Geography of Europe facts for kids
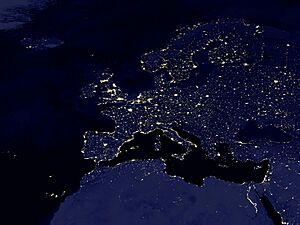
 Several of the oldest cities of Northwestern Europe are highlighted in this astronaut's photograph from 00:25 GMT on 10 August 2011  |
|
| Area | 10,180,000 km2 (3,930,000 sq mi) (6th) |
|---|---|
| Population | 742,452,000 (2013; 3rd) |
| Population density | 72.9/km2 (188/sq mi) (2nd) |
| Demonym | European |
| Countries | 50 sovereign states 5 with limited recognition |
| Dependencies | 4 dependencies |
| Languages | ~225 languages |
| Time zones | UTC−1 to UTC+5 |
Europe is one of the world's seven continents. It is a large peninsula that sticks out from the western part of Eurasia. Eurasia is the huge landmass that includes both Europe and Asia. Asia is located to the east of Europe.
The border between Europe and Asia is usually the Ural Mountains in Russia. Russia is the largest country in Europe. The border then follows the Ural River or the Emba River. It continues to the Caspian Sea, the Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea. The Bosporus, the Sea of Marmara, and the Dardanelles complete the border with Asia. To the south, the Mediterranean Sea separates Europe from Africa. The Atlantic Ocean forms Europe's western border. Iceland is also considered part of Europe because it is closer to Europe than to North America.
Contents
- Europe's Shape and Features
- Europe's Geology
- Population of Europe
- Rivers of Europe
- Lakes and Inland Seas
- Major Islands of Europe
- Plains and Lowlands
- Mountain Ranges
- Temperature and Precipitation
- Climate Zones
- Landlocked Countries
- Countries Made of Islands or Parts of Islands
- Countries Bordering or Spanning Other Continents
- Countries by Number of Neighbors
- See also
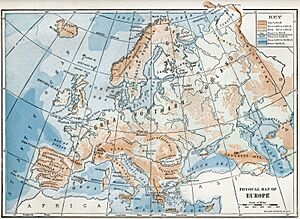
Europe's Shape and Features
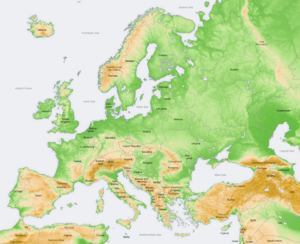
Some geographers think of Europe and Asia as one big continent called Eurasia. This is because Europe is not fully surrounded by water. Also, its southeastern border has been defined differently over many centuries.
Europe's shape is like a collection of connected peninsulas and nearby islands. The two biggest peninsulas are Europe itself and Scandinavia in the north. They are separated by the Baltic Sea. Three smaller peninsulas stick out from the southern part of the mainland. These are Iberia, Italy, and the Balkans.
The Balkan peninsula is separated from Asia by the Black and Aegean Seas. Italy is separated from the Balkans by the Adriatic Sea. The Mediterranean Sea separates Italy from Iberia. This sea also separates Europe from Africa. To the east, mainland Europe gets wider, like a funnel. It widens until it reaches the border with Asia at the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, and Caucasus Mountains.
Europe has many different types of land, even in small areas. The southern parts are very mountainous. As you go north, the land gets lower. It goes from high mountains like the Alps, Pyrenees, and Carpathians. Then it turns into hilly areas, and finally into wide, low plains in the north. These plains are huge in the east. There are also uplands along the northwestern coast. These start in southwestern Ireland, go through western and northern Great Britain, and up the mountainous, fjord-filled coast of Norway.
This is a simple description. Places like Iberia and Italy have their own complex land features. Mainland Europe also has many plateaus, river valleys, and basins. These make the general land pattern more complicated. Iceland and the British Isles are special. Iceland was formed by volcanoes in the North Atlantic. The British Isles used to be connected to the mainland. They were cut off when sea levels rose after the last ice age.
Europe: A Peninsula of Peninsulas
Europe is often called a "peninsula of peninsulas." This name highlights that Europe is a relatively small part of Asia. It also shows that a large part of Europe is made up of many peninsulas. In ancient times, Britain and Ireland were also part of a very large European peninsula. This was before sea levels rose after the ice age.
Some of Europe's Peninsulas
- Balkan peninsula
- Brittany
- Cotentin Peninsula
- Crimea
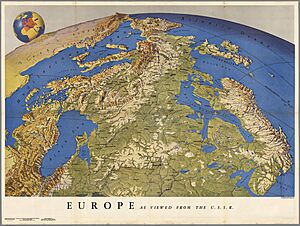
- Fennoscandian Peninsula (includes Kola Peninsula and Scandinavian Peninsula)
- Iberian Peninsula
- Italian Peninsula
- Jutland
- Kanin Peninsula
Europe's Geology

Europe's most important geological feature is the difference between its highlands and mountains in Southern Europe and a huge northern plain. This plain is partly underwater. It stretches from Great Britain in the west to the Ural Mountains in the east. The mountain ranges of the Pyrenees and the Alps/Carpathians separate these two halves.
The northern plains are bordered in the west by the Scandinavian mountains and the mountains of the British Isles. The main shallow seas covering parts of the northern plains are the Celtic Sea, the North Sea, the Baltic Sea, and the Barents Sea.
The northern plain includes the old continent of Baltica. So, it can be seen as the "main continent." The mountains and highlands in the south and west are pieces from other ancient continents. Europe's geology is very diverse and complex. This is why the continent has so many different landscapes. These range from the Scottish Highlands to the flat plains of Hungary.
Population of Europe
Throughout history, Europe's population has changed a lot. This is due to people moving in and out, diseases, and wars. The number of people in Europe changes depending on how its borders are defined. In 2005, the United Nations said Europe had 701 million people. This was based on the standard physical borders. In 2000, the population was 857 million. This number included all of Russia and Turkey, which are partly in Asia. Europe's population grows slowly. Also, the average age of people in Europe is higher compared to other continents.
Rivers of Europe
Some of the most important rivers in Europe are the Danube, Volga, Rhine, Elbe, Oder, and Dnieper.
Longest Rivers in Europe
Here are some of the longest rivers in Europe. They flow directly into the World Ocean or into inland basins:
- Volga - 3,690 km (2,290 mi)
- Danube - 2,860 km (1,780 mi)
- Ural - 2,428 km (1,509 mi)
- Dnieper - 2,290 km (1,420 mi)
- Don - 1,950 km (1,210 mi)
- Pechora - 1,809 km (1,124 mi)
- Dniester - 1,352 km (840 mi)
- Rhine - 1,236 km (768 mi)
- Elbe - 1,091 km (678 mi)
- Vistula - 1,047 km (651 mi)
- Tagus - 1,038 km (645 mi)
- Daugava - 1,020 km (630 mi)
- Loire - 1,012 km (629 mi)
- Ebro - 960 km (600 mi)
- Prut - 953 km (592 mi)
Rivers by Water Flow
These are the rivers in Europe with the largest average water flow (discharge). They flow directly into the ocean or inland basins:
- Volga - 8,087 m³/s (the biggest river in Eastern Europe)
- Danube - 6,450 m³/s (the biggest river in Central Europe)
- Pechora - 4,380m³/s
- Northern Dvina - 3,330m³/s
- Neva - 2,490 m³/s
- Rhine - 2,315 m³/s (the biggest river in Western Europe)
- Rhône - 1,900 m³/s (the biggest river in France)
- Dnieper - 1,700 m³/s
- Po - 1,460 m³/s (the biggest river in Italy)
- Vistula - 1,080 m³/s (the biggest river in Poland)
- Don - 890 m³/s
- Mezen - 890 m³/s
- Loire - 889 m³/s (the longest river in France)
- Elbe - 860 m³/s
- Glomma - 709 m³/s (Norway's longest and largest river)
Lakes and Inland Seas
Europe has many lakes and inland seas. These include large bodies of water like the Caspian Sea (partially in Europe) and many smaller lakes across the continent.
Major Islands of Europe
Europe has many important islands. Some of the major ones are:
- Aegean Islands
- Åland
- Balearic Islands
- British Isles
- Corsica
- Crete
- Cyprus (close to Asia)
- Fyn
- Faroe Islands
- Gotland
- Hinnøya
- Iceland
- Ionian Islands
- Malta
- North Jutlandic Island
- Saaremaa
- Sardinia
- Senja
- Sicily
- Svalbard
- Zealand
Plains and Lowlands
Europe has many flat areas and lowlands. These are often used for farming and are home to many cities. Some of the largest are:
- Great European Plain: This is the biggest flat area in Europe.
- East European Plain
- Lower Danubian Plain: Found between the Balkan Mountains and the Southern Carpathians.
- North European Plain
- East European Plain
- Beauce, France
- British Lowlands
- Central Swedish lowland
- Ebro Basin: Located between the Pyrenees and Sistema Ibérico.
- Meseta Central: A high flat area in central Spain.
- Pannonian Plain: Between the Alps, Dinaric Mountains, and Carpathian Mountains.
- Po Valley: Also called Padan Plain, between the Alps and Apennines.
- Swiss Central Plateau: Between the Jura Mountains and Swiss Alps.
- Upper Rhine Plain: Between Vosges Mountains and Black Forest Mountains.
- Upper Thracian Plain: Between Balkan Mountains and Rila-Rhodope massif.
Mountain Ranges
Europe has many famous mountain ranges. Some of the major ones include:
- Alps: In Central Western Europe, divided into Western, Eastern, Southern, and Northern Alps.
- Apennines: Run through Italy.
- Baetic System: In Spain, part of the Iberian Peninsula.

- Balkan Mountains: Mainly in Bulgaria, in the central Balkan Peninsula.
- Bohemian Massif: Older mountain ranges like the Jura Mountains, Vosges, Black Forest, and Sudetes.
- Cantabrian Mountains: Run across northern Spain.
- Carpathian Mountains: A major range in Central and Southern Europe, including the Tatra Mountains.
- Caucasus Mountains: These mountains also form part of the border between Europe and Asia.
- Crimean Mountains

- Dinaric Alps: A mountain range in the Balkans.
- Pindus Mountains: In Albania and Greece.
- Pyrenees: The natural border between France and Spain.
- Rila-Rhodope mountain system: Mainly in Bulgaria.
- Šar-Korab-Jakupica-Baba-Kajmakčalan-Olympus: In Albania, North Macedonia, and Greece.
- Scandinavian Mountains: Run through the Scandinavian Peninsula.
- Scottish Highlands: In the United Kingdom.
- Sierra Morena: In Spain.
- Sistema Ibérico: In Spain.
- Sistema Central: In Spain.
- Ural Mountains: Form the boundary between Europe and Asia.

Temperature and Precipitation

High mountain areas in Europe are colder and get more rain and snow. This is true for mountains everywhere. Eastern Europe gets less rain than central and western Europe. The difference between summer and winter temperatures increases as you go from the coast of northwest Europe to the inland southeast. For example, Ireland has only a 10°C difference between its warmest and coldest months. But the area north of the Caspian Sea has a 40°C difference.
In January, average temperatures range from 13°C in southern Spain to -20°C in northeastern Russia. Desert climates can be found in the European part of Kazakhstan and in southeastern Spain.
Western and parts of Central Europe usually have a mild maritime climate. Southern Europe mostly has a Mediterranean climate. The north-central part and east into central Russia have a humid continental climate. The very northern part of the continent has a subarctic climate. In the extreme north, bordering the Arctic Ocean, it's a tundra climate. Mountain ranges like the Alps have a highland climate. This means temperatures and weather change a lot depending on how high up you are and how far north or south.
Climate Zones
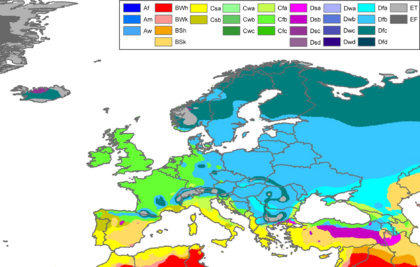
Europe has many different climate zones. These range from mild and wet along the Atlantic coast to cold and dry in the far east. The mountains also create their own unique climates.
Landlocked Countries
A landlocked country is one that is completely surrounded by land and has no access to the sea. The landlocked countries in Europe are:
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Belarus
- Czech Republic
- Hungary
- Kosovo
- Liechtenstein (which is doubly landlocked, meaning it's surrounded by other landlocked countries)
- Luxembourg
- North Macedonia
- Moldova
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Switzerland
- Vatican City
Eight of these countries form a continuous group in Central Europe and the Balkans. They stretch from Geneva to Skopje. These are Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Austria, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Serbia, and North Macedonia. The other landlocked countries in Europe do not border any other landlocked European country.
Countries Made of Islands or Parts of Islands
Some European countries are made up entirely of islands or parts of islands:
Countries Bordering or Spanning Other Continents
Some countries in Europe also have land or territories on other continents:
| Eurasia | Armenia, Azerbaijan, Republic of Cyprus, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Russia, Turkey, Greece (some Aegean islands and Kastelorizo island) |
| Europe-Africa | Malta, Spain (Ceuta, Melilla and Canary Islands), Italy (Lampedusa and Lampione), Portugal (Madeira), France (Réunion and Mayotte) |
| Europe-South America | France (French Guiana) |
| Europe-North America | France (Guadeloupe, Martinique, and St. Pierre et Miquelon), Iceland, Denmark (Greenland), the Netherlands (Bonaire, Saba, and St. Eustatius), Portugal (Corvo Island, Flores Island) |
Countries by Number of Neighbors
Here is a list of European countries based on how many other countries they share a border with:
| 14 | Russia (including Kaliningrad) |
| 11 | France (including overseas departments and territories) |
| 9 | Germany |
| 8 | Austria, Serbia, Turkey |
| 7 | Hungary, Poland, Ukraine |
| 6 | France (excluding overseas departments), Italy |
| 5 | Azerbaijan, Belarus, Bulgaria, Croatia, Kazakhstan, Romania, North Macedonia, Slovakia, Spain (including Ceuta and Melilla), Switzerland |
| 4 | Albania, Armenia, Belgium, the Czech Republic, Georgia, Greece, Kosovo, Latvia, Lithuania, Montenegro, Slovenia |
| 3 | Bosnia and Herzegovina, Finland, the Netherlands (including Sint Maarten), Norway, Luxembourg |
| 2 | Andorra, Estonia, Liechtenstein, Moldova, Sweden |
| 1 | Denmark, Ireland, Monaco, Portugal, San Marino, the United Kingdom, Vatican City |
| 0 | Iceland, Cyprus, Malta |
See also
 In Spanish: Geografía de Europa para niños
In Spanish: Geografía de Europa para niños
- Regions of Europe
- European Union
- Western Europe
- Central Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Northern Europe
- Southern Europe
- Southeast Europe
- Extreme points of Europe
- List of mountain ranges
 | DeHart Hubbard |
 | Wilma Rudolph |
 | Jesse Owens |
 | Jackie Joyner-Kersee |
 | Major Taylor |