Geography of Greece facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Geography of Greece |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Continent | Europe |
| Region | South Europe |
| Coordinates | 39°00′N 22°00′E / 39.000°N 22.000°E |
| Area | Ranked 95th |
| • Total | 131,957 km2 (50,949 sq mi) |
| • Land | 99.13% |
| • Water | 0.87% |
| Coastline | 13,676 km (8,498 mi) |
| Borders | 689.76 km (428.60 mi) |
| Highest point | Mount Olympus 2,918 metres (9,573 ft) |
| Lowest point | Epitalio −6 metres (−20 ft) |
| Longest river | Haliacmon 297 kilometres (185 mi) |
| Largest lake | Lake Trichonida 98.6 km2 (38.07 sq mi) |
| Terrain | 80% mountainous, plains (east and north-east) |
| Natural Resources | petroleum, magnetite, lignite, bauxite, hydropower, marble, limestone, fish |
| Natural Hazards | earthquakes, floods, droughts and wildfires |
| Environmental Issues | air pollution, water pollution |
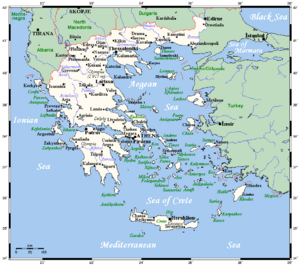
Greece is a country in Southeastern Europe, located on the Balkan Peninsula. It shares borders to the north with Albania, North Macedonia, and Bulgaria. To the east, it borders Turkey. Greece is surrounded by several seas: the Aegean Sea to the east, the Cretan and Libyan seas to the south, and the Ionian Sea to the west, which separates Greece from Italy.
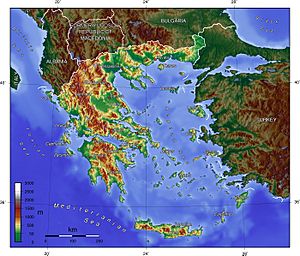
The country's mainland is mostly mountainous. It forms a peninsula that reaches into the Mediterranean Sea. Two smaller peninsulas also extend from the mainland: the Chalkidiki and the Peloponnese. The Peloponnese is connected to the mainland by the Isthmus of Corinth. Greece also has many islands of different sizes. The biggest ones are Crete, Euboea, Lesvos, Rhodes, Chios, Kefalonia, and Corfu. Groups of smaller islands include the Dodecanese and the Cyclades. Greece has the longest coastline in the Mediterranean Sea, stretching for 13,676 kilometres (8,498 mi).
Greece is located between 35°N and 42°N latitude and 19°E and 28°E longitude. This wide range, along with its varied landscape, gives the country many different climates.
Contents
Exploring Greece's Amazing Landscape
Greece is in South Eastern Europe. It borders the Ionian Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. It is a country made up of a peninsula and about 3,000 islands.
Greece has a total area of 131,957 km2 (50,949 sq mi). Most of this is land, about 130,647 km2. Its lakes and rivers cover 1,310 km2. Greece shares land borders with Albania (212 km), North Macedonia (234 km), Bulgaria (472 km), and Turkey (192 km). These borders add up to about 1,110 km. About 83% of Greece's land is on the mainland, and 17% is on its islands. Greece also has a large exclusive economic zone in the sea, covering 505,572 km2 (195,202 sq mi). This is the 53rd largest in the world.
Greece's coastline is very long, measuring 13,676 km (8,498 mi).
Mountains and Plains
About 80% of Greece is mountainous. The Pindus mountain range runs through the center of the country from northwest to southeast. Its highest point is 2,637 meters. This mountain range also extends into the Peloponnese and even underwater across the Aegean Sea. It forms many of the Aegean Islands, including Crete. It also connects to the Taurus Mountains in southern Turkey. Central and western Greece have high, steep peaks. These are cut by many canyons and karstic landscapes. Famous examples include the Meteora rocks and the Vikos Gorge. The Vikos Gorge is one of the deepest canyons in the world, dropping over 1,100 meters.
Mount Olympus is the highest point in Greece. It rises to 2,917 meters above sea level. It is the 7th highest and 9th most prominent mountain in mainland Europe. The Rhodope Mountains form the border between Greece and Bulgaria. This area is covered with large, thick forests.
Flat plains are found in eastern Thessaly, central Macedonia, and Thrace.
Highest and Lowest Points
- Highest point: Mount Olympus: 2,917 m (9,570 ft)
- Lowest point: Epitalio: −6 m (−20 ft)
Extreme Points of Greece
These are the very edges of Greece:
- North: Ormenio village (41°45′41″ N, 26°13′15″ E)
- South: Gavdos island (34°48′11″ N, 24°07′25″ E)
- East: Strongyli island (36°06′17″ N, 29°38′39″ E)
- West: Othonoi island (39°51′11″ N, 19°22′41″ E)
Greece's Natural Riches
Greece has important natural resources. These include petroleum, magnetite, lignite, and bauxite. It also has hydropower, marble, and limestone. Ancient Greeks used limestone to build many strong structures, like the Parthenon. Greece's seas are full of marine life, with lots of fish.
How Land is Used
- Farmable land: 19.71%
- Permanent crops: 8.95%
- Other uses: 71.37% (2012 estimate)
Irrigated land: 15,550 km2 (2007)
|
Sporades
Islands
Epirus
Central Greece
Thrace
Dodecanese
North Aegean
Islands
Ionian
Islands
|
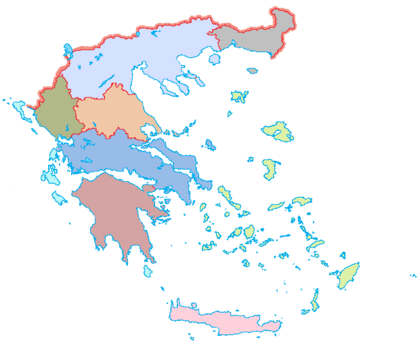
| Regions of Greece |
| Cities and islands of Greece |
Mainland Greece: A Closer Look
Mainland Greece is the southernmost part of the Balkan peninsula. Two smaller peninsulas, the Chalkidiki and the Peloponnese, extend from it. The northern part of the country includes the regions of Macedonia and Thrace. Further south, the mainland becomes narrower. Here you find the regions of Epirus, Thessaly, and Central Greece. The capital city, Athens, is located in the Attica region within Central Greece. The Peloponnese peninsula is separated from the rest of the mainland by the Corinthian and Saronic Gulfs. However, it is connected by the Isthmus of Corinth.
Mainland Greece makes up about 80% of the country's total area. It is largely mountainous. The biggest mountain range is the Pindus range. This range is a southern extension of the Dinaric Alps. It forms the "spine" of the Greek mainland, separating Epirus from Thessaly and Macedonia. Greece's tallest mountain is Mount Olympus. It also separates Thessaly from Macedonia. Its highest peak reaches 2,918 meters above sea level. This makes it the second highest peak on the Balkan peninsula.
Greece's Many Islands
The number of Greek islands varies greatly, from 1,200 to 6,000. Travel guides often say there are 1,425 islands, with 166 of them being inhabited. The Greek Tourism Organization reports 6,000 islands, with 227 inhabited. Some sources even suggest there are 9,841 islands, but only 169 have people living on them all the time.
Greek islands make up about 20% of the country's total land. They differ a lot in size and climate. The largest island is Crete, and Euboea is the second largest. Other big Greek islands include Rhodes and Lesbos in the Aegean Sea. In the Ionian Sea, you'll find Corfu and Cephalonia. Many smaller Greek islands form groups or chains, called archipelagos. Good examples are the Cyclades and the Sporades in the Aegean Sea.
Islands of the Aegean Sea
The islands in the Aegean Sea are located between mainland Greece to the west and north, Anatolia (Turkey) to the east, and the island of Crete to the south. These islands are usually divided into seven main groups, from north to south:
- North Aegean Islands
- Sporades
- Euboea
- Saronic Islands
- Cyclades
- Dodecanese (also called Southern Sporades)
- Crete
Ionian Islands
The Ionian Islands are a group of seven islands. Six of these islands are off the western coast of Greece, in the Ionian Sea. The seventh island, Kythira, is off the southern tip of the Peloponnese. Kythira is part of the modern administrative region of Attica, not the Ionian Islands. It's important to remember that the Ionian Islands are different from the historical region of Ionia, which is now part of western Turkey.
Crete: Greece's Largest Island
Crete is the biggest island in Greece. It is also the second largest in the Eastern Mediterranean, after Cyprus. The island stretches 260 km from east to west. It is 60 km wide at its widest point. Near Ierapetra, Crete narrows to only 12 km wide. Crete covers an area of 8,336 km2 (3,219 sq mi). Its coastline is 1046 km long. To the north, it is surrounded by the Sea of Crete. To the south, it has the Libyan Sea. The Myrtoan Sea is to the west, and the Karpathion Sea is to the east. Crete is about 160 km south of the Greek mainland.
Crete has a mountain range that crosses the island from west to east. This range is made up of three different parts:
- The White Mountains or Lefka Ori (2,452 m high);
- The Idi Range (Psiloritis (35°11′N 24°49′E / 35.18°N 24.82°E) 2,456 m high);
- The Dikti Mountains (2,148 m high).
These mountains surround fertile flat areas called plateaus, such as Lasithi, Omalos, and Nidha. There are also many caves, like Diktaion and Idaion. Deep valleys called gorges are also common, such as the Samariá Gorge. The protected area of the Samariá Gorge is home to the Cretan goat, also known as the kri-kri. The endangered Bearded vulture (or lammergeyer) lives in the mountains and gorges of Crete.
Crete's rivers include the Ieropotamos River in the southern part of the island.
Greece's Environment and Climate
Greece is mostly a mountainous country with a very long coastline. It has many peninsulas and islands.
The climate in Greece can vary a lot. It ranges from semi-desert areas to cold mountain forests.
Greece faces natural challenges like strong earthquakes, floods, droughts, and wildfires. Current environmental issues in Greece include air pollution and water pollution.
Understanding Greece's Climate
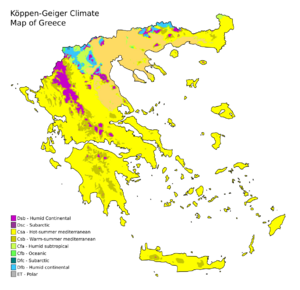
Greece generally has a mild climate. A Mediterranean climate is found along the coast and on the islands. In the mountainous areas inland, a Continental climate is common. Summers are hot and dry, while winters are cool and wet. Summer usually has no rain and very few clouds for about three months. In July and August, temperatures often reach 30–35 °C, and can even go above 40 °C. In the eastern part of the country, especially on the islands, a cooling Etesian wind blows in the summer. However, in big cities like Athens, it can still feel very hot. This wind can sometimes be very strong, making sailing difficult.
A special feature of Greek weather is how much sunshine it gets. Even in winter, there are five hours of sunshine a day. In summer, this can increase to 12–14 hours daily. Most of the rain falls in winter. Snow can be found all over Greece, but it is rare on the islands. In low-lying areas, snow hardly ever stays on the ground. On the highest mountain peaks, snow can remain well into the summer months. Spring and autumn are short in-between seasons with changing weather.
Large forest fires are a problem almost every year in late summer. Sometimes, these fires lead to many people being evacuated and can even cause deaths.
| Measurement location | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Athens (dry east) |
13 °C 6 °C 62 mm |
14 °C 7 °C 37 mm |
16 °C 8 °C 37 mm |
20 °C 11 °C 23 mm |
25 °C 16 °C 23 mm |
30 °C 20 °C 14 mm |
33 °C 23 °C 6 mm |
33 °C 23 °C 7 mm |
29 °C 19 °C 15 mm |
24 °C 15 °C 51 mm |
19 °C 12 °C 56 mm |
15 °C 8 °C 71 mm |
| Naxos (archipelago) |
15 °C 10 °C 91 mm |
15 °C 10 °C 73 mm |
16 °C 11 °C 69 mm |
20 °C 13 °C 19 mm |
23 °C 16 °C 12 mm |
26 °C 20 °C 11 mm |
27 °C 22 °C 2 mm |
28 °C 22 °C 1 mm |
24 °C 18 °C 11 mm |
20 °C 15 °C 45 mm |
17 °C 12 °C 48 mm |
15 °C 8 °C 93 mm |
Images for kids
-
Crete (NASA photograph)
-
Volcanic crater, Santorini
-
Potidea Kanal, Chalkidiki
-
Landscape of Stymfalia with Mount Kyllini
-
Navagio, Zakynthos
See also
- Geography of Europe
- Greek names of mountains
- List of earthquakes in Greece
- List of islands of Greece
- National parks of Greece
- Wildlife of Greece
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |