Plant facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Plants |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Superdivisions | |
|
|
| Synonyms | |
|

Plants are a huge group of living things. They are autotrophs, which means they make their own food. Plants have complex cells and usually cannot move around on their own. They mostly grow by getting bigger.
Common plants include trees, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. Scientists who study plants are called botanists. They have found about 350,000 different kinds, or species, of plants alive today. Things like fungi and non-green algae are not considered plants.
Most plants grow in the ground. They have stems above and roots below. Some plants, however, float on water. Roots take in water and nutrients from the soil. This water travels up the stem to the leaves. Water then leaves the plant through tiny holes in the leaves. This process is called transpiration.
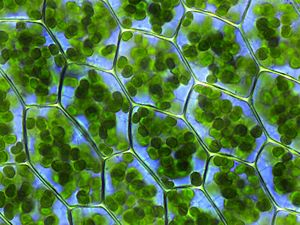
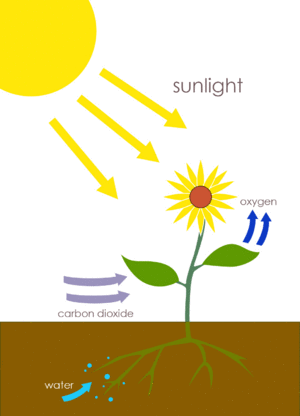
Plants need sunlight, carbon dioxide, minerals, and water to make their food. They do this through a process called photosynthesis. A green substance called chlorophyll helps plants capture the sun's energy. Chlorophyll is mostly found in plastids, which are inside the leaf cells. You can think of a leaf as a food factory! Leaves come in many shapes and sizes. They are perfectly designed to catch sunlight. Once food is made in the leaves, it moves to other parts of the plant, like stems and roots.
The word "plant" can also mean to put something in the earth. For example, farmers plant seeds in the ground to grow crops.
Contents
Types of Plants
Plants are divided into different groups based on their features.
- Green algae: These are simple plants that often live in water.
- Land plants (embryophytes): These plants are adapted to live on land.
- Non-vascular plants (bryophytes): These plants do not have special tubes to carry water.
-
- Vascular plants (tracheophytes): These plants have special tubes to move water and nutrients.
- Lycopodiophyta—clubmosses
- Pteridophyta: the ferns
- Pteridopsida: typical ferns
- Sphenopsida: horsetails
- Marattiopsida: a different group of ferns
- Psilotopsida: a group related to other ferns
- Seed plants (spermatophytes): These plants reproduce using seeds.
- †Pteridospermatophyta: the seed ferns (now extinct)
- Pinophyta: the conifers (like pine trees)
- Cycadophyta: the cycads
- Ginkgophyta: the ginkgos
- Gnetophyta: a unique group of plants
- Magnoliophyta or Angiosperms (flowering plants): These plants produce flowers.
- Vascular plants (tracheophytes): These plants have special tubes to move water and nutrients.
* Dicotyledons * Monocotyledons
How Plants Make Food
Many plant cells have special parts called plastids. These plastids help plants make their own food using photosynthesis. With sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide, the plastids create sugars. These sugars are the basic building blocks the plant needs to grow. A cool thing is that oxygen (O2) is released into the air as a leftover product of photosynthesis.
Later, inside the plant's cells, these sugars can be changed into other important things. They can become amino acids for proteins, nucleotides for DNA and RNA, and carbohydrates like starch. To do all this, plants need certain minerals from the soil. These include nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus, iron, and magnesium.
Plant Nutrients
Plants need specific chemical elements to grow healthy and strong. These are divided into two main groups:
- Macronutrients: Plants need these in larger amounts.
- N = Nitrogen (important for proteins)
- P = Phosphorus (helps with energy)
- K = Potassium (manages water in the plant)
- Ca = Calcium (helps move other nutrients)
- Mg = Magnesium (used in many enzymes)
- S = Sulfur (found in some amino acids)
- Si = Silicon (strengthens cell walls)
- Micronutrients (trace elements): Plants need these in smaller amounts.
- Cl = Chlorine (helps with water balance)
- Fe = Iron (important for photosynthesis)
- B = Boron (helps move sugar and with cell division)
- Mn = Manganese (helps build chloroplasts)
- Na = Sodium (used for various functions)
- Zn = Zinc (found in many enzymes)
- Cu = Copper (helps with photosynthesis)
- Ni = Nickel (part of an enzyme)
- Mo = Molybdenum (helps enzymes work)
Roots and Their Job
The roots of plants have two main jobs. First, they hold the plant firmly in the ground, like an anchor. Second, they soak up water and different nutrients from the soil. Plants use this water to make their food. Water also helps the plant stand up straight. If a plant doesn't get enough water, it becomes limp and its leaves droop. Plants that live in very dry places, like deserts, have special roots to find water.
Water travels from the roots to the rest of the plant through special tubes. When the water reaches the leaves, some of it evaporates into the air. Many plants get help from fungi to make their roots work better. This helpful team-up between plants and fungi is called mycorrhiza. Also, tiny Rhizobia bacteria live in bumps on the roots of some plants. They help these plants get nitrogen from the air.
Flowering Plant Reproduction
Flowers and Pollination
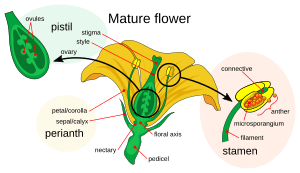
Flowers are the special parts that help flowering plants (Angiosperms) reproduce. The colorful petals of a flower often have a nice smell. This helps attract insects and other animals that help with pollination.
The male part of the flower is called the stamen. It has a stalk called the filament and a top part called the anther. The anther makes pollen, which is needed to make seeds.
The female part of the flower is called the carpel. The top sticky part of the carpel is the stigma. Below that is the style, which is like a neck. At the bottom is the ovary, which is where the seeds grow. A sepal is a small leaf that protects the flower when it is still a bud.
Pollination is when pollen moves from one flower to another. This can happen in different ways. Bees are attracted to bright, scented flowers. When a bee visits a flower to collect nectar, pollen sticks to its legs. When the bee visits another flower, the sticky stigma catches the pollen.
Some flowers use the wind to carry their pollen. These flowers often have small, dull petals. Their stamens hang out and produce lots of light pollen that the wind can easily pick up. Their stigmas are often feathery and hang outside to catch the wind-blown pollen.
Seed Travelers
Plants produce many spores or seeds. Simpler plants like mosses and ferns make spores. More complex plants, like Gymnosperms and Angiosperms, make seeds. If all the seeds just fell right next to the parent plant, the area would get too crowded. There wouldn't be enough water and minerals for all the new plants to grow.
So, seeds have ways to travel to new places. Some seeds are light and can be carried by the wind. Others can float on water. Seeds inside juicy fruits are often eaten by animals. The animals then carry the seeds far away before dropping them. Sometimes, seeds have hooks or sticky parts that attach to animals' fur or feathers, helping them travel to new spots.
Plant Fossils

When we talk about the oldest plant fossils, it depends on what we mean by "plant."
- If "plants" means living things that use chlorophyll to make food, then the oldest fossils are cyanobacteria found in stromatolites. These are about 3,450 million years old! Scientists can tell their age very precisely because they were found between layers of ancient lava.
- If "plants" means green plants (called Viridiplantae), then the first fossils are green algae. Many botanists agree with this. There's good evidence that charophyte green algae are closely related to land plants.
- Some tiny fossils called Acritarchs might be reproductive parts of green algae. If so, they are from about 1000 million years ago.
- Otherwise, there was a big increase in tiny algae around 540 million years ago, during the Cambrian period.
- If "plants" means land plants, then the first fossils are from the Silurian period.
By the Silurian period, we find fossils of whole plants, like the lycophyte Baragwanathia longifolia. From the Devonian period, we have detailed fossils of rhyniophytes. These early plant fossils even show the individual cells inside the plant tissue. The Devonian period also saw the first tree in the fossil record, called Wattezia. This tree looked like a fern, had a trunk with fronds, and produced spores.
The Coal measures are a great place to find ancient plant fossils. Many different groups of plants lived during this time. The piles of waste from coal mines are good places to look for fossils. Coal itself is made from the remains of fossilized plants, but you usually can't see the plant's details in the coal. In the Fossil Forest in Glasgow, you can see the stumps of Lepidodendron trees still standing where they grew long ago.
Related Pages
Images for kids
-
Green algae from Ernst Haeckel's Kunstformen der Natur, 1904.
-
A variety of fungi species
-
Range of pangaea glossopteris.
-
The leaf is usually the primary site of photosynthesis in plants.
-
The Venus flytrap, a species of carnivorous plant.
-
A rose espalier at Niedernhall in Germany.
-
Capitals of ancient Egyptian columns decorated to resemble papyrus plants. (at Luxor, Egypt)
-
Barbara McClintock (1902–1992) was a pioneering cytogeneticist who used maize (corn) to study the mechanism of inheritance of traits.
-
Musk Thistle are invasive species in texas.
See also
 In Spanish: Plantae para niños
In Spanish: Plantae para niños