Car facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Car |
|
|---|---|

|
|
| Classification | Vehicle |
| Industry | Various |
| Application | Transportation |
| Fuel source | Gasoline, diesel, natural gas, electric, hydrogen, solar, vegetable oil |
| Powered | Yes |
| Self-propelled | Yes |
| Wheels | 3–4 |
| Axles | 2 |
| Inventor | Karl Benz |

A car is a road vehicle that carries people. Most cars have four wheels and an engine or motor to make them move. Cars are also called automobiles. This name comes from the Greek word "auto" (meaning "self") and the French word "mobile" (meaning "moving"). So, an automobile is a "self-moving" vehicle. It doesn't need horses or other outside power to go!
Contents
Exploring Different Types of Cars
Cars come in many shapes and sizes. They are designed for different needs. Here are some common types of cars you might see:
- A convertible is a car with a roof that can open or be taken off. This lets you enjoy an open-air drive. Sportier convertibles are sometimes called roadsters.
- A hatchback is a smaller car. It has a cargo area that is part of the main cabin. This is different from a separate trunk. Hatchbacks offer a mix of sportiness and storage space.
- A station wagon (or estate car in British English) is like a hatchback. However, it has a less sloped back window. This gives it more room for passengers and luggage.
- A pickup truck is a type of truck. It has a separate cabin for people and an open cargo area called a "bed."
- A sedan is a car with four doors. It has a sloped back window and a separate trunk.
- A coupé (or coupe in American English) is similar to a sedan. But it usually has only two doors. Coupés are often seen as sportier than sedans.
- An SUV (sport utility vehicle) is a tough vehicle. It has a combined area for passengers and cargo. SUVs are very popular because they are useful for many things.
- A van is a large, box-shaped vehicle. It's made for carrying lots of people or cargo. There are different sizes of vans. For example, minivans are popular for families.
How Cars Get Their Energy
Cars need energy to make their wheels turn and move. This energy can come from chemical energy in gasoline. Or it can be electrical energy stored in a battery. The power of a car's engine or motor tells you how quickly it can send energy to the wheels. Car power is often measured in kilowatts or horsepower.
Cars That Use Gasoline
Most cars today still burn fuel to run an internal combustion engine. This engine is sometimes called a "motor." The power from the engine goes to the wheels through a transmission. This part has gears that help the car go faster or slower. The most common fuel is petrol, also known as "gasoline" or "gas."
Gasoline is a fossil fuel. It comes from tiny fossils that formed millions of years ago. Over time, these fossils turned into oil. This oil is then drilled up from deep inside the Earth. It is then changed into fuel. Older gasoline cars were noisy. Their exhaust made city air dirty, which could make people sick. But cars made after the mid-2010s are much cleaner.
Burning gasoline creates carbon dioxide. This gas contributes to global warming. Because of this, fewer gasoline cars are being made since 2017. Some places, like Amsterdam, plan to ban gasoline cars in the future.
Electric Cars and Batteries
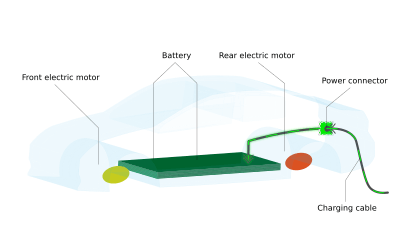
The cleanest cars are electric vehicles. They usually plug into a power outlet or a charging station. They store electricity in a battery pack, often located at the bottom of the car. This electricity powers an electric motor, which turns the wheels. Some electric cars have two motors, one for the front wheels and one for the back. A few even have four motors, one for each wheel!
Other Ways Cars Get Power
Some cars use diesel fuel, which is common in big trucks and buses. A few even use wood gas. In countries like Brazil and Sweden, a mix of ethanol and gasoline is used. This mix is called "gasohol" in Brazil and "E85" in Sweden. Other fuels include propane, natural gas, compressed air, and ethanol (which comes from plants). Some special cars, called "flex-fuel" cars, can run on more than one type of fuel.
A few cars create electricity from hydrogen fuel cells. An example is the Honda Clarity. Right now, most hydrogen comes from burning fossil fuels. But scientists and engineers are working to make hydrogen from renewable energy cheaper and easier to use.
Some cars even use solar cells to get electricity from the sun. These are not very common for everyday driving. But there is a competition each year where people design cars to go the farthest using only solar energy.
There's also a type of car that uses both a gasoline engine and an electric motor. This is called a hybrid electric vehicle. The Toyota Prius is a famous example.
Regenerative Brakes
All cars have brakes that use friction to stop the car. Electric cars also have regenerative brakes. These brakes slow the car down by turning its movement energy back into electricity. It's like the electric motor working in reverse! So, "regenerative" means the electricity is made again.
A Brief History of Cars
The very first vehicles that moved on their own were steam engines attached to wagons. This was in the late 18th century. These early steam wagons were heavy and slow. Better steam cars became more common in the late 1800s.
In the early 1900s, some cars were powered by electricity. But they were slow and heavy. They weren't used much until the idea came back later in the century.
The internal combustion engine changed cars forever. This engine uses gasoline, diesel, or kerosene. When the fuel explodes inside a cylinder, it pushes a piston. This movement then turns the wheels.
Many people tried to build a successful car. But most people agree that Karl Benz invented the modern automobile. In 1886, he used a four-stroke internal combustion engine to power his Benz Patent-Motorwagen. He started making and selling many cars in Germany in 1888.
In North America, the first modern car was made by brothers Charles and J. Frank Duryea. This happened in Springfield, Massachusetts. The Duryea brothers' car also won the first-ever car race in 1895. They raced against cars made by Benz. The race was 53 miles long, in Chicago, Illinois. The Duryeas then started making cars for everyday use in 1896. That year, they built 13 cars by hand.

Karl Benz invented the first modern car. The Duryeas made the first car to be sold. But Henry Ford sold the most cars to the most people. In 1910, he started making and selling his Ford Model T. It was a huge success! Many people could afford this car, not just the rich. This was because Ford used mass production. This means he made many Model Ts quickly in a factory. People say the Model T "put America on wheels." It was popular because it was cheap but still good quality.
Since then, many different cars have been designed. These range from minivans to sports cars. In the 1950s, the United States made and used more cars than the rest of the world combined. Fifty years later, China became the biggest maker and user of cars.
Benefits of Having a Car

Cars are faster than walking or riding a bike for long distances. They can carry more than one person and a lot of luggage. Depending on local public transport, cars can be faster and more convenient than buses, bicycles, or trains. Cars can also go to places where public transport cannot. 4-wheel drive vehicles are especially good for bad roads or rough land. However, they cost more and use more fuel.
Most cars protect people and cargo from the weather. They have a roof, doors, and windows. Modern cars also have safety features like seat belts, airbags, and crumple zones. These features protect people in case of crashes. They would be too expensive or impossible on two-wheeled vehicles or most buses.
With regular check-ups, cars can last a long time. In some countries, like Australia, cars must be checked by mechanics regularly. This ensures they are safe to drive. You can take your car to a mechanic. Or a mobile mechanic can come to you for repairs.
Challenges of Car Ownership
Buying and running a car costs a lot of money. This is especially true for newer, good-quality cars. You have to pay for the car itself, fuel, and parts like tyres. There are also costs for maintenance, repairs, and insurance (to cover crashes or theft). You might also pay for parking, toll roads, and taxes or licensing fees from the government.
When cars crash, they can get damaged and hurt people. A person's life is more important than keeping a car from damage. When too many cars try to go the same way, traffic congestion happens. This slows everyone down. Cars can cause air pollution, especially in cities. The pollution from cars around the world also contributes to climate change.
Many places with lots of people have public transportation. This includes buses, trains, trams, and subways. These can help people travel more quickly and cheaply than by car, especially when there are traffic jams. Some problems can be reduced by carpooling. This means many people ride together in one car.
Traffic jams and accidents can be dangerous for other road users. This includes people riding bicycles or walking. This is especially true in old towns not built for many cars. Some towns built in the 20th century were designed mainly for cars. This can cause more pollution and traffic. It also means fewer people walk. Communities can be divided by big roads. Pedestrians are in danger where there are not enough footbridges or safe crossings.
Images for kids
-
Steam Machine Of Verbiest, in 1678 (Ferdinand Verbiest)
-
Gustave Trouvé's tricycle, the first ever electric automobile to be shown in public
-
Carl Benz, the inventor of the modern car
-
Bertha Benz, the first long distance driver
-
Ransom E. Olds founded Olds Motor Vehicle Company (Oldsmobile) in 1897.
-
Henry Ford founded Ford Motor Company in 1903.
-
Kiichiro Toyoda, president of the Toyota Motor Corporation 1941–1950
-
The Toyota Corolla is the best-selling car of all-time.
-
2011 Nissan Leaf electric car
-
In the Ford Model T the left-side hand lever sets the rear wheel parking brakes and puts the transmission in neutral. The lever to the right controls the throttle. The lever on the left of the steering column is for ignition timing. The left foot pedal changes the two forward gears while the centre pedal controls reverse. The right pedal is the brake.
-
A Chevrolet Suburban extended-length SUV weighs 3,300 kg (7,200 lb) (gross weight).
-
Road congestion is an issue in many major cities (pictured is Chang'an Avenue in Beijing).
-
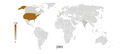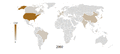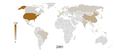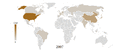
Vehicles in use per country from 2001 to 2007. It shows the significant growth in BRIC.
-
A robotic Volkswagen Passat shown at Stanford University is a driverless car.
See also
 In Spanish: Automóvil para niños
In Spanish: Automóvil para niños
 | John T. Biggers |
 | Thomas Blackshear |
 | Mark Bradford |
 | Beverly Buchanan |