Connecticut facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Connecticut
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
Nickname(s):
|
|||
Motto(s):
|
|||
| Anthem: "Yankee Doodle" |
|||
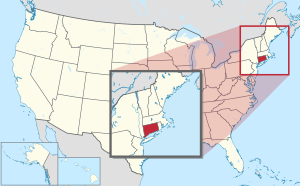
Location of Connecticut within the United States
|
|||
| Country | United States | ||
| Before statehood | Connecticut Colony | ||
| Admitted to the Union | January 9, 1788 (5th) | ||
| Capital | Hartford | ||
| Largest city | Bridgeport | ||
| Largest county or equivalent | Capitol | ||
| Largest metro and urban areas | New York (combined) Greater Hartford (metro and urban) |
||
| Legislature | General Assembly | ||
| • Upper house | Senate | ||
| • Lower house | House of Representatives | ||
| Judiciary | Connecticut Supreme Court | ||
| U.S. senators | Richard Blumenthal (D) Chris Murphy (D) |
||
| U.S. House delegation | 5 Democrats (list) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 5,543 sq mi (14,356 km2) | ||
| • Land | 4,849 sq mi (12,559 km2) | ||
| • Water | 698 sq mi (1,809 km2) 12.6% | ||
| Area rank | 48th | ||
| Dimensions | |||
| • Length | 70 mi (113 km) | ||
| • Width | 110 mi (177 km) | ||
| Elevation | 500 ft (150 m) | ||
| Highest elevation
(Massachusetts border on south slope of Mount Frissell)
|
2,379 ft (725 m) | ||
| Lowest elevation | 0 ft (0 m) | ||
| Population
(2024)
|
|||
| • Total | |||
| • Rank | 29th | ||
| • Density | 745/sq mi (288/km2) | ||
| • Density rank | 4th | ||
| • Median household income | $91,700 (2023) | ||
| • Income rank | 6th | ||
| Demonym(s) |
|
||
| Language | |||
| • Official language | None | ||
| Time zone | UTC−05:00 (Eastern) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 (EDT) | ||
| USPS abbreviation |
CT
|
||
| ISO 3166 code | US-CT | ||
| Traditional abbreviation | Conn. | ||
| Latitude | 40°58′ N to 42°03′ N | ||
| Longitude | 71°47′ W to 73°44′ W | ||
Connecticut (![]() i/kəˈnɛtɪkət/ KƏ-net-IK-ət) is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It shares borders with Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, and New York to the west. To the south, it meets Long Island Sound.
i/kəˈnɛtɪkət/ KƏ-net-IK-ət) is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It shares borders with Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, and New York to the west. To the south, it meets Long Island Sound.
The capital city of Connecticut is Hartford. The largest city by population is Bridgeport. Connecticut is located between the big cities of New York City and Boston. It is the third-smallest state by area in the U.S. It is also one of the most densely populated states.
The state gets its name from the Connecticut River. This river is the longest in New England. Its name comes from a Mohegan-Pequot word, Quinnetuket. This means "long tidal river." Before Europeans arrived, different Algonquian tribes lived here.
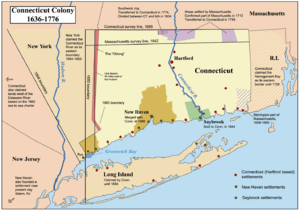
In 1633, the Dutch built a small settlement called House of Hope in Hartford. But the first main settlements were started by the English. Thomas Hooker led people from the Massachusetts Bay Colony to form the Connecticut Colony. Other English settlers founded the Saybrook Colony and the New Haven Colony. These all joined together by 1664.
Connecticut's official nickname is "The Constitution State." This is because of the Fundamental Orders adopted in 1639. Some people consider this to be the first written constitution in Western history. Connecticut was one of the Thirteen Colonies that fought against British rule in the American Revolution. It helped shape the federal government of the United States.
In 1787, Roger Sherman and Oliver Ellsworth from Connecticut suggested a compromise for the U.S. Congress. This idea led to the two-house system we have today. One house has members based on population, and the other has an equal number from each state. In January 1788, Connecticut was the fifth state to approve the U.S. Constitution.
Today, Connecticut is a developed and wealthy state. It has many good schools, like Yale University in New Haven. The United States Coast Guard Academy is in New London. The state is also known for aerospace companies like Pratt & Whitney and Sikorsky Aircraft. Historically, it made arms and hardware. Now, its economy focuses on finance, insurance, and real estate. Many big companies in these areas are in Hartford and Fairfield County.
Contents
History of Connecticut
Early Explorers and Settlers
The first European to explore Connecticut was Adriaen Block from the Netherlands in 1614. Dutch fur traders later built a fort called "House of Hope" in what is now Hartford.
The name "Connecticut" comes from the Mohegan Indian word "Quinnehtukqut." It means "Long River Place" or "Beside the Long Tidal River."
The first English settlers arrived in 1633. They were Puritans from Massachusetts, led by Reverend Thomas Hooker. They started the Connecticut Colony. Other colonies were also set up at Old Saybrook and New Haven. These later became part of Connecticut.
Because there were more English settlers than Dutch, the Dutch left their fort in 1654.
Connecticut's Constitution
Connecticut's first constitution, called the "Fundamental Orders," was adopted on January 14, 1639. This document helped set up the government. Connecticut was the fifth of the original thirteen states to join the United States.
The state's borders have changed over time. Originally, Connecticut's charter in 1662 said it owned all the land to the "South Sea," which meant the Pacific Ocean. But agreements with New York and Pennsylvania later set the state's current boundaries.
- Connecticut in the 21st Century
-
George W. Bush, born in Connecticut, was a U.S. President.
-
Tropical Storm Irene hit Connecticut in 2011.
-
Hurricane Sandy caused a lot of damage in 2012.
Geography and Climate
- Landmarks and Cities of Connecticut
-
Mount Frissell, the highest point in the state.
-
Lake McDonough from the Tunxis Trail.
-
The Connecticut River near Connecticut Route 82.
Connecticut is bordered by Long Island Sound to the south. New York is to the west, Massachusetts to the north, and Rhode Island to the east. The capital city is Hartford. Other large cities include Bridgeport, New Haven, and Stamford.
The highest point in Connecticut is on the southern slope of Mount Frissell. Its peak is actually in Massachusetts. Many coastal towns are very close to sea level.
The Connecticut River flows through the middle of the state. It empties into Long Island Sound. Even though Connecticut is small, its landscape changes a lot. In the northwest, you'll find rolling mountains. Along the coast, there are marshes and beaches.
The state has both rural areas and busy cities. The northeast and northwest parts are more rural. Cities like Stamford, Bridgeport, and New Haven are industrial and located along the coast.
Areas managed by the National Park Service include parts of the Appalachian Trail. Also, the Quinebaug and Shetucket Rivers Valley National Heritage Corridor and Weir Farm National Historical Park.
Connecticut's Weather

Most of Connecticut has a humid continental climate. This means cold winters and hot, humid summers. The far southern and coastal areas have a milder, humid temperate climate. This brings hot, humid summers and cool to cold winters with a mix of rain and snow. Connecticut usually gets a good amount of rain or snow throughout the year.
Thunderstorms happen often in the summer. They can be strong, and the state usually sees about one tornado each year. Tropical storms can also affect the region during hurricane season.
Plants and Trees
Connecticut has many different kinds of trees and plants. Forests in the southern parts have oak trees. In the northwest, you'll find New England–Acadian forests.
The state flower is the Mountain Laurel. It grows on low ridges. The Rosebay Rhododendron is also native to eastern Connecticut. You can find some of the largest wild rhododendrons in the U.S. at Pachaug State Forest.
Government and Laws

Hartford has been the only capital of Connecticut since 1875. Before that, New Haven and Hartford took turns being the capital.
Why "Constitution State"?
Connecticut is called the "Constitution State." This nickname likely comes from its important role in the 1787 U.S. Constitutional Convention. During this meeting, Roger Sherman and Oliver Ellsworth from Connecticut helped create the "Connecticut Compromise." This plan combined ideas from other states to form a two-house legislature for the U.S. Congress. This design is still used today.
The nickname also refers to the Fundamental Orders of 1638–39. These orders were the first formal government framework written by a representative group in Connecticut.
How the Government Works
Connecticut's government has three main parts:
- Executive Branch: This branch is led by the Governor. The Governor makes sure state laws are carried out. In 1974, Ella Grasso became the first woman in U.S. history to be elected governor without her husband having been governor first.
- Legislative Branch: This is called the General Assembly. It has two parts: the State Senate (36 senators) and the House of Representatives (151 representatives). They make the laws for the state.
- Judicial Branch: The highest court is the Connecticut Supreme Court. It decides if laws are fair and constitutional.
Local Government
Connecticut does not have county governments like most other states. Instead, it is divided into 169 towns. These towns are the main local government areas. Many cities in Connecticut, like Bridgeport and New Haven, have their city government combined with their town government.
People of Connecticut
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 237,946 | — | |
| 1800 | 251,002 | 5.5% | |
| 1810 | 261,942 | 4.4% | |
| 1820 | 275,248 | 5.1% | |
| 1830 | 297,675 | 8.1% | |
| 1840 | 309,978 | 4.1% | |
| 1850 | 370,792 | 19.6% | |
| 1860 | 460,147 | 24.1% | |
| 1870 | 537,454 | 16.8% | |
| 1880 | 622,700 | 15.9% | |
| 1890 | 746,258 | 19.8% | |
| 1900 | 908,420 | 21.7% | |
| 1910 | 1,114,756 | 22.7% | |
| 1920 | 1,380,631 | 23.9% | |
| 1930 | 1,606,903 | 16.4% | |
| 1940 | 1,709,242 | 6.4% | |
| 1950 | 2,007,280 | 17.4% | |
| 1960 | 2,535,234 | 26.3% | |
| 1970 | 3,031,709 | 19.6% | |
| 1980 | 3,107,576 | 2.5% | |
| 1990 | 3,287,116 | 5.8% | |
| 2000 | 3,405,565 | 3.6% | |
| 2010 | 3,574,097 | 4.9% | |
| 2020 | 3,605,944 | 0.9% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 3,617,176 | 1.2% | |
| Sources: | |||
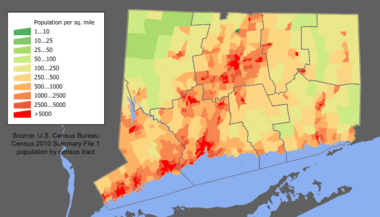
As of 2020, Connecticut has a population of over 3.6 million people. About 20% of the population is under 18 years old.
Most of western and southern Connecticut is closely linked to New York City. This area is known for being wealthy. The center of Connecticut's population is in the town of Cheshire.
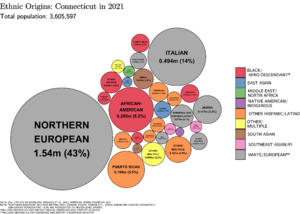
Connecticut has a diverse population. While most people are non-Hispanic white, the number of Hispanic/Latino and Asian Americans has grown. In 2000, about 81% of residents spoke English at home. Spanish was the next most common language.
Many people in Connecticut have Italian, Irish, English, German, or Polish backgrounds. The state also has immigrants from India, Jamaica, and the Dominican Republic.
Religion in Connecticut
Many people in Connecticut identify as Protestant or Roman Catholic. There are also Jewish, Orthodox, Hindu, Buddhist, and Muslim communities. A large number of people also say they are not religious.
Connecticut's Economy

Connecticut is a wealthy state. Its economy is strong, especially in finance, insurance, and real estate. Many major companies in these fields are located here. For example, The Hartford and Travelers are big insurance companies.
Manufacturing is also important, with companies like Raytheon Technologies (which includes Pratt & Whitney) and Sikorsky Aircraft. Sikorsky makes helicopters in Stratford. Electric Boat in Groton builds submarines.
Tourism is a big part of the economy too. Foxwoods Resort Casino and Mohegan Sun are popular places to visit. They are also major employers in the state.
Connecticut's farms produce nursery plants, milk, eggs, vegetables, and fruit.
Getting Around Connecticut
Roads and Highways
Major highways in Connecticut include I-95 along the coast, I-84 in the center, and I-91 going north-south. The Merritt Parkway and Wilbur Cross Parkway are also important roads. These roads used to have tolls, but they were removed in 1988.
I-95 between New Haven and New York City can get very crowded. The state encourages people to use trains or carpool to reduce traffic.
Connecticut has a strong bicycling community. New Haven has one of the highest rates of people who bike to work on the East Coast.
Trains
Trains are a popular way to travel between New Haven and New York City. The Metro-North Railroad serves southwestern Connecticut. Amtrak also runs frequent trains through the state.
A new commuter train service, the Hartford Line, started in 2018. It connects New Haven and Springfield, Massachusetts.
Buses
Connecticut Transit provides bus service across the state. Bus networks are very important in cities like Hartford and New Haven. CTfastrak is a special bus rapid transit service between New Britain and Hartford.
Airports

Connecticut's largest airport is Bradley International Airport near Hartford. Many people also use airports in New York for international travel. Smaller airports serve regional flights.
Ferries
Several ferry services cross Long Island Sound. They connect Connecticut to Long Island. Ferries also go from New London to places like Orient, New York and Block Island, Rhode Island. Two ferries cross the Connecticut River. The Rocky Hill–Glastonbury ferry has been running since 1655, making it the oldest continuously operating ferry in the U.S.
Education in Connecticut

Connecticut is known for its strong education system. It often ranks high for educational performance in the U.S.
Schools for Kids
Hartford Public High School (founded in 1638) is one of the oldest high schools in the country. The Connecticut State Board of Education oversees public schools for students from kindergarten to 12th grade.
Connecticut also has many private schools. Some well-known ones include Choate Rosemary Hall and The Hotchkiss School.
Colleges and Universities

Connecticut was home to the first law school in the nation, Litchfield Law School, from 1773 to 1833. Today, famous universities in the state include Yale University, Wesleyan University, and the University of Connecticut (UConn). The United States Coast Guard Academy is located in New London.
Sports in Connecticut
Connecticut has several professional and college sports teams.
Professional Teams
Connecticut has two teams in the American Hockey League: the Bridgeport Islanders and the Hartford Wolf Pack. In baseball, the Hartford Yard Goats and Norwich Sea Unicorns play here. The Connecticut Sun is a women's basketball team in the WNBA. Hartford Athletic is a soccer team that started in 2019.

The state also hosts big sporting events. The Travelers Championship is a PGA Tour golf tournament held in the Hartford area. Lime Rock Park in Salisbury is a famous road racing course.
College Sports
The Connecticut Huskies (UConn) play NCAA Division I sports. Their men's and women's basketball teams have won many national championships. In 2004 and 2014, UConn became the only school to win both men's and women's basketball national titles in the same year. The UConn women's team holds a record for the longest winning streak in college basketball.
New Haven hosts "The Game" between Yale and Harvard every two years. Walter Camp, known as the "Father of American Football," helped create modern football while living in New Haven.
Connecticut's Name and Symbols
| Song |
|
|---|---|
| Dance | Square dance |
| Bird | American robin |
| Fish | American shad |
| Flower | Mountain laurel |
| Tree | Charter Oak, a white oak |
| Insect | European mantis |
The name "Connecticut" comes from the Mohegan word quonehtacut. This means "place of long tidal river."
Connecticut's official nickname is "The Constitution State." This was adopted in 1959. It refers to its colonial constitution from 1638–1639, which was very important.
The state is also unofficially called "The Nutmeg State." The reason for this nickname is not fully known. It might come from sailors bringing nutmeg back from voyages. Or from early peddlers who sold nutmeg grinders. Some even say it's because peddlers from Connecticut would sell fake wooden nutmegs!
George Washington called Connecticut "The Provisions State." This was because the state provided a lot of help during the American Revolutionary War. Connecticut is also known as "The Land of Steady Habits."
A person from Connecticut is called a "Connecticuter" or sometimes a "Nutmegger" or "Yankee".
The official state song is "Yankee Doodle". The short form for the state's name is "Conn." The official postal abbreviation is CT.
Commemorative stamps from the U.S. Postal Service with Connecticut themes include Nathan Hale and the whaling ship Charles W. Morgan.
-
The Charter Oak.
| State aircraft | Vought F4U Corsair |
| State hero | Nathan Hale |
| State heroine | Prudence Crandall |
| State composer | Charles Edward Ives |
| State statues in National Statuary Hall | Roger Sherman and Jonathan Trumbull |
| State poet laureate | Margaret Gibson |
| Connecticut State Troubadour | Nekita Waller |
| State composer laureate | Jacob Druckman |
Notable People from Connecticut
See also
 In Spanish: Connecticut para niños
In Spanish: Connecticut para niños