The Walt Disney Company facts for kids

Logo used since 2012
|
|

The Walt Disney Studios, the company's headquarters in Burbank, California in July 2016.
|
|
|
Formerly
|
|
|---|---|
| Public | |
| Traded as | |
| ISIN | [https://isin.toolforge.org/?language=en&isin=US2546871060 US2546871060] |
| Industry |
|
| Predecessor | Laugh-O-Gram Studio |
| Founded | October 16, 1923 |
| Founders | |
| Headquarters | The Walt Disney Studios,
,
United States
|
|
Area served
|
Worldwide |
|
Key people
|
|
| Revenue | |
|
Operating income
|
|
| Total assets | |
| Total equity | |
|
Number of employees
|
225,000 (FY23) |
| Divisions |
|
| Subsidiaries | List of assets owned by the Walt Disney Company |
| Footnotes / references Financials as of September 30, 2023[update]. References: |
|
The Walt Disney Company, often called simply Disney, is a huge American company that focuses on media and entertainment. Its main office is in Burbank, California, at the Walt Disney Studios complex. Disney started on October 16, 1923, as a small animation studio. It was founded by two brothers, Walt Disney and Roy Oliver Disney, and was first called Disney Brothers Cartoon Studio. Over the years, it changed names to Walt Disney Studio and Walt Disney Productions before becoming The Walt Disney Company in 1986.
In 1928, Disney became a leader in animation with the short film Steamboat Willie. This film was special because it used synchronized sound, meaning the sounds matched the actions on screen. It also made Mickey Mouse very popular. Mickey Mouse soon became Disney's main character and a symbol for the company.
After becoming successful in the early 1940s, Disney started making live-action movies, television shows, and theme parks in the 1950s. After Walt Disney passed away in 1966, the company's profits, especially in animation, began to drop. In 1984, Michael Eisner became the CEO. He helped the company grow again by expanding theme parks around the world and creating the very successful Disney Renaissance period for animation from 1989 to 1999.
In 2005, Bob Iger became the new CEO. Under his leadership, Disney grew even bigger by buying other major entertainment companies. These included Pixar in 2006, Marvel Entertainment in 2009, Lucasfilm in 2012, and most of 21st Century Fox in 2019. In 2020, Bob Chapek took over as head of Disney after Iger retired. However, Chapek left in 2022, and Iger returned as CEO.
Disney's film studio includes famous names like Walt Disney Pictures, Walt Disney Animation Studios, Pixar, Marvel Studios, Lucasfilm, 20th Century Studios, and Searchlight Pictures. Disney also owns the ABC television network and cable channels such as Disney Channel, ESPN, Freeform, FX, and National Geographic. The company also has divisions for publishing, merchandise, music, and theater. It offers direct-to-consumer streaming services like Disney+, ESPN+, Hulu, and Hotstar. Finally, Disney Experiences manages several theme parks, resort hotels, and cruise lines worldwide.
Disney is one of the largest and most famous companies globally. In 2023, it was ranked 87th on the Forbes Global 2000 list and 48th on the Fortune 500 list of the biggest companies in the United States by revenue. Since it started, Disney has won 135 Academy Awards, with 26 of them going to Walt Disney himself. The company has made many films that are considered among the greatest of all time. It has also played a key role in developing the theme park industry. Disney has been a public company since 1940, meaning its shares are traded on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE). It has been part of the Dow Jones Industrial Average since 1991. The company celebrated its 100th anniversary on October 16, 2023.
Contents
- Disney's Journey Through Time
- Early Days: Founding and First Characters (1921–1934)
- Golden Age of Animation and World War II (1934–1949)
- New Ventures: Live-Action, TV, and Disneyland (1950–1967)
- After Walt: Roy's Leadership and New Parks (1967–1984)
- Michael Eisner's Era and the Disney Renaissance (1984–2005)
- Bob Iger's First Time as CEO (2005–2020)
- Recent Years: Leadership Changes and Growth (2020–Present)
- How Disney Works: Company Units
- Who Leads Disney: Leadership Team
- Awards and Impact
- See also
Disney's Journey Through Time
Early Days: Founding and First Characters (1921–1934)
In 1921, animators Walt Disney and Ub Iwerks started Laugh-O-Gram Studio in Kansas City, Missouri. They made short films there. Their last film in 1923 was Alice's Wonderland, which mixed a real child actress with animated characters. The studio went out of business, and Walt Disney moved to Los Angeles to be with his brother Roy O. Disney.
Soon after, a film distributor named Margaret J. Winkler bought Alice's Wonderland. It became popular. Walt signed a deal with Winkler to make more "Alice Comedies." On October 16, 1923, Walt and Roy Disney officially started Disney Brothers Cartoon Studio to make these films. In 1926, they moved to a new studio and changed the name to Walt Disney Studio.
In 1927, Disney created a new character called Oswald the Lucky Rabbit. However, Disney lost the rights to Oswald in a business dispute. This led Walt and Ub Iwerks to create a new character: a mouse first named Mortimer, then changed to Mickey Mouse by Walt's wife.
In May 1928, Mickey Mouse first appeared in test screenings of Plane Crazy and The Gallopin' Gaucho. Later that year, the studio made Steamboat Willie, which was its first film with synchronized sound. This meant the sounds and music matched the animation perfectly. Steamboat Willie was a huge hit, and Mickey Mouse became incredibly popular.
In 1929, the company started the Silly Symphony series, which featured music-themed cartoons. The first Mickey Mouse Club for children started in theaters in 1929, with about 1,200 kids attending the first meeting. In 1930, a Mickey Mouse comic strip began appearing in newspapers.
On December 16, 1930, the company became a corporation called Walt Disney Productions. It also created a division for selling merchandise. Walt Disney and his wife owned 60% of the company, and Roy Disney owned 40%.
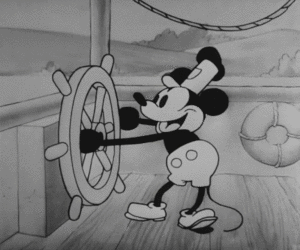
The Mickey Mouse comic strip became very popular, appearing in many newspapers worldwide. Disney realized that selling merchandise with their characters could make a lot of money. Mickey Mouse became the first character to be officially licensed for products. By 1934, Disney was making more money from Mickey Mouse merchandise than from his films.
The Waterbury Clock Company made a Mickey Mouse watch that was so popular it saved the company from going out of business during the Great Depression. Millions of these watches were sold. As Mickey Mouse became more of a hero, Disney needed a new character for funny situations. In 1934, Donald Duck first appeared in The Wise Little Hen. He later got his own series of cartoons.
Disney also started making cartoons in color. In 1932, Flowers and Trees became the first full-color cartoon and won an Academy Award. In 1933, The Three Little Pigs was released and also won an Academy Award. Its song, "Who's Afraid of the Big Bad Wolf?", became very famous.
Golden Age of Animation and World War II (1934–1949)
In 1934, Walt Disney announced a big project: a full-length animated movie called Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs. This was a risky idea because no one had ever made a full-length animated film in the US before. Roy Disney worried it would cost too much and bankrupt the studio. Walt wanted the animators to make the characters look very realistic.
While making Snow White, the company invented the multiplane camera. This camera used layers of drawings to create a feeling of depth in the backgrounds. Snow White cost $1.5 million to make, which was ten times its original budget.
Snow White took three years to finish and premiered on December 12, 1937. It was a huge success with both critics and audiences. It became the highest-grossing film of its time. With the money from Snow White, Disney built a new 51-acre studio in Burbank, California, where the company is still located today. In 1940, Walt Disney Productions became a public company, selling shares to raise money.
Work began on Disney's next films, Pinocchio and Bambi. Pinocchio was released in February 1940 and won two Academy Awards. However, it did not do well at the box office because World War II affected international sales.
The company's third feature, Fantasia (1940), introduced new sound technology called Fantasound, an early surround sound system. But Fantasia also struggled at the box office. In 1941, many of Disney's animators went on strike for better pay and working conditions. This caused problems for the studio.

To help with financial problems, Disney quickly made Dumbo (1941) on a smaller budget. This film did well and brought in much-needed money. After the US entered World War II, many Disney animators joined the army. The United States Navy asked Disney to make propaganda films to support the war effort. Disney agreed, and most employees worked on these projects.
In August 1942, Disney released Bambi, which had been in development for five years. It did not perform well at the box office. Disney then released "package films," which were collections of short cartoons grouped together as feature films, like Saludos Amigos (1942) and The Three Caballeros (1944). These also did not earn much money. Disney continued this strategy with films like Make Mine Music (1946) and The Adventures of Ichabod and Mr. Toad (1949).
Disney also started making live-action films mixed with animation, such as Song of the South (1946). To help with profits, the Walt Disney Music Company was founded in 1949.
New Ventures: Live-Action, TV, and Disneyland (1950–1967)
In the 1950s, Disney returned to making full-length animated films. Cinderella (1950) was a big success and helped Disney recover financially. It was the most successful film since Snow White. Walt Disney started focusing less on animation and more on other projects, including live-action films like Treasure Island (the studio's first), television, and amusement parks.
In 1950, Disney entered television with "One Hour in Wonderland" on NBC. Alice in Wonderland (1951) was not financially successful. In 1953, Peter Pan was released and did well. After this, Disney stopped working with RKO and created its own distribution company, Buena Vista Distribution.
Walt Disney had the idea for an amusement park where families could have fun together. He first planned a small "Mickey Mouse Park" near the studio, but soon realized it needed to be much bigger. The park's name changed to Disneyland. A new company, WED Enterprises (now Walt Disney Imagineering), was formed in 1952 to design the park. Walt wanted Disneyland to focus on storytelling and cleanliness, which was new for amusement parks.
The plan to build in Burbank was dropped, and Disney bought 160 acres of land in Anaheim, California, for the park. Construction began in July 1954. To pay for Disneyland, Disney sold his home and promoted the park with a television series on ABC. The Disneyland TV series was very popular. In August, Walt formed Disneyland, Inc. to help fund the park, which cost $17 million to build.
In October 1954, ABC allowed Disney to produce The Mickey Mouse Club, a variety show for children. It featured daily cartoons, news, and a talent show with "Mouseketeers." Millions of children watched it daily, and millions of Mickey Mouse ears were sold. In December 1954, the miniseries Davy Crockett premiered as part of Disneyland. It became a national sensation, selling millions of coonskin caps and records of its theme song. In June 1955, Disney's animated film Lady and the Tramp was released and did better at the box office than any Disney film since Snow White.
Disneyland opened on July 17, 1955. It was a huge media event, broadcast live on ABC, and watched by over 90 million viewers. The opening day had some problems, but the park quickly became a success. In its first year, 3.6 million people visited, and it became more popular than the Grand Canyon.
Disney continued to make animated films, with top animators known as the Nine Old Men. Films from this period included Sleeping Beauty (1959), One Hundred and One Dalmatians (1961), and The Sword in the Stone (1963). Sleeping Beauty was expensive and lost money. One Hundred and One Dalmatians used a new animation technique that changed the art style.
In 1956, the Sherman Brothers, Robert and Richard, were hired as exclusive songwriters for Disney. They wrote many popular songs for Disney films and theme parks. In the late 1950s, Disney also made successful live-action comedies like The Shaggy Dog (1959) and The Absent-Minded Professor (1961), both starring Fred MacMurray.
Disney also made live-action films based on children's books, such as Pollyanna (1960) and Swiss Family Robinson (1960). Child actress Hayley Mills starred in Pollyanna and won an award. She also starred in five other Disney films, including The Parent Trap. Another child actor, Kevin Corcoran, appeared in many Disney live-action films like Old Yeller (1957).
In 1964, the musical film Mary Poppins, which mixed live-action and animation, was released. It was a huge success, winning five Academy Awards, including Best Actress for Julie Andrews and Best Song for "Chim Chim Cher-ee" by the Sherman Brothers.
Throughout the 1960s, Dean Jones starred in ten Disney films, including That Darn Cat! (1965) and The Love Bug (1968). Kurt Russell also became a prominent child actor for Disney in the late 1960s.
In 1959, Walt had an idea for another park in Florida, a "City of Tomorrow." In 1964, the company bought 27,000 acres southwest of Orlando, Florida. On November 15, 1965, Walt, Roy, and Florida's governor announced plans for Walt Disney World. It would include Magic Kingdom, a larger version of Disneyland, and the "City of Tomorrow," which Walt later called Experimental Prototype Community of Tomorrow (Epcot).
By 1967, Disneyland had expanded with new rides like Walt Disney's Enchanted Tiki Room, which used Audio-Animatronics (animated robots), and Walt Disney's Carousel of Progress.

On December 15, 1966, Walt Disney passed away at age 65 from lung cancer.
After Walt: Roy's Leadership and New Parks (1967–1984)
After Walt's death, his brother Roy O. Disney, who was ready to retire, decided to lead the company to ensure Walt's dream of Disney World came true. He became the first CEO and chairman of the company. Roy changed the park's name to Walt Disney World to honor his brother.
In 1967, the last two films Walt had worked on were released: the animated film The Jungle Book and the live-action musical The Happiest Millionaire. The Jungle Book was very successful. After Walt's death, the company made fewer animated films and focused more on live-action movies.
Roy worked to get special laws passed in Florida that would give Disney World its own local government. This area was called the Reedy Creek Improvement District.
After 18 months of construction and costing about $400 million, Walt Disney World's first park, the Magic Kingdom, opened on October 1, 1971. It featured the Cinderella Castle as its main symbol.
On December 21, 1971, Roy O. Disney passed away. Donn Tatum became the first CEO who was not a member of the Disney family. Card Walker became president. By 1973, Disney had over 23,000 employees. In November, the animated film Robin Hood was released and became Disney's biggest international success at the time.
Throughout the 1970s, Disney released live-action films like Escape to Witch Mountain (1975) and Freaky Friday (1976). In 1977, Roy E. Disney, Roy O. Disney's son, left his executive role due to disagreements with company decisions.
In 1977, the animated film The Rescuers was successful. In 1979, Disney released The Black Hole, its first film with a PG rating and its most expensive film yet. It used a lot of computer-generated imagery (CGI).
In September 1979, some animators, led by Don Bluth, left Disney to start their own company. In 1981, Disney began releasing its films on VHS (home video), starting with Dumbo. In 1981, The Fox and the Hound was released and became the highest-grossing animated film up to that point. It was the first major Disney animated film not directly involving Walt Disney.
As profits declined, Epcot (then called EPCOT Center) opened on October 1, 1982, as the second theme park in Walt Disney World. It cost over $900 million to build. The animation industry continued to struggle, and 69% of the company's profits came from its theme parks. In 1982, Disney lost $27 million.
On April 15, 1983, Tokyo Disneyland, Disney's first park outside the US, opened in Urayasu. It cost about $1.4 billion to build. Within ten years, over 140 million people visited the park. On April 18, Disney launched Disney Channel, a pay-to-watch cable television channel showing Disney films and shows.
In 1983, Walt's son-in-law Ron W. Miller became CEO. Miller wanted the studio to make more content for older audiences. So, Disney started a new film label called Touchstone Pictures in 1984 to produce movies for adults and teenagers. Splash (1984) was the first film released under this label and was a big success. Disney's first R-rated film, Down and Out in Beverly Hills (1986), was also a hit.
In 1984, a businessman named Saul Steinberg tried to buy Disney. Disney rejected his offer and bought back his shares, which put the company into significant debt.
Michael Eisner's Era and the Disney Renaissance (1984–2005)
In 1984, shareholders, including Roy E. Disney, brought in Michael Eisner, a former president of Paramount Pictures, as CEO. Frank Wells became president. Eisner wanted to make Disney a major film studio again. He appointed Jeffrey Katzenberg as head of animation. Eisner aimed to release a new animated film every 18 months.
Under Eisner, Disney also became more involved in television, creating Touchstone Television and producing hit shows like The Golden Girls. The company spent money promoting its theme parks, which increased visitor numbers. In 1984, Disney released The Black Cauldron, its most expensive animated film at $40 million. It was also the first animated film to use CGI and have a PG rating. However, the film did not do well at the box office.
In 1986, the company changed its name from Walt Disney Productions to The Walt Disney Company, to show it was more than just a film studio. The animated film The Great Mouse Detective was a much-needed financial success, earning $25 million. To make more money from merchandise, Disney opened its first retail store, Disney Store, in Glendale in 1987. By 1990, there were 215 Disney Stores across the US.
In 1987, Disney signed a deal with the Government of France to build a resort called Euro Disneyland in Paris. It would include two theme parks, a golf course, and hotels.
In 1988, Disney's animated film Oliver & Company was released and became the first animated film to earn over $100 million. Disney became the top Hollywood studio at the box office for the first time, with hit films like Who Framed Roger Rabbit (1988). The company's revenue and profits grew significantly.
On May 1, 1989, Disney opened Disney-MGM Studios, its third amusement park at Walt Disney World. It later became Hollywood Studios. This park showed visitors how movies were made. In June 1989, Disney opened the water park Typhoon Lagoon. In 1989, Disney also planned to buy The Jim Henson Company and its Muppet characters, but the deal fell through after Jim Henson passed away in 1990.
On November 17, 1989, Disney released The Little Mermaid. This film marked the beginning of the Disney Renaissance, a period of highly successful and critically acclaimed animated films. The Little Mermaid earned $233 million and won two Academy Awards. During this time, composer Alan Menken and lyricist Howard Ashman wrote many famous Disney songs.
To produce music for movie soundtracks and the mainstream, Disney started the record label Hollywood Records in 1990. Disney's first animated sequel, The Rescuers Down Under (1990), was the first feature film to be made entirely using digital software developed by Disney and Pixar.
In May 1991, Disney was added to the Dow Jones Industrial Average, showing its importance in the economy. Disney's next animated film, Beauty and the Beast, released on November 13, 1991, earned nearly $430 million. It was the first animated film to win a Golden Globe for Best Picture and was nominated for six Academy Awards, including Best Picture.
In 1992, Disney founded the National Hockey League team The Mighty Ducks of Anaheim to go along with the film The Mighty Ducks. Disney's animated feature Aladdin was released on November 11, 1992, and earned $504 million, becoming the highest-grossing animated film at that time. It won two Academy Awards, and its song "A Whole New World" was the first Disney song to win a Grammy for Song of the Year.
In 1993, Disney bought the independent film distributor Miramax Films for $60 million, expanding its range of films for older audiences. The same year, Disney bought 8,500 acres of Everglades land in Florida to protect native animals and plants, creating the Disney Wilderness Preserve.
On April 3, 1994, Frank Wells passed away in a helicopter crash. On June 15, The Lion King was released and was a massive success, becoming the highest-grossing animated film of all time with $969 million. It won two Academy Awards. Soon after, Jeffrey Katzenberg left the company and co-founded DreamWorks SKG.
In 1994, Disney's yearly revenue reached $10 billion. Pixar's and Disney's first co-release was Toy Story, the first-ever fully computer-generated film. It was released on November 19, 1995, to great reviews and earned $361 million. It won a special Academy Award and was the first animated film nominated for Best Original Screenplay.
In 1995, Disney announced it would buy the television network Capital Cities/ABC Inc. for $19 billion, which was one of the largest company takeovers in US history at the time. This deal gave Disney ownership of ABC, a majority stake in ESPN, and other networks. Following this, Disney launched Radio Disney, a radio program for young people, in 1996. The Walt Disney Company also launched its official website, disney.com, in 1996.
On June 19, 1996, the animated film The Hunchback of Notre Dame was released, earning $325 million. In 1996, Michael Ovitz was fired as the company's president. In 1998, Disney bought the Major League Baseball team California Angels for $110 million, renaming them the Anaheim Angels. Hercules (1997) earned $252 million, which was less than earlier films.
In February 1998, Disney and Pixar signed a ten-year deal to make five films together, sharing costs and profits. During the Disney Renaissance, Touchstone Pictures also had successful films like Pretty Woman (1990) and Armageddon (1998), which was the highest-grossing film of 1998.
At Disney World, the company opened Disney's Animal Kingdom on April 22, 1998. It was the largest theme park in the world, covering 580 acres, with over 2,000 animals and the Tree of Life at its center. Disney's animated film Mulan and the Disney-Pixar film A Bug's Life were released in 1998 and were both very successful.
In 1998, Disney bought a large stake in the Internet search engine Infoseek and later acquired the rest of the company. In 1999, they launched the web portal Go.com. In 1994, Disney announced it would start its own cruise line. The first two ships of the Disney Cruise Line were named Disney Magic and Disney Wonder. Disney also bought a private island called Castaway Cay for its cruise line. On July 30, 1998, Disney Magic began its first voyage.
Tarzan (1999) marked the end of the Disney Renaissance. It earned $448 million and won an Academy Award for its song "You'll Be in My Heart" by Phil Collins. The Disney-Pixar film Toy Story 2 was released in 1999 and earned $511 million.
In January 2000, Bob Iger became Disney's president and chief operating officer. In 2001, Disney had another huge success with Pixar's Monsters, Inc.. Later, Disney bought the children's cable network Fox Family Worldwide for $3 billion.
In 2001, Disney faced financial losses due to a decline in ABC viewership and reduced tourism after the September 11 attacks. To save money, Disney laid off employees and closed many Disney Stores. In 2003, Disney sold the Anaheim Angels baseball team. In 2003, Roy E. Disney announced his retirement and called for Eisner to retire as well. Roy and another board member started the "Save Disney" campaign.
In 2004, Disney shareholders voted to remove Eisner as chairman. George J. Mitchell replaced him. In April, Disney bought The Muppets franchise from the Jim Henson Company for $75 million. Following the success of Disney-Pixar films Finding Nemo (2003) and The Incredibles (2004), Pixar looked for a new distributor as its deal with Disney was ending. Disney sold its Disney Stores chain in 2004 and the Mighty Ducks hockey team in 2005. Roy E. Disney rejoined the company as a consultant.
Bob Iger's First Time as CEO (2005–2020)
In March 2005, Bob Iger became CEO after Eisner retired. Iger officially took over on October 1. Disney's eleventh theme park, Hong Kong Disneyland, opened on September 12, costing $3.5 billion to build. On January 24, 2006, Disney began talks to buy Pixar from Steve Jobs for $7.4 billion. Iger appointed Pixar's chief creative officer John Lasseter and president Edwin Catmull to lead Walt Disney Animation Studios.
A week later, Disney traded ABC Sports commentator Al Michaels to NBCUniversal in exchange for the rights to Oswald the Lucky Rabbit and 26 cartoons featuring the character. In February 2006, Disney merged its ABC Radio networks with Citadel Broadcasting. The Disney Channel movie High School Musical aired and its soundtrack became very popular.
Disney's 2006 live-action film Pirates of the Caribbean: Dead Man's Chest was Disney's biggest hit at the time, earning $1 billion. In 2007, the sequel High School Musical 2 broke cable rating records. The Muppets Holding Company was renamed Muppets Studios to relaunch the division. Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End was the highest-grossing film of 2007. Disney-Pixar films Ratatouille (2007) and WALL-E (2008) were huge successes, with WALL-E winning an Oscar for Best Animated Feature.
In 2009, Iger introduced D23 as Disney's official fan club. Disney also made a deal with DreamWorks Pictures to distribute 30 of its films. The 2009 film Up earned $735 million and won Best Animated Feature at the Academy Awards. Later that year, Disney launched a television channel called Disney XD for older children.
In August 2009, Disney bought Marvel Entertainment and its characters for $4 billion. In September, Disney partnered with News Corporation and NBCUniversal to own parts of the streaming service Hulu. On December 16, Roy E. Disney passed away.
In March 2010, Disney sold the Power Rangers franchise back to Haim Saban. Disney also sold Miramax Films. During this time, Disney released the live-action Alice in Wonderland and the Disney-Pixar film Toy Story 3. Both films earned over $1 billion, with Toy Story 3 becoming the first animated film to reach that milestone. Disney was the first studio to release two $1-billion-earning films in one year.
In 2011, Disney released its last traditionally animated film, Winnie the Pooh. Pirates of the Caribbean: On Stranger Tides earned over $1 billion, becoming Disney's highest-grossing film internationally at the time. In April, Disney began building its new theme park, Shanghai Disney Resort, costing $4.4 billion.
On October 30, 2012, Disney announced it would buy Lucasfilm for $4.05 billion from George Lucas. This deal gave Disney access to franchises like Star Wars and Indiana Jones. Disney planned to release a new Star Wars film every two to three years.
By March 2012, Iger became Disney's chairman. The Marvel film The Avengers became the third-highest-grossing film of all time with $1.3 billion. In 2013, the Marvel film Iron Man 3 earned over $1.2 billion. The same year, Disney's animated film Frozen was released and became the highest-grossing animated film of all time with $1.2 billion. Merchandise for Frozen was so popular it earned $1 billion within a year.
In March 2013, Iger announced Disney would no longer develop 2D animated films, and the hand-drawn animation division was closed. In 2014, Disney acquired Maker Studios, a large network on YouTube, for $950 million.
In June 2015, Disney merged its consumer products and interactive divisions into a new subsidiary called Disney Consumer Products and Interactive Media. In August, Marvel Studios became part of the Walt Disney Studios division. Disney's 2015 releases included the successful animated film Inside Out and the Marvel film Avengers: Age of Ultron. Star Wars: The Force Awakens earned over $2 billion, becoming the third-highest-grossing film of all time.
Shanghai Disneyland opened on June 16, 2016. To start a streaming service, Disney bought a 33% stake in the technology company Bamtech for $1 billion in August. In 2016, four Disney films earned over $1 billion: Zootopia, Captain America: Civil War, Finding Dory, and Rogue One: A Star Wars Story. Disney became the first studio to earn over $3 billion at the domestic box office.
On March 23, 2017, Disney announced Iger would stay as CEO until July 2019. On August 8, 2017, Disney announced it would end its distribution deal with Netflix to launch its own streaming platform by 2019. Disney also planned to start an ESPN streaming service. In November, John Lasseter, the CCO, took a break from his role due to personal reasons. The same month, Disney and 21st Century Fox began talks for Disney to acquire most of Fox's assets.
In 2017, two Disney films earned over $1 billion: the live-action Beauty and the Beast and Star Wars: The Last Jedi. Disney launched the subscription sports streaming service ESPN+ on April 12, 2018. In June 2018, Lasseter left Disney, and Jennifer Lee became head of Walt Disney Animation Studios, while Pete Docter became head of Pixar.
Comcast offered to buy 21st Century Fox, but Disney countered with a higher bid of $71 billion, which was accepted. Disney received approval from the US government to acquire Fox. In 2018, Disney again earned over $7 billion at the box office with three films that made over $1 billion: Marvel's Black Panther and Avengers: Infinity War (which earned over $2 billion), and Pixar's Incredibles 2.
On March 20, 2019, Disney acquired most of 21st Century Fox's assets for $71 billion. This was the biggest acquisition in Disney's history. Through this purchase, Disney gained 20th Century Fox, National Geographic Partners, Fox Networks Group, and a larger stake in Hulu. Disney became the first film studio to have seven films earn $1 billion in one year, including Marvel's Captain Marvel, the live-action Aladdin, Pixar's Toy Story 4, the CGI remake of The Lion King, Star Wars: The Rise of Skywalker, and Avengers: Endgame, which became the highest-grossing film of all time with $2.8 billion.
On November 12, 2019, Disney launched the Disney+ streaming service in the US, Canada, and the Netherlands. On its first day, it had over 10 million subscribers. By 2022, it had over 135 million subscribers and was available in over 190 countries. In early 2020, Disney removed the "Fox" name from its acquired assets, rebranding them as 20th Century Studios and Searchlight Pictures.
Recent Years: Leadership Changes and Growth (2020–Present)
Bob Chapek, who had been chairman of Disney Parks, Experiences and Products, became CEO on February 25, 2020, after Iger resigned. Iger stayed on as Executive Chairman to help with creative strategy. In April 2020, Iger temporarily resumed more operational duties to help the company during the COVID-19 pandemic.
During the pandemic, Disney temporarily closed all its theme parks, delayed movie releases, and stopped cruises. Disney announced it would stop paying 100,000 employees but still provide healthcare benefits, saving the company $500 million a month. Iger gave up his salary, and Chapek took a 50% pay cut.
In the second fiscal quarter of 2020, Disney reported a $1.4 billion loss. By August, two-thirds of the company was owned by large financial institutions. In September, the company laid off 28,000 employees from its Parks, Experiences and Products division. In November, Disney laid off another 4,000 employees.
In December 2020, Touchstone Television stopped operations. In March 2021, Disney announced a new division called 20th Television Animation to focus on shows for older audiences. Disney also closed its animation studio Blue Sky Studios in April 2021. Later that month, Disney and Sony made a deal to give Disney access to Sony's films for streaming on Disney+. Although it did not do well at the box office due to COVID-19, Disney's animated film Encanto (2021) was a big hit during the pandemic, and its song "We Don't Talk About Bruno" topped the US music charts.
After Iger's term as executive chairman ended on December 31, 2021, he resigned as chairman. Susan Arnold became Disney's first female chairperson. In March 2022, Disney stopped operations in Russia due to the invasion of Ukraine. In March 2022, some employees protested the company's initial silence on a Florida law. Chapek later stated the company had made a mistake and pledged support for the LGBTQ+ community. Amid Disney's response, the Florida Legislature passed a bill to remove Disney's special government district, Reedy Creek.
In June 2022, Disney's board gave Chapek a three-year contract extension. In August, Disney Streaming had more total subscribers than Netflix.
On November 20, 2022, Iger returned as Disney's CEO after Chapek was dismissed due to poor financial performance and unpopular decisions. The board asked Iger to serve for two years to develop a new growth strategy and find a successor.
In January 2023, Mark Parker replaced Susan Arnold as the company's chairperson. In February 2023, Disney announced it would cut $5.5 billion in costs, including eliminating 7,000 jobs, which was 3% of its workforce. Disney reorganized into three main divisions: Entertainment, ESPN, and Parks, Experiences and Products. In April 2023, the second and largest wave of job cuts happened across these divisions.
In 2023, Disney began its "100 Years of Wonder" campaign to celebrate its 100th anniversary. This included a new animated logo for Walt Disney Pictures, a touring exhibition, and special events at the parks.
In October 2023, Disney announced it was entering sports betting through a partnership with Penn Entertainment, launching the ESPN Bet app. This was a big change from Iger's earlier stance against gambling, driven by the potential to attract younger audiences and secure ESPN's financial future. In November 2023, Disney shortened the name of Disney Parks, Experiences and Products to Disney Experiences.
In February 2024, Debra O'Connell was appointed president of a new news division that includes ABC News. Also in February, Walt Disney and Reliance Industries announced they would merge their India TV and streaming media assets.
In July 2024, a Californian man hacked and leaked over a terabyte of the company's Slack messages. He claimed his motive was dislike of AI-generated art, but it was later found he tried to extort employees.
In October 2024, Disney announced James P. Gorman would replace Mark Parker as chairman in January 2025. They also announced that a successor to CEO Bob Iger would be named in early 2026.
On May 7, 2025, Disney announced its seventh resort, Disneyland Abu Dhabi, planned for Yas Island. Like Tokyo Disney Resort, it will not be owned or managed by Disney directly.
How Disney Works: Company Units
The Walt Disney Company has three main parts:
- Disney Entertainment handles all of the company's entertainment media and content around the world. This includes Walt Disney Studios, Disney General Entertainment Content, Disney Streaming, and Disney Platform Distribution.
- ESPN manages all of Disney's sports content, products, and experiences globally, including its international sports channels.
- Disney Experiences is in charge of theme parks and resorts, cruise and vacation experiences, and consumer products like toys, clothes, books, and video games.
Who Leads Disney: Leadership Team
Current Leaders
- Board of Directors
- James P. Gorman (Chairman)
- Mary Barra
- Amy Chang
- Jeremy Darroch
- Carolyn Everson
- Michael Froman
- Bob Iger
- Maria Elena Lagomasino
- Calvin McDonald
- Derica W. Rice
- Executives
- Bob Iger, Chief Executive Officer
- Asad Ayaz, Chief Brand Officer
- Alan Bergman, Co-Chairman, Disney Entertainment
- Sonia Coleman, Senior Executive Vice President and Chief Human Resources Officer
- Josh D'Amaro, Chairman, Disney Experiences
- Horacio Gutierrez, Senior Executive Vice President, Chief Legal and Compliance Officer
- Hugh Johnston, Senior Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer
- James Pitaro, Chairman, ESPN
- Kristina Schake, Senior Executive Vice President and Chief Communications Officer
- Dana Walden, Co-Chairman, Disney Entertainment
Past Leaders
- Executive Chairmen
- Bob Iger (2020–2021)
- Chairmen
- Walt Disney (1945–1960)
- Roy O. Disney (1964–1971)
- Donn Tatum (1971–1980)
- Card Walker (1980–1983)
- Raymond Watson (1983–1984)
- Michael Eisner (1984–2004)
- George J. Mitchell (2004–2006)
- John E. Pepper Jr. (2007–2012)
- Bob Iger (2012–2021)
- Susan Arnold (2022–2023)
- Mark Parker (2023–2025)
- James P. Gorman (2025–present)
- Vice Chairmen
- Roy E. Disney (1984–2003)
- Sanford Litvack (1999–2000)
- Presidents
- Walt Disney (1923–1945)
- Roy O. Disney (1945–1968)
- Donn Tatum (1968–1971)
- Card Walker (1971–1980)
- Ron W. Miller (1980–1984)
- Frank Wells (1984–1994)
- Michael Ovitz (1995–1997)
- Michael Eisner (1997–2000)
- Bob Iger (2000–2012)
- Chief Executive Officers (CEO)
- Roy O. Disney (1929–1971)
- Donn Tatum (1971–1976)
- Card Walker (1976–1983)
- Ron W. Miller (1983–1984)
- Michael Eisner (1984–2005)
- Bob Iger (2005–2020; 2022–present)
- Bob Chapek (2020–2022)
- Chief Operating Officers (COO)
- Card Walker (1968–1976)
- Ron W. Miller (1980–1984)
- Frank Wells (1984–1994)
- Thomas O. Staggs (2015–2016)
Awards and Impact
As of 2022, The Walt Disney Company has won 135 Academy Awards. Walt Disney himself received 32 of them. The company has won many awards for its animated short films, original songs, animated features, and visual effects. Disney has also won 29 Golden Globe Awards, 51 British Academy of Film and Television Arts (BAFTA) awards, and 36 Grammy Awards.
Disney is one of the world's largest entertainment companies. It is known for being a pioneer in the animation industry, having produced 790 features, including 122 animated films. Many of its films, like Pinocchio, Toy Story, Bambi, Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs, and Mary Poppins, are considered among the greatest of all time. Disney has also created some of the most famous characters ever, such as Mickey Mouse, Woody, Captain America, Jack Sparrow, Iron Man, and Elsa.
Disney is recognized for changing the animation industry. Making the first animated feature, Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs, was a big risk that "changed cinema." The company, especially through Walt, introduced new technologies and advanced animation techniques. Some of Disney's innovations include the multiplane camera, xerography, and CAPS. Many songs from Disney films have become extremely popular, with several reaching number one on the Billboard's Hot 100 charts.
In 2023, Disney was ranked 48th on the Fortune 500 list of the largest US companies by revenue. Smithsonian Magazine has called Disney theme parks "well-established cultural icons." Disney is a major player in the theme park industry, with 12 parks worldwide. All of its parks were among the top 25 most-visited parks in 2018. Disney theme parks had over 157 million visitors, making it the most-visited theme park company globally. The Magic Kingdom alone had 20.8 million visitors, making it the most-visited theme park in the world. When Disney first entered the theme park industry, it "changed the entire theme park industry."
See also
 In Spanish: The Walt Disney Company para niños
In Spanish: The Walt Disney Company para niños
 | Precious Adams |
 | Lauren Anderson |
 | Janet Collins |