Prussia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Prussia
Preußen
|
|
|---|---|
| 1525–1947 | |
Prussia (blue), at its peak, the leading state of the German Empire
|
|
| Capital | Königsberg, later Berlin |
| Common languages | German (official) |
| Religion | Protestantism, Roman Catholicism |
| Government | Monarchy |
| Duke1 | |
|
• 1525–1568
|
Albert I (first) |
|
• 1688–1701
|
Frederick III (last) |
| King1 | |
|
• 1701–1713
|
Frederick I (first) |
|
• 1888–1918
|
Wilhelm II (last) |
| Prime Minister1, 2 | |
|
• 1918–1920
|
Paul Hirsch (first) |
|
• 1933–1945
|
Hermann Göring (last) |
| Historical era | Early modern Europe to Contemporary |
|
• Duchy of Prussia
|
10 April 1525 |
|
• Union with Brandenburg
|
27 August 1618 |
|
• Kingdom of Prussia
|
18 January 1701 |
|
• Free State of Prussia
|
9 November 1918 |
|
• Abolition (de facto)
|
30 January 1934 |
|
• Abolition (de jure)
|
25 February 1947 |
| Area | |
| 1907 | 348,702 km2 (134,635 sq mi) |
| 1939 | 297,007 km2 (114,675 sq mi) |
| Population | |
|
• 1816
|
103490003 |
|
• 1871
|
24689000 |
|
• 1939
|
41915040 |
| Currency | Reichsthaler |
| Today part of | Germany, Poland, Russia, Lithuania, Denmark, Belgium, Czech Republic, Switzerland |
|
1 The heads of state listed here are the first and last to hold each title over time. For more information, see individual Prussian state articles (links in above History section).
2 The position of Ministerpräsident was introduced in 1792 when Prussia was a Kingdom; the prime ministers shown here are the heads of the Prussian republic. 3 Population estimates: |
|
Prussia (German: Preußen, Polish: Prusy, Lithuanian: Prūsija) was a powerful state in Central Europe. It existed from 1525 until 1947. For a long time, it was the biggest and most important part of Germany. It also included land that is now in Poland, Russia, and Lithuania.
The name "Prussia" has been used in many ways:
- It first referred to the land of the Baltic Prussians. This area is now parts of southern Lithuania, Kaliningrad, and north-eastern Poland.
- Later, it meant the lands controlled by the Teutonic Knights, a group of religious soldiers.
- It also referred to a part of the Polish Crown called Royal Prussia.
- A smaller area, Ducal Prussia, was controlled by the Hohenzollern family from Brandenburg.
- Eventually, "Prussia" came to mean all the lands ruled by the Hohenzollern family.
- It became an independent state from the 17th century until 1871.
- From 1871 to 1945, Prussia was the largest part of the German Empire, the Weimar Republic, and the country under the Nazis.
In 1934, the Nazis stopped using the name Prussia for that area. Then, in 1947, the Allies (countries that won World War II) officially ended the state of Prussia. Its land was divided among them and the new States of Germany. Today, the name Prussia is mostly used for history, geography, or culture.
The name Prussia comes from the Borussi or Prussi people who lived in the Baltic region. For a long time, Ducal Prussia was connected to the Kingdom of Poland. Many German-speaking Prussians believed in a special "Prussian way of life." This included:
- Being very organized.
- Being willing to make sacrifices for others.
- Always obeying the law.
By the late 18th century, Prussia had a lot of power in northern Germany. It was the strongest in politics and business, and it had the most people. In 1871, a leader named Otto von Bismarck created the German Empire, and Prussia was at its very center.
Contents
Where Was Prussia?
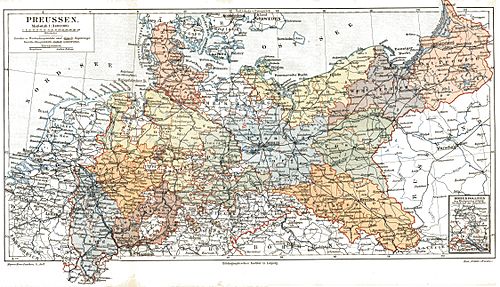
Prussia started as a small area in what is now northern Poland. Over time, more Germans moved there. By 1934, Germany's borders included parts of France, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Lithuania. Many parts of eastern Poland were once in Prussia. Before 1918, much of western Poland was also part of Prussia. Between 1795 and 1807, Prussia even controlled Warsaw and central Poland.
Before 1934, Prussia included these regions:
- West Prussia and East Prussia (now in Poland and Russia).
- Pomerania.
- Silesia.
- Brandenburg.
- Lusatia.
- Province of Saxony (now Saxony-Anhalt).
- Kingdom of Hanover.
- Schleswig-Holstein.
- Westphalia.
- Parts of Hesse.
- The Rhineland.
- Some small areas in the south, like Württemberg-Hohenzollern, which was the home of Prussia's leaders.
However, some regions were never part of Prussia. These included Oldenburg, Mecklenburg, and the Hanse city-states.
Most people in north-east Germany were Protestant, so Prussians were mainly Protestant. But there were many Catholic people in areas like the Rhineland, East Prussia, Posen, Silesia, West Prussia, and Ermland. The states in southern Germany, especially Austria and Bavaria, were mostly Catholic. This made them less willing to accept Prussia's growing power. While Prussia was mostly German, the new Polish areas added in the late 18th century had many Polish people. In 1918, these Polish areas became part of Poland again.
Early History of Prussia
In 1226, a Polish prince named Conrad of Mazovia asked the Teutonic Knights to help him. The Knights were a group of religious soldiers from Transylvania. He wanted them to fight the Prussian tribes living near his borders. The Knights fought for over 100 years. After their victories, they created a new state. This state eventually controlled much of what is now Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and parts of northern Poland.
By 1466, the Knights were under the control of the King of Poland and Lithuania. In 1525, the leader of the Knights became a Protestant. He turned part of the Knights' land into the Duchy of Prussia, which was part of the Kingdom of Poland.
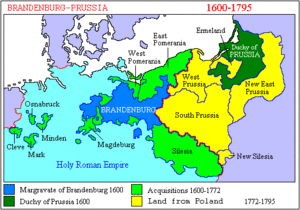
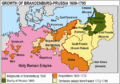
At that time, the Duchy of Prussia was only the area east of the Vistula River. In 1618, the new Duke of Prussia was also the Elector John Sigismund of Brandenburg. He was the ruler of Brandenburg, which was controlled by the powerful Hohenzollern family. The Duchy of Prussia was important to the Hohenzollern family because it was outside the Holy Roman Empire. The new combined state was called Brandenburg-Prussia. Even though Polish land was in the middle of this state, Brandenburg-Prussia was becoming more independent from Poland. Under Frederick William, known as the Great Elector, Prussia gained new lands in Magdeburg and areas west of the Rhine River.
The Kingdom of Prussia
In 1701, the Holy Roman Emperor and the Polish King allowed Brandenburg-Prussia to be called the "Kingdom of Prussia." Its first king was Frederick I. Later, under Frederick II ("the Great"), Prussia fought wars and took Silesia from Austria. These wars ended in 1763. Prussia was now the strongest state in eastern Germany. Other parts of Germany, like Pomerania, also became part of Prussia through marriages or family deaths.
During this time, the Prussian army became very strong, and its government system grew. These became key parts of the German state until 1945. Between 1772 and 1795, Prussia, Russia, and Austria divided Poland into parts. This was called the Partitions of Poland. Prussia gained land far to the east, including Warsaw.
Frederick William II led Prussia into war with France in 1792. Prussia lost at Valmy and had to give some western land to France. Frederick William III started another war but lost at Jena. He had to give even more land to France in the Treaties of Tilsit.
In 1813, Prussia went to war again with Napoleonic France. In 1815, Prussia won back its lost land. It also gained all of the Rhineland and Westphalia, plus other areas. This land in the west was very important, especially the Ruhr valley. It became the new center for Germany's industries and weapons production. After the Napoleonic Wars, Prussia was the biggest power in Germany, even stronger than Austria.
In the early 19th century, many Germans wanted a single, democratic Germany. Others, called conservatives, wanted Germany to remain a group of weak, independent states. In 1848, there were revolutions across Europe. This gave the people who wanted democracy a chance. Frederick William IV was worried. He allowed a National Assembly and a constitution. The new Frankfurt Parliament wanted to make Frederick William the king of all Germany, but he refused. He said that revolutionaries could not choose kings. Prussia then got a partly democratic constitution. However, the wealthy landowners (called Junkers) still held most of the power, especially in the eastern parts.
Imperial Prussia
In 1862, Prussian King William I appointed Otto von Bismarck as his new Minister-President (like a prime minister). Bismarck wanted to weaken both the democratic groups and the conservatives. He aimed to create a strong, united Germany, but one led by the Junkers, not by the democratic groups from western Germany. To do this, he started three wars:
- With Denmark in 1864, which gave Prussia Schleswig-Holstein.
- With Austria in 1866 (Austro-Prussian War), allowing Prussia to take Hanover and most other northern German lands that had sided with Austria.
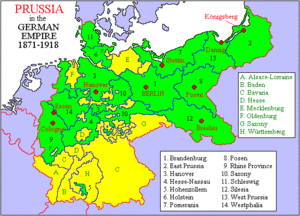
- With France in 1870 (Franco-Prussian War). This war helped Bismarck gain control over states like Mecklenburg, Bavaria, Baden, Württemberg, and Saxony. After this, these states (but not Austria) joined to form a united German Empire. King William I then became the Emperor (Kaiser).
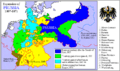
This was a high point for Prussia. Its economy and political future looked bright, if its leaders were smart. But after only 99 days, in 1888, the state had a new leader, William II. He fired Bismarck in 1890 and began a new foreign policy. He made the army and navy much bigger and took many risks. These actions led Germany into World War I. After Germany's defeat, the Prussian Junkers lost their power. The Prussian king and the other German kings had to leave. Germany became the Weimar Republic. In 1919, the Treaty of Versailles created the new Polish state. Prussia had to give up much of its land. The Polish Corridor was created, separating East Prussia from the rest of Germany.
The End of Prussia
After World War I, the Treaty of Versailles took away West Prussia to create the Free City of Danzig and the Polish Corridor. Some people wanted to divide Prussia into smaller states, but the idea of keeping Prussia together won. Prussia became the "Prussian Free State" (Freistaat Preußen). It was the largest state in the Weimar Republic, making up 60% of its land. The industrial Ruhr area and Berlin were in Prussia, making it a center for left-wing politics. The Social Democrats and the Catholic Centre held power for most of the 1920s.
In 1932, Germany's conservative Chancellor Franz von Papen took control of Prussia. This ended Prussia's democratic constitution and was a step towards the end of German democracy. In 1933, Hermann Göring became the Interior Minister of Prussia, which gave him a lot of power. In 1934, the Nazis took away the power of all German states.
In 1945, the Soviet Union's army took control of all of eastern and central Germany, including Berlin. Poland received all the land east of the Oder-Neisse line, such as Silesia, Pomerania, eastern Brandenburg, and East Prussia. The Soviet Union took the northern third of East Prussia, including Königsberg, which is now Kaliningrad. About ten million Germans had to leave these areas. Polish and Russian people then moved in. Because of this, and because the Communist government took control of land in East Germany, the Junker class and the idea of Prussia were finished.
In 1947, the United States, Britain, France, and the Soviet Union officially agreed to end Prussia. In the Soviet Zone (which became East Germany in 1949), the Prussian lands became the states of Brandenburg and Saxony-Anhalt. The Prussian parts of Pomerania went to Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. In 1952, the East German government stopped using states and used districts instead. In 1990, when East Germany ended, the states returned. In West Germany (which became the Federal Republic of Germany in 1949), the Prussian lands became part of North Rhine-Westphalia, Lower Saxony, Hesse, Rhineland-Palatinate, and Schleswig-Holstein. Baden-Württemberg took the Hohenzollern land.
The idea of Prussia is not completely gone in Germany. Some people want to combine the states of Brandenburg, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, and Berlin and call them Prussia. However, German politicians are not interested in this idea. The constitution of Berlin allows Berlin and Brandenburg to become one state, but the people of Berlin voted against this idea on May 5, 1996.
Images for kids
-
Prussian Homage by Jan Matejko. After admitting the dependence of Prussia to the Polish Crown, Albert of Prussia receives Ducal Prussia as a fief from King Sigismund I the Old of Poland in 1525
-
The "Great Elector" and his wife
-
King Frederick William I, "the Soldier-King"
-
King Frederick II, "the Great"
-
King Frederick William IV
-
Emperor Wilhelm I
-
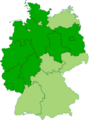
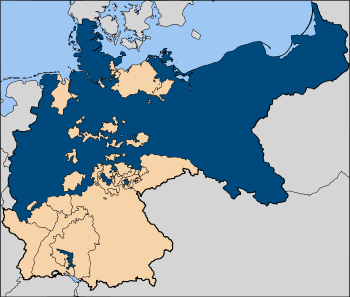
Map of the current states of Germany (in dark green) that are completely or mostly situated inside the old borders of Imperial Germany's Kingdom of Prussia
-
In 1649, Kursenieki settlements along the Baltic coastline of East Prussia spanned from Memel (Klaipėda) to Danzig (Gdańsk).
-
King Frederick William I of Prussia welcoming the expelled Salzburg Protestants
-
Prussian deportations (Polenausweisungen) were the mass expulsions of ethnic Poles between 1885 and 1890.
See also
 In Spanish: Prusia para niños
In Spanish: Prusia para niños
 | Madam C. J. Walker |
 | Janet Emerson Bashen |
 | Annie Turnbo Malone |
 | Maggie L. Walker |