African bush elephant, Earth's largest living land animal.
-
A size comparison between a human and 4 moa species: 1. Dinornis novaezealandiae 2. Emeus crassus 3. Anomalopteryx didiformis 4. Dinornis robustus
-
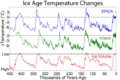
This graph shows how global climate change has happened in cycles over the last 450,000 years.
-
Leedsichthys was a filter-feeding fish from the mid-Jurassic period. It could grow to be 7 to 16.5 meters (23-54 feet) long.
-
The Spinosaurus (left) was the largest land predator ever. It was 12.6 to 18 meters (41-59 feet) long.
-
Reconstructed jaws of C. megalodon at the Baltimore Aquarium.
-
Titanis walleri was a terror bird that moved into North America. It was 2.5 meters (8 feet) tall.
-
Macrauchenia was the last and largest litoptern from South America. It might have had a short trunk like a saiga or nostrils like a moose.
See also
 In Spanish: Megafauna para niños
In Spanish: Megafauna para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |