Southwestern United States facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Southwestern United States
|
|
|---|---|
| American Southwest, the Southwest | |
|
Monument Valley, AZ
Cathedral Rock – Sedona, AZ
Route 66 in downtown Albuquerque, New Mexico
Palace of the Governors in Santa Fe, NM
Mojave Desert willow
|
|
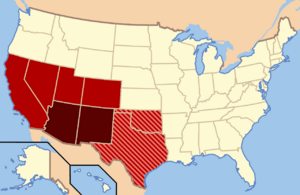
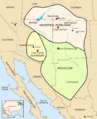
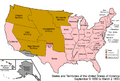
Though regional definitions vary from source to source, Arizona and New Mexico (in dark red) are almost always considered the core, modern-day Southwest. The brighter red and striped states may or may not be considered part of this region. The brighter red states (California, Colorado, Nevada, and Utah) are also classified as part of the West by the U.S. Census Bureau, though the striped states are not; Oklahoma and Texas are classified as part of the South.
|
|
| Country | United States |
| States | Core: Arizona New Mexico Others, depending on boundaries used: California Colorado Nevada Utah Oklahoma Texas |
The Southwestern United States is a special area of the United States. It is also called the American Southwest or just the Southwest. This region includes Arizona and New Mexico. It also has parts of California, Colorado, Nevada, Oklahoma, Texas, and Utah.
Some of the biggest cities here are Phoenix, Las Vegas, El Paso, Albuquerque, and Tucson.
Contents
- Exploring the Southwest: Geography
- Southwest Weather: Climate
- Plants and Landscapes: Vegetation and Terrain
- Animals of the Southwest: Wildlife
- Amazing Places: National Parks, Monuments, and Forests
- Big Cities: Cities and Urban Areas
- A Look Back: History
- People of the Southwest: Demographics
- Southwest Style: Culture
- Places to Visit
- Fun Facts About the Southwest
- Images for kids
- See also
Exploring the Southwest: Geography


The Southwest has amazing landforms!
- Deserts: A lot of the Southwest is covered in deserts. These include the Mojave, Sonoran, and Chihuahuan Deserts. They are hot and dry. But they are also home to unique plants and animals. You can find cacti and lizards here.
- Colorado Plateau: This is a large, high desert area. It has flat-topped hills called mesas. It also has steep-sided canyons.
- Mountains: There are also mountains in the Southwest. The Rocky Mountains are one example. These mountains have cooler temperatures and lots of trees.
- Grand Canyon: The Grand Canyon is a huge, deep canyon. The Colorado River carved it in Arizona. It is one of the most famous landmarks in the United States! The Grand Canyon is 277 miles long. It is 18 miles wide and one mile deep in some parts!
- Rivers: The two main rivers in this region are the Colorado River and the Rio Grande. The Rio Grande is 1,885 miles long.
Southwest Weather: Climate
The Southwest is known for its hot and dry climate.
- Little Rain: The deserts in the Southwest get very little rain. Some areas get less than 10 inches of rain each year!
- Hot Summers: Summers are very hot. Temperatures often reach over 100 degrees Fahrenheit (38 degrees Celsius).
- Mild Winters: Winters are mild. Temperatures rarely drop below freezing.
- Lots of Sunshine: Many places in the Southwest have over 300 days of sunshine every year!
Plants and Landscapes: Vegetation and Terrain

The plants in the Southwest are special. You can find different types of yucca plants. There are also many kinds of cacti. These include saguaro cactus, barrel cactus, and prickly pear cactus. Other plants are desert spoon, creosote bush, sagebrush, and greasewood. Many native cacti grow in Nevada, Utah, Colorado, and west Texas.
The landscape has mountains, canyons, and mesas. You can also see flat-topped hills called buttes. There are high basins, plateaus, and desert lands. Some areas also have plains. The entire Southwest is mostly dry or very dry. For example, the Texas Hill Country has dry, rocky hills. South Texas is mostly flat with scrub and bare soil.
Animals of the Southwest: Wildlife
The Southwest has many different kinds of animals.
Birds of the Southwest
This region has many bird species. Over 400 species can be found in the Chiricahua Mountains in Arizona alone.
- Famous Birds: The roadrunner is the state bird of New Mexico. It is found in all Southwest states.
- Water Birds: You can see Canadian and snow geese. There are also sandhill cranes.
- Birds of Prey: Many birds of prey live here. These include the red-tailed hawk, golden eagles, and osprey. Different types of owls also live here, like the barn owl and the great horned owl.
- Other Birds: Other birds include the northern cardinal, hummingbirds, and Gambel's quail. You can also find different types of doves.
Mammals of the Southwest
Many mammals live in the Southwest.
- Common Mammals: You can find bobcats, coyotes, and black bears. Other animals include desert bighorn sheep, mule deer, and mountain lions.
- Unique Mammals: Elk live in parts of Colorado, New Mexico, Utah, and Arizona. White-nosed coati and collared peccary (also called javelina) are found near the Mexican border. Jaguars can be found in parts of New Mexico. The Mexican wolf was brought back to Arizona and New Mexico in 1998.
Reptiles and Amphibians
The Southwest is home to many snakes, lizards, and turtles.
- Snakes: There are many types of snakes. Some are the rosy boa and different kinds of kingsnakes. Rattlesnakes are also common, like the western diamondback rattlesnake. The ridge-nosed rattlesnake is the state reptile of Arizona.
- Lizards: Lizards are very common. The Gila monster is a unique lizard found only in the American Southwest and Mexico. The New Mexico whiptail is the state reptile of New Mexico. You can also find horned lizards and spiny lizards.
- Turtles: A few types of turtles live here. These include the desert box turtle and the desert tortoise.
- Amphibians: Many toads and frogs live in the Southwest. The Colorado River toad is one example. There are also salamanders like the Arizona tiger salamander.
Fish of the Southwest
Even though the Southwest is dry, some unique fish live in its waters.
- Unique Fish: The Apache trout and Gila trout are special fish found only here.
- Desert Pupfish: Pupfishes are small fish that live in isolated ponds. They can survive in very hot water. Many of these fish are endangered. This is because their homes are shrinking due to human water use.
Amazing Places: National Parks, Monuments, and Forests

The Southwestern United States has many famous national parks.
- Arizona: Grand Canyon, Petrified Forest, and Saguaro are here. You can also visit Monument Valley, which is a Navajo Nation park.
- California: Death Valley and Joshua Tree are in Southern California.
- Colorado: Great Sand Dunes, Black Canyon of the Gunnison, and Mesa Verde are found here.
- Nevada: Great Basin is Nevada's national park.
- New Mexico: Carlsbad Caverns and White Sands are in New Mexico.
- Texas: Big Bend and Guadalupe Mountains are in West Texas.
- Utah: Arches, Bryce Canyon, Canyonlands, Capitol Reef, and Zion are all in Utah.
There are also many national monuments and forests to explore!
Big Cities: Cities and Urban Areas
The Southwest has many large cities. Phoenix is one of the biggest cities in the whole country. Albuquerque and Las Vegas have grown very fast.
The largest city areas are around Phoenix (over 5 million people), Las Vegas (over 2.2 million), Tucson (over 1 million), Albuquerque (over 900,000), and El Paso (over 840,000).
-
2. El Paso (5th largest MSA)
-
3. Las Vegas (2nd largest MSA)
-
4. Albuquerque (also the 4th largest MSA)
-
5. Tucson (3rd largest MSA)

Top 5 Largest Cities (2020 Census)
| Rank | City | State | Population | Metro Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Phoenix | Arizona | 1,608,139 | 4,845,832 |
| 2 | El Paso | Texas | 678,815 | 868,859 |
| 3 | Las Vegas | Nevada | 641,903 | 2,265,461 |
| 4 | Albuquerque | New Mexico | 564,559 | 916,528 |
| 5 | Tucson | Arizona | 542,629 | 1,043,433 |
A Look Back: History
The Southwest has a long and interesting history.
- Native Americans: Native Americans have lived in the Southwest for thousands of years. Some major tribes include the Navajo, Pueblo, Apache, and Hopi. Hundreds of years ago, the Ancestral Pueblo and Hohokam peoples built large houses. They used mud bricks and stone. Some were built on the sides of cliffs. You can still see these ruins today at Mesa Verde National Park.
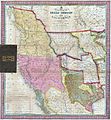
- Spanish Explorers: Spanish explorers arrived in the 1500s. They claimed the land for Spain. They built missions and settlements.
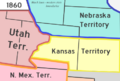
- Mexican Territory: Later, the Southwest became part of Mexico.
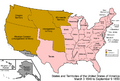
- American Southwest: In the mid-1800s, the United States gained much of the Southwest. This happened after a war with Mexico. The land was acquired under the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo.
- Statehood: Over time, the territories in the Southwest became states in the United States.
People of the Southwest: Demographics
Many different groups of people live in the Southwest.
- Hispanic Americans: You can find many Hispanic Americans in every major city. For example, in El Paso (80%) and Albuquerque (47%). Over 60% of the Latino population here are Mexican American.
- Asian Americans: The largest Asian American groups are in California and Texas. There is also a notable Asian population in Phoenix.
- Native Americans: The biggest Native American populations are in New Mexico and Arizona. More than 20% of all Native Americans in the U.S. live in the Southwest.
Before 1700, the only permanent Spanish settlements were along the Rio Grande in New Mexico.
Southwest Style: Culture
The Southwest has a unique culture. It is a mix of Native American, Spanish, and Mexican traditions.
- Food: Southwestern food is known for its bold flavors. It often uses chili peppers. Popular dishes include tacos, enchiladas, and chili.
- Music: Southwestern music mixes Native American, Spanish, and Mexican styles.
- Art: Southwestern art includes pottery, weaving, and painting. Many designs are inspired by nature and Native American traditions.
- Architecture: Southwestern buildings often feature adobe (mud brick) with flat roofs. They also have courtyards. The Spanish brought their Baroque style. This led to a unique style called Churrigueresque.
Places to Visit
The Southwest has many amazing places to visit!
- Grand Canyon National Park (Arizona): A huge canyon carved by the Colorado River. It offers breathtaking views and hiking trails.
- Arches National Park (Utah): Home to over 2,000 natural sandstone arches.
- Mesa Verde National Park (Colorado): See ancient cliff dwellings built by the Ancestral Pueblo people.
- White Sands National Park (New Mexico): A vast landscape of white gypsum sand dunes.
- Death Valley National Park (California): The hottest, driest, and lowest national park in the United States.
- Big Bend National Park (Texas): A remote park with mountains, desert, and the Rio Grande River.
- Bryce Canyon National Park (Utah): Known for its unique rock formations called hoodoos.
- Zion National Park (Utah): Features steep red cliffs and the Virgin River.
Fun Facts About the Southwest
- The Grand Canyon is so big that it can have different weather at the top and the bottom!
- The Sonoran Desert is the only place in the world where the saguaro cactus grows naturally.
- The city of Santa Fe, New Mexico, was founded in 1610. It is the oldest capital city in the United States.
- The Hoover Dam is a huge dam on the Colorado River. It provides water and electricity to the Southwest.
- The Carlsbad Caverns National Park in New Mexico has 83 caves. It is home to over a million bats!
Images for kids
-
The Delicate Arch at Arches National Park.
-
White Sands National Park, New Mexico.
-
Little Finland in Gold Butte National Monument, Nevada.
-
Mountains in Zion National Park, Utah.
-
Ancestral Puebloan ruins at Chaco Canyon.
-
1846 map: Mexican Alta California (Upper California) in pink.
See also
 In Spanish: Suroeste de Estados Unidos para niños
In Spanish: Suroeste de Estados Unidos para niños
- Pacific Southwest
- Southwest Conference (for a different division of the US for sports)
- Water Education Foundation
- Western United States