Nordic countries facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Nordic countries
|
|
|---|---|
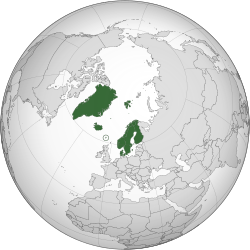
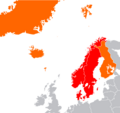
Land controlled by the Nordic countries shown in dark green. Bouvet Island and Antarctic claims not shown.
|
|
| Capitals | |
| Largest city | |
| Official languages | |
| Recognised regional languages | |
| Religion | Mainly Lutheranism |
| Composition | 5 sovereign states 2 autonomous territories 1 autonomous region 2 unincorporated areas 1 dependency 2 Antarctic claims |
| Establishment | |
|
• Inauguration of the Nordic Council
|
12 February 1953 |
|
• Helsinki Treaty
|
23 March 1962 |
|
• Inauguration of the Nordic Council of Ministers
|
July 1971 |
| Population | |
|
• 2021 estimate
|
27,562,156 (52nd) |
|
• 2000 census
|
24,221,754 |
|
• Density
|
7.62/km2 (19.7/sq mi) (225th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2019 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$1.6 trillion |
|
• Per capita
|
$58,000 (13th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2021 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$1.8 trillion (10th) |
|
• Per capita
|
$66,900 (15th) |
| Currency |
|
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code |
|
The Nordic countries (also called the Nordics or Norden) are a special group of countries and areas in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic. They include five main countries: Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden. They also include the self-governing areas of the Faroe Islands, Greenland, and Åland.
These countries share a lot, like their way of life, history, religion, and how their societies and economies work. They have a long history of working together and even forming political unions. Today, they don't form one single country, but they cooperate closely. This cooperation is based on the Helsinki Treaty from 1962, which guides groups like the Nordic Council and the Nordic Council of Ministers.
The Nordic countries are often ranked very high in many important areas. This includes things like education, how strong their economies are, how much freedom people have, and how good life is there. Even though each country has its own way of doing things, they all share parts of the "Nordic model." This means they have a mix of market economy and strong worker groups. They also have a good welfare system, which helps everyone and is paid for by taxes. This system helps people be independent and move up in society. They also have fair income distribution and respect for private ownership.
Most people in the Nordic region (over three-quarters) are North Germanic peoples. In Finland, most people are Baltic Finnic peoples. Other groups include the Greenlandic Inuit and the Sami people. Long ago, the main religion was Norse paganism. Later, people became Catholic, and after the Protestant Reformation, most became Lutheran. Lutheranism is still the main religion in several Nordic countries.
Even though people in the Nordic countries speak different languages, their shared language history helps create a Nordic identity. Most Nordic languages come from three main groups: North Germanic languages, Finno-Ugric languages, and Eskimo–Aleut languages. Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish are quite similar, so people speaking them can often understand each other. These three languages are used in the main political groups of the region. Learning Swedish is required in Finnish schools, and Danish is taught in Faroese and Icelandic schools.
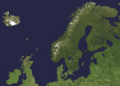
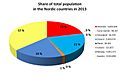
The total area of the Nordic countries is huge, about 3.4 million square kilometers. About half of this area is covered by ice caps and glaciers, mostly in Greenland. In 2021, over 27 million people lived in the region. Sometimes, people use "Scandinavia" to mean the same as the Nordic countries. But "Scandinavia" usually refers only to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden.
Contents
Countries and Regions of the Nordics
Main Countries
Here are the five main countries that make up the Nordic region. You can see their flags, coats of arms, and some interesting facts about each one.
| Sovereign state | Kingdom of Denmark | Republic of Finland | Iceland | Kingdom of Norway | Kingdom of Sweden |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flag |  |
 |
 |
||
| Coat of arms |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Official local name | Kongeriget Danmark | Suomen tasavalta Republiken Finland |
Ísland | Kongeriket Norge Kongeriket Noreg Norgga gonagasriika |
Konungariket Sverige |
| Local common name | Danmark | Suomi Finland |
Ísland | Norge Noreg Norga |
Sverige |
| English common name | Denmark | Finland | Iceland | Norway | Sweden |
| Population (2021 estimate) | 5,894,687 | 5,587,442 | 354,234 | 5,509,591 | 10,261,767 |
| Area | 43,094 km2 | 338,145 km2 | 103,000 km2 | 385,207 km2 | 450,295 km2 |
| Population density (2015 estimate) | 129.5/km2 | 16.2/km2 | 3.2/km2 | 13.5/km2 | 22.9/km2 |
| Capital city | Copenhagen | Helsinki | Reykjavík | Oslo | Stockholm |
| Largest urban areas |
Copenhagen – 2,135,634 Aarhus – 330,639 Odense – 213,558 Aalborg – 205,809 Esbjerg – 116,032 |
Helsinki – 1,576,438 Tampere – 370,084 Turku – 315,751 Oulu – 200,400 Jyväskylä – 140,812 |
Reykjavík – 247,590 Akureyri – 18,103 Reykjanesbær – 14,000 Akranes – 6,699 Selfoss – 6,512 |
Oslo – 1,546,706 Bergen – 265,470 Stavanger/Sandnes – 229,911 Trondheim – 191,771 Fredrikstad/Sarpsborg – 117,510 |
Stockholm – 2,415,139 Gothenburg – 1,015,974 Malmö – 707,120 Helsingborg – 272,873 Uppsala – 253,704 |
| Form of government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy | Unitary parliamentary republic | Unitary parliamentary republic | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| Current head of state and government | Frederik X (King) Mette Frederiksen (Prime Minister) |
Alexander Stubb (President) Petteri Orpo (Prime Minister) |
Halla Tómasdóttir (President) Bjarni Benediktsson (Prime Minister) |
Harald V (King) Jonas Gahr Støre (Prime Minister) |
Carl XVI Gustaf (King) Ulf Kristersson (Prime Minister) |
| Official languages | Danish | Finnish and Swedish | Icelandic | Norwegian and Sami | Swedish |
| Main religions | 74.8% Lutheran 5.3% Islam 19.9% other, unspecified or no religion |
67.8% Lutheran 1.1% Orthodox 1.7% other religion 29.4% unspecified or no religion |
63.5% Lutheran 11.7% other Christian 3.3% other religion 21.5% unspecified or no religion |
68.7% Lutheran 7.0% other Christian 3.4% Islam 0.8% other religion 20.2% no religion |
60.2% Lutheran 8.5% other 31.3% no religion |
| Currency | Danish krone | Euro | Icelandic króna | Norwegian krone | Swedish krona |
| Human Development Index rank (2021 data, 2022 report) | 6 | 11 | 3 | 2 | 7 |
| Corruption Perceptions Index rank (2022) | 1 | 2 | 14 | 4 | 5 |
| Press Freedom Index rank (2022) | 2 | 5 | 15 | 1 | 3 |
| The figures in this table do not include the Faroe Islands, Greenland, Åland, Jan Mayen, Svalbard, Bouvet Island, Peter I Island, and Queen Maud Land. | |||||
Self-Governing Areas
Besides the five main countries, the Nordic region also includes several self-governing areas. These areas have their own governments but are still connected to one of the main Nordic countries.
| Territory / Area | Faroe Islands | Greenland | Åland | Svalbard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flag |  |
 |
||
| Coat of arms |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Official local name | Føroyar Færøerne |
Kalaallit Nunaat Grønland |
Landskapet Åland | Svalbard |
| Population (2016 estimate) |
49,188 | 56,483 | 29,013 | 2,667 |
| Area | 1,393 km2 | 2,166,086 km2 | 1,580 km2 | 61,022 km2 |
| Population density | 35.5/km2 | 0.028/km2 | 18.36/km2 | 0.044/km2 |
| Capital city | Tórshavn | Nuuk | Mariehamn | Longyearbyen |
| Largest urban areas |
Tórshavn – 12,648 Klaksvík – 4,681 Hoyvík – 2,951 Argir – 1,907 Fuglafjørður – 1,542 |
Nuuk – 16,464 Sisimiut – 5,598 Ilulissat – 4,541 Qaqortoq – 3,229 Aasiaat – 3,142 |
Mariehamn – 11,521 Jomala – 4,646 Finström – 2,529 Lemland – 1,991 Saltvik – 1,827 |
Longyearbyen – 2,144 Barentsburg – 471 Ny-Ålesund – ~30–130 Isbjørnhamna – ~10–12 |
| Sovereign state | ||||
| Status | Autonomous territory | Autonomous region | Unincorporated area | |
| Form of government | Devolved parliamentary within a constitutional monarchy |
Devolved parliamentary within a constitutional monarchy |
Unitary parliamentary republic | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| Current head of state and government | Frederik X (King) Aksel V. Johannesen (Premier) |
Frederik X (King) Múte Bourup Egede (Premier) |
Alexander Stubb (President) Katrin Sjögren (Lantråd) |
Harald V (King) Jonas Gahr Støre (Prime Minister) |
| Main languages | Faroese, Danish | Greenlandic, Danish | Swedish | Norwegian |
| Main religions | 89.3% Lutheran 6% unspecified 3.8% none |
96.08% Lutheran 0.79% Inuit spiritual beliefs 2.48% atheist+agnostic |
72.0% Lutheran 1.3% Other religion 26.7% No religion |
|
| Currency | Faroese króna Danish krone |
Danish krone | Euro | Norwegian krone |
Nordic History Timeline
This timeline shows how the different Nordic political areas have changed over the centuries.
| Century | Danes | Greenlanders | Faroese | Icelanders | Norwegians | Swedes | Finns |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8th | Prehistoric Danish (East-Norse) |
Prehistoric Greenlandic (Paleo-Eskimo and West-Norse) |
Prehistoric Faroese (West-Norse) |
Prehistoric Icelandic (West-Norse) |
Prehistoric Norwegian (West-Norse) |
Prehistoric Swedish (East-Norse) |
Prehistoric Finnish (Finnic) |
| 9th | Kingdom of Norway | ||||||
| 10th | Kingdom of Denmark | Icelandic Commonwealth | |||||
| 11th | |||||||
| 12th | Kingdoms of Sweden | ||||||
| 13th | |||||||
| 14th | |||||||
| 15th | Kalmar Union | ||||||
| 16th | Denmark-Norway | Sweden | |||||
| 17th | |||||||
| 18th | |||||||
| 19th | Denmark | United Kingdoms of Sweden and Norway | Grand Duchy of Finland | ||||
| 20th | Denmark | Greenland | Faroe Islands | Iceland | Norway | Sweden | Finland |
| 21st | |||||||
Italics indicates a dependent territory.
National Symbols
Many Nordic countries, including the Faroe Islands and Åland, have a similar flag design. They are all based on the Dannebrog, which is the Danish flag. These flags have a cross that is not in the very center, but closer to the side where the flag is attached to the pole. This is called the "Nordic cross" or "Scandinavian cross." Each flag has its own unique size and shape. Greenland and Sápmi (the Sami people's region) have flags without the Nordic cross. However, their flags both feature a circle that is also placed off-center, similar to the cross.
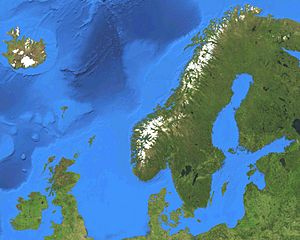
Geography of the Nordic Region
The Nordic countries and their self-governing regions have very different geographies. The total area is huge, covering about 3.5 million square kilometers. This large area means it spans five different time zones! To the east, the region shares a border with Russia. On a clear day, you can even see the Canadian coastline from Greenland in the west.
Even if you don't count Greenland and the Norwegian islands of Svalbard and Jan Mayen, the rest of the Nordic countries still cover about 1.3 million square kilometers. This is roughly the same size as France, Germany, and Italy put together. To the south, the Nordic countries are close to the Baltic states, Poland, Germany, and the United Kingdom. To the north, you'll find the cold Arctic Ocean.
Some amazing natural features in the Nordic countries include the stunning Norwegian fjords (long, narrow inlets of the sea). There's also the Archipelago Sea between Finland and Sweden, which has thousands of islands. Iceland is famous for its many volcanoes and hot springs. And, of course, Greenland is the largest island in the entire world!
The southernmost point of the Nordic countries is Gedser in Denmark. The northernmost point is Kaffeklubben Island in Greenland, which is actually the northernmost piece of land on Earth! The biggest cities and capitals, like Helsinki, Oslo, and Stockholm, are mostly in the southern parts of the region. The only exception is Reykjavík, the capital of Iceland, which is further north.
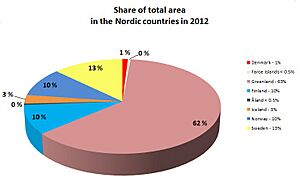
Population and Area Facts
Here's a quick look at the population, area, and how crowded each Nordic country and region is.
| Country | Inhabitants | Area | Pop. density |
|---|---|---|---|
| Denmark | 5,806,014 | 42,933 | 135 |
| Faroe Islands | 50,322 | 1,393 | 36 |
| Finland | 5,520,535 | 338,424 | 16 |
| Iceland | 355,620 | 102,775 | 3.5 |
| Norway | 5,323,933 | 385,203 | 14 |
| Sweden | 10,313,447 | 450,295 | 23 |
| Åland | 29,884 | 1,580 | 18 |
| Total | 27,301,531 | 1,322,603 | 21 |
| Source: | |||
Denmark has the most people living per square kilometer. Sweden, Norway, and Finland have fewer people spread out over larger areas. Iceland has the smallest population and the lowest population density. This is because large parts of Finland, Norway, Sweden, and most of Iceland are not populated at all. Denmark, however, has no unpopulated areas.
Land and Water Areas
This table shows the land area, the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), and the continental shelf area for each Nordic country. The EEZ is the area of sea where a country has special rights to explore and use marine resources.
| Rank | Country | Area | EEZ | Shelf | EEZ+TIA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sweden | 447,420 | 160,885 | 154,604 | 602,255 |
| 2 | Norway | 385,203 | 2,385,178 | 434,020 | 2,770,404 |
| 3 | Finland | 338,534 | 87,171 | 85,109 | 425,590 |
| 4 | Iceland | 103,440 | 751,345 | 108,015 | 854,345 |
| 5 | Denmark (including Greenland) | 2,210,579 | 2,551,238 | 495,657 | 4,761,811 |
| Total (excluding Greenland) | 1,318,158 | 3,751,563 | - | 5,064,065 | |
| Total | 3,484,244 | 5,935,817 | 1,277,405 | 9,414,405 | |
Denmark's Waters
The Kingdom of Denmark includes the self-governing areas of the Faroe Islands and Greenland. This table shows their water and land areas.
| Region | EEZ & TW Area (km2) |
Land area | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Denmark | 105 989 | 42 394 | 149 083 |
| Faroe Islands | 260 995 | 1 399 | 262 394 |
| Greenland | 2 184 254 | 2 166 086 | 4 350 340 |
| Total | 2 551 238 | 2 210 579 | 4 761 817 |
Images for kids
-
Effigy of Queen Margaret, founder and ruler of the Kalmar Union
-
Nordic prime ministers at the Nordic Council meeting in 2014 in Stockholm
-
The Öresund Bridge between Malmö in Sweden and Copenhagen in Denmark
-
Copenhagen Central Station with S-Trains
-
Statfjord oil platform in Norway is owned and operated by Equinor, which is the largest company in the Nordic countries
-
During the recent years, Denmark has invested heavily in windfarms
-
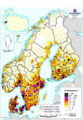
Population density map of the Nordic countries (1996)
-
Sami man at Honningsvåg, Norway, wearing the traditional Gákti
-
ABBA is one of the best-selling music artists of all time
-
Søren Kierkegaard is considered to be the first existentialist philosopher
-
Swedish author Astrid Lindgren together with Finnish author Tove Jansson in Stockholm in 1958
-
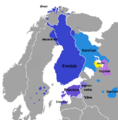
The Finnic languages in Northern Europe
-
The Sami languages in Northern Europe
-
Life expectancy at birth in the Nordic countries in 2012
See also
 In Spanish: Países nórdicos para niños
In Spanish: Países nórdicos para niños
 | Roy Wilkins |
 | John Lewis |
 | Linda Carol Brown |