Belarus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of Belarus
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Anthem:
Дзяржаўны гімн Рэспублікі Беларусь (Belarusian) Dziaržaŭny Himn Respubliki Biełaruś Государственный гимн Республики Беларусь (Russian) Gosudarstvennyy gimn Respubliki Belarus "State Anthem of the Republic of Belarus" |
|
|
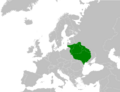
Location of Belarus (green)
on the European continent (dark grey) — [Legend] |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Minsk 53°55′N 27°33′E / 53.917°N 27.550°E |
| Official languages | |
| Recognized minority languages | |
| Ethnic groups
(2019)
|
|
| Religion
(2020)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Belarusian |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic under a dictatorship |
| Alexander Lukashenko | |
| Roman Golovchenko | |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Council of the Republic | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Formation | |
| 882 | |
| 25 March 1918 | |
|
• Socialist Soviet Republic of Byelorussia
|
1 January 1919 |
| 31 July 1920 | |
|
• Declaration of State Sovereignty
|
27 July 1990 |
| 25 August 1991 | |
| 19 September 1991 | |
|
• Current constitution
|
15 March 1994 |
| 8 December 1999 | |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
207,595 km2 (80,153 sq mi) (84th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
1.4% (2.830 km2 or 1.093 sq mi) |
| Population | |
|
• 2024 estimate
|
9,155,978 (98th) |
|
• Density
|
45.8/km2 (118.6/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2019) | ▲ 25.3 low |
| HDI (2022) | very high · 69th |
| Currency | Belarusian ruble (BYN) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (MSK) |
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +375 |
| ISO 3166 code | BY |
| Internet TLD |
|
|
|
Belarus (officially called Republic of Belarus) is a country in Eastern Europe. About nine million people live there. Its capital city is Minsk. Belarus was part of the Soviet Union until 1991. Alexander Lukashenko has been the president of Belarus since 1994.
Belarus shares borders with Russia, Ukraine, Poland, Lithuania, and Latvia. More than 40% of its land, which is about 207,600 square kilometres (80,200 sq mi), is covered by forests.
Belarus is a member of many international groups. These include the UN, the CIS, and the Union State with Russia.
Before the 1900s, the land that is now Belarus was part of different countries. These included the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Later, it became part of the Russian Empire. After the Russian Revolution, Belarus joined the Soviet Union. It was then called the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR).
In 1939, Belarus got its modern borders. Some lands from Poland were added after the Soviet invasion of Poland. The country was badly damaged during World War II. Belarus lost about one-third of its people and more than half of its economy. In 1945, the BSSR became one of the first members of the United Nations.
Belarus declared its independence on 27 July 1990. It became fully independent on 25 August 1991, when the Soviet Union broke apart.
Most of Belarus's 9.49 million people live in cities. Over 80% of the people are ethnic Belarusians. Others are Russians, Poles, and Ukrainians. The country has two official languages: Belarusian and Russian. The main religion is Russian Orthodox Christianity. Roman Catholicism is the second most common religion.
Contents
History of Belarus

Early History of Belarus
Evidence of early humans like Homo erectus and Neanderthals has been found in this area. Around 5,000 to 2,000 BCE, early farming cultures lived here. Later, Cimmerians and then Slavs moved in. The Huns and Avars also passed through.
Slavic tribes first settled the region of Belarus in the 6th century. They met Varangians, who were Scandinavian warriors and traders. Together, they formed Kievan Rus' in 862.
After the ruler Yaroslav the Wise died, Kievan Rus' split into smaller states. Parts of Belarus later joined the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. This duchy then formed a union with Poland. In 1795, this union ended, and Belarus became part of the Russian Empire. It stayed with Russia until World War I, when it was taken by the German Empire.
Belarus After Independence
Belarus declared itself free from Germany on 25 March 1918. They created the Belarusian People's Republic. After the Polish–Soviet War, part of Belarus under Russian rule became the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic in 1919. Other parts were divided between Poland and the Soviet Union. The Belorussian SSR became a founding member of the Soviet Union in 1922.
In 1939, Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union invaded Poland. Parts of Poland were added to the Belorussian SSR. These areas are now known as West Belarus.
In 1941, Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union. The BSSR was hit hardest during World War II. Germany destroyed most of its cities and industries. Between two and three million people died. Belarus's population did not return to its pre-war size until 1971.
After the war, Joseph Stalin wanted Belarus to be more like Russia. Russians were sent to work in the government. The use of the Belarusian language was limited. This continued even after Stalin died in 1953.
In 1986, the BSSR was affected by nuclear fallout from the Chernobyl disaster. This happened at a power plant in the nearby Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic.
Belarus declared its freedom on 27 July 1990. With support from the Communist Party, the country's name changed to the Republic of Belarus on 25 August 1991.
Geography of Belarus
Belarus is a landlocked country, meaning it has no coastlines. It is mostly flat and has many marshy areas. There are many streams and about 11,000 lakes. Three main rivers flow through Belarus: the Neman, the Pripyat, and the Dnieper.
The highest point in Belarus is Dzyarzhynskaya Hara, which is 345 metres (1,132 ft) tall. Belarus has a humid continental climate. This means it has warm summers and cold, snowy winters.
Belarus has natural resources like peat, small amounts of oil and natural gas, granite, and clay. About 70% of the radiation from the 1986 Chernobyl disaster in Ukraine spread into Belarus. Because of this, some farmland is still affected by radiation.
Politics and Government
Belarus is a presidential republic. It is led by a president and the National Assembly.
Human Rights in Belarus
The current president, Alexander Lukashenko, has described his way of ruling as "authoritarian." This means he has a lot of power. Western countries have called Belarus a dictatorship. The Council of Europe has not allowed Belarus to join since 1997 due to concerns about undemocratic voting.
Belarusian Military
The Armed Forces of Belarus have three main parts: the Army, the Air Force, and the Ministry of Defense joint staff. Lieutenant General Yuri Zhadobin leads the Ministry of Defense. President Alexander Lukashenko is the Commander-in-Chief.
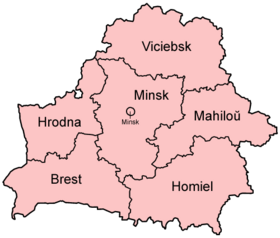
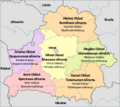
Regions of Belarus
Belarus is divided into six main regions. Each region is named after its main city.
Regions (with their main cities):
- Brest Region (Brest)
- Gomel Region (Gomel)
- Grodno Region (Grodno)
- Mogilev Region (Mogilev)
- Minsk Region (Minsk)
- Vitebsk Region (Vitebsk)
Special administrative district:
- Minsk City (the capital)
Economy of Belarus
Most of Belarus's economy is controlled by the state. It has been described as "Soviet-style." The country depends on Russia for some imports, like oil. Belarus's main exports include heavy machinery (like tractors), farm products, and energy products.
People of Belarus
According to a 2019 census, Belarus has 9.41 million people. Most of them (84.9%) are ethnic Belarusians. Other large groups include Russians (7.5%), Poles (3.1%), and Ukrainians (1.7%).
About 70% of the population lives in cities. The capital, Minsk, is the largest city with about 1.9 million people in 2015. Gomel is the second-largest city with 481,000 people. Other big cities are Mogilev (365,100), Vitebsk (342,400), Hrodna (314,800), and Brest (298,300).
|
Largest cities or towns in Belarus
http://www.geonames.org/BY/largest-cities-in-belarus.html |
||
|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Pop. |
| 1 | Minsk | 1,992,685 |
| 2 | Homyel | 536,938 |
| 3 | Mahilyow | 383,313 |
| 4 | Vitsyebsk | 378,459 |
| 5 | Hrodna | 373,547 |
| 6 | Brest | 350,616 |
| 7 | Babruysk | 216,793 |
| 8 | Baranavichy | 179,000 |
| 9 | Barysaw | 142,681 |
| 10 | Pinsk | 137,960 |
Culture of Belarus
Belarusian Literature

Belarusian literature started with religious writings between the 11th and 13th centuries. In the 16th century, Francysk Skaryna from Polotsk translated the Bible into Belarusian. Modern Belarusian literature began in the late 1800s. A famous writer from this time was Yanka Kupala. Many writers left Belarus during the Nazi occupation and returned in the 1960s. Important writers like Vasil Bykaŭ and Uladzimir Karatkievich published novels in the 1960s.
Belarusian Music
In the 1800s, Polish composer Stanisław Moniuszko created operas and chamber music while living in Minsk. By the end of the 19th century, major Belarusian cities had their own opera and ballet companies.
The National Academic Theatre of Ballet in Minsk won a top award in 1996. Rock music has become popular recently. The Belarusian government has tried to limit how much foreign music is played on the radio. Since 2004, Belarus has sent artists to the Eurovision Song Contest.
Traditional Dress
Traditional Belarusian clothing comes from the Kievan Rus' period. Because of the cool weather, clothes were made to keep people warm. They were usually made from flax or wool.
Belarusian Food

Belarusian food mainly uses vegetables, meat (especially pork), and different kinds of bread. Meals are often cooked slowly or stewed. A typical Belarusian eats a light breakfast and two bigger meals, with dinner being the largest. Wheat and rye breads are common. Rye is grown more easily because of the harsh weather. To show hospitality, hosts often offer bread and salt to guests.
Popular drinks include Russian wheat vodka and kvass. Kvass is made from fermented brown bread or rye flour. Kvass can also be added to sliced vegetables to make a cold soup called okroshka.
World Heritage Sites in Belarus
Belarus has four World Heritage Sites. These are special places recognized by UNESCO. They include the Mir Castle Complex, the Nesvizh Castle, and the Białowieża Forest (which is shared with Poland). The Struve Geodetic Arc is also a site, shared with nine other countries.
Images for kids
-
Kievan Rus' principalities before the Mongol and Lithuanian invasions
-
A map of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in the 15th century. Belarus was fully within its borders.
-
German soldiers in Minsk, August 1941
-
Khatyn Memorial; during World War II the Germans murdered civilians in many places in occupied Soviet Belarus.
-
Alexander Lukashenko has ruled Belarus since 1994.
-
Victory Square in Minsk
-
President Alexander Lukashenko, shaking hands with Russian President Vladimir Putin, 2015
-
Soldiers patrol in the Białowieża Forest on the Belarusian border with Poland.
-
Graffiti in Gdańsk showing Belarusian human rights activist Ales Bialiatski.
-
Victoria Azarenka, a professional tennis player and former world No. 1
See also
 In Spanish: Bielorrusia para niños
In Spanish: Bielorrusia para niños