New Hampshire facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
New Hampshire
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Nickname(s):
Granite State
White Mountain State |
|||
| Motto(s): | |||
| Anthem: "Old New Hampshire" | |||
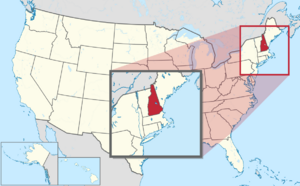
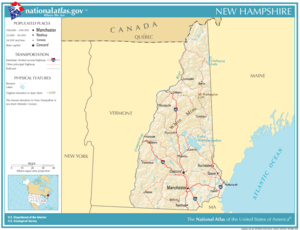
Location of New Hampshire within the United States
|
|||
| Country | United States | ||
| Before statehood | Province of New Hampshire | ||
| Admitted to the Union | June 21, 1788 (9th) | ||
| Capital | Concord | ||
| Largest city | Manchester | ||
| Largest county or equivalent | Hillsborough | ||
| Largest metro and urban areas | Greater Boston (combined and metro) Nashua (urban) |
||
| Legislature | General Court | ||
| • Upper house | Senate | ||
| • Lower house | House of Representatives | ||
| Judiciary | New Hampshire Supreme Court | ||
| U.S. senators | Jeanne Shaheen (D) Maggie Hassan (D) |
||
| U.S. House delegation | 1: Chris Pappas (D) 2: Maggie Goodlander (D) (list) |
||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 9,350 sq mi (24,216 km2) | ||
| • Land | 8,954 sq mi (23,190 km2) | ||
| • Water | 396 sq mi (1,026 km2) 4.2% | ||
| Area rank | 46th | ||
| Dimensions | |||
| • Length | 190 mi (305 km) | ||
| • Width | 68 mi (110 km) | ||
| Elevation | 1,000 ft (300 m) | ||
| Highest elevation | 6,288 ft (1,916.66 m) | ||
| Lowest elevation
(Atlantic Ocean)
|
0 ft (0 m) | ||
| Population
(2024)
|
|||
| • Total | 1,409,032 | ||
| • Rank | 41st | ||
| • Density | 150.70/sq mi (58.1860/km2) | ||
| • Density rank | 21st | ||
| • Median household income | $96,800 (2023) | ||
| • Income rank | 7th | ||
| Demonym(s) | Granite Stater New Hampshirite |
||
| Language | |||
| • Official language | English (French allowed for official business with Quebec; other languages allowed for certain specific uses) |
||
| Time zone | UTC−05:00 (Eastern) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 (EDT) | ||
| USPS abbreviation |
NH
|
||
| ISO 3166 code | US-NH | ||
| Traditional abbreviation | N.H. | ||
| Latitude | 42° 42′ N to 45° 18′ N | ||
| Longitude | 70° 36′ W to 72° 33′ W | ||
| Bird | Purple finch Haemorhous purpureus |
|---|---|
| Fish | Freshwater: Brook trout Salvelinus fontinalis Saltwater: Striped bass Morone saxatilis |
| Flower | Purple lilac Syringa vulgaris |
| Tree | White birch Betula papyrifera |
| Insect | Ladybug Coccinellidae |
| Sport | Skiing |
New Hampshire is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It shares borders with Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, and Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east. To the north, it borders the Canadian province of Quebec.
New Hampshire is the seventh-smallest U.S. state by land area and the tenth-least populated. In 2020, it had about 1.3 million residents. Concord is the state capital, and Manchester is its largest city.
The state's motto, "Live Free or Die", shows its important role in the American Revolutionary War. Its nickname, "The Granite State", comes from its many granite rock formations and quarries. New Hampshire is also famous for holding the very first primary election for U.S. presidents, which makes it a big deal in American politics.
After World War II, New Hampshire's factories became less important. The state's economy then grew to include financial services, real estate, education, and high-tech industries. Many people moved here from the Greater Boston area, making it one of the wealthiest and most educated states. New Hampshire is special because it does not have a state income tax or a sales tax. This means it relies a lot on local property taxes to pay for schools.
New Hampshire has many mountains and forests, making it a popular place for tourists. People enjoy outdoor activities like skiing, hiking, and watching the beautiful fall leaves. Mount Monadnock is one of the most climbed mountains in the world. The White Mountain National Forest is also a big attraction, with parts of the Appalachian Trail and the Mount Washington Auto Road.
Contents
- History of New Hampshire
- Geography of New Hampshire
- Wildlife of New Hampshire
- Government of New Hampshire
- Population and People
- Economy of New Hampshire
- Transportation in New Hampshire
- Education in New Hampshire
- Media in New Hampshire
- Sports in New Hampshire
- Culture of New Hampshire
- Notable People from New Hampshire
- Images for kids
- See also
History of New Hampshire
For thousands of years, different Abenaki tribes lived in the area that is now New Hampshire. These tribes spoke Algonquian languages. Archeological digs show that indigenous people lived near Keene, New Hampshire as far back as 12,000 years ago.
European explorers from England and France visited New Hampshire in the early 1600s. The first permanent European settlement was at Hilton's Point, which is now Dover. In 1629, the area was named the "Province of New Hampshire" after a county in England.
New Hampshire's Role in the American Revolution
New Hampshire was one of the Thirteen Colonies that fought against British rule during the American Revolution. In December 1774, Paul Revere warned American Patriots that the British would send more troops to Fort William and Mary. The next day, John Sullivan led a raid on the fort to take weapons. This event, where British soldiers fired at the rebels, happened about five months before the famous Battles of Lexington and Concord.
On January 5, 1776, New Hampshire became the first colony to declare its independence from Great Britain. This was almost six months before the United States Declaration of Independence was signed by the Continental Congress. New Hampshire later sent soldiers, ships, and supplies to help in the war against Britain.
On June 21, 1788, New Hampshire was the ninth state to approve the United States Constitution. This act officially put the Constitution into effect for the United States.
Growth and Industry
In the mid-1800s, New Hampshire became a strong supporter of President Franklin Pierce, who was from the state. Factories, especially textile mills, grew rapidly. These mills attracted many immigrants from Quebec (French Canadians) and Ireland. The Amoskeag Manufacturing Company in Manchester was once the largest cotton textile factory in the world.
After 1960, the textile industry faced challenges, but New Hampshire's economy recovered. It became a center for high technology and services. Since 1952, New Hampshire has gained national attention for its very early presidential primary election, which helps decide who will run for president.
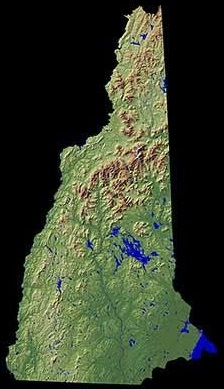
Geography of New Hampshire
New Hampshire is part of the New England region. It has a short coastline on the Atlantic Ocean, only about 18 miles (29 km) long.
Mountains and Lakes

The White Mountains are in the north-central part of the state. This range includes Mount Washington, the tallest mountain in the northeastern U.S. Mount Washington is known for having some of the "World's Worst Weather" because of its very strong winds and cold temperatures.
In southwestern New Hampshire, Mount Monadnock is a famous landmark. It's so unique that it gave its name to a type of mountain called a monadnock, which is an isolated peak rising from a flat area.
New Hampshire has more than 800 lakes and ponds. The largest is Lake Winnipesaukee, which covers about 71 square miles (184 km²).
Rivers and Borders
Major rivers include the Merrimack River, which flows south through the state, and the Connecticut River, which forms the western border with Vermont. The border with Vermont is actually at the low-water mark on the Vermont side, meaning the entire river belongs to New Hampshire along that stretch.
The Piscataqua River flows into the Atlantic Ocean at Portsmouth, creating the state's only major ocean port.
Forests and Climate
New Hampshire is covered in forests, especially the New England-Acadian forests with their conifer and hardwood trees. These forests are very popular in autumn for "leaf peepers" who come to see the bright fall colors.
The northern part of the state, called the "north country," is very sparsely populated. It relies on tourism, especially for skiing, snowboarding, and hiking, to help its economy.
New Hampshire has a humid continental climate. This means it has warm, humid summers and long, cold, snowy winters. Precipitation is spread out evenly throughout the year. The coastal areas have slightly milder winters, while the northern and mountainous areas are much colder.
Wildlife of New Hampshire
New Hampshire is home to many animals. You can find black bears, white-tailed deer, and moose across the state. There are also less common animals like the marten and the Canadian lynx.
Government of New Hampshire
New Hampshire's government has a governor and a five-member executive council. The council helps the governor make decisions, like approving state contracts and appointments. New Hampshire does not have a lieutenant governor; the Senate president takes over if the governor cannot do their job.
The state's legislature is called the General Court. It has two parts: the House of Representatives and the Senate. The House has 400 representatives, making it one of the largest elected groups in the world that speaks English. The Senate has 24 senators. Legislators are paid a very small salary, so most are like volunteers.
The highest court in the state is the New Hampshire Supreme Court.
Local Government
New Hampshire has 10 counties and 234 cities and towns. Most towns use a "town meeting" style of government, where citizens vote directly on local laws. Larger towns and cities have a council-manager or council-mayor system.
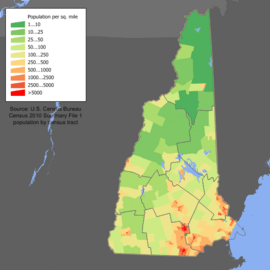
Population and People
In 2020, New Hampshire had about 1.37 million people. The population has been growing fastest in the southern part of the state, especially near the Massachusetts border. This is because many people who work in Boston and other Massachusetts cities live in New Hampshire.
The most populated areas are along the Merrimack River Valley and in the Seacoast Region. The northern part of the state is much less populated.
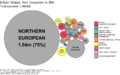
Many people in New Hampshire have French American ancestry, which is the highest percentage in the U.S. after Maine. This is because many French Canadians moved to New Hampshire for factory jobs in the past.
Religion in New Hampshire
New Hampshire is one of the least religious states in the United States. Many people in New Hampshire say they are not connected to any religion. Among those who are religious, the largest groups are Catholics and Protestants.
Economy of New Hampshire

New Hampshire's economy has changed a lot over time. In the past, it was known for textiles (making cloth), shoemaking, and small machine shops. Today, these industries are much smaller.
Now, New Hampshire has a diverse and growing economy. Its biggest economic areas include real estate, business services, manufacturing, government, and health care.
New Hampshire is unique because it does not have a general sales tax or a personal income tax. However, it does have other taxes, like on meals, lodging, and property. This means that local property taxes are very important for funding schools and other services.
The state's unemployment rate is usually very low. Most jobs are in the private sector, with many people working for smaller companies.
Largest Employers
Some of the largest private employers in New Hampshire include:
- Dartmouth–Hitchcock Medical Center (Lebanon)
- Fidelity Investments (Merrimack)
- BAE Systems North America (Nashua)
- Liberty Mutual (Dover)
- Elliot Hospital (Manchester)
- Dartmouth College (Hanover)
- Southern New Hampshire University (Manchester)
Transportation in New Hampshire
New Hampshire has a good network of highways, including Interstate highways, U.S. highways, and state highways. The state highway signs still show the image of the Old Man of the Mountain, even though the rock formation collapsed in 2003.
Major Highways
 Interstate 89: Runs northwest from near Concord to the Vermont border.
Interstate 89: Runs northwest from near Concord to the Vermont border. Interstate 93: The main Interstate, running north from the Massachusetts border to the Vermont border. It connects the southern part of the state to the Lakes Region and White Mountains.
Interstate 93: The main Interstate, running north from the Massachusetts border to the Vermont border. It connects the southern part of the state to the Lakes Region and White Mountains. Interstate 95: Briefly runs along New Hampshire's short coastline, serving Portsmouth.
Interstate 95: Briefly runs along New Hampshire's short coastline, serving Portsmouth. U.S. Route 3: The longest numbered route, running completely through the state from Massachusetts to Canada.
U.S. Route 3: The longest numbered route, running completely through the state from Massachusetts to Canada.
Airports

New Hampshire has 25 public airports. The busiest is Manchester-Boston Regional Airport, which serves the Greater Boston area.
Public Transportation
You can travel long distances by train on Amtrak's Vermonter and Downeaster lines. Bus companies like Greyhound and Concord Coach also provide connections to other cities.
There are also local and regional bus services around the state. Some groups are working to bring commuter train service from Massachusetts further into New Hampshire.
Education in New Hampshire

High Schools
New Hampshire has over 80 public high schools. Many of these schools serve students from more than one town. The largest is Pinkerton Academy in Derry. There are also about 30 private high schools.
New Hampshire is home to several well-known private preparatory schools, like Phillips Exeter Academy and St. Paul's School.
Colleges and Universities
New Hampshire has many colleges and universities, including:
- Dartmouth College
- University of New Hampshire
- Southern New Hampshire University
- Saint Anselm College
- Keene State College
- Plymouth State University
- And several community colleges
Media in New Hampshire
Daily Newspapers
- Concord Monitor
- New Hampshire Union Leader (Manchester)
- The Portsmouth Herald
- Keene Sentinel
- Foster's Daily Democrat (Dover)
- Laconia Daily Sun
- Berlin Daily Sun
Television Stations
- ABC affiliate WMUR, Channel 9, Manchester
- PBS affiliate Channel 11, Durham (New Hampshire Public Television)
Sports in New Hampshire
New Hampshire has several sports teams:
- New Hampshire Fisher Cats: A professional baseball team that plays in Manchester. They are part of the Double-A Eastern League.
- Nashua Silver Knights: A collegiate summer baseball team.
- Seacoast United Phantoms: A semi-professional soccer team.
The sport of paintball was actually invented in Henniker in 1981!
The New Hampshire Motor Speedway in Loudon is a popular place for car races, including NASCAR Cup Series events.
New Hampshire has two universities that compete in NCAA Division I sports: the Dartmouth Big Green and the New Hampshire Wildcats.
Culture of New Hampshire
In the spring, many "sugar houses" in New Hampshire have open houses where you can see how maple syrup is made. In the summer and early autumn, the state hosts many county fairs. The biggest is the Hopkinton State Fair.
New Hampshire's Lakes Region, especially around Lake Winnipesaukee, is a popular spot for summer vacations and camps. The Peterborough Players and the Barnstormers Theatre are famous summer theaters that have been performing for many years.
In September, New Hampshire hosts the New Hampshire Highland Games, celebrating Scottish culture. The beautiful fall foliage usually peaks in mid-October, attracting many visitors. In winter, people enjoy skiing, snowboarding, and snowmobiling. When the lakes freeze, you can see many small ice fishing huts, called bobhouses, on the ice.
Funspot in Laconia is known as the world's largest video arcade.
Notable People from New Hampshire
Many famous people have come from New Hampshire, including:
- Franklin Pierce: The 14th President of the United States.
- Daniel Webster: A famous Senator.
- Alan Shepard: An astronaut, the first American in space.
- Robert Frost: A well-known poet.
- Adam Sandler: A popular actor and comedian.
- Dean Kamen: An inventor.
- Sarah Silverman and Seth Meyers: Comedians.
- Richard and Maurice McDonald: The founders of McDonald's.
- Triple H: A famous WWE wrestler.
Images for kids
-
Downtown Manchester
See also
 In Spanish: Nuevo Hampshire para niños
In Spanish: Nuevo Hampshire para niños
 | Stephanie Wilson |
 | Charles Bolden |
 | Ronald McNair |
 | Frederick D. Gregory |