English language facts for kids
Quick facts for kids English |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | British Isles (originally) Worldwide |
|||
| Native speakers | 360–400 million (date missing) L2 speakers: 400 million; as a foreign language: 600–700 million |
|||
| Language family | ||||
| Early forms: | ||||
| Writing system |
|
|||
| Official status | ||||
| Official language in |
Various organisations
|
|||
| Linguasphere | 52-ABA | |||
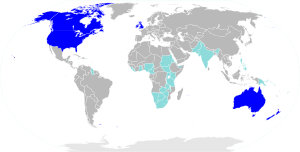
Countries of the world where English is a majority native language Countries where English is official but not a majority native language
|
||||
|
||||
English is a Germanic language that started in England. It came from the Anglo-Saxons, who were Germanic settlers. They brought their Anglo-Frisian and Old Saxon dialects to Britain in the early Middle Ages.
Today, English is a global lingua franca. This means it's a common language used by people from different countries to talk to each other. It became so widespread because of traders and the British Empire's colonies. The word "English" comes from the "Angles" tribe, who moved to England.
Frisian is the language most similar to English. English has borrowed many words over time. It took words from other Germanic languages and later from Romance languages, especially French.
English is an official language in almost 60 countries. These include the United Kingdom, Ireland, the United States, Canada, Singapore, India, Hong Kong, and South Africa. It's also widely spoken in Australia, New Zealand, parts of the Caribbean, Africa, and South Asia.
About 375 million people speak English as their first language. This makes it one of the most spoken native languages, after Chinese Mandarin and Spanish. Many people learn English as a second language. It's the official language of the United Nations and the European Union. English is the most spoken Germanic language, used by over 70% of all Germanic speakers. Around 220 million more people use it as a second language. It is often used for work, travel, and trade. About a billion people are currently learning English. This makes English the second most spoken language overall and the most international language in the world.
English has changed a lot over time, just like all languages. Many words came from Latin and Old French. These words joined Old English to form the English we speak today.
English grammar is now very different from other Germanic languages. It also doesn't sound much like Romance languages. Because nearly 60% of its words come from Latin, English is sometimes called the most "Latin" of the Germanic languages. People sometimes even mistake it for a Romance language.
Contents
The History of English
How English Began
Germanic tribes like the Saxons, Angles, and Jutes came to Britain around 449 AD. They settled in the south and east of the island. They pushed out the Celtic Britons or made them speak English. Some people in Wales still speak Welsh, a Celtic language. Gaelic is spoken by some in Scotland. "Scots" is a dialect of English. Irish Gaelic is spoken by very few people today.
The different Germanic dialects spoken by these tribes became what we call Old English. Old English sounded and looked very different from modern English. If you heard or read Old English today, you would only understand a few words.
Languages Similar to English
The language closest to English today is Frisian. About 500,000 people speak it in the Netherlands, Germany, and Denmark. Frisian is very similar to English, and many words are the same. The two languages were even closer before Old English changed into Middle English. Today, speakers of English and Frisian cannot understand each other.
Dutch is spoken by over 20 million people and is more distant from English. German is even more widely spoken and even more different. All these languages belong to the same West Germanic family as English.
New Words from Other Cultures
Many other people came to England later, bringing their own languages. These languages added more words to English. For example, around 800 AD, many Danish and Norse Vikings came to England. They settled in an area called the Danelaw. Because of this, English borrowed many words from Norse. Their languages were also Germanic, but they were North Germanic languages.
In 1066 AD, William the Conqueror took over England. He brought his nobles who spoke Norman, a language similar to French. English changed a lot during this time. For about 300 years, official documents were written in Norman French. English was mostly spoken, not written. English borrowed many words from Norman French. It also started to lose its old word endings. The English spoken during this time is called Middle English. Geoffrey Chaucer is a famous writer from the Middle English period. After more sound changes, Middle English became Modern English.
English kept borrowing new words from other languages. It took many words from French (about 30% to 40% of its words). It also borrowed words from Chinese, Hindi, Urdu, Japanese, Dutch, Spanish, and Portuguese. Scientists from different countries needed to communicate. They often used Greek and Latin words for scientific terms. These words also came into English. For example, photography comes from Greek words meaning "light" and "writing." A photograph is a picture made with light.
So, English is a mix of Old English, Danish, Norse, and French words. It has also been changed by Latin, Greek, Chinese, Hindi, Japanese, Dutch, Spanish, and words from many other languages.
How English Grammar Changed
English grammar has also become simpler and less Germanic. A big change was losing case in grammar. Grammatical case shows the role of a noun or pronoun in a sentence. In Latin, this is done by adding suffixes to words. But English usually doesn't do this. In English, the meaning is made clear more by the context and syntax (word order).
English Around the World
The British Empire helped spread English around the globe. Today, English is an important language in many places. In Australia, Canada, India, Pakistan, South Africa, and the United States, English is the main language. Many countries in the Commonwealth of Nations also use English.
The United Kingdom and the United States have been powerful in commerce (business) and government. Because of this, many people find it helpful to learn English. It helps them communicate in science, business, and diplomacy (talking between countries). This is called learning English as an additional language, or English as a Second Language (ESL).
English literature has many famous stories and plays. William Shakespeare was a famous English writer of poems and plays. His English is Early Modern English, which is a bit different from what people speak today. Early Modern English sounded different because the language was going through a "great vowel shift." Later, many short stories and novels were written in English. The modern novel first appeared in 18th-century English. Today, many famous songs and movies use the English language.
English Spelling Differences
Written English has a unique spelling. The same letters or letter groups can make very different sounds. For example, the letters "-ough" can sound different in words like "through" (sounds like "threw"), "rough" (sounds like "ruff"), "dough" (sounds like "doe"), or "cough" (sounds like "coff"). This can make English a difficult language to learn.
Many English-speaking countries spell words differently. In the United States, some words are spelled differently from how they are spelled in the United Kingdom and other countries like those in the Commonwealth of Nations. These different spellings are sometimes called "American English" and "British English." For example, "colour" in British English is spelled "color" in the USA. "Programme" in British English is "program" in the USA. Even the word "spelled" is different; in British English, it can be "spelt."
English Vocabulary: Where Words Come From
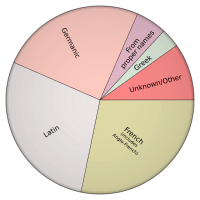
About 60% of English words come from Latin and languages that grew from Latin (like French).
Here's a breakdown:
- French: About 29.3% of words.
- Latin: About 28.7% of words. This includes modern scientific and technical Latin.
- Germanic languages: About 24% of words. These words come from Old English, Proto-Germanic, Old Norse, and other Germanic sources.
- Greek: About 5.32% of words.
- Italian, Spanish, and Portuguese: About 4.03% of words.
- Words from proper names: About 3.28% of words.
- All other languages: Less than 1% of words.
However, if you look at the most common words we use every day, a much higher number of them are of Germanic origin. Also, many common phrases and expressions in English come from Germanic languages.
Related Pages
- Indian English
- American English
- Australian English
- British English
- Canadian English
- Jamaican English
- South African English
- New Zealand English
- Pakistani English
- Scottish English
Images for kids
-
The beginning of the Old English epic poem Beowulf. It is handwritten in a style called half-uncial script.
-
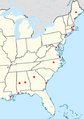
This map shows where rhoticity is common in North American English.
See also
 In Spanish: Idioma inglés para niños
In Spanish: Idioma inglés para niños