List of Solar System objects facts for kids
This is a list of objects in our Solar System, ordered by how far away they are from the Sun. Most of the objects mentioned here are quite large, usually more than 500 kilometers (about 310 miles) across.
Our Solar System is a busy place! It includes our Sun, eight main planets, and many other smaller objects like dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, and comets. Everything in the Solar System orbits the Sun, which is a star.
Contents
The Sun
The Sun is the center of our Solar System. It's a yellow dwarf star, which means it's a medium-sized star that gives off light and heat. Without the Sun, there would be no life on Earth!
Inner Solar System
The inner Solar System is the part closest to the Sun. It contains four rocky planets, often called terrestrial planets.
Mercury
Mercury is the smallest planet and the closest to the Sun. It's a very hot world with no moons.
- Some small asteroids, called Mercury-crossing minor planets, have orbits that cross Mercury's path.
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It's known for its thick, toxic atmosphere and extreme heat.
- Venus-crossing minor planets are small objects that cross Venus's orbit.
- One interesting object is 524522 Zoozve, which is a quasi-satellite of Venus. This means it orbits the Sun but stays close to Venus for a long time.
Earth
Earth is our home planet, the third from the Sun. It's the only known planet with liquid water and life.
- Moon is Earth's only natural satellite.
- Near-Earth asteroids are asteroids that come close to Earth's orbit. One famous example is 99942 Apophis.
- An Earth trojan is an asteroid that shares Earth's orbit, staying in a stable spot. One example is 2010 TK7.
- Earth also has its own quasi-satellites, which are objects that orbit the Sun but stay near Earth.
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun, often called the "Red Planet." Scientists are very interested in Mars because it might have once had conditions suitable for life.
- Deimos and Phobos are Mars's two small moons.
- Mars trojans are asteroids that share Mars's orbit.
- Mars-crossing minor planets are small objects that cross Mars's orbit.
Asteroid Belt
Between Mars and Jupiter is the asteroid belt. This is a region filled with millions of rocky objects called asteroids.
- Ceres is the largest object in the asteroid belt and is considered a dwarf planet.
- Other large asteroids include Pallas, Vesta, and Hygiea.
- Many asteroids have their own tiny moons, called Asteroid moons.
Outer Solar System
The outer Solar System is home to the giant planets, which are much larger than the terrestrial planets and are mostly made of gas or ice.
Jupiter
Jupiter is the largest planet in our Solar System. It's a gas giant, famous for its Great Red Spot, a giant storm.
- Rings of Jupiter are faint rings around the planet.
- Jupiter has many moons! The four largest are called the Galilean moons:
- Jupiter trojans are a large group of asteroids that share Jupiter's orbit.
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun, known for its magnificent system of rings. It's also a gas giant.
- Rings of Saturn are made of countless ice particles and rocks.
- Saturn has many moons, including:
- Mimas
- Enceladus (which has geysers erupting from its south pole)
- Tethys (with its own small trojan moons, Telesto and Calypso)
- Dione (with its own trojan moons, Helene and Polydeuces)
- Rhea (which might have its own faint rings)
- Titan (Saturn's largest moon, with a thick atmosphere and lakes of liquid methane)
- Hyperion
- Iapetus
- Phoebe
- Shepherd moons are small moons that help keep Saturn's rings in shape.
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet, an ice giant that rotates on its side.
- Rings of Uranus are dark and narrow.
- Uranus has several moons, including:
- A Uranus trojan like 2011 QF99 shares Uranus's orbit.
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun. It's another ice giant, known for its strong winds.
- Rings of Neptune are faint and clumpy.
- Neptune has several moons, including:
- Neptune trojans are asteroids that share Neptune's orbit.
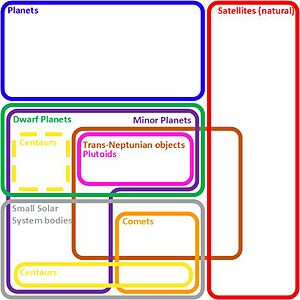
Other Minor Planets
Beyond the main planets, there are other small objects:
- Centaurs are icy bodies that orbit between Jupiter and Neptune.
- Damocloids are objects that have very long, comet-like orbits but don't show comet activity.
Trans-Neptunian Objects
Trans-Neptunian objects are objects that orbit the Sun beyond Neptune.
Kuiper Belt
The Kuiper Belt is a region beyond Neptune, similar to the asteroid belt but much larger and filled with icy bodies.
- Plutinos are objects in the Kuiper Belt that are locked in a special orbit with Neptune.
- Pluto is the most famous plutino and a dwarf planet. It has several moons:
- Charon (Pluto's largest moon)
- Pluto is the most famous plutino and a dwarf planet. It has several moons:
- Cubewanos are Kuiper Belt objects that have more circular orbits.
- Haumea is a dwarf planet with two moons, Namaka and Hiʻiaka.
- Makemake is another dwarf planet.
- 50000 Quaoar has a moon named Weywot.
- Other large cubewanos include (307261) 2002 MS4, 120347 Salacia, and 20000 Varuna.
Scattered Disc
Scattered-disc objects are icy bodies that were "scattered" by Neptune's gravity into very wide, elliptical orbits.
- Eris is a dwarf planet in the scattered disc, with a moon named Dysnomia.
- Other large scattered-disc objects include 225088 Gonggong (with its moon Xiangliu) and (84522) 2002 TC302.
Detached Objects
Detached objects are very distant objects with orbits that are not strongly influenced by Neptune.
- Examples include 2004 XR190 and 90377 Sedna. Sedna might even be part of the inner Oort cloud.
Oort Cloud
The Oort cloud is a hypothetical (meaning we think it's there but haven't seen it directly) spherical cloud of icy objects far beyond the Kuiper Belt. It's thought to be the source of many comets.
- It's divided into the inner Oort cloud (or Hills cloud) and the outer Oort cloud.
Other Solar System Objects
The Solar System also contains:
- Comets are icy bodies that release gas and dust, forming a "tail" when they get close to the Sun.
- Small objects like:
- Meteoroids are small pieces of rock or dust in space.
- Interplanetary dust is tiny dust particles spread throughout the Solar System.
- Human-made objects orbiting the Sun and planets, including active satellites and old space junk.
- The Heliosphere is a giant bubble of charged particles, called the solar wind, that the Sun creates around itself.
- The Heliosheath is the outer part of this bubble.
- The Heliopause is the very edge of the heliosphere, where the solar wind meets the interstellar medium (the space between stars).
See also
- Outline of the Solar System
- Lists of astronomical objects
- List of natural satellites
- List of Solar System objects by size
- List of Solar System objects most distant from the Sun
- Ring system
- Solar System models
| The Solar System | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||||
| Sun • Heliosphere |
Planets ☾ = moon(s) ∅ = rings |
Mercury | Venus | Earth ☾ | Mars ☾ | ||
| Jupiter ☾ ∅ | Saturn ☾ ∅ | Uranus ☾ ∅ | Neptune ☾ ∅ | ||||
| Dwarf planets | Ceres | Pluto ☾ | Haumea ☾ | Makemake | |||
| Eris ☾ | |||||||
| Small Solar System bodies |
Asteroids (minor planets) |
Groups and families: Vulcanoids · Near-Earth asteroids · Asteroid belt Jupiter Trojans · Centaurs · Neptune Trojans · Asteroid moons · Meteoroids · Pallas · Juno · Vesta · Hygiea · Interamnia · Europa |
|||||
| See also the list of asteroids. | |||||||
| Trans- Neptunians |
Kuiper belt – Plutinos: Orcus · Ixion – Cubewanos: Varuna · Quaoar · Huya |
||||||
| Scattered disc: Sedna | |||||||
| Comets | Periodic comets and non-periodic comets Damocloids · Oort cloud |
||||||
| See also the list of solar system objects | |||||||