Organisation of African, Caribbean and Pacific States facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Organisation of African, Caribbean and Pacific States
Organisation des États d'Afrique, des Caraïbes et du Pacifique
|
|
|---|---|
|
Flag
|
|
 |
|
| Secretariat | Brussels, |
| Official languages | |
| Government | |
|
• Secretary General
|
Moussa Saleh Batraki |
| Establishment | 6 June 1975 |
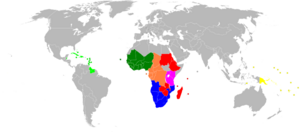
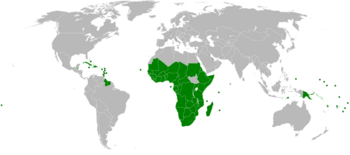
The Organisation of African, Caribbean and Pacific States (OACPS) is a group of countries from Africa, the Caribbean, and the Pacific. It was formed by the Georgetown Agreement in 1975. The group used to be called the African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States (ACP).
The main goals of the OACPS are to help its member countries grow in a healthy way, reduce poverty, and become more involved in the world's economy. All member countries, except for Cuba, have signed a special agreement with the European Union called the Cotonou Agreement.
Together, the OACPS and the EU represent over 1.5 billion people. They also hold more than half of the seats at the United Nations.
Contents
Partnership with Europe
The Cotonou Agreement, signed in Cotonou, Benin, in 2000, is a major partnership between the OACPS countries and the European Union. It replaced an older agreement called the Lomé Convention.
A key part of this new agreement is that it includes more than just governments. Groups like community organizations, private businesses, and local leaders can now help plan how their countries develop. They can also get funding and help carry out projects. This helps make sure that development plans meet the real needs of the people.
Who are the Members?
The OACPS is made up of countries from three main regions. These countries often work in smaller groups to trade and cooperate with the European Union.
African Countries
The African members are divided into five groups that work on trade deals, called Economic Partnership Agreements, with the EU.
"West Africa group" (ECOWAS plus Mauritania)
|
EAC group
"Eastern and Southern Africa group" (COMESA related)
|
Caribbean Countries
All of these countries are part of a group called CARIFORUM, which works on trade deals with the EU.
Pacific Countries
These countries, which are all developing nations from the Pacific Islands Forum group plus Timor-Leste, also work together on trade with the EU.
Special Support for Some Countries
The Cotonou Agreement understands that some countries face bigger challenges than others. Because of this, countries that are less developed, surrounded by land, or are small islands get extra help and better treatment.
Least-Developed Countries
These are countries with the lowest incomes and toughest economic challenges. The OACPS gives them special support to help them grow. Some of these countries are: Benin, Burundi, Chad, Ethiopia, Haiti, Liberia, Mali, Rwanda, Somalia, and Uganda.
Landlocked Countries
These countries have no access to the sea, which can make trading difficult. The OACPS helps them overcome these challenges. Examples include: Botswana, Burkina Faso, Eswatini, Lesotho, Malawi, Niger, and Zimbabwe.
Island Countries
Small island nations often face unique problems, like rising sea levels and distance from major markets. The OACPS provides special assistance to them. Some island members are: Barbados, Cuba, Fiji, Jamaica, Mauritius, Samoa, and Seychelles.
See also
- The Courier (ACP-EU) : A magazine about the partnership between the OACPS and the European Union.
- Everything but Arms: A special program that helps the poorest countries sell goods to the EU.