Northamptonshire facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
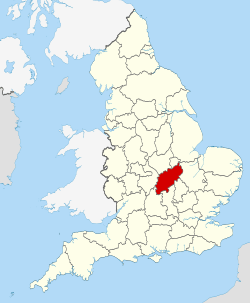
Northamptonshire
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Constituent country | England | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Region | East Midlands | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time zone | UTC±00:00 (Greenwich Mean Time) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+01:00 (British Summer Time) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Members of Parliament | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Northamptonshire, often called Northants., is a county in the East Midlands of England. It is known as "The Rose of the Shires" because of its beautiful countryside. In 2015, about 723,000 people lived here.
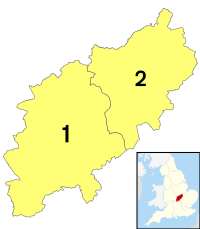
The county is managed by two main local councils: North Northamptonshire and West Northamptonshire. These are called unitary authorities because they handle all local government services.
Northamptonshire covers an area of 2,364 square kilometres (913 sq mi). It is surrounded by eight other counties. These include Warwickshire to the west and Cambridgeshire to the east. It is the most southern county in the East Midlands.
The main town is Northampton. Other important towns are Kettering, Corby, Wellingborough, Rushden, and Daventry. The county flower of Northamptonshire is the Cowslip.
Contents
History of Northamptonshire
Northamptonshire's early history shows few signs of human life. This was during the Paleolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic periods. Around 500 BC, the Iron Age began in the area. People from Europe brought the Hallstatt culture here. Over the next century, several hill-forts were built. Famous ones include Hunsbury Hill.
In the 1st century BC, the area became part of the Catuvellauni tribe's land. This was a Belgic tribe. The Romans then conquered the Catuvellauni in 43 AD.
A Roman road called Watling Street went through the county. An important Roman town, Lactodorum, was where Towcester is today. Other Roman settlements were in Northampton and Kettering. A large fort was built at Longthorpe.
After the Romans left, the area became part of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Mercia. Northampton became an important centre. In 654 AD, the Mercians became Christian.
Around 889, the Danes conquered the area. It became part of the Danelaw. Watling Street was the border. In 917, the English king Edward the Elder took it back. The Vikings of York conquered it again in 940. But the English retook it in 942. Because of this, the county has both Saxon and Danish town names.
The county was first mentioned in 1011. It was called Hamtunscire. This meant the shire (county) of Hamtun (the homestead). The "North" was added later to tell it apart from Southampton.
Rockingham Castle was built for William the Conqueror. It was a Royal fortress until the Elizabethan era. In 1460, during the Wars of the Roses, the Battle of Northampton happened. King Henry VI was captured. Fotheringhay Castle, now in ruins, held Mary, Queen of Scots, before her execution.
George Washington, the first President of the United States, had family from Northamptonshire. His ancestor, Lawrence Washington, bought Sulgrave Manor in 1539. George Washington's great-grandfather, John Washington, moved from Northants to Virginia in 1656.
During the English Civil War, Northamptonshire supported the Parliamentarians. The Royalist forces lost badly at the Battle of Naseby in 1645. King Charles I was held at Holdenby House in 1647.
In the 18th and 19th centuries, parts of Northamptonshire became industrialised. The main industry was shoemaking and leather. By the late 1800s, it was a world leader in boot and shoe making.
Corby became a new town in 1950. Northampton followed in 1968. The government is still encouraging new development in the area.
Peterborough's Connection
The Soke of Peterborough was historically linked to Northamptonshire. Its cathedral is important to the county's church area. However, Peterborough had its own local government. In 1974, it became part of Cambridgeshire.
Geography and Towns
Northamptonshire is a landlocked county. This means it has no coastline. It is in the southern part of the East Midlands. The county has the watershed between the River Severn and The Wash. Several important rivers start here. These include the River Nene and the "Warwickshire Avon". The highest point in the county is Arbury Hill at 225 metres (738 ft).
Northampton is the largest town. In 2011, the county had 691,952 people. Northampton had 212,069 residents.
Here are the towns with over 10,000 people:
| Rank | Town | Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Northampton | 212,100 (2011) |
| 2 | Kettering | 67,635 (2011) |
| 3 | Corby | 56,514 (2011) |
| 4 | Wellingborough | 49,087 (2011) |
| 5 | Rushden | 29,265 (2011) |
| 6 | Daventry | 25,026 (2011) |
| 7 | Brackley | 13,018 (2011) |
| 8 | Desborough | 10,697 (2011) |
As of 2010, there are 16 towns with a town charter. These include Brackley, Corby, Daventry, Kettering, Northampton, and Wellingborough.
Climate of Northamptonshire
Like the rest of the British Isles, Northamptonshire has an oceanic climate. This means it has mild winters and cool summers. It also has rainfall throughout the year.
| Climate data for Moulton, Northants | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 7 (45) |
8 (46) |
11 (52) |
13 (55) |
17 (63) |
19 (66) |
22 (72) |
23 (73) |
19 (66) |
14 (57) |
10 (50) |
7 (45) |
14 (58) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 2 (36) |
2 (36) |
4 (39) |
4 (39) |
7 (45) |
10 (50) |
12 (54) |
12 (54) |
10 (50) |
8 (46) |
5 (41) |
3 (37) |
7 (44) |
| Average precipitation cm (inches) | 4.51 (1.78) |
3.39 (1.33) |
2.87 (1.13) |
4.39 (1.73) |
3.49 (1.37) |
4.66 (1.83) |
4.21 (1.66) |
4.69 (1.85) |
5.49 (2.16) |
5.68 (2.24) |
4.8 (1.9) |
4.98 (1.96) |
53.16 (20.94) |
Transport Links
The gap in the hills at Watford Gap is important. It means many routes from south-east to north-west pass through Northamptonshire. Old Roman roads, canals, railways, and major roads all use this route.
Roads in Northamptonshire
Major roads like the M1 motorway (London to Leeds) and the A14 (Rugby to Felixstowe) cross the county. These roads help people travel north-south and east-west. The A43 connects the M1 to the M40 motorway. The A45 links Northampton with Wellingborough and Peterborough.
Rivers and Canals

Two major canals, the Oxford and the Grand Union, meet in the county at Braunston. You can see a flight of 17 locks on the Grand Union at Rothersthorpe. There is also a canal museum at Stoke Bruerne. The Blisworth tunnel is 2,813 metres (3,077 yd) long. It is the third-longest canal tunnel in the UK.
A branch of the Grand Union Canal connects to the River Nene in Northampton. This part is called the Nene Navigation. It is known for its special guillotine locks.
Railways in Northamptonshire

Two main railway lines cross the county: the Midland Main Line and the West Coast Main Line. In the past, Northamptonshire had 75 railway stations. Now, it has only six. These are at Northampton, Long Buckby, Kettering, Wellingborough, Corby, and King's Sutton.
Before 1948, three big railway companies operated here. These were the London, Midland and Scottish Railway, London and North Eastern Railway, and Great Western Railway. Today, the county is served by Chiltern Railways, East Midlands Railway, Avanti West Coast, and West Midlands Trains.
Corby's Rail History
For a long time, Corby was the largest town in Britain without a railway station. The line through Corby was mainly for freight. An experimental passenger service ran in the 1980s but stopped. On February 23, 2009, a new station opened. It provides direct hourly trains to London St Pancras. After Corby's station opened, Rushden became the largest town in the UK without a direct railway station.
Closed Lines and Future Plans
Many railway services in Northamptonshire closed in the 1960s. This was due to the Beeching cuts. The line connecting Northampton to Peterborough was closed. This left eastern Northamptonshire without railways. Part of this route reopened in 1977 as the Nene Valley Railway. Another closed line, the Northampton to Market Harborough line, is now a heritage railway called the Northampton & Lamport Railway. It is also part of the National Cycle Network.
The planned High Speed 2 railway line will go through the south of the county. However, it will not have any stations in Northamptonshire.
Buses and Airports
Most buses are run by Stagecoach Midlands. Some town routes have special names like Corby Star and Connect Kettering. Stagecoach's X4 route connects towns across the county. It runs between Northampton, Wellingborough, Kettering, Corby, Oundle, and Peterborough.
Sywell Aerodrome is near Sywell village. It has three grass runways and one concrete runway. It is not long enough for large passenger jets.
Culture and Entertainment
Northamptonshire has been home to several rock and pop bands. These include Bauhaus and The Communards. Richard Coles, a musician from The Communards, is now a vicar in Finedon.
The film Kinky Boots (2005) was based on a true story from a Northamptonshire shoe factory. Later, it became a stage musical.
Places to Visit
| Key | |
| Owned by the National Trust | |
| Owned by English Heritage | |
| Owned by the Forestry Commission | |
| A Country Park | |
| An Accessible open space | |
| Museum (free) | |
| Museum (charges entry fee) | |
| Heritage railway | |
| Historic House | |
- 78 Derngate

- Althorp
- Barnwell Country Park

- Barnwell Manor

- Billing Aquadrome
- Borough Hill Daventry (Iron Age hill fort)
- Boughton House (home of the Dukes of Buccleuch)

- Blisworth tunnel
- Brackley
- Brampton Valley Way (linear park on a disused railway line)
- Brixworth Country Park

- Burghley House (in the Soke of Peterborough, so formerly in Northants),

- Canons Ashby House
- Castle Ashby (home of the Marquess of Northampton),

- Coton Manor Garden
- Cottesbrooke Hall

- Daventry Country Park

- Deene Park

- Delapré Abbey
- Derngate and Royal Theatre
- Easton Neston

- Elton Hall

- Fermyn Woods Country Park

- Fotheringhay Castle & Church
- Franklin's Gardens
- Geddington's Eleanor cross
- Holdenby House

- Irchester Country Park

- Jurassic Way (long-distance footpath)
- Kelmarsh Hall

- Kirby Hall

- Knuston Hall

- Lamport Hall

- Lilford Hall

- Lyveden New Bield
- Pitsford Reservoir
- Prebendal Manor House, Nassington

- Naseby Field
- Northampton Cathedral
- Northampton & Lamport Railway
- Northamptonshire Ironstone Railway
- Piddington Roman Villa
- Rockingham Castle

- Rockingham Forest
- Rockingham Motor Speedway
- Rushden Hall
- Rushden, Higham and Wellingborough Railway
- Rushden Station Railway Museum
- Rushton Triangular Lodge

- Salcey Forest
- Silverstone Circuit
- Southwick Hall

- Stanwick Lakes

- Stoke Bruerne Canal Museum

- Sulgrave Manor

- Summer Leys nature reserve
- Syresham
- Sywell Country Park

- The Castle Theatre
- Watford Locks
- Wellingborough Museum

- Whittlewood Forest
- Wicksteed Park
Annual Events
- Gretton Barn dance
- British Grand Prix at Silverstone
- Burghley Horse Trials
- Crick Boat Show
- Hollowell Steam Rally
- Northampton Balloon Festival
- Rothwell Fair
- Rushden Cavalcade
- St Crispin Street Fair
- Wellingborough Carnival
- World Conker Championships
Economy and Industry

In the past, Northamptonshire was famous for making boots and shoes. Many factories closed in the 1980s, causing job losses. However, some shoe companies like Dr. Martens still have bases here.
Today, large employers include:
- Weetabix (breakfast cereals) in Burton Latimer
- Carlsberg brewery in Northampton
- Avon Products
- Siemens
- Barclaycard
- Saxby Bros Ltd
- Golden Wonder
The Daventry International Railfreight Terminal is a major rail freight hub. It is located near Rugby. Wellingborough also has a smaller rail freight depot.
Here is a chart showing the region's economic output in millions of British Pounds Sterling:
| Year | Regional Gross Value Added | Agriculture | Industry | Services |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 7,139 | 112 | 2,157 | 3,870 |
| 2000 | 9,743 | 79 | 3,035 | 6,630 |
| 2003 | 10,901 | 90 | 3,260 | 7,551 |
The area of Northamptonshire, Oxfordshire, and the South Midlands is known as "Motorsport Valley". It is a global centre for the motor sport industry. Formula One teams like Mercedes GP and Force India have bases here. Cosworth and Mercedes-Benz High Performance Engines are also in the county.
International motor racing takes place at Silverstone Circuit and Rockingham Motor Speedway. Santa Pod Raceway is nearby. A study found that motorsport sites in Northamptonshire attract over 2.1 million visitors each year. These visitors spend more than £131 million in the county.
Growth Area Plans
Northamptonshire is part of the Milton Keynes and South Midlands Growth area. This area is expected to have many new homes and jobs built between 2010 and 2020. Over 52,000 new homes and 47,000 new jobs are planned for North Northamptonshire. In West Northamptonshire, over 48,000 homes and 37,000 jobs are planned.
Sports in Northamptonshire
Rugby Union
Northamptonshire has many rugby union clubs. The top team is Northampton Saints. They play in the Aviva Premiership. In 2000, they won the European championship. They also won the Aviva Premiership in 2014. The Saints play at Franklin's Gardens, which can hold 15,249 fans.
Football (Soccer)
Northamptonshire has 24 football clubs. These clubs play in the top ten levels of the English football league system. The sport is managed by the Northamptonshire Football Association.
Northampton Town F.C.
The only fully professional football club in the county is Northampton Town. They have been part of the Football League since 1920. Their home ground is Sixfields Stadium, which opened in 1994. The stadium can hold up to 7,500 people.
Other Football Clubs
The county also has semi-professional teams. These include Kettering Town, Brackley Town, AFC Rushden & Diamonds, and Corby Town F.C.. Many teams also play in the United Counties League.
Cricket
Northamptonshire County Cricket Club is also known as The Steelbacks. They play their home games at the County Cricket Ground, Northampton. They have been runners-up in the County Championship four times.
In 2013, the club won the Friends Life t20 competition. In 2016, they won the Natwest t20 Blast trophy for the second time. They have also won the NatWest Trophy twice and the Benson & Hedges Cup once.
Motor Sport
Silverstone Circuit is a major motor racing track. It is famous for hosting the British Grand Prix. Part of the circuit is in Buckinghamshire. Rockingham Speedway was near Corby. It was one of the largest motor sport venues in the UK. It closed in 2018. The Santa Pod drag racing circuit is just over the border in Bedfordshire.
Two Formula One teams are based in Northamptonshire. Mercedes is in Brackley. Aston Martin is in Silverstone. Mercedes also builds engines for other teams in Brixworth.
Swimming and Diving
There are seven competitive swimming clubs in the county. These include Northampton Swimming Club and Wellingborough Amateur Swimming Club. There is also one diving club, Corby Steel Diving Club. The main pool is Corby East Midlands International Pool. It has an 8-lane 50m swimming pool.
Ellie Robinson, a paralympian from 2016, is from Northamptonshire. She trained at Northampton Swimming Club. She won three bronze and one silver medal at the 2016 IPC Swimming European Championships.
Education in Northamptonshire
Schools
Northamptonshire County Council used to manage the state-funded secondary schools. Since May 2021, education is managed by North Northamptonshire Council and West Northamptonshire Council.
The county's music and performing arts trust helps schools with music teaching. It also supports 15 local music and performing arts centres.
Colleges
There are seven colleges in the county. Tresham College of Further and Higher Education has four campuses. These are in Corby, Kettering, and Wellingborough. Tresham offers vocational courses and helps students retake GCSEs. It also offers higher education courses with universities. Other colleges include Moulton College and Northampton College.
University
Northamptonshire has one university, the University of Northampton. It has two campuses. About 10,000 students attend. It offers many courses, from basic to advanced degrees. These include arts, humanities, sciences, and product design.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Northamptonshire para niños
In Spanish: Northamptonshire para niños