Syracuse, New York facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Syracuse
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Downtown Syracuse
JMA Wireless Dome
Hanover Square
Columbus Circle Historic District
Panorama of Columbus Circle Historic District
|
|||
|
|||
| Nickname(s):
The Salt City
|
|||
| Country | |||
| State | |||
| Region | Central New York | ||
| Statistical area | Syracuse Metropolitan | ||
| County | |||
| Incorporated (village) | 1825 | ||
| Incorporated (city) | 1847 | ||
| Named for | Syracuse, Sicily | ||
| Government | |||
| • Type | Strong mayor-council | ||
| Area | |||
| • City | 25.64 sq mi (66.41 km2) | ||
| • Land | 25.06 sq mi (64.90 km2) | ||
| • Water | 0.58 sq mi (1.51 km2) 2.15% | ||
| Elevation | 380–440 ft (116–135 m) | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • City | 148,620 | ||
| • Density | 5,930.80/sq mi (2,289.88/km2) | ||
| • Urban | 413,660 (US: 102nd) | ||
| • Urban density | 2,291.3/sq mi (884.7/km2) | ||
| • Metro | 662,057 (US: 91st) | ||
| • CSA | 738,305 (US: 72nd) | ||
| Demonym(s) | Syracusan | ||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (Eastern Daylight Time) | ||
| ZIP Code |
132xx
|
||
| Area codes | 315, 680 | ||
| FIPS code | 36-73000 | ||
| GNIS feature ID | 0966966 | ||
Syracuse (/ˈsɪrəkjuːz, ˈsɛr-, -kjuːs/ sirr-Ə-kewz-,_-serr--,_--kewss) is a city in New York, United States. It is the main city of Onondaga County, New York. About 148,620 people live here. This makes it the fifth-largest city in New York State.
Syracuse was officially started in 1820. It was named after the ancient Greek city of Syracuse in Italy. The two cities have similar natural features. Syracuse has always been an important meeting point. First, it was where the Erie Canal and other canals met. Later, it became a major railway hub. Today, two big highways, I-81 and I-90, cross paths here. Its airport, Syracuse Hancock International Airport, is the biggest in the Central New York area.
Syracuse is a center for business and education in Central New York. It has many places for big events and is home to important schools. These include Syracuse University, SUNY Upstate Medical University, SUNY ESF, and Le Moyne College.
Contents
History of Syracuse
Early European Settlers
French missionaries were the first Europeans to arrive in this area. They came in the mid-1600s to work with the Native Americans. The Onondaga Nation, part of the Iroquois Confederacy, invited a Jesuit priest named Simon Le Moyne. He set up a mission called Ste. Marie de Gannentaha on the shore of Onondaga Lake.
These missionaries found salty springs around "Salt Lake," which is now Onondaga Lake. French fur traders also traded with the Iroquois. Later, Dutch and English colonists traded here too. The English claimed the area from their base in Albany, New York.
The Salt City's Beginnings
After the American Revolutionary War, settlers moved into central New York. The state of New York set aside this area as the Onondaga Salt Springs Reservation. This led to a big salt-making industry from the late 1700s to the early 1900s. Salt came from wells that tapped into salt beds near Tully, New York. This fast-growing industry gave the area its nickname: "The Salt City."
The first settlement in Syracuse was a mix of small towns. It didn't even have a post office because it didn't have a name. In 1820, John Wilkinson suggested the name "Syracuse." He had read about Syracuse, Sicily and saw how similar it was with its lake and salt springs. On February 4, 1820, the village officially became "Syracuse."
Industry and Growth
The first Solvay Process Company plant in the United States was built near Onondaga Lake in 1884. This plant made soda ash from salt and limestone. This new process was a big improvement for making chemicals. The Syracuse Solvay plant helped create a large chemical industry. However, this industry also caused Onondaga Lake to become very polluted.
After the Civil War, the salt industry slowed down. But new factories took its place. In the late 1800s and early 1900s, many businesses started here. These included the Franklin Automobile Company, which made the world's first air-cooled engine. The Smith Corona company and Gustav Stickley's Craftsman Workshops also grew here.
Education and Events
Syracuse University was founded on March 24, 1870. It was one of the first universities to allow both men and women to study. This policy attracted many female students.
The first New York State Fair was held in Syracuse in 1841. After moving around for many years, it found a permanent home in Syracuse. It has been an annual event since then, except during World War II and in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Unique Traffic Light
Syracuse is home to the only "green on top" traffic light. It was put in place in 1928. Local youths used to throw rocks at the "British red" light that was originally on top. These locals were called "stonethrowers." Today, the Tipperary Hill Heritage Memorial remembers this history.
Modern Challenges and Changes
World War II brought many new industries to Syracuse. After the war, big car companies like General Motors and Chrysler had operations here. Carrier Corporation and Crouse-Hinds also had their headquarters or major plants in the city.
However, in the 1970s, many factories started to close or move away. This led to higher unemployment. General Electric moved its TV factory, and Carrier Corporation moved its headquarters. Even though the city's population has gone down since 1950, the wider Syracuse area has stayed about the same size.
Today, the Syracuse Community Grid project is changing downtown Syracuse. It is removing a highway to improve the city.
-
Historic Clinton Square
-
Erie Canal in Syracuse
Geography and Environment
Syracuse is located at 43°2′49″N 76°8′40″W / 43.04694°N 76.14444°W. It is about 87 miles (140 km) east of Rochester and 145 miles (230 km) west of Albany. It is also about halfway between New York City and Toronto.
The city covers about 66 square kilometres (25.6 square miles) of land and water. It is at the northeast edge of the Finger Lakes region. While the center of Syracuse is flat, many neighborhoods are on small hills. The land north of the city is flat, but to the south, it is hilly.
Trees and Water
About 27% of Syracuse is covered by trees. This is more than in other nearby cities like Albany or Rochester. The Labor Day Storm in 1998 destroyed about 30,000 trees. The most common tree is the sugar maple.
Syracuse gets its water from Skaneateles Lake. This is one of the cleanest lakes in the country. It is about 15 mi (24 km) southwest of the city. Water from Onondaga Lake cannot be used for drinking because it was heavily polluted by industries for many years.
Onondaga Creek flows through downtown Syracuse. The Onondaga Creekwalk runs along it, connecting different neighborhoods.
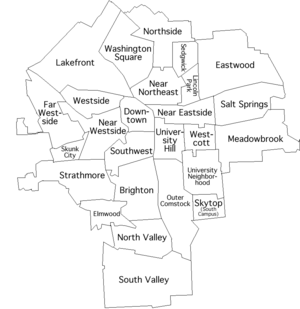
City Neighborhoods
Syracuse has 26 official neighborhoods. Some of these were once separate villages that joined the city. Syracuse also owns and runs Syracuse Hancock International Airport, which is north of the city.
Syracuse's neighborhoods show its diverse population. For example, Irish, Polish, and Ukrainian Americans settled on the west side. German and Italian Americans lived on the north side. African Americans settled on the south side. Recently, many refugees from the Middle East have moved to the north side.
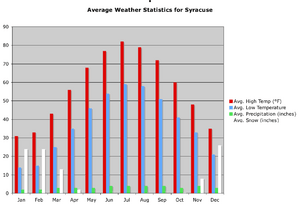
Climate and Snowfall
Syracuse has a climate with warm summers. It is famous for its heavy snowfall, getting about 115.6 inches (2.94 meters) of snow each year. This is the most snow of any major city in the United States. Syracuse often wins the Golden Snowball Award for the most snow among upstate New York cities.
The most snow in one season was 192.1 in (4.88 m) in 1992–93. The snowiest month was January 2004, with 78.1 in (1.98 m). This heavy snow comes from both the "lake effect" of nearby Lake Ontario and storms from the Atlantic Ocean. Snow often falls in small amounts almost every day during winter.
Big snowstorms happen sometimes. The Blizzard of 1993 brought 42.9 in (109 cm) of snow in just two days. Syracuse got more snow than any other city during this storm.
Syracuse gets about 38.47 inches (977 millimeters) of rain and snow each year. July through September are the wettest months. The average temperature ranges from 23.6 °F (−4.7 °C) in January to 71.3 °F (21.8 °C) in July. The hottest day ever was 102 °F (39 °C) in July 1936. The coldest was −26 °F (−32 °C).
| Climate data for Syracuse Hancock International Airport, New York (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1902–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 70 (21) |
75 (24) |
87 (31) |
92 (33) |
96 (36) |
100 (38) |
102 (39) |
101 (38) |
98 (37) |
89 (32) |
81 (27) |
72 (22) |
102 (39) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 57.1 (13.9) |
54.3 (12.4) |
66.9 (19.4) |
80.6 (27.0) |
87.8 (31.0) |
91.2 (32.9) |
92.8 (33.8) |
91.4 (33.0) |
88.4 (31.3) |
79.6 (26.4) |
68.7 (20.4) |
59.1 (15.1) |
94.3 (34.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 31.7 (−0.2) |
33.6 (0.9) |
42.4 (5.8) |
56.4 (13.6) |
69.2 (20.7) |
77.3 (25.2) |
81.7 (27.6) |
80.3 (26.8) |
73.1 (22.8) |
60.1 (15.6) |
48.3 (9.1) |
37.1 (2.8) |
57.6 (14.2) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 24.1 (−4.4) |
25.5 (−3.6) |
33.8 (1.0) |
46.3 (7.9) |
58.2 (14.6) |
67.0 (19.4) |
71.8 (22.1) |
70.4 (21.3) |
62.9 (17.2) |
51.3 (10.7) |
40.5 (4.7) |
30.4 (−0.9) |
48.5 (9.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 16.5 (−8.6) |
17.5 (−8.1) |
25.2 (−3.8) |
36.2 (2.3) |
47.3 (8.5) |
56.7 (13.7) |
62.0 (16.7) |
60.4 (15.8) |
52.7 (11.5) |
42.4 (5.8) |
32.7 (0.4) |
23.7 (−4.6) |
39.4 (4.1) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | −6.1 (−21.2) |
−3.0 (−19.4) |
5.3 (−14.8) |
23.2 (−4.9) |
34.1 (1.2) |
43.9 (6.6) |
51.9 (11.1) |
49.3 (9.6) |
38.0 (3.3) |
28.8 (−1.8) |
17.5 (−8.1) |
3.6 (−15.8) |
−9.6 (−23.1) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −26 (−32) |
−26 (−32) |
−16 (−27) |
7 (−14) |
25 (−4) |
34 (1) |
44 (7) |
38 (3) |
25 (−4) |
18 (−8) |
−1 (−18) |
−26 (−32) |
−26 (−32) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 2.58 (66) |
2.46 (62) |
3.04 (77) |
3.48 (88) |
3.42 (87) |
3.56 (90) |
3.86 (98) |
3.70 (94) |
3.38 (86) |
3.89 (99) |
3.23 (82) |
3.28 (83) |
39.88 (1,013) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 34.0 (86) |
30.3 (77) |
19.8 (50) |
3.0 (7.6) |
0.1 (0.25) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.51) |
9.8 (25) |
30.6 (78) |
127.8 (325) |
| Average extreme snow depth inches (cm) | 12.9 (33) |
13.5 (34) |
11.1 (28) |
1.4 (3.6) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
4.1 (10) |
9.9 (25) |
18.5 (47) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 18.9 | 16.6 | 15.5 | 14.5 | 13.2 | 12.0 | 11.7 | 10.7 | 11.1 | 15.1 | 15.9 | 18.5 | 173.7 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 17.8 | 15.2 | 10.1 | 2.5 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 5.9 | 13.6 | 65.5 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 73.2 | 72.3 | 69.6 | 65.2 | 67.1 | 69.9 | 70.5 | 74.9 | 76.4 | 74.3 | 75.4 | 76.8 | 72.1 |
| Average dew point °F (°C) | 15.3 (−9.3) |
16.3 (−8.7) |
24.1 (−4.4) |
33.3 (0.7) |
45.1 (7.3) |
55.0 (12.8) |
59.9 (15.5) |
59.7 (15.4) |
53.1 (11.7) |
41.7 (5.4) |
32.7 (0.4) |
21.7 (−5.7) |
38.2 (3.4) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 102.8 | 116.7 | 172.5 | 204.4 | 243.1 | 260.6 | 289.3 | 247.1 | 193.0 | 144.3 | 76.7 | 69.0 | 2,119.5 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 35 | 40 | 47 | 51 | 53 | 57 | 62 | 57 | 51 | 42 | 26 | 25 | 48 |
| Source: NOAA (relative humidity, dew point, and sun 1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
People and Population
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1850 | 22,271 | — | |
| 1860 | 28,119 | 26.3% | |
| 1870 | 43,051 | 53.1% | |
| 1880 | 51,792 | 20.3% | |
| 1890 | 88,143 | 70.2% | |
| 1900 | 108,374 | 23.0% | |
| 1910 | 137,249 | 26.6% | |
| 1920 | 171,717 | 25.1% | |
| 1930 | 209,326 | 21.9% | |
| 1940 | 205,967 | −1.6% | |
| 1950 | 220,583 | 7.1% | |
| 1960 | 216,038 | −2.1% | |
| 1970 | 197,208 | −8.7% | |
| 1980 | 170,105 | −13.7% | |
| 1990 | 163,855 | −3.7% | |
| 2000 | 146,070 | −10.9% | |
| 2010 | 145,170 | −0.6% | |
| 2020 | 148,620 | 2.4% | |
| Historical Population Figures 2020 | |||
| Race / Ethnicity (NH = Non-Hispanic) | Pop 2000 | Pop 2010 | Pop 2020 | % 2000 | % 2010 | % 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White alone (NH) | 91,928 | 76,653 | 68,206 | 62.41% | 52.80% | 45.89% |
| Black or African American alone (NH) | 36,246 | 40,672 | 43,568 | 24.61% | 28.02% | 29.32% |
| Native American or Alaska Native alone (NH) | 1,538 | 1,390 | 1,170 | 1.04% | 0.96% | 0.79% |
| Asian alone (NH) | 4,929 | 7,971 | 10,346 | 3.35% | 5.49% | 6.96% |
| Pacific Islander alone (NH) | 54 | 37 | 57 | 0.04% | 0.03% | 0.04% |
| Some Other Race alone (NH) | 350 | 303 | 897 | 0.24% | 0.21% | 0.60% |
| Mixed Race or Multi-Racial (NH) | 4,493 | 6,108 | 8,751 | 3.05% | 4.21% | 5.89% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 7,768 | 12,036 | 15,625 | 5.27% | 8.29% | 10.51% |
| Total | 147,306 | 145,170 | 148,620 | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
In 2010, there were 145,170 people living in Syracuse. The city had 57,355 households. About 29% of these households had children under 18. The average household had 2.31 people.
The population of Syracuse is very diverse. Many people have Italian, Irish, Polish, German, and English backgrounds. In 2020, Syracuse saw its population grow for the first time in over 70 years.

Religious Communities
| Religion | % of Population |
|---|---|
| Percent religious | 56.0% |
| Catholicism | 36.2% |
| Other Christian | 16.3% |
| Islam | 1.4% |
| Eastern religion (Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism) | 1.2% |
| Judaism | 0.9% |
Many Christians in Syracuse are Catholic. This is because many Irish, German, Italian, and Eastern European Catholics moved to the city long ago. Syracuse has the Roman Catholic Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception. The historic Basilica of the Sacred Heart of Jesus also offers services in English and Polish.
Other Christian groups, like the Episcopal church, also have large communities. The Episcopal St. Paul's Cathedral is another important church.
Syracuse also has communities for Buddhism, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism, and Sikhism. There are also two Unitarian Universalist societies.
Economy and Jobs

Syracuse used to be a big manufacturing city. But over the years, many factory jobs have left. Now, the main jobs are in education, health care, and services. Some high-tech manufacturing still exists.
University Hill is a fast-growing area. This is because Syracuse University and Upstate Medical University are expanding. Many small medical offices are also opening there.
Major Employers

The biggest employers in Syracuse are:
- State University of New York Upstate Medical University: 10,959 employees
- Syracuse University: 5,700 employees
- St. Joseph's Health (Syracuse, New York): 4,755 employees
- Wegmans Food Markets: 3,713 employees
- Crouse Hospital: 3,100 employees
- Amazon: 2,500 employees
- Loretto (elder care services): 2,476 employees
- Lockheed Martin Corp.: 2,300 employees
- National Grid USA: 2,200 employees
- Carrier Corporation: 1,552 employees
- SRC Inc: 1,500 employees
- Syracuse VA Medical Center: 1,400 employees
- Baxter (Welch Allyn): 1,000 employees
Micron Technology Complex

Micron Technology plans to build a huge computer chip factory complex near Syracuse. This could be the largest private investment in New York's history. Micron plans to start building in 2024. This project could create 9,000 direct jobs and 40,000 other jobs over the next 20 years.
This big investment was helped by the CHIPS and Science Act. This law helps grow the computer chip industry in the United States.
Tallest Buildings
The State Tower Building has been the tallest building in Syracuse since 1927.
| Name | Height | Floors | Use | Built |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| State Tower Building | 95 m | 23 | Office | 1928 |
| AXA Tower I | 82 m | 19 | Commercial office | 1966 |
| AXA Tower II | 82 m | 19 | Commercial office | 1971 |
Shopping and Business Areas
Besides the large Destiny USA shopping mall, Syracuse has many active business areas in its neighborhoods:
- Downtown: Armory Square is the main area for shops and restaurants. It has about 30 places to eat and 20 bars. Hanover Square is another smaller business area.
- Eastwood: This area calls itself "the village within the city." It has shops along James Street.
- Little Italy: This neighborhood has Italian roots. It features bakeries, restaurants, and shops.
- University Hill: Marshall Street has many stores, bars, and restaurants. They mostly serve the students and workers on "The Hill."
- Westcott: This neighborhood is known for its unique and artistic feel. It has restaurants, bars, and shops on Westcott Street. It also hosts the Westcott Street Cultural Fair every September.
-
Buildings in Downtown
Arts and Culture

Performing Arts
Syracuse hosts two annual outdoor jazz music festivals: the Syracuse Jazz Festival and the CNY Jazz Arts Foundation's Jazz in the Square Festival. Famous musicians like Smokey Robinson and Aretha Franklin have performed here. The Polish Festival also features Grammy-winning artists.
The Syracuse Symphoria, started in 2013, is a professional orchestra. The Clinton String Quartet has been playing for over 15 years. The Society for New Music supports new classical music.
The Syracuse Opera Company performs three operas each season. They also offer free outdoor concerts. The Syracuse Shakespeare Festival performs plays by William Shakespeare for free in Thornden Park.
Syracuse Stage puts on experimental and creative plays. Some of their shows have even moved to Broadway. The Red House Arts Center offers performances and art exhibits. Syracuse also has a lively music scene, especially for heavy metal, hardcore, and punk rock.
Museums and Art Galleries
- Everson Museum of Art opened in 1968. It has one of the largest pottery collections in the U.S. It also shows American art from the 1700s to today.
- Erie Canal Museum teaches about the history of the Erie Canal and how it helped Syracuse grow.
- International Mask and Puppet Museum in Little Italy focuses on masks and puppets. They also use puppets for educational shows for kids.
- Milton J. Rubenstein Museum of Science and Technology (MOST) has exhibits about science and technology.
- Onondaga Historical Association Museum & Research Center shows exhibits about Syracuse's past. It also has historical records and a display about the Underground Railroad.
- Syracuse and Onondaga County Fire Museum will be in an old fire station on Wolf Street.
Public Libraries
The Onondaga County Public Library (OCPL) runs Syracuse's public libraries. This includes the Central Library and ten city libraries. You can use a library card from any OCPL library at any other OCPL library.
City Libraries
- Central Library
- Beauchamp Branch Library
- Betts Branch Library
- Hazard Branch Library
- Mundy Branch Library
- Northeast Community Center Library
- Paine Branch Library
- Petit Branch Library
- Soule Branch Library
- Southwest Community Center Library
- White Branch Library
Suburban Libraries
- Baldwinsville Public Library
- Brewerton NOPL
- Cicero NOPL
- DeWitt Community Library
- East Syracuse Free Library
- Elbridge Free Library
- Fairmount Community Library
- Fayetteville Free Library
- Jordan Bramley Library
- LaFayette Public Library
- Liverpool Public Library
- Manlius Library
- Marcellus Free Library
- Maxwell Memorial Library
- Minoa Library
- North Syracuse NOPL
- Onondaga Free Library
- Salina Library
- Skaneateles Library
- Solvay Public Library
- Tully Free Library
Education in Syracuse
Schools for Kids
The Syracuse City School District has 34 schools and 4 special education programs. In the 2014–2015 school year, about 20,084 students were enrolled. The district works with Say Yes to Education. Their goal is for every student to graduate high school ready for college or other training.
Colleges and Universities

Syracuse is home to several important universities.
- Syracuse University is a major research university on University Hill. In 2017–2018, it had 22,484 students.
- SUNY Upstate Medical University is right next to Syracuse University. It is one of the country's academic medical centers. It provides over 10,000 jobs and has a medical school.
- SUNY College of Environmental Science and Forestry (SUNY ESF) is also next to Syracuse University.
- Le Moyne College is on the eastern edge of the city.
- Onondaga Community College has its main campus nearby and two smaller campuses in the city.
- Other colleges include a branch of SUNY's Empire State College and Bryant & Stratton College. There are also nursing colleges at Crouse Hospital and St. Joseph's Hospital.
-
Joe Biden speaking at Syracuse University
Parks and Recreation
Syracuse has over 170 parks and recreation areas, covering more than 1,000 acres (4.0 km2).
- Burnet Park has the first public golf course in the United States (from 1901) and the Rosamond Gifford Zoo.
- Other big parks include Thornden Park, Schiller Park, Sunnycrest Park, Onondaga Park, and Kirk Park.
- The city has 12 public swimming pools and two public ice rinks.
- Onondaga Park in the Strathmore neighborhood has Hiawatha Lake and a beautiful gazebo.
Just outside the city, along Onondaga Lake, is Onondaga Lake Park. On Sundays in the summer, the parkway is closed to cars. This lets people walk, run, bike, and rollerblade safely. During the holidays, the park hosts Lights on the Lake, a two-mile (3.2 km) drive-through light show.
-
Upper Onondaga Park in Strathmore
-
Inner harbor at Onondaga Lake
Sports in Syracuse

Local Sports Teams
| Club | Sport | League | Founded | Venue | League titles |
Championship years |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syracuse Mets | Baseball | IL | 1934 | NBT Bank Stadium | 8 | 1935, 1942, 1943, 1947, 1954, 1969, 1970, 1976 |
| Syracuse Stallions | Basketball | TBL | 2018 | Manlius Pebble Hill School | 0 | N/A |
| Syracuse Crunch | Ice hockey | AHL | 1994 | Upstate Medical University Arena | 0 | N/A |
| Syracuse FC | Soccer | NPSL | 2017 | Onondaga Community College | 0 | N/A |
College Sports
| School | Nickname | Colors | Association | Conference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syracuse University | Orange | Orange and blue | NCAA Division I-A | ACC |
| Le Moyne College | Dolphins | Green and gold | NCAA Division I | NEC |
| Onondaga Community College | Lazers | Carolina blue and white | NJCAA Division III | Mid-State Athletic Conference |
| SUNY Environmental Science and Forestry | Mighty Oaks | Green, white and gold | USCAA | HVIAC |
Sports at Syracuse University are very popular. Basketball games often have over 30,000 fans. Football games have over 40,000 fans. Many famous professional players, like Ernie Davis and Jim Brown, came from Syracuse University. Both teams play in the JMA Wireless Dome.
Syracuse was also home to some top professional teams in the past. The Syracuse Nationals basketball team won a championship in 1955 before moving to Philadelphia.
Media and News
Syracuse.com is the most popular local news website in Central New York. Advance Media NY owns syracuse.com and also produces The Post-Standard newspaper. These two media groups reach many people in the Syracuse area.
Radio Stations
Syracuse has many AM and FM radio stations.
| Frequency | Call sign | Format | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| AM 570 | WSYR | News/Talk | Also heard on 106.9 WSYR-FM (Solvay) |
| AM 620 | WHEN | Urban adult contemporary | Also heard on 101.7 W269DT in Syracuse |
| AM 1070 | WZUN | Classic hits | Licensed to Sandy Creek-Pulaski, New York and heard on 106.1 W291BU in Fulton (See also: WZUN-FM) |
| AM 1200 | WTLA | Sports | Also heard on 97.7 W249BC (Mattydale) and 1440 WSGO (Oswego) |
| AM 1260 | WSKO | Sports | |
| AM 1300 | WOSW | Sports | Licensed to Fulton and is heard on 98.5 W253BZ in Fulton |
| AM 1340 | WMBO | Classic hits | Licensed to Auburn and is heard on 106.1 W291CV in Auburn. (See also: WSEN-FM Mexico) |
| AM 1390 | WFBL | Classic hits | Also heard on 107.5 W298DC in Liverpool. (See slso: WSEN-FM) |
| AM 1440 | WSGO | Sports | Licensed to Oswego and is heard on 100.1 W261AC in Oswego |
| AM 1490 | WOLF | Sports | Also heard on 92.5 W223CP in Syracuse |
| AM 1540 | WSIV | Christian radio | Licensed to East Syracuse and is heard on 106.3 W292EY in Syracuse |
| AM 1670 | WERW | Free-form | Syracuse University |
| FM 87.7 | WVOA-LD | Sports | Licensed to Westvale (See also: WOLF) |
| FM 88.3 | WAER | Jazz/News/Sports | |
| FM 88.7 | WTMI | Religious (Catholic) | Licensed to Fleming |
| FM 88.9 | WNYO | College radio | Licensed to Oswego |
| FM 89.1 | WJPZ-FM | Rhythmic contemporary | |
| FM 89.9 | WRVO | Public radio | Licensed to Oswego |
| FM 90.1 | WRCU-FM | Free-form | Licensed to Fairport |
| FM 90.3 | WRVD | Public radio | Satellite of WRVO, Oswego |
| FM 90.5 | WBXL | Variety | Licensed to Baldwinsville |
| FM 90.5 | WMVQ | Public radio | Licensed to Fenner |
| FM 91.3 | WCNY-FM | Classical music | |
| FM 92.1 | WOLF-FM | Country music | |
| FM 93.1 | WNTQ | CHR/Top 40 | |
| FM 94.5 | WYYY | Adult contemporary | |
| FM 95.7 | WAQX | Alternative rock | |
| FM 96.7 | WCIO | Contemporary Christian | Licensed to Oswego (See: WCIS-FM) |
| FM 99.5 | WTKW | Classic rock | |
| FM 100.3 | WMVN | Rhythmic top 40 | Licensed to Sylvan Beach. Also heard on 96.5 W243AB in Westvale |
| FM 100.9 | WKRL | Active rock | |
| FM 101.7 | WGKV | Contemporary Christian | Licensed to Pulaski (K-Love) |
| FM 102.1 | WZUN-FM | Classic hits | Licensed to Phoenix |
| FM 102.9 | WMHN | Christian radio | |
| FM 103.3 | WSPJ-LP | Community radio/Variety | Also heard on 93.7 W229CU Syracuse |
| FM 103.9 | WSEN-FM | Classic hits | Licensed to Mexico, NY |
| FM 104.7 | WBBS | Country music | Licensed to Fulton |
| FM 105.1 | WCIS-FM | Contemporary Christian | Licensed to DeRuyter |
| FM 105.5 | WTKW | Classic rock | Licensed to Minetto |
| FM 105.9 | WLKZ | Contemporary Christian | |
| FM 106.5 | WKRH | Classic rock | Licensed to Fair Haven |
| FM 106.9 | WSYR-FM | News/Talk | Licensed to Solvay |
| FM 107.9 | WWHT | CHR/Top 40 |
To see a complete list of radio stations in Syracuse including the surrounding area, please see: (Syracuse radio)
Television Channels
Syracuse is the fifth-largest TV market in New York State. Six main TV stations serve the city:
- WSTM-TV 3 (NBC)
- WTVH 5 (CBS)
- WSYR-TV 9 (ABC)
- WCNY-TV 24/cable 11 (PBS)
- WSPX-TV 56/cable 4 (Ion)
- WSYT 68/cable 8 (Fox)
Syracuse University has its own student-run TV station called CitrusTV. Charter Spectrum is the main cable TV provider. They offer a 24-hour local news channel.
Newspapers
Syracuse has one main daily newspaper, The Post-Standard. It covers local news from Central New York. It is available in many stores from the Canadian border to the Pennsylvania border.
The Daily Orange is the student newspaper for Syracuse University and SUNY ESF. It is read by over 20,000 people daily. The Dolphin is the weekly student newspaper for Le Moyne College.
Other free newspapers include the City Eagle and Table Hopping, which focuses on restaurants. CNY Vision is a weekly newspaper for Syracuse's African American community. The CNY Latino newspaper is a monthly publication for the Hispanic community.
Magazines
The Good Life, Central New York Magazine (also called Central New York Magazine) is a local lifestyle magazine. It comes out every two months and covers positive stories about local shops, travel, food, and art in the Syracuse area.
City Infrastructure
Public Transportation
Syracuse has public bus service run by the Central New York Regional Transportation Authority, or Centro. Centro buses serve Syracuse and its nearby towns.
Train and Bus Travel
Syracuse (station stop code SYR) has train service from Amtrak. You can take trains like the Empire Service, Lake Shore Limited, and Maple Leaf. Amtrak's station is at the William F. Walsh Regional Transportation Center.
The Empire Service runs twice a day between Niagara Falls and New York City. The Maple Leaf goes all the way to Toronto. The Lake Shore Limited travels between Chicago and Boston or New York City.
Long-distance bus services like Greyhound Lines, Megabus, OurBus, and Trailways also serve Syracuse. They go to cities like New York City, Boston, and Toronto.
Air Travel
Syracuse is served by the Syracuse Hancock International Airport. It is located in nearby Salina. The airport has flights from 8 major airlines to important cities like Atlanta, Chicago, and New York City. You can reach New York City in less than an hour by plane.
Major Roads and Highways
 Interstate 81 goes north and south through Syracuse. It connects to Canada and Pennsylvania. The part of I-81 in downtown Syracuse is very narrow. Soon, it will be rerouted around the city.
Interstate 81 goes north and south through Syracuse. It connects to Canada and Pennsylvania. The part of I-81 in downtown Syracuse is very narrow. Soon, it will be rerouted around the city. Interstate 90, also called the New York State Thruway, runs east and west just north of the city. It is a toll road that connects to Rochester, Buffalo, and Albany.
Interstate 90, also called the New York State Thruway, runs east and west just north of the city. It is a toll road that connects to Rochester, Buffalo, and Albany. Interstate 690 runs east and west through the city. It connects to I-90 and the suburbs.
Interstate 690 runs east and west through the city. It connects to I-90 and the suburbs. Interstate 481 forms a loop around the eastern side of the city. It continues north to Fulton and Oswego. This highway will soon become part of Interstate 81.
Interstate 481 forms a loop around the eastern side of the city. It continues north to Fulton and Oswego. This highway will soon become part of Interstate 81.
Community Grid Project In May 2023, the Community Grid project was approved. This plan will remove the I-81 highway that goes through downtown. It will be replaced with a boulevard. The main I-81 traffic will be sent around the city on the existing I-481. This project will cost about $2.25 billion and will take several years to complete.
US Highways
 U.S. Highway 11 runs north and south through downtown Syracuse.
U.S. Highway 11 runs north and south through downtown Syracuse. U.S. Highway 20 passes south of Syracuse.
U.S. Highway 20 passes south of Syracuse.
New York State Expressways
New York State Routes
 New York State Route 5
New York State Route 5 New York State Route 80
New York State Route 80 New York State Route 92
New York State Route 92 New York State Route 173
New York State Route 173 New York State Route 175
New York State Route 175 New York State Route 290
New York State Route 290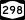 New York State Route 298
New York State Route 298 New York State Route 370
New York State Route 370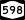 New York State Route 598
New York State Route 598
City Services
The Department of Public Works (DPW) provides public services. These include garbage pickup, street plowing, and sewage.
Syracuse gets its drinking water from Skaneateles Lake. This lake is known for having very clean water. The water is carried into the city without being filtered.
The Syracuse Police Department (SPD) keeps the city safe. The SPD uses a network of 521 surveillance cameras called the Criminal Observation and Protection System (COPS). These cameras help police watch for suspicious activity.
The Syracuse Fire Department (SFD) protects the city from fires and other dangers. They also respond to medical calls and hazardous material incidents. The SFD has a top rating for fire safety, which can affect fire insurance costs. The department operates out of 11 fire stations.
Sister Cities
Syracuse has several sister cities around the world:
 Chiayi City, Taiwan
Chiayi City, Taiwan Fuzhou, Fujian, China
Fuzhou, Fujian, China Taiz, Yemen
Taiz, Yemen Tampere, Finland
Tampere, Finland Irpin, Ukraine
Irpin, Ukraine Boise, Idaho
Boise, Idaho
|
See also
 In Spanish: Syracuse (Nueva York) para niños
In Spanish: Syracuse (Nueva York) para niños
 | Claudette Colvin |
 | Myrlie Evers-Williams |
 | Alberta Odell Jones |