Invasion of the United States facts for kids

Have you ever wondered if another country could invade the United States? An invasion of the United States means a foreign army attacking and taking over parts of the country. It's a big topic in military planning! The U.S. has been invaded a few times in its history. This happened during the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War, and the Mexican Border War. There were also three attacks on American soil during World War II. During the Cold War, the U.S. military mainly prepared to stop an attack from the Soviet Union.
Contents
Early Attacks on U.S. Soil
The military story of the United States started with a foreign army on its land. This was the British Army during the American Revolutionary War. After America became independent, the next attack was during the War of 1812. Again, it was against Britain. This was the only time since the Revolution that a foreign power took over the U.S. capital, Washington, D.C.. The city of Philadelphia was also captured by the British during the Revolution.
On April 25, 1846, Mexican soldiers entered Brownsville, Texas. They had long said this land belonged to Mexico. They attacked U.S. troops near the Rio Grande. This event, called the Thornton Affair, started the Mexican–American War. The fighting in Texas was the only part of this war on U.S. soil. The rest of the war happened in California and New Mexico, which were then part of Mexico, and in other parts of Mexico.
The American Civil War (1861-1865) also saw armies invade each other's home areas. Both the Confederate and Union armies entered enemy territory. After the Civil War, the chance of a foreign invasion seemed small. It wasn't until the 1900s that real military plans were made for an attack on America.
During the Mexican Revolution in 1915, Mexican rebels tried to carry out the Plan of San Diego. This plan aimed to take back Arizona, New Mexico, California, and Texas. They wanted to create a special place for Native Americans, Mexican Americans, Asian Americans, and African Americans. The plan also called for killing all white males over 16 in these areas. To do this, the rebels started the Bandit War. They launched violent raids into Texas from Mexico. U.S. President Woodrow Wilson recognized Venustiano Carranza as Mexico's leader. This was in exchange for Carranza's help to stop the border raids.
On March 9, 1916, Mexican revolutionary Pancho Villa and his fighters invaded Columbus, New Mexico. This was a response to President Wilson supporting Carranza. This event, the Battle of Columbus, led to the Pancho Villa Expedition. Major General John J. Pershing led U.S. troops into Mexico to find Villa.
Later, the Zimmermann Telegram was found and shared with the American public. This message showed that Germany offered to help Mexico take back its lost lands if Mexico joined Germany in a war against the U.S. This helped push the U.S. to declare war on Germany and join World War I.
European Threats
Before the 1900s, the biggest threat to attack the United States was thought to be the British Empire. U.S. coastal defenses were built to stop a British attack. Military plans were made to prevent a British invasion and to invade Canada. For example, "War Plan Red" was a secret U.S. plan to deal with a British attack and then invade Canada. There were also plans for a war with Mexico, but Mexico's army was not seen as strong enough to invade the U.S.
Interestingly, Canada also had a plan to invade the U.S. in 1921, called Defence Scheme No. 1. This plan said Canada would invade the U.S. quickly if war broke out. The goal was to gain a foothold in the northern U.S. This would give Canada time to prepare for war and get help from Britain. Canadian troops would try to seize cities like Seattle, Spokane, and Portland. Other troops would attack Fargo and Great Falls. Soldiers from Quebec would try to take Albany. Troops from the Maritime Provinces would invade Maine. If U.S. resistance grew, Canadian soldiers would retreat. They would destroy bridges and railways to slow down the U.S. army. Some people thought this plan was not realistic, but others believed it could work.
The British military thought it would be impossible to defend Canada against the much larger U.S. army. They felt that sacrificing Canada to distract U.S. troops would be best for the British Empire. A full invasion of the U.S. was not seen as possible. A naval blockade was thought to be too slow. The Royal Navy also knew that Great Britain was very weak if its supplies were cut off. If the United States Navy came near the British Isles, the United Kingdom would have to surrender quickly. So, the British planned for a big naval battle against the U.S. Navy. This battle would likely happen near Bermuda. Other British ships would attack American merchant ships and protect British convoys. The British also planned to attack U.S. coastal bases with bombs, shelling, and landings by sea. Soldiers from British India and Australia would help attack Manila. This would stop U.S. attacks on British ships in Asia and prevent an attack on Hong Kong. The British government hoped these actions would make the war unpopular in America. This would force the U.S. government to agree to peace talks.
Meanwhile, Imperial German plans for the invasion of the United States were also made between 1897 and 1906. These were mostly military exercises. Early plans involved a naval battle off Norfolk, Virginia, then bombing cities on the East Coast. Later plans imagined landing troops to take over New York City and Boston. However, these plans were never taken seriously. Germany did not have enough soldiers or resources to carry them out. In reality, Kaiser Wilhelm II wanted to have good relations with the U.S. and avoid making them angry. This policy continued until the U.S. joined World War I in 1917.
From 1914 to 1917, German spies in the U.S. worked secretly. They tried to delay or destroy military supplies being sent from American factories to the Allied Powers. These efforts led to acts of sabotage, like the Black Tom explosion in 1916 and the Kingsland explosion in 1917.
World War II
During World War II, defending Hawaii and the mainland U.S. was very important. The American Campaign Medal was given to military members who served on the U.S. mainland. Those in Hawaii received the Asiatic-Pacific Campaign Medal.
Nazi Germany
When Germany declared war on the U.S. in 1941, the German military leaders knew they could not attack or invade the United States directly. Their strategy focused on submarine warfare. German U-boats attacked American ships in the Battle of the Atlantic. This included a major attack on U.S. merchant ships called Operation Drumbeat.
Adolf Hitler did not think America was a serious threat. He said the country had no "racial purity" and therefore no fighting strength. He also claimed that "The American public is made up of Jews and Negroes." However, other German leaders, like Albert Speer, had more realistic views. They saw America's huge factory power and rich food supplies.
In 1942, German military leaders briefly looked into the idea of an attack across the Atlantic. This included the Amerika Bomber project, which aimed to build long-range bombers. Only a few test planes were built. This plan had to be dropped because Germany lacked bases in the Western Hemisphere. Also, Germany's ability to build such planes quickly decreased as the war went on. After this, Germany's best hope for an attack on America was to see what happened in the war between the U.S. and Japan. By 1944, with many U-Boat losses and the occupation of Greenland and Iceland, it was clear Germany could not attack the U.S. directly. In the end, Germany's military strategy was actually to surrender to America. Many battles on the Western Front were fought just to escape the advancing Red Army and surrender to the Western Allies instead.
One of the few times German soldiers officially landed in the U.S. was during Operation Pastorius. Eight German sabotage agents were dropped off by U-Boats. One team landed in New York, the other in Florida. The teams were quickly caught. They were tried as spies, not prisoners-of-war, because of their mission. Six agents were executed in the electric chair. The other two were not killed. They received prison terms because they helped the FBI by telling them about the mission. In 1948, after the war, the two were freed and sent back to Allied-occupied Germany.
The Luftwaffe (German air force) started planning for possible long-range bombing missions early in World War II. Albert Speer wrote in his book that Adolf Hitler loved the idea of New York City burning. Even before he came to power in 1933, Hitler thought the U.S. would be the next big enemy after the Soviet Union. The plan for the Amerika Bomber project was given to Hermann Göring in 1942. This was about six months after the attack on Pearl Harbor. Only a few test planes were built by Junkers and Messerschmitt before the war ended.
Imperial Japan

A full invasion of Hawaii and the U.S. mainland by Imperial Japan was not really possible. Japan did not have enough soldiers or supplies to do it. Minoru Genda of the Imperial Japanese Navy suggested invading Hawaii after the attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941. He believed Japan could use Hawaii as a base to threaten the U.S. mainland. This might help them end the war. After Pearl Harbor, many Americans on the West Coast of the United States feared a Japanese landing. There was even a false alarm about a raid in the Battle of Los Angeles.
The Japanese military never seriously planned to invade Hawaii after Pearl Harbor. However, they did carry out Operation K on March 4, 1942. Two Japanese planes dropped bombs on Honolulu to disrupt repair work after Pearl Harbor. This caused only minor damage.
On June 3-4, 1942, the Japanese Navy attacked the Territory of Alaska. This was part of the Aleutian Islands campaign. They bombed Dutch Harbor in Unalaska, causing damage and killing 43 Americans. A few days later, 6,000–7,000 Japanese troops landed and took over the Aleutian Islands of Attu and Kiska. U.S. and Canadian forces drove them out a year later, between May and August 1943. The Aleutian Islands campaign was the only foreign invasion of U.S. soil during World War II. It was also the first major foreign occupation of American soil since the War of 1812. Japan also attacked the U.S. using fire balloons. Six American civilians were killed by these attacks. Japan also launched two manned air attacks on Oregon. There were also two times when Japanese submarines shelled the U.S. West Coast.
While Alaska was the only U.S. territory that was fully part of the U.S. that Japan invaded, Japan did successfully invade other U.S. territories in the Pacific shortly after Pearl Harbor. These included Wake Island, Guam, and the Philippines.
Cold War Threats
During the Cold War, the main threat to the United States was from the Soviet Union. If an attack happened, it was almost certain to involve nuclear weapons. This would mainly be through intercontinental ballistic missile attacks. Also, Soviet Navy submarines could launch SLBMs at U.S. coastal cities.
The first Cold War plan against a Soviet attack was made in 1948. It became a stronger policy after the Soviet Union developed nuclear weapons in 1949. By 1950, the U.S. had a defense plan. It aimed to stop Soviet nuclear bombers using interceptor planes and anti-aircraft missiles. The U.S. also planned to send its own bombers into Soviet airspace from bases in Alaska and Europe. By the late 1950s, both the Soviet Union and the U.S. had nuclear submarines and long-range nuclear missiles. These could strike in just ten to thirty minutes. Bombers took four to six hours to reach their targets. This led to the idea of the nuclear triad. This meant using all three types of weapons (land-based missiles, submarine missiles, and bombers) together for a powerful first strike. This would be followed by a counterstrike and "mopping up" missions by nuclear bombers.
Operation Washtub was a top-secret project. It was a joint effort between the United States Air Force and the Federal Bureau of Investigation. Its main goal was to leave secret agents in Alaska Territory to gather information. A second goal was to create safe places for U.S. forces to hide and escape.
On June 22, 1955, a U.S. Navy plane with 11 crew members was attacked. Two Soviet Air Forces fighter planes attacked it. This happened along the International Date Line in international waters over the Bering Straits, between Siberia and Alaska. The U.S. plane crashed near the village of Gambell. Villagers rescued the crew. Three were wounded by Soviet fire, and four were hurt in the crash.
American nuclear war planning was almost put to the test during the Cuban Missile Crisis. The blockade of Cuba added a fourth part to American nuclear strategy: surface ships. It also raised the possibility of small nuclear attacks against deployed fleets. The U.S. had already tested nuclear attacks on ships during Operation Crossroads. It is said that one Soviet submarine almost launched a nuclear torpedo at an American warship. But the three officers needed to launch it could not agree to do so.
By the 1970s, the idea of mutually-assured destruction (MAD) became central. This meant that if one side attacked with nuclear weapons, the other side would also attack. This would destroy both sides. This nuclear strategy stayed mostly the same until the end of the Cold War.
Modern Era Threats
In the 21st century, U.S. military planners face new threats. These include direct attacks, terrorism, and new types of warfare. This includes cyberwarfare or economic attacks on U.S. investments and money.
Direct Attack
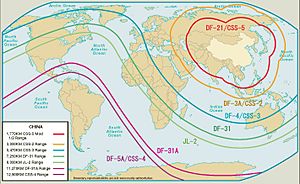
Several modern armies have nuclear weapons that can travel thousands of kilometers. So, the U.S. could be attacked by nuclear powers like the United Kingdom, Russia, China, France, and India. However, the UK and France are part of NATO and are long-time U.S. allies. India is also a close partner. So, an attack on the U.S. by any of these countries is very unlikely.
The United States Northern Command and the United States Indo-Pacific Command are the main U.S. military groups. They are in charge of defending the mainland U.S. and Hawaii.
Cyber and Economic Attacks
The risk of cyberattacks on computer systems is now well known. These targets include civilian, government, and military networks. For example, China has been suspected of using government-funded hackers. These hackers try to disrupt American banking systems, defense industries, and communication systems. They also target power grids, utility controls, and air traffic systems. Even some military systems, like those for command and missile launches, are at risk.
Attacks on the U.S. economy are also seen as a way a foreign power might attack the country. This could include trying to lower the value of the dollar or controlling trade markets to isolate the U.S.
Why Invasion is Hard
Many experts believe it is very hard to invade the U.S. This is because of its strong industries and fast supply lines. The country is also very large. Its location and population size make it difficult to invade. Plus, it has natural barriers like deserts in the Southwest and the Great Lakes in the Midwest. These protect major cities from invasion.
An invasion from outside North America would need very long supply lines across the Pacific or Atlantic Oceans. This would greatly reduce an enemy's power. No country today has enough power to threaten the U.S. on the North American continent. This is because Canada and Mexico are friendly with the U.S. and have much weaker militaries.
Military expert Dylan Lehrke noted that a sea attack on either the West or East Coast would be too small to get a strong foothold. Even if an enemy could sneak in without being seen, they could not build up a large force before being pushed back into the sea. Also, Hawaii is protected by 40,000 U.S. military personnel. This acts as a huge deterrent to any foreign invasion of the island state and the mainland U.S.
So, an invasion of the mainland would likely have to come from the land borders with Canada or Mexico. An attack from Mexico is possible. But California and Texas have the most defense industries and military bases in the country. These provide a strong defense. The Southwestern desert also divides any invasion into two parts. An attack from Canada on the Midwest or the West would be limited to light infantry. It would fail to take over cities or important strategic points. This is because there are mostly farms and empty national parks along the border. Powerful airbases are located hundreds of miles south. This gives U.S. military personnel or local groups an advantage to fight a guerrilla war. Because of all these reasons, many people call the U.S. "uninvadable."
In Popular Culture
Many films and other media show made-up stories about attacks on the U.S. by foreign powers.
- The film Red Dawn (1984) shows an attack on the U.S. by the Soviet Union, Cuba, and Nicaragua. A 2012 remake shows a similar attack by North Korea and Russian ultranationalists.
- Other films include Invasion U.S.A., Olympus Has Fallen, and White House Down.
- The Day After and By Dawn's Early Light both show nuclear war between U.S. and Soviet forces.
- The 1999 film South Park: Bigger, Longer & Uncut shows Canadian forces invading a Colorado town.
- The 1987 miniseries Amerika shows a bloodless Soviet takeover.
- Invasion U.S.A. (1985) stars Chuck Norris fighting Soviet and Cuban-led guerrillas.
- In Philip K. Dick's book The Man in the High Castle, the United States is taken over by Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan. They are separated by a neutral zone after invasions of both coasts.
- A terrorist takeover of Washington, D.C. was shown in a G.I. Joe cartoon episode. Serpentor led Cobra forces to occupy the capital. A similar takeover was seen in G.I. Joe: Retaliation.
- In The Simpsons' episode "You Only Move Twice," Homer Simpson works for a terrorist group. Their leader threatens violence if demands are not met. The terrorists end up taking control of the U.S. East Coast.
Video games also explore this idea:
- In Call of Duty: Modern Warfare 2, Russia invades parts of the U.S., including Washington, D.C. This is in response to a supposed U.S.-helped terrorist attack in Russia. In Call of Duty: Modern Warfare 3, the battle spreads to New York.
- Homefront shows an invasion of the U.S. by a unified Korea. Homefront: The Revolution shows North Korea invading and taking over the U.S.
- In World in Conflict, Soviet forces invade the Pacific Northwest region of the U.S. They are eventually pushed back.
- Turning Point: Fall of Liberty is set in an alternate universe. The Axis Powers win World War II and invade the U.S. in 1953.
- Bethesda Softworks's Wolfenstein: The New Order and The New Colossus are set in a world where Germany won World War II. This includes a mainland invasion of the U.S. after a nuclear bomb hit New York City.
- The 2003 video game Freedom Fighters is set in an alternate history where the Soviet Union won the Cold War. They conquered most of the world and invaded the U.S. from Alaska and New York City.
- In Command & Conquer: Red Alert 2, the Soviet Union launches a huge invasion of the U.S. They use psychic beacons to control the population.
See also
 In Spanish: Anexo:Ataques en territorio de Estados Unidos para niños
In Spanish: Anexo:Ataques en territorio de Estados Unidos para niños
 | Lonnie Johnson |
 | Granville Woods |
 | Lewis Howard Latimer |
 | James West |