Pierce County, Washington facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Pierce County
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|

Old City Hall in Tacoma.
|
|||
|
|||
Location within the U.S. state of Washington
|
|||
 Washington's location within the U.S. |
|||
| Country | |||
| State | |||
| Founded | December 22, 1852 | ||
| Named for | Franklin Pierce | ||
| Seat | Tacoma | ||
| Largest city | Tacoma | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 1,806 sq mi (4,680 km2) | ||
| • Land | 1,670 sq mi (4,300 km2) | ||
| • Water | 137 sq mi (350 km2) 7.6%% | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • Total | 921,130 | ||
| • Estimate
(2023)
|
928,696 |
||
| • Density | 510.04/sq mi (196.93/km2) | ||
| Time zone | UTC−8 (Pacific) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−7 (PDT) | ||
| Congressional districts | 6th, 8th, 10th | ||


Pierce County is a large area of land in the U.S. state of Washington. It is like a big neighborhood with many towns and cities. In 2020, about 921,130 people lived here. This makes it the second-most populated county in Washington, after King County. It is also the 59th most populated county in the whole United States.
The main city and county seat is Tacoma. Pierce County was created on December 22, 1852. It was named after U.S. President Franklin Pierce. The county is part of the larger Seattle metropolitan area, which includes Tacoma and Bellevue.
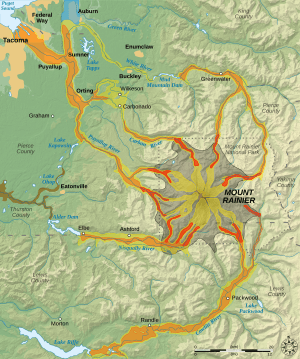
Pierce County is home to Mount Rainier, a huge volcano. It is the tallest mountain in the Cascade Range. Mount Rainier last erupted between 1820 and 1854. Scientists believe it will erupt again someday, but there is no immediate danger. If it does erupt, parts of Pierce County could be affected by mudslides (called lahars), lava, or hot ash and gas (called pyroclastic flows). To keep people safe, the Mount Rainier Volcano Lahar Warning System was set up in 1998. This system helps warn people in the Puyallup River valley if an eruption is happening.
Contents
- Exploring Pierce County's Geography
- Understanding Pierce County's Population
- A Look at Pierce County's History
- Pierce County's Economy and Jobs
- Learning and Education in Pierce County
- Getting Around: Transportation in Pierce County
- Arts and Culture in Pierce County
- Law Enforcement in Pierce County
- Communities in Pierce County
- Notable People from Pierce County
- See also
Exploring Pierce County's Geography
Pierce County covers a total area of about 1,806 square miles. Most of this is land (1,670 square miles), and a smaller part is water (137 square miles). The highest point in Washington state, Mount Rainier, is located here. It stands at 14,410 feet tall. Local Native American tribes call Mount Rainier "Tahoma" or "Takhoma."
Important Geographic Features
Pierce County has many interesting natural places:
- Anderson Island
- Carbon River
- Cascade Range
- Case Inlet
- Commencement Bay
- Fox Island
- Herron Island
- Ketron Island
- Key Peninsula
- Lake Tapps
- McNeil Island
- Mount Rainier, the tallest point in the county and Washington state.
- Nisqually River
- Puget Sound
- Puyallup River
- Raft Island
- Tacoma Narrows
The county also includes the Clearwater Wilderness area, a protected natural space.
Neighboring Counties of Pierce County
Pierce County shares borders with several other counties:
- King County to the north
- Yakima County to the east
- Lewis County to the south
- Thurston County to the west and southwest
- Mason County to the west and northwest
- Kitsap County to the north and northwest
Protected Natural Areas
Parts of these national protected areas are found in Pierce County:
- Mount Baker-Snoqualmie National Forest
- Mount Rainier National Park
- Nisqually National Wildlife Refuge
Understanding Pierce County's Population
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1860 | 1,115 | — | |
| 1870 | 1,409 | 26.4% | |
| 1880 | 3,319 | 135.6% | |
| 1890 | 50,940 | 1,434.8% | |
| 1900 | 55,515 | 9.0% | |
| 1910 | 120,812 | 117.6% | |
| 1920 | 144,127 | 19.3% | |
| 1930 | 163,842 | 13.7% | |
| 1940 | 182,081 | 11.1% | |
| 1950 | 275,876 | 51.5% | |
| 1960 | 321,590 | 16.6% | |
| 1970 | 411,027 | 27.8% | |
| 1980 | 485,643 | 18.2% | |
| 1990 | 586,203 | 20.7% | |
| 2000 | 700,820 | 19.6% | |
| 2010 | 795,225 | 13.5% | |
| 2020 | 921,130 | 15.8% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 928,696 | 16.8% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790–1960 1900–1990 1990–2000 2010–2020 |
|||
Population in 2020
In 2020, Pierce County had 921,130 people living in 339,840 households. About 23% of the population was under 18 years old. Around 14% of people were over 65 years old. The population was almost evenly split between females (49.8%) and males (50.2%).
The average household had 2.65 people. The median income for a household was $82,574. This means half of the households earned more than this, and half earned less. About 8.2% of the people in Pierce County lived below the poverty line.
Population in 2010
In 2010, there were 795,225 people in Pierce County. The population density was about 476 people per square mile. Most people (74.2%) were white. Other groups included African American (6.8%), Asian (6.0%), Native American (1.4%), and Pacific Islander (1.3%). About 9.2% of the population was of Hispanic or Latino background.
The median age in 2010 was 35.9 years. The median income for a household was $57,869. About 11.6% of the population lived below the poverty line. This included 15% of those under 18.
A Look at Pierce County's History
Long ago, the area of Pierce County was home to several Native American tribes. These included the Nisqually, Puyallup, Squaxin, Steilacoom, and Muckleshoot tribes. They had well-established trade routes and villages.
In 1792, British explorer Captain George Vancouver arrived by ship. He named many places in the area, including Mt. Rainier.
In 1832, the British Hudson's Bay Company built Fort Nisqually. This was the first permanent European settlement in the Salish Sea region. They worked with local tribes and built a storehouse.
In 1839, the Nisqually Methodist Episcopal Mission was started. This brought the first U.S. citizens to settle in the Puget Sound area.
In 1841, the United States Exploring Expedition came to map the waters of Puget Sound. Later, in 1843, a second Fort Nisqually was built. It focused more on farming and raising cattle. The fort was given to American control in 1859.
In 1846, the Oregon Treaty set the border between British Canada and the United States. This placed Pierce County in U.S. territory. To deal with growing tensions between Native Americans and settlers, the U.S. Army built Fort Steilacoom in 1849.
In 1850, Captain Lafayette Balch started the town of Port Steilacoom. By 1854, Steilacoom became the first official town in Washington Territory.
The Treaty of Medicine Creek
In 1854, the Treaty of Medicine Creek was signed. This treaty was between the United States and the local Native American tribes of the Salish Sea. Tribes like the Nisqually and Puyallup were part of this treaty. Governor Isaac I. Stevens signed it for the U.S. government.
The tribes were told the treaty would help them by paying for some of their land. However, it ended up taking away valuable farmland and moving the tribes to difficult reservations. Chief Leschi of the Nisqually tribe spoke out against the treaty. He and his people tried to protest, but Governor Stevens ordered them away. This led to conflict, and Chief Leschi was later arrested.
After a trial, Chief Leschi was found guilty. He was executed in 1858. However, in 2004, a special court in Pierce County reviewed his case. They decided that Chief Leschi was a soldier fighting in a war and should not have been held responsible for the death of an enemy soldier. This ruling cleared his name.
Pierce County's Economy and Jobs
The biggest public employer in Pierce County is Joint Base Lewis–McChord. This military base provides about 60,000 jobs for military members and civilians. The largest private employers are MultiCare Health System and Virginia Mason Franciscan Health. These companies run the two biggest hospitals in the county.
Farming has been important to Pierce County for almost 150 years. However, in the last 50 years, much of the farmland has been used for homes. Pierce County is working to protect its remaining farms. They created the Pierce County Farm Advisory Commission. This group helps farmers with rules and promotes local produce. Even with less farmland, Pierce County still grows about half of all the rhubarb in the United States!
Learning and Education in Pierce County
Pierce County has many public school districts. Some of these districts also serve parts of other counties.
Public School Districts
- Auburn School District
- Bethel School District
- Carbonado School District
- Clover Park School District
- Dieringer School District
- Eatonville School District
- Fife School District
- Franklin Pierce School District
- Orting School District
- Peninsula School District
- Puyallup School District
- Steilacoom Historical School District
- Sumner-Bonney Lake School District
- Tacoma Public Schools
- University Place School District
- White River School District
- Yelm School District
Private Schools
Some private schools in the county include:
- Cascade Christian Schools
- Life Christian School and Academy
- Bellarmine
- Annie Wright Schools
- Charles Wright Academy
Chief Leschi Schools, which is connected to the Bureau of Indian Education, is also in the county.
Colleges and Universities
For higher education, the biggest schools are:
- University of Puget Sound in Tacoma
- Pacific Lutheran University in Parkland
Both of these are private universities with religious connections.
Public community colleges include:
- Tacoma Community College in Tacoma
- Pierce College in Steilacoom
There are also public technical colleges:
- Bates Technical College
- Clover Park Technical College
Other universities with campuses in Pierce County are:
- Central Washington University (Steilacoom campus)
- University of Washington Tacoma (a branch of University of Washington)
- The Evergreen State College (Tacoma campus)
Library System
Pierce County has several library systems, including the Pierce County Library System, the Tacoma Library System, and the Puyallup Public Library.
The Pierce County Library System is the fourth largest in Washington state. It has 20 branches, including:
- Administrative Center and Library
- Anderson Island
- Bonney Lake
- Buckley
- Dupont
- Eatonville
- Fife
- Gig Harbor
- Graham
- Key Center
- Lakewood
- Milton/Edgewood
- Orting
- Parkland/Spanaway
- South Hill
- Steilacoom
- Summit
- Sumner
- Tillicum
- University Place
The Pierce County Library System was started in 1944. It serves many cities and towns, and has over 1 million physical items like books and videos. It also has more than 480,000 online items.
Getting Around: Transportation in Pierce County
The Port of Tacoma is a very busy port. It is the sixth busiest container port in North America. This means many ships come and go, bringing goods from all over the world. The port covers 2,400 acres and has many facilities. It creates over 28,000 jobs in Pierce County.
Pierce County also has two airports for smaller planes: Pierce County Airport and Tacoma Narrows Airport.
Pierce Transit is the official transportation provider for the county. It offers buses, special transport for people with disabilities, and rideshare options. Sound Transit runs the Tacoma Link light rail line in downtown Tacoma. It also has express buses and a commuter train called Sounder. The Sounder train stops in Sumner, Puyallup, Tacoma, South Tacoma, and Lakewood. Amtrak trains also travel through the county, stopping in Tacoma.
On December 18, 2017, an Amtrak train had an accident in the county. It went off the tracks over Interstate 5. This sad event caused injuries to many people and resulted in some deaths.
Main Roads and Highways
Here are some of the major highways in Pierce County:
 Interstate 5
Interstate 5 Interstate 705
Interstate 705 State Route 7
State Route 7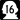 State Route 16 (which includes the Tacoma Narrows Bridge)
State Route 16 (which includes the Tacoma Narrows Bridge)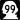 State Route 99
State Route 99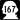 State Route 167
State Route 167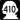 State Route 410
State Route 410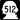 State Route 512
State Route 512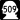 State Route 509
State Route 509
Ferry Services
Ferries help people travel across the water:
- Point Defiance–Tahlequah ferry (run by Washington State Ferries)
- Steilacoom–Anderson Island ferry (run by Pierce County)
Arts and Culture in Pierce County
Pierce County has a lively arts scene. There are many groups and places for arts and culture, such as:
- Broadway Center for the Performing Arts
- Grand Cinema
- Lakewood Playhouse
- Museum of Glass
- Northwest Sinfonietta
- Speakeasy Arts Cooperative
- Tacoma Art Museum
- Tacoma Little Theater
- Tacoma Concert Band
- Tacoma Musical Playhouse
- Tacoma Opera
- Symphony Tacoma
- Dance Theater Northwest
- Washington State History Museum
The city of Tacoma has an event called "Art at Work" month every November. It encourages people to enjoy and support local art. In 2012, LeMay-America's Car Museum opened in Tacoma. The Karpeles Manuscript Library Museum also has a large collection of old, original documents.
Two big annual events are:
- The Pierce County Daffodil Festival and Parade, held every April.
- The Washington State Fair, held every September in Puyallup.
Law Enforcement in Pierce County
The Pierce County Sheriff's Department was created in 1853. This was soon after the county was officially formed. They work to keep the community safe.
Communities in Pierce County
Pierce County is made up of many different cities, towns, and smaller communities.
Cities in Pierce County
- Auburn (partly in another county)
- Bonney Lake
- Buckley
- DuPont
- Edgewood
- Fife
- Fircrest
- Gig Harbor
- Lakewood
- Milton (partly in another county)
- Orting
- Pacific (partly in another county)
- Puyallup
- Roy
- Ruston
- Sumner
- Tacoma (the county seat)
- University Place
Towns in Pierce County
Census-Designated Places (CDPs)
CDPs are areas that are like towns but are not officially incorporated as cities or towns.
- Alder
- Alderton
- Anderson Island
- Artondale
- Ashford
- Browns Point
- Canterwood
- Clear Lake
- Clover Creek
- Crocker
- Dash Point
- Elbe
- Elk Plain
- Fife Heights
- Fort Lewis
- Fox Island
- Frederickson
- Graham
- Greenwater
- Herron Island
- Home
- Kapowsin
- Ketron Island
- Key Center
- La Grande
- Lake Tapps
- Longbranch
- Maplewood
- McChord AFB
- McKenna
- McMillin
- Midland
- North Fort Lewis
- North Puyallup
- Parkland
- Prairie Heights
- Prairie Ridge
- Purdy
- Raft Island
- Rosedale
- South Creek
- South Hill
- Spanaway
- Stansberry Lake
- Summit
- Summit View
- Vaughn
- Waller
- Wauna
- Wollochet
Unincorporated Communities
These are smaller communities that are not part of any city or town.
- American Lake
- Bee
- Burnett
- Crescent Valley
- Cromwell
- Electron
- Elgin
- Firwood
- Glencove
- Lakebay
- McNeil Island
- National
- Ohop
- Paradise
- Point Fosdick
- Shore Acres
- Shorewood Beach
- Sunny Bay
- Sylvan
- Tehaleh
- Victor
- Villa Beach
Notable People from Pierce County
- Jessie Kastner (1873-1957), a teacher and state politician.
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Pierce (Washington) para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Pierce (Washington) para niños