List of tallest buildings facts for kids

This article lists the world's tallest buildings. We are talking about very tall buildings, like skyscrapers. These are buildings with many floors where people can live or work. They must be at least 350 meters (about 1,150 feet) tall. This list does not include structures like radio towers, which are not buildings.
Contents
History of Tall Buildings
For a very long time, the Great Pyramid of Giza in Egypt was the tallest man-made structure. It held this record for over 3,800 years! Then, in 1311, Lincoln Cathedral in England became taller. The Strasbourg Cathedral in France was the world's tallest building from 1439 until 1874.
The first building called a "skyscraper" was the Home Insurance Building in Chicago. It was built in 1885 and was 42 meters (138 feet) tall. For most of the 20th century, the United States had the world's tallest building.
This changed in 1998 when the Petronas Towers were finished in Malaysia. After that, Taipei 101 in Taiwan became the tallest in 2004. Then, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai took the title in 2009. Since the early 2000s, many super tall skyscrapers have been built in the Middle East, China, and Southeast Asia.
How We Measure Tall Buildings
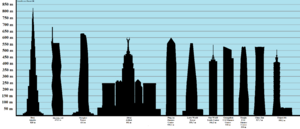
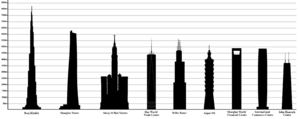
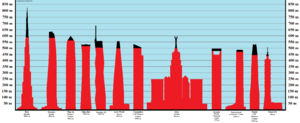
The Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat (CTBUH) is a group that decides which building is the "World's Tallest." They set the rules for how buildings are measured. They also keep a list of the 100 tallest completed buildings. The CTBUH currently says the Burj Khalifa in Dubai is the tallest at 828 meters (2,717 feet).
In 1996, there was a debate about whether the Petronas Towers or the Willis Tower (which used to be called the Sears Tower) was taller. To solve this, the CTBUH created four ways to measure buildings:
- Height to the top of the building's design: This includes spires, which are part of the building's look.
- Height to the highest floor where people work or live: This is the highest floor that is regularly used.
- Height to the top of the roof: This category was removed in 2009 because modern buildings often don't have a clear "roof."
- Height to the very top of any part of the building: This includes antennas or flagpoles.
All these measurements start from the lowest main entrance for people.
Spires are seen as part of a building's design. Changing a spire would change how the building looks. Antennas, however, can be added or removed without changing the building's main design. This is why the Petronas Towers, with their spires, were considered taller than the Willis Tower, which had antennas.
Before 1996, the tallest building was measured by its highest architectural part, including spires but not antennas. In 1930, this rule caused a rivalry between the Bank of Manhattan Building and the Chrysler Building. The Chrysler Building secretly built a large spire inside itself. When it was finished, it popped out the spire to claim the title of the world's tallest building!
Today, the Burj Khalifa is the tallest no matter which measurement rule you use.
World's Tallest Buildings
As of July 2025, this list includes 97 buildings that are completed or have reached their full height. They are all 350 meters (1,150 feet) or taller. A building is considered "topped out" when its main structure is complete, it has its outer covering, and its highest design parts are in place.
Almost half of these super tall buildings are in China. Six of the last seven buildings that held the "tallest building" record are still on this list. The only one missing is the North Tower of the original World Trade Center. It was 417 meters (1,368 feet) tall before it was destroyed in 2001. If it were still standing, it would be among the top 40 tallest buildings today.
| Clear | Denotes building that is or was once the tallest in the world |
| Name | Height | Floors | Image | City | Country | Year | Comments | Ref | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | ft | |||||||||
| 1 | Burj Khalifa | 828 m | 2,717 ft | 163 (+ 2 below ground) |  |
Dubai | 2010 | Tallest building in the world since 2009 | ||
| 2 | Merdeka 118 | 678.9 m | 2,227 ft | 118 (+ 5 below ground) |  |
Kuala Lumpur | 2024 | Tallest building in Southeast Asia and Malaysia | ||
| 3 | Shanghai Tower | 632 m | 2,073 ft | 128 (+ 5 below ground) |  |
Shanghai | 2015 | Tallest building in East Asia and China and contains the highest luxury hotel in the world; Tallest twisted building | ||
| 4 | The Clock Towers | 601 m | 1,972 ft | 120 (+ 3 below ground) |  |
Mecca | 2012 | Tallest building in Saudi Arabia, tallest clock tower and contains the highest museum in the world | ||
| 5 | Ping An International Finance Centre | 599.1 m | 1,966 ft | 115 (+ 5 below ground) |  |
Shenzhen | 2017 | Tallest all-office building in the world; tallest in Guangdong Province | ||
| 6 | Lotte World Tower | 554.5 m | 1,819 ft | 123 (+ 6 below ground) |  |
Seoul | 2017 | Tallest building in South Korea and the OECD | ||
| 7 | One World Trade Center | 541.3 m | 1,776 ft | 94 (+ 5 below ground) |  |
New York City | 2014 | Tallest building outside of Asia; tallest building in the Western Hemisphere, the Americas, North America and the USA; tallest building on an island; tallest building in the world with fewer than 100 floors | ||
| 8 | Guangzhou CTF Finance Centre | 530 | 1,740 | 111 (+ 5 below ground) |  |
Guangzhou | 2016 | |||
| Tianjin CTF Finance Centre |
97 (+ 4 below ground)
|
 |
Tianjin | 2019 | Tallest completed building in Tianjin | |||||
| 10 | China Zun | 527.7 m | 1,731 ft | 109 (+ 8 below ground) |  |
Beijing | 2018 | Tallest building in Beijing | ||
| 11 | Taipei 101 | 508 m | 1,667 ft | 101 (+ 5 below ground) |  |
Taipei | 2004 | Tallest building in the world from 2004 till 2009; tallest building in Taiwan | ||
| 12 | Shanghai World Financial Center | 492 m | 1,614 ft | 101 (+ 3 below ground) |  |
Shanghai | 2008 | Tallest building in the world with a hole | ||
| 13 | International Commerce Centre | 484 m | 1,588 ft | 108 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
Hong Kong | 2010 | Tallest building in Hong Kong | ||
| 14 | Wuhan Greenland Center | 475.6 m | 1,560 ft | 101 (+ 6 below ground) |  |
Wuhan | 2023 | Tallest building in Hubei Province | ||
| 15 | Central Park Tower | 472.4 m | 1,550 ft | 98 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
New York City | 2021 | Tallest residential building | ||
| 16 | Lakhta Center | 462 m | 1,516 ft | 87 (+ 3 below ground) |  |
Saint Petersburg | 2019 | Tallest building in Europe and Russia; Northernmost skyscraper in the world | ||
| 17 | Landmark 81 | 461.2 m | 1,513 ft | 81 (+ 3 below ground) |  |
Ho Chi Minh City | 2018 | Tallest building in Vietnam | ||
| 18 | Chongqing International Land-Sea Center | 458 m | 1,503 ft | 98 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
Chongqing | 2024 | Tallest building in Southern China | ||
| 19 | The Exchange 106 | 453.6 m | 1,488 ft | 95 (+ 6 below ground) |  |
Kuala Lumpur | 2019 | |||
| 20 | Changsha IFS Tower T1 | 452.1 m | 1,483 ft | 94 (+ 5 below ground) |  |
Changsha | 2018 | Tallest building in Hunan Province | ||
| 21 | Petronas Tower 1 | 451.9 | 1,483 | 88 (+ 5 below ground) |  |
Kuala Lumpur | 1998 | Tallest building in the world from 1998 till 2004; tallest building built in the 20th century; Tallest twin buildings | ||
| Petronas Tower 2 | ||||||||||
| 23 | Zifeng Tower | 450 | 1,480 | 89 (+ 5 below ground) |  |
Nanjing | 2010 | Tallest building in Jiangsu Province, tied with Suzhou IFS | ||
| Suzhou IFS |
95 (+ 5 below ground)
|
 |
Suzhou | 2019 | Tallest building in Jiangsu Province, tied with Zifeng Tower | |||||
| 25 | Wuhan Center | 443.1 m | 1,454 ft | 88 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
Wuhan | 2019 | |||
| 26 | Willis Tower | 442.1 m | 1,450 ft | 108 (+ 3 below ground) |  |
Chicago | 1974 | Tallest building in the world from 1974 till 1998 as Sears Tower | ||
| 27 | KK100 | 441.8 m | 1,449 ft | 98 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
Shenzhen | 2011 | |||
| 28 | Guangzhou International Finance Center | 438.6 m | 1,439 ft | 101 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
Guangzhou | 2010 | |||
| 29 | 111 West 57th Street | 435.3 m | 1,428 ft | 84 (+ 2 below ground) |  |
New York City | 2021 | Thinnest skyscraper in the world with a width-to-height ratio of about 1:24 | ||
| 30 | Shandong International Financial Center | 428 m | 1,404 ft | 88 (+ 4 below ground) | Jinan | 2025 | Tallest building in Shandong Province | |||
| 31 | One Vanderbilt | 427 m | 1,401 ft | 62 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
New York City | 2020 | |||
| 32 | Nanjing Financial City Phase II Plot C Tower 1 | 426 m | 1,398 ft | 88 | Nanjing | 2025 | ||||
| 33 | 432 Park Avenue | 425.7 m | 1,397 ft | 85 (+ 3 below ground) |  |
New York City | 2015 | |||
| 34 | Marina 101 | 425 m | 1,394 ft | 101 (+ 6 below ground) |  |
Dubai | 2017 | |||
| 35 | Trump International Hotel and Tower | 423.2 m | 1,388 ft | 98 (+ 2 below ground) |  |
Chicago | 2009 | |||
| 36 | JPMorgan Chase World Headquarters | 423 m | 1,388 ft | 60 |  |
New York City | 2025 | |||
| 37 | Minying International Trade Center 1 | 422.6 m | 1,386 ft | 85 (+ 3 below ground) |  |
Dongguan | 2021 | |||
| 38 | Jin Mao Tower | 420.5 m | 1,380 ft | 88 (+ 3 below ground) |  |
Shanghai | 1999 | |||
| 39 | Princess Tower | 413.4 m | 1,356 ft | 101 (+ 6 below ground) |  |
Dubai | 2012 | |||
| 40 | Al Hamra Tower | 412.6 m | 1,354 ft | 80 (+ 3 below ground) |  |
Kuwait City | 2011 | Tallest building in Kuwait | ||
| 41 | Two International Finance Centre | 412 m | 1,352 ft | 88 (+ 6 below ground) |  |
Hong Kong | 2003 | |||
| 42 | Haeundae LCT The Sharp Landmark Tower | 411.6 m | 1,350 ft | 101 (+ 5 below ground) |  |
Busan | 2019 | Tallest building in Busan | ||
| 43 | Ningbo Central Plaza | 409 m | 1,342 ft | 80 |  |
Ningbo | 2024 | Tallest building in Zhejiang Province | ||
| 44 | Guangxi China Resources Tower | 402.7 m | 1,321 ft | 86 (+ 3 below ground) |  |
Nanning | 2020 | Tallest building in Guangxi Province | ||
| 45 | Guiyang International Financial Center T1 | 401 m | 1,316 ft | 79 (+ 5 below ground) |  |
Guiyang | 2020 | Tallest building in Guizhou Province | ||
| 46 | Iconic Tower | 393.8 m | 1,292 ft | 77 (+ 2 below ground) | New Administrative Capital | 2023 | Tallest building in Africa and Egypt | |||
| 47 | China Merchants Bank Global Headquarters Main Tower | 393 m | 1,289 ft | 77 | Shenzhen | 2025 | ||||
| 48 | China Resources Tower | 392.5 m | 1,288 ft | 68 (+ 5 below ground) |  |
2018 | ||||
| 49 | 23 Marina | 392.4 m | 1,287 ft | 88 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
Dubai | 2012 | |||
| 50 | CITIC Plaza | 390.2 m | 1,280 ft | 80 (+ 2 below ground) |  |
Guangzhou | 1996 | |||
| 51 | Citymark Centre | 388.3 m | 1,274 ft | 70 (+ 7 below ground) |  |
Shenzhen | 2022 | |||
| 52 | Shum Yip Upperhills Tower 1 | 388.1 m | 1,273 ft | 80 (+ 3 below ground) |  |
2020 | ||||
| 53 | 30 Hudson Yards | 387.1 m | 1,270 ft | 73 (+ 1 below ground) |  |
New York City | 2019 | |||
| 54 | Public Investment Fund Tower | 385 m | 1,263 ft | 72 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
Riyadh | 2021 | Tallest building in Riyadh | ||
| 55 | Shun Hing Square | 384 m | 1,260 ft | 69 (+ 3 below ground) |  |
Shenzhen | 1996 | |||
| 56 | Eton Place Dalian Tower 1 | 383.2 m | 1,257 ft | 80 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
Dalian | 2016 | Tallest building in Liaoning Province | ||
| 57 | Autograph Tower | 382.9 m | 1,256 ft | 75 (+ 6 below ground) |  |
Jakarta | 2022 | Tallest building in Indonesia. Tallest building in the Southern Hemisphere. | ||
| 58 | Logan Century Center 1 | 381.3 m | 1,251 ft | 82 (+ 4 below ground) | Nanning | 2018 | ||||
| 59 | Burj Mohammed bin Rashid | 381.2 m | 1,251 ft | 88 (+ 5 below ground) |  |
Abu Dhabi | 2014 | |||
| 60 | Empire State Building | 381 m | 1,250 ft | 102 (+ 1 below ground) |  |
New York City | 1931 | Tallest building in the world from 1931 till 1972; tallest pre-WWII building | ||
| 61 | Elite Residence | 380.5 m | 1,248 ft | 87 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
Dubai | 2012 | |||
| 62 | Riverview Plaza | 376 | 1,234 | 73 (+ 3 below ground) |  |
Wuhan | 2021 | |||
| Guangdong Business Center |
60
|
Guangzhou | 2024 | |||||||
| 64 | Dabaihui Plaza | 375.6 m | 1,232 ft | 70 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
Shenzhen | 2021 | |||
| 65 | Central Plaza | 373.9 m | 1,227 ft | 78 (+ 3 below ground) |  |
Hong Kong | 1992 | Contains the highest church in the world | ||
| 66 | Federation Tower (East Tower) | 373.7 m | 1,226 ft | 93 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
Moscow | 2016 | Tallest building in Moscow | ||
| 67 | Hengfeng Guiyang Center Tower 1 | 373.5 m | 1,225 ft | 77 (+ 5 below ground) | Guiyang | 2025 | ||||
| 68 | Dalian International Trade Center | 370.2 m | 1,215 ft | 86 (+ 7 below ground) |  |
Dalian | 2019 | |||
| 69 | Shanghai International Trade Center Tower 1 | 370 | 1,210 | 75 |  |
Shanghai | 2025 | |||
| Address Boulevard |
73 (+ 3 below ground)
|
 |
Dubai | 2017 | ||||||
| 71 | Haitian Center Tower 2 | 368.9 m | 1,210 ft | 73 (+ 6 below ground) |  |
Qingdao | 2021 | |||
| 72 | Golden Eagle Tiandi Tower A | 368.1 m | 1,208 ft | 77 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
Nanjing | 2019 | |||
| 73 | Bank of China Tower | 367.4 m | 1,205 ft | 72 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
Hong Kong | 1990 | |||
| 74 | Bank of America Tower | 365.8 m | 1,200 ft | 55 (+ 3 below ground) |  |
New York City | 2009 | |||
| 75 | Ciel Tower | 365.5 | 1,199 | 81 | Dubai | 2025 | Tallest hotel in the world | |||
| 76 | St. Regis Chicago | 362.9 m | 1,191 ft | 101 (+ 5 below ground) |  |
Chicago | 2020 | Tallest structure in the world designed by a woman | ||
| 77 | Almas Tower | 360 | 1,180 | 68 (+ 5 below ground) |  |
Dubai | 2008 | |||
| Ping An Finance Center Tower 1 |
62 (+ 3 below ground)
|
Jinan | 2023 | |||||||
| 79 | Huiyun Center | 359.2 | 1,178 | 80 | Shenzhen | 2023 | ||||
| 80 | Hanking Center | 358.9 m | 1,177 ft | 65 (+ 5 below ground) |  |
2018 | ||||
| 81 | Greenland Group Suzhou Center | 358 | 1,175 | 77 (+ 3 below ground) | Suzhou | 2024 | ||||
| City Tower 1 |
94
|
Dubai | 2025 | |||||||
| 83 | Gevora Hotel | 356.3 m | 1,169 ft | 75 (+ 2 below ground) |  |
2017 | ||||
| 84 | Galaxy World Tower 1 | 356 | 1,168 | 71 (+ 5 below ground) | Shenzhen | 2023 | ||||
| Galaxy World Tower 2 | ||||||||||
| Il Primo Tower |
79
|
 |
Dubai | 2022 | ||||||
| 87 | JW Marriott Marquis Dubai Tower 1 | 355.4 | 1,166 | 82 (+ 2 below ground) |  |
2012 | ||||
| JW Marriott Marquis Dubai Tower 2 |
2013
|
|||||||||
| 89 | Emirates Office Tower | 354.6 m | 1,163 ft | 54 |  |
2000 | ||||
| 90 | Raffles City Chongqing T3N | 354.5 | 1,163 | 79 (+ 3 below ground) |  |
Chongqing | 2019 | |||
| Raffles City Chongqing T4N |
74 (+ 3 below ground)
|
|||||||||
| 92 | OKO – South Tower | 354.2 m | 1,162 ft | 90 (+ 2 below ground) |  |
Moscow | 2015 | |||
| 93 | CBRT Tower | 352 | 1,155 | 59 |  |
Istanbul | 2024 | Tallest building in Turkey | ||
| The Marina Torch |
86 (+ 4 below ground)
|
 |
Dubai | 2011 | ||||||
| 95 | Forum 66 Tower 1 | 350.6 m | 1,150 ft | 68 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
Shenyang | 2015 | |||
| 96 | The Pinnacle | 350.3 m | 1,149 ft | 60 (+ 6 below ground) |  |
Guangzhou | 2012 | |||
| 97 | Xi'an Glory International Financial Center | 350 m | 1,148 ft | 75 (+ 4 below ground) |  |
Xi'an | 2021 | |||
Other Ways to Measure Height
Sometimes, buildings are measured in different ways. Here are a few examples:
Height to the Highest Point
This measurement looks at the very highest point of a building. It doesn't matter if it's part of the building's design or just an antenna. This way of measuring is useful for things like air traffic. It also gives a clear, simple height. However, it includes parts that can be easily added or removed from a building.
This measurement became more common when the Petronas Towers became taller than the Willis Tower. The Petronas Towers were taller because their spires were considered part of the building's design. The Willis Tower's antennas were not. This led to different ways of defining "tallest."
| † | Denotes building with pinnacle height higher than architectural |
| Rank | Building | City | Country | Height | Floors | Built | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Burj Khalifa† | Dubai | 829.8 m | 2,722 ft | 163 | 2010 | |
| 2 | Merdeka 118† | Kuala Lumpur | 680.1 m | 2,231 ft | 118 | 2023 | |
| 3 | Shanghai Tower | Shanghai | 632 m | 2,073 ft | 128 | 2015 | |
| 4 | Abraj Al-Bait Towers | Mecca | 601 m | 1,971 ft | 120 | 2012 | |
| 5 | Ping An Finance Center | Shenzhen | 599.1 m | 1,965 ft | 115 | 2016 | |
| 6 | Lotte World Tower† | Seoul | 555.7 m | 1,823 ft | 123 | 2016 | |
| 7 | One World Trade Center† | New York City | 546.2 m | 1,792 ft | 104 | 2014 | |
| 8 | Tianjin CTF Finance Centre† | Tianjin | 530.4 m | 1,740 ft | 98 | 2019 | |
| 9 | Guangzhou CTF Finance Centre | Guangzhou | 530 m | 1,739 ft | 111 | 2016 | |
| 10 | China Zun | Beijing | 528 m | 1,732 ft | 108 | 2018 | |
| 11 | Willis Tower† | Chicago | 527 m | 1,729 ft | 108 | 1974 | |
| 12 | Taipei 101 | Taipei | 508 m | 1,667 ft | 101 | 2004 | |
| 13 | Shanghai World Financial Center† | Shanghai | 494.3 m | 1,622 ft | 101 | 2008 | |
| 14 | International Commerce Centre | Hong Kong | 484 m | 1,588 ft | 118 | 2010 | |
| 15 | Wuhan Greenland Center | Wuhan | 475.6 m | 1,560 ft | 97 | 2021 | |
| 16 | Central Park Tower | New York City | 472.4 m | 1,550 ft | 98 | 2020 | |
| 17 | Landmark 81† | Ho Chi Minh City | 469.5 m | 1,540 ft | 81 | 2018 | |
| 18 | Lakhta Center | St. Petersburg | 462 m | 1,516 ft | 86 | 2019 | |
| 19 | International Land-Sea Center | Chongqing | 458.2 m | 1,503 ft | 98 | 2022 | |
| 20 | John Hancock Center† | Chicago | 456.9 m | 1,499 ft | 100 | 1969 | |
| 21 | The Exchange 106 | Kuala Lumpur | 453.6 m | 1,488 ft | 95 | 2019 | |
| 22 | Changsha IFS Tower T1 | Changsha | 452.1 m | 1,483 ft | 94 | 2018 | |
| 23 | Petronas Tower 1 | Kuala Lumpur | 451.9 m | 1,483 ft | 88 | 1998 | |
| 23 | Petronas Tower 2 | Kuala Lumpur | 451.9 m | 1,483 ft | 88 | 1998 | |
| 25 | Zifeng Tower | Nanjing | 450 m | 1,476 ft | 89 | 2010 | |
| 25 | Suzhou IFS | Suzhou | 450 m | 1,476 ft | 98 | 2019 | |
| 27 | Empire State Building† | New York City | 443.2 m | 1,454 ft | 102 | 1931 | |
| 28 | Kingkey 100 | Shenzhen | 441.8 m | 1,449 ft | 100 | 2011 | |
| 29 | Guangzhou International Finance Center | Guangzhou | 438.6 m | 1,445 ft | 103 | 2009 | |
| 30 | Wuhan Center | Wuhan | 438 m | 1,437 ft | 88 | 2019 | |
| 31 | 111 West 57th Street | New York City | 435.3 m | 1,428 ft | 82 | 2020 | |
| 32 | Dongguan International Trade Center 1 | Dongguan | 426.9 m | 1,401 ft | 88 | 2020 | |
| 33 | One Vanderbilt | New York City | 427 m | 1,401 ft | 58 | 2020 | |
| 34 | 432 Park Avenue | New York City | 425.5 m | 1,396 ft | 85 | 2015 | |
| 35 | Marina 101 | Dubai | 425 m | 1,394 ft | 101 | 2017 | |
| 36 | Trump International Hotel and Tower | Chicago | 423.2 m | 1,388 ft | 96 | 2009 | |
| 37 | Jin Mao Tower | Shanghai | 421 m | 1,381 ft | 88 | 1998 | |
| 38 | Princess Tower† | Dubai | 414 m | 1,358 ft | 101 | 2012 | |
| 39 | Al Hamra Tower | Kuwait City | 412.6 m | 1,354 ft | 80 | 2010 | |
| 40 | Two International Finance Centre | Hong Kong | 412 m | 1,352 ft | 88 | 2003 | |
| 41 | Haeundae LCT The Sharp Landmark Tower | Busan | 411.6 m | 1,350 ft | 101 | 2019 | |
| 42 | Guangxi China Resources Tower | Nanning | 402.7 m | 1,321 ft | 85 | 2019 | |
| 43 | Guiyang Financial Center Tower 1 | Guiyang | 401 m | 1,316 ft | 79 | 2021 | |
Height to Occupied Floor
This measurement looks at the highest floor inside the building that people use regularly. This means floors with offices, apartments, or observation decks.
| Rank | Building | City | Country | Height | Floors | Built |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Burj Khalifa | Dubai | 585.4 m (1,921 ft) | 163 | 2010 | |
| 2 | Shanghai Tower | Shanghai | 583.4 m (1,914 ft) | 128 | 2015 | |
| 3 | Ping An Finance Center | Shenzhen | 562.2 m (1,844 ft) | 115 | 2016 | |
| 4 | China Zun | Beijing | 515.5 m (1,691 ft) | 108 | 2018 | |
| 5 | Merdeka 118 | Kuala Lumpur | 502.8 m (1,650 ft) | 118 | 2023 | |
| 6 | Lotte World Tower | Seoul | 497.6 m (1,633 ft) | 123 | 2016 | |
| 7 | Guangzhou CTF Finance Centre | Guangzhou | 495.5 m (1,626 ft) | 111 | 2016 | |
| 8 | Abraj Al-Bait Towers | Mecca | 494.4 m (1,622 ft) | 120 | 2012 | |
| 9 | Shanghai World Financial Center | Shanghai | 474 m (1,555 ft) | 101 | 2008 | |
| 10 | International Commerce Centre | Hong Kong | 468.8 m (1,538 ft) | 118 | 2010 | |
| 11 | Tianjin CTF Finance Centre | Tianjin | 439.4 m (1,442 ft) | 97 | 2018 | |
| 12 | Taipei 101 | Taipei | 438 m (1,437 ft) | 101 | 2004 | |
| 13 | Central Park Tower | New York City | 431.8 m (1,417 ft) | 98 | 2020 | |
| 14 | Changsha IFS Tower T1 | Changsha | 431 m (1,414 ft) | 94 | 2017 | |
| 15 | International Land-Sea Center | Chongqing | 429.8 m (1,410 ft) | 98 | 2022 | |
| 16 | KK100 | Shenzhen | 427.1 m (1,401 ft) | 98 | 2011 | |
| 17 | Guangzhou International Finance Center | Guangzhou | 415.1 m (1,362 ft) | 101 | 2010 | |
| 18 | Willis Tower | Chicago | 412.7 m (1,354 ft) | 108 | 1974 |
Height to Roof
This list ranks completed skyscrapers by their height to the roof. It includes buildings that are 300 meters (984 feet) or taller. Only buildings with floors that people can use are included. This means structures like towers are not on this list. Some people prefer this measurement because the "architectural feature" rule can be tricky. However, in 2009, the CTBUH stopped using roof height. This is because many modern tall buildings don't have a clear, flat roof.
| Rank | Building | City | Country | Height (m) | Height (ft) | Floors | Built | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Burj Khalifa | Dubai | 739.4 m | 2,426 ft | 163 | 2010 | ||
| 2 | Shanghai Tower | Shanghai | 574.5 m | 1,885 ft | 127 | 2015 | ||
| 3 | Ping An Finance Center | Shenzhen | 555 m | 1,821 ft | 115 | 2016 | ||
| 4 | China Zun | Beijing | 524 m | 1719 ft | 109 | 2018 | ||
| 5 | Merdeka 118 | Kuala Lumpur | 518.2 m | 1,700 ft | 118 | 2023 | ||
| 6 | Guangzhou CTF Finance Centre | Guangzhou | 518 m | 1,699 ft | 111 | 2016 | ||
| 7 | Abraj Al-Bait Towers | Mecca | 508 m | 1,666 ft | 120 | 2012 | ||
| 8 | Lotte World Tower | Seoul | 497.6 m | 1,633 ft | 123 | 2016 | ||
| 9 | Shanghai World Financial Center | Shanghai | 487.41 m | 1,599 ft | 101 | 2008 | ||
| 10 | International Commerce Centre | Hong Kong | 479.83 m | 1,574 ft | 118 | 2010 | ||
| 11 | Central Park Tower | New York City | 472.44 m | 1,550 ft | 131 | 2019 | ||
| 12 | Tianjin CTF Finance Centre | Tianjin | 471.1 m | 1,545 ft | 97 | 2019 | ||
| 13 | Taipei 101 | Taipei | 449.20 m | 1,471 ft | 101 | 2004 | ||
| 14 | Willis Tower | Chicago | 442.14 m | 1,451 ft | 108 | 1974 | ||
| 15 | KK100 | Shenzhen | 442 m | 1,449 ft | 100 | 2011 | --> | |
| 16 | Guangzhou International Finance Center | Guangzhou | 432 m | 1,417 ft | 103 | 2009 | ||
| 17 | 432 Park Avenue | New York City | 425.5 m | 1,396 ft | 96 | 2015 | --> | |
| 18 | One World Trade Center | New York City | 417 m | 1,368 ft | 104 | 2014 | ||
| 19 | Haeundae LCT Landmark Tower | Busan | 411.6 m | 1,350 ft | 101 | 2019 | ||
| 20 | International Finance Centre | Hong Kong | 401.1 m | 1,316 ft | 88 | 2003 | ||
| 21 | Princess Tower | Dubai | 392 m | 1,286 ft | 101 | 2012 | ||
| 22 | Jin Mao Tower | Shanghai | 382.5 m | 1,255 ft | 88 | 1998 | ||
| 23 | Zifeng Tower | Nanjing | 381.3 m | 1,251 ft | 89 | 2009 | ||
| 24 | Empire State Building | New York City | 381 m | 1,250 ft | 102 | 1931 | ||
| 25 | Petronas Tower 1 | Kuala Lumpur | 378.5 m | 1,250 ft | 88 | 1998 | ||
| Petronas Tower 2 | Kuala Lumpur | 378.5 m | 1,250 ft | 88 | 1998 | |||
| 27 | Marina 101 | Dubai | 371 m | 1,207 ft | 80 | 2014 | ||
| Al Hamra Tower | Kuwait City | 368 m | 1,207 ft | 80 | 2011 | |||
| 29 | Trump International Hotel and Tower | Chicago | 357.8 m | 1,174 ft | 96 | 2009 | ||
| 30 | Tuntex Sky Tower | Kaohsiung | 347.5 m | 1,140 ft | 85 | 1997 | ||
| 31 | Aon Center | Chicago | 346.25 m | 1,136 ft | 83 | 1973 | ||
| 32 | John Hancock Center | Chicago | 343.5 m | 1,127 ft | 100 | 1969 | ||
| 33 | Haeundae LCT the Sharp I | Busan | 339.1 m | 1,112 ft | 85 | 2019 | ||
| 34 | Mercury City Tower | Moscow | 339 m | 1,112 ft | 75 | 2012 | ||
| 35 | Haeundae LCT the Sharp II | Busan | 333.1 m | 1,093 ft | 85 | 2019 | ||
| China World Trade Center Tower 3 | Beijing | 333 m | 1,093 ft | 74 | 2008 | |||
| Parc1 Tower 1 | Seoul | 333 m | 1,093 ft | 69 | 2020 | |||
| 38 | Ryugyong Hotel | Pyongyang | 330 m | 1,083 ft | 105 | 1992 | ||
| 39 | The Index | Dubai | 328 m | 1,076 ft | 80 | 2009 | ||
| 40 | Azabudai Hills Mori JP Tower | Tokyo | 325.4 m | 1,067 ft | 64 | 2023 | ||
| 41 | Shun Hing Square | Shenzhen | 324.8 m | 1,066 ft | 69 | 1996 | ||
| 42 | Four Seasons Place KLCC | Kuala Lumpur | 323 m | 1,076 ft | 74 | 2018 | ||
| 43 | CITIC Plaza | Guangzhou | 321.9 m | 1,056 ft | 80 | 1997 | ||
| 44 | Nina Tower | Hong Kong | 318.8 m | 1,046 ft | 80 | 2006 | ||
| 45 | Rose Tower | Dubai | 315 m | 1,033 ft | 72 | 2008 | ||
| Bank of China Tower | Hong Kong | 315 m | 1,033 ft | 72 | 1990 | |||
| 47 | Bank of America Plaza | Atlanta | 311.8 m | 1,023 ft | 55 | 1992 | ||
| 48 | Emirates Office Tower | Dubai | 311 m | 1,020 ft | 56 | 2000 | ||
| 49 | U.S. Bank Tower | Los Angeles | 310.3 m | 1,018 ft | 73 | 1989 | ||
| 50 | Menara Telekom | Kuala Lumpur | 309.9 m | 1,017 ft | 55 | 2001 | ||
| 51 | Almas Tower | Dubai | 310 m | 1,017 ft | 74 | 2008 | ||
| The Shard | London | 310 m | 1,017 ft | 72 | 2012 | |||
| 53 | Central Plaza | Hong Kong | 309 m | 1,014 ft | 78 | 1992 | ||
| 54 | One57 | New York City | 306m | 1,005 ft | 73 | 2014 | ||
| 55 | The Address Downtown Burj Khalifa | Dubai | 306 m | 1,004 ft | 78 | 2008 | ||
| 56 | JPMorgan Chase Tower | Houston | 305.4 m | 1,002 ft | 75 | 1982 | ||
| 57 | Northeast Asia Trade Tower | Incheon | 305.1 m | 1,001 ft | 68 | 2010 | ||
| 58 | Baiyoke Tower II | Bangkok | 304 m | 997 ft | 85 | 1997 | ||
| 59 | Wells Fargo Plaza | Houston | 302.4 m | 992 ft | 71 | 1983 | ||
| 60 | Kingdom Centre | Riyadh | 302 m | 991 ft | 41 | 2002 | ||
| 61 | Moscow Tower | Moscow | 302 m | 989 ft | 76 | 2010 | ||
| 62 | Haeundae Doosan We've the Zenith 101 | Busan | 300 m | 984 ft | 80 | 2011 | ||
| Abeno Harukas | Osaka | 300 m | 984 ft | 60 | 2014 |
Buildings Being Built
This section lists buildings taller than 350 meters (1,150 feet) that are currently under construction. Buildings that were being built but are now on hold are in a separate table.
Under Construction
| Rank | Building | Planned architectural height | Floors | Planned completion | Country | City | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jeddah Tower | 1,008 m (3,307 ft) | 167+ | 2028 | Jeddah | ||
| 2 | Burj Azizi | 725 m (2,379 ft) | 133 | 2028 | Dubai | ||
| 3 | Goldin Finance 117 | 597 m (1,959 ft) | 128 | 2027 | Tianjin | ||
| 4 | Burj Binghatti Jacob & Co Residences | 595 m (1,952 ft) | 105 | 2026 | Dubai | ||
| 5 | Senna Tower | 544 m (1,784 ft) | 154 | 2030 | Balneário Camboriú | ||
| 6 | Tiger Sky Tower | 532 m / 1,745 ft | 116 | 2029 | Dubai | ||
| 7 | Six Senses Residences Dubai Marina | 517 m (1,696 ft) | 125 | 2028 | |||
| 8 | The Line | 500 m (1,640 ft.) | ? | 2030 | Neom | ||
| 9 | HeXi Yuzui Tower A | 498.8 m (1,636 ft) | 84 | Nanjing | |||
| 10 | Panda Tower - Tianfu Center | 488.9 m (1,604 ft) | 95 | 2026 | Chengdu | ||
| 11 | Rizhao Center | 485 m (1,591 ft) | 94 | 2028 | Rizhao | ||
| 12 | North Bund Tower | 480 m (1,575 ft) | 97 | 2027 | Shanghai | ||
| 13 | Torre Rise | 475 m (1,559 ft) | 88 | 2026 | Monterrey | ||
| 14 | Wuhan CTF Centre | 475 m (1,558 ft) | 84 | 2029 | Wuhan | ||
| 15 | Suzhou CSC Fortune Center | 470 m (1,540 ft) | 100 | 2028 | Suzhou | ||
| 16 | Chengdu Greenland Tower | 468 m (1,535 ft) | 101 | 2026 | Chengdu | ||
| 17 | Aeternitas Tower | 450 m (1,480 ft) | 106 | Dubai | |||
| 18 | China Resources Land Center | 436.1 m (1,431 ft) | 98 | 2026 | Dongguan | ||
| 19 | Haikou Tower 1 | 428 m (1,404 ft) | 93 | 2027 | Haikou | ||
| 20 | Tour F | 421 m (1,381 ft) | 75 | 2026 | Abidjan | ||
| 21 | Tsingshan Holdings Group Global Headquarters Tower 1 | 418 m (1,371 ft) | |||||
| 22 | Great River Center | 400 m (1,300 ft) | 82 | 2026 | Wuhan | ||
| 23 | Mukaab | 400 m (1,300 ft) | 2030 | Riyadh | |||
| 24 | Hangzhou West Railway Station Hub Tower 1 | 399.8 m (1,312 ft) | 83 | Hangzhou | |||
| 25 | China Merchants Group West Headquarters | 396 m (1,299 ft) | 82 | Chengdu | |||
| 26 | Shenzhen Bay Super Headquarters Base Tower B | 394.4 m (1,294 ft) | 81 | Shenzhen | |||
| 27 | Shenzhen Bay Super Headquarters Base Tower C-1 | 394 m (1,293 ft) | 78 | 2027 | Shenzhen | ||
| 28 | Lucheng Square | 388.8 m (1,276 ft) | 79 | 2026 | Wenzhou | ||
| 29 | Guohua Financial Center Tower 1 | 388 m (1,273 ft) | 79 | Wuhan | |||
| 30 | Torch Tower | 385 m (1,263 ft) | 62 | 2028 | Tokyo | ||
| 31 | Shekou Prince Bay Tower | 380 m (1,250 ft) | 70 | Shenzhen | |||
| 32 | Shenzhen Luohu Friendship Trading Centre | 379.9 m (1,246 ft) | 83 | 2026 | |||
| 33 | China Merchants Prince Bay Tower | 374 m (1,227 ft) | 59 | 2028 | |||
| 34 | Hengli Global Operations Headquarters Tower 1 | 369 m (1,211 ft) | Suzhou | ||||
| 35 | Shenyang International Center Tower 1 | 366 m (1,201 ft) | 75 | 2027 | Shenyang | ||
| 36 | Taipei Twin Tower 1 | 360 m (1,181 ft) | 70 | 2027 | Taipei | ||
| 37 | Naga 3 Tower 1 | 358 m (1,175 ft) | 70 | Phnom Penh | |||
| 38 | Bay Area Smart Plaza | 358 m (1,175 ft) | 77 | 2027 | Shenzhen | ||
| 39 | Guohong Center | 356 m (1,168 ft) | 71 | 2028 | Wenzhou | ||
| 40 | Shenzhen Bay Super Headquarters Base Tower C-2 | 355.7 m (1,167 ft) | 68 | 2027 | Shenzhen | ||
| 41 | SkyTower at Pinnacle One Yonge | 351.4 m (1,153 ft) | 106 | 2026 | Toronto | ||
| 42 | Poly Liangxi Plaza | 350 m (1,150 ft) | Foshan |
On Hold
These buildings were being built but their construction has stopped for now.
| Rank | Building | Planned architectural height | Floors | Planned completion | Country | City | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tower M | 700 m (2,297 ft) | 145 | Kuala Lumpur | |||
| 2 | Evergrande Hefei Center T1 | 518 m (1,699 ft) | 112 | Hefei | |||
| 3 | Greenland Jinmao International Financial Center | 499.8 m (1,640 ft) | 102 | Nanjing | |||
| 4 | Suzhou Zhongnan Center | 499.2 m (1,638 ft) | 103 | Suzhou | |||
| 5 | China International Silk Road Center | 498 m (1,634 ft) | 101 | Xi'an | |||
| 6 | Chushang Building | 475 m (1,558 ft) | 111 | Wuhan | |||
| 7 | Fosun Bund Center T1 | 470 m (1,540 ft) | |||||
| 8 | Evergrande City Light | 453.5 m (1,488 ft) | 88 | Ningbo | |||
| 9 | Tianshan Gate of the World Plots 27 and 28 | 450 m (1,480 ft) | 106 | Shijiazhuang | |||
| 10 | Dubai Towers Doha | 436.5 m (1,432 ft) | 91 | Doha | |||
| 11 | One Bangkok | 436.1 m (1,431 ft) | 92 | Bangkok | |||
| 12 | Burj Almasa | 432 m (1,417 ft) | 93 | Jeddah | |||
| 13 | Greenland Center Tower 1 | 428 m (1,404 ft) | Kunming | ||||
| 14 | Najning Olympic Suning Tower | 419.8 m (1,377 ft) | 99 | Nanjing | |||
| 15 | Dongfeng Plaza Landmark Tower | 407 m (1,335 ft) | 100 | Kunming | |||
| 16 | One Tower | 405.3 m (1,330 ft) | 108 | Moscow | |||
| 17 | Haiyun Plaza Tower 1 | 390 m (1,280 ft) | 86 | Rizhao | |||
| 18 | Icon Towers 1 | 384 m (1,260 ft) | 77 | Jakarta | |||
| Forum 66 Tower 2 | 384 m (1,260 ft) | 76 | Shenyang | ||||
| 19 | Guiyang World Trade Center Landmark Tower | 380 m (1,250 ft) | 92 | Guiyang | |||
| 20 | Greenland Star City Light Tower | 379.9 m (1,246 ft) | 83 | Changsha | |||
| 21 | Nanchang Ping An Financial Center | 373 m (1,224 ft) | 72 | Nanchang | |||
| 22 | Kweichow Moutai Tower | 369 m (1,211 ft) | Guiyang | ||||
| 23 | VietinBank Business Center Office Tower | 363.2 m (1,192 ft) | 68 | Hanoi | |||
| 24 | Wanda One | 360 m (1,180 ft) | 86 | Xi'an | |||
| 25 | Fosun Bund Center T2 | 356 m (1,168 ft) | Wuhan | ||||
| 26 | Global Port Tower 1 | 350 m (1,150 ft) | Lanzhou | ||||
| Global Port Tower 2 | |||||||
| Guowei ZY Plaza | 62 | Zhuhai | |||||
| Baolixian Village Old Reform Project Main Building | 70 | Guangzhou |
Tallest Buildings by Continent
This list shows the tallest completed building on each continent, from tallest to shortest.
| Continent | Building | Height | Floor count | Completed | Country | City |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asia | Burj Khalifa | 828 m (2,717 ft) | 163 | 2010 | Dubai | |
| North America | One World Trade Center | 541.3 m (1,776 ft) | 94 | 2014 | New York City | |
| Europe | Lakhta Center | 462 m (1,516 ft) | 86 | 2018 | Saint Petersburg | |
| Africa | Iconic Tower | 393.8 m (1,292 ft) | 79 | 2023 | New Administrative Capital | |
| Oceania | Q1 | 323 m (1,060 ft) | 78 | 2005 | Gold Coast | |
| South America | Gran Torre Santiago | 300 m (980 ft) | 64 | 2012 | Santiago | |
| Antarctica | Vostok Station | 17.5 m (57 ft) | 2 | 2023 | - |
Countries with Many Tall Buildings
This list shows the countries that have the most buildings on the main list of the world's tallest buildings. They are ordered from most to least.
| Rank | Country | Number of skyscrapers on list | City(s) with most skyscrapers on list | Tallest building | Height of tallest building |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 48 | Shenzhen | Shanghai Tower | 632 m (2,073 ft) | |
| 2 | 16 | Dubai | Burj Khalifa | 828 m (2,717 ft) | |
| 3 | 12 | New York City | One World Trade Center | 541.3 m (1,776 ft) | |
| 4 | 4 | Kuala Lumpur | Merdeka 118 | 678.9 m (2,227 ft) | |
| 4 | Hong Kong | International Commerce Centre | 484 m (1588 ft) | ||
| 6 | 3 | Moscow | Lakhta Center | 462 m (1,516 ft) | |
| 7 | 2 | Mecca, Riyadh | The Clock Towers | 601 m (1,972 ft) | |
| 2 | Seoul, Busan | Lotte World Tower | 554.5 m (1,819 ft) | ||
| 9 | 1 | Taipei | Taipei 101 | 508 m (1,667 ft) | |
| 1 | Ho Chi Minh City | Landmark 81 | 461.2 m (1,513 ft) | ||
| 1 | Kuwait City | Al Hamra Tower | 412.6 m (1,354 ft) | ||
| 1 | New Administrative Capital | Iconic Tower (Egypt) | 393.8 m (1,292 ft) | ||
| 1 | Jakarta | Autograph Tower | 382.9 m (1,256 ft) | ||
| 1 | Istanbul | CBRT Tower | 352 m (1,155 ft) |
See also
 In Spanish: Anexo:Rascacielos más altos del mundo para niños
In Spanish: Anexo:Rascacielos más altos del mundo para niños
- List of tallest structures
- History of the world's tallest buildings
- History of the world's tallest structures
- Tallest structures by category
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |