Sweden facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Kingdom of Sweden
Konungariket Sverige (Swedish)
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
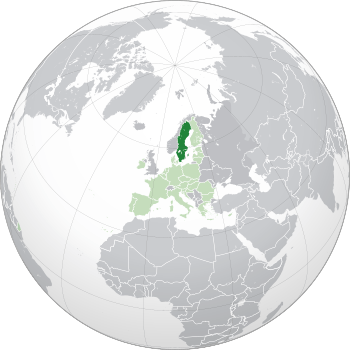
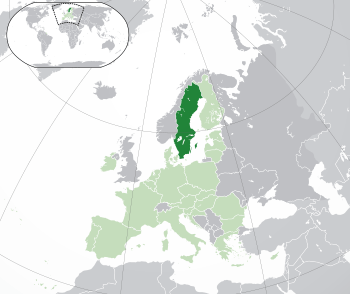
Location of Sweden (dark green)
– on the European continent (green & dark grey) |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Stockholm 59°21′N 18°4′E / 59.350°N 18.067°E |
| Official languages | Swedish |
| National minority languages | |
| Religion
(2020)
|
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
• Monarch
|
Carl XVI Gustaf |
|
• Riksdag Speaker
|
Andreas Norlén |
| Ulf Kristersson | |
| Legislature | Riksdag |
| History | |
|
• A unified Swedish kingdom established
|
By the late 10th century |
|
• Part of the Kalmar Union
|
17 June 1397 – 6 June 1523 |
| 1611 – 1721 | |
|
• Joined the European Union
|
1 January 1995 |
|
• Joined NATO
|
7 March 2024 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
450,295 km2 (173,860 sq mi) (55th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
8.97 (2022) |
| Population | |
|
• 31 May 2023 estimate
|
|
|
• Density
|
25/km2 (64.7/sq mi) (198th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2022) | ▲ 27.6 low |
| HDI (2022) | very high · 5th |
| Currency | Swedish krona (SEK) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Driving side | right |
| ISO 3166 code | SE |
| Internet TLD | .se |
|
Website
sweden.se |
|
Sweden (Swedish: Sverige) is a Nordic country located in Scandinavia, a region in northern Europe. It shares borders with Finland and Norway. Sweden is also connected to Denmark in the south by a bridge. It is a highly developed country, known for its strong social support system. People who live in Sweden are called Swedes.
Sweden has a population of about 10 million people. Its capital and largest city is Stockholm, home to almost one million people. Other major cities include Gothenburg and Malmö. These cities are mostly in the southern part of the country, where the weather is milder.
Swedes enjoy traditional foods like filmjölk, a fermented milk product. Glögg, a spiced mulled wine, is popular around Christmas. It often contains red wine, sugar, orange peel, and various spices. A common meal is yellow pea soup with pork or pork sausages, served with mustard.
Sweden is a constitutional monarchy, meaning it has a king, Carl XVI Gustaf, but he does not hold political power. It is also a parliamentary state. This means the government is chosen by the parliament, which is elected by the people. The country is a democracy, led by an elected Prime Minister. Ulf Kristersson became Prime Minister in October 2022.
The official language of Sweden is Swedish (called svenska in Swedish). Sweden also recognizes five official minority languages: Finnish, Yiddish, Sami, Meänkieli, and Romani.
Sweden joined the European Union (EU) on 1 January 1995. Unlike many EU countries, Sweden does not use the euro. The people voted against it, so the national currency remains the Swedish krona (Swedish crown).
Contents
Sweden's Past: A Thousand Years of History
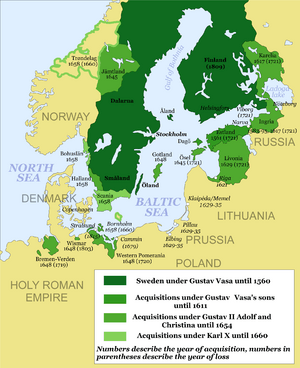
Sweden has a long history, stretching back over a thousand years. During the Middle Ages, Sweden, Denmark, and Norway sometimes shared the same king. In the early 16th century, Sweden gained its own king, Gustav Vasa.
The Swedish Empire and Later Years
In the 17th century, Sweden became a very powerful country. It took control of areas like Estonia, Latvia, Finland, and parts of Norway, Germany, and Russia. However, in the 18th century, Sweden's power faded, and it lost these territories.
In the early 19th century, a new king, Jean Baptiste Bernadotte, was chosen by the Swedish parliament. He helped Norway form a personal union with Sweden. This was Sweden's last war. Sweden has been peaceful for over 200 years.
In 1905, the union with Norway ended. Sweden remained neutral in many major conflicts, including World War I and World War II. Being neutral meant it did not choose sides. During World War II, Sweden traded with both the British and the Germans to protect its neutrality.
Exploring Sweden's Geography
Sweden is located in Northern Europe, west of the Baltic Sea and Gulf of Bothnia. It forms the eastern part of the Scandinavian Peninsula. To the west, the Scandinavian Mountains separate Sweden from Norway. Finland is to Sweden's north-east.
Sweden also has sea borders with Denmark, Germany, Poland, Russia, Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia. It is connected to Denmark by the Öresund Bridge. Sweden's border with Norway is 1,619 km long, making it the longest uninterrupted border in Europe.
Size and Landscape Features

Sweden covers about 449,964 square kilometers. This makes it the 55th largest country in the world. It is also the 4th largest country entirely within Europe and the largest in Northern Europe.
The lowest point in Sweden is near Kristianstad, about 2.41 meters below sea level. The highest point is Kebnekaise mountain, which is 2,111 meters above sea level.
Sweden has 25 traditional provinces called landskap. These provinces are important for people's identity, even though they have no political role. They are grouped into three main parts: Norrland in the north, Svealand in the center, and Götaland in the south. Norrland is sparsely populated and covers almost 60% of the country.
The Vindelfjällens Nature Reserve in Sweden is one of Europe's largest protected areas. It covers about 5,628 square kilometers.
Waterways and Islands
About 15% of Sweden lies north of the Arctic Circle. Southern Sweden is mostly farmland, with more forests as you go north. Forests cover about 65% of Sweden's land.
The most populated areas are in southern Sweden, especially around the Øresund Region, along the western coast, and near Stockholm and Lake Mälaren. Sweden's largest islands are Gotland and Öland. Its largest lakes are Vänern and Vättern. Vänern is the third largest lake in Europe.
In the 19th century, the Göta Canal was built. This canal connects the Baltic Sea to Gothenburg using a network of lakes and rivers. It made travel and trade much easier.
Sweden's Climate and Weather
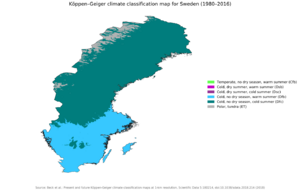
Most of Sweden has a temperate climate with four clear seasons. Winters in the far south are usually mild, with only short periods of snow and cold. The country has three main climate types:
- The southernmost part has an oceanic climate.
- The central part has a humid continental climate.
- The northernmost part has a subarctic climate.
Sweden is warmer and drier than other places at similar northern latitudes. This is mainly due to the Gulf Stream and westerly winds. These factors make Sweden's winters milder than those in parts of Russia, Canada, and the northern United States.
The amount of daylight changes a lot because of Sweden's high latitude. North of the Arctic Circle, the sun never sets for part of the summer. It also never rises for part of the winter. In Stockholm, daylight lasts over 18 hours in late June but only about 6 hours in late December.
July temperatures are quite similar across the country, usually between 15°C and 17.5°C. However, January temperatures vary much more, from around freezing point in the south to below -15°C near the Finnish border.
The highest temperature ever recorded in Sweden was 38°C in Målilla in 1947. The coldest was -52.6°C in Vuoggatjålme in 1966.
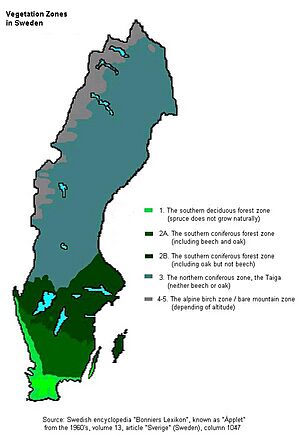
Vegetation Zones and Plant Life
Sweden's long north-to-south distance means there are big climate differences, especially in winter. This affects what plants can grow naturally in different areas. Sweden is divided into five main vegetation zones:
- The southern deciduous forest zone
- The southern coniferous forest zone
- The northern coniferous forest zone, also known as the Taiga
- The alpine-birch zone
- The bare mountain zone
Southern Deciduous Forest Zone
This zone is in the very south of Sweden. It is part of a larger area that includes Denmark and much of Central Europe. A lot of this land is now used for farming, but many forests still exist. This region has a wide variety of trees and shrubs. The beech is the most common tree. Other important trees include oak, hornbeam, linden, maple, and ash.
Southern Coniferous Forest Zone
This zone is located between the southern deciduous zone and the Taiga further north. Here, you find coniferous trees like spruce and pine mixed with various deciduous trees. Birch trees grow almost everywhere.
Northern Coniferous Forest Zone (Taiga)
This zone starts north of where oak trees naturally grow. The birch is the only significant deciduous tree here. Pine and spruce are the main trees, but the forests become less dense as you go further north. In the far north, the trees are very spread out.
Alpine-Birch and Bare Mountain Zones
In the Scandinavian Mountains, the alpine-birch zone is where only a smaller type of birch tree can grow. This depends on both how far north it is and how high up it is. Beyond this zone, no trees grow at all. This area is called the bare mountain zone.
How Sweden is Governed
Sweden is a constitutional monarchy. This means it has a king, Carl XVI Gustaf, who is the head of state. However, the king's role is mostly ceremonial. He performs official duties but has no real political power. For example, the King opens the yearly parliament session and meets regularly with the Prime Minister.
Parliament and Government

The power to make laws is held by the unicameral Riksdag, which is Sweden's parliament. It has 349 members. General elections are held every four years. Both the government and members of parliament can suggest new laws. Members are chosen based on proportional representation for a four-year term.
The Government is a team of ministers led by the Prime Minister. The Prime Minister is chosen by the Speaker of the Riksdag and then elected by a vote in the Riksdag. The Prime Minister appoints and removes other ministers. The government is the highest executive power and is responsible to the Riksdag.
Justice System
The justice system is independent. This means it operates separately from the parliament and the government. Courts are not bound by past decisions, but they are often influenced by them.
Divisions of Sweden
Sweden is divided into twenty-one counties. These counties help organize the country's administration. Some of these counties include Stockholm, Uppsala, Skåne, and Västra Götaland.
Sweden's Economy and Trade

Sweden is one of the richest countries in the world. Its citizens enjoy a high standard of living. Sweden has a mixed economy that relies heavily on exports. Its main natural resources are timber, hydropower, and iron ore.
The engineering sector is very important, making up 50% of Sweden's production and exports. Other key industries include telecommunications, the automotive industry, and pharmaceuticals. Sweden is also a major arms exporter. Farming makes up a small part of the economy. Sweden has high rates of telephone and Internet access.
Many workers in Sweden are part of trade unions and covered by collective agreements. This means that unions and employers work together to set rules for workplaces.
In 2010, Sweden had one of the lowest levels of income inequality among developed countries. This means wealth was shared more evenly among its people.
Key Industries and Companies
The Swedish economy is known for its large, knowledge-based, and export-focused manufacturing sector. It also has a growing business service sector and a large public service sector. Big companies, both in manufacturing and services, are very important to Sweden's economy.
Some of the largest Swedish companies include Volvo, Ericsson, Vattenfall, Skanska, Electrolux, TeliaSonera, Sandvik, Scania, Hennes & Mauritz, and IKEA. Most of Sweden's industries are owned by private companies.
Sweden uses its own currency, the Swedish krona (SEK). Its biggest trading partners are Germany, the United States, Norway, the United Kingdom, Denmark, and Finland.
Religion in Sweden
Sweden has been a Christian country for a thousand years. It is traditionally Protestant. However, Sweden is now one of the least religious countries in the world. Many people in Sweden are agnostic or atheists, meaning they do not believe in a god.
About 6.4 million people, or 67% of the population, are members of the Church of Sweden. But only about 2% of these members attend church regularly.
Music from Sweden

Sweden has produced many famous popular music artists. Bands like ABBA, Roxette, and Ace of Base have had many hit songs over the years. Other well-known Swedish musicians include Avicii and Tove Lo.
Sports in Sweden

Sweden has many talented athletes. In soccer, Zlatan Ibrahimović is a famous player. Sweden has won two bronze medals and one silver medal in the World Cup in football (soccer). The top soccer league in Sweden is called Allsvenskan.
Sweden has also done very well in ice hockey. The men's top ice hockey league is the SHL. Famous Swedish athletes include table tennis players Stellan Bengtsson and Jan-Ove Waldner. Alpine skiers like Ingemar Stenmark, Pernilla Wiberg, and Anja Pärson are also well-known. Biathlete Magdalena Forsberg and tennis players Björn Borg, Mats Wilander, and Stefan Edberg are also Swedish sports legends.
Sweden has achieved great success in cross-country skiing, winning many medals at the Olympic Games.
Swedish Cuisine and Food Traditions

Traditional Swedish food, like that in other Scandinavian countries, was simple. Fish (especially herring), meat, potatoes, and dairy products were very important. Spices were not used much.
Popular Swedish dishes include meatballs, usually served with gravy, boiled potatoes, and lingonberry jam. Pancakes are also common. The smörgåsbord is a famous Swedish buffet with many different dishes. Traditional flat and dry crisp bread is still popular today.
Some regional foods include surströmming (fermented fish) in northern Sweden and eel in Scania in southern Sweden. Many traditional Swedish dishes, some hundreds of years old, are still eaten today.
In August, Swedes celebrate with a traditional kräftskiva or crayfish party. They eat large amounts of crayfish boiled with dill.
Images for kids
-
Swedish knäckebröd (crisp bread).
-
Viking expeditions (blue): Swedish Vikings traveled into Russia.
-
The Battle of Poltava in 1709.
-
Swedish emigrants boarding a ship in Gothenburg in 1905.
-
Prime Minister Tage Erlander (left) served from 1946 to 1969.
-
Sweden joined the European Union in 1995 and signed the Lisbon Treaty in 2007.
-
Fredrik Reinfeldt's center-right government ruled Sweden from 2006 until 2014.
-
Swedish Prime Minister Stefan Löfven participated in Stockholm Pride parade, 2 August 2014.
-
Bonde Palace in Stockholm, seat of the Supreme Court of Sweden.
-
The Saab JAS 39 Gripen is an advanced Swedish multi-role fighter aircraft.
-
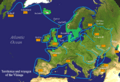
Gross Regional Product (GRP) per capita in thousands of kronor (2014).
-
Ringhals Nuclear Power Plant, south of Gothenburg.
-
The Öresund Bridge between Malmö and Copenhagen in Denmark.
-
Alfred Nobel, inventor of dynamite and founder of the Nobel Prize.
-
Swedish–ESO Submillimetre Telescope.
-
Uppsala University (established 1477).
-
Headquarters of Sveriges Television in Stockholm.
-
The writer and playwright August Strindberg.
-
Walpurgis Night bonfire in Sweden.
See also
 In Spanish: Suecia para niños
In Spanish: Suecia para niños
 | Aurelia Browder |
 | Nannie Helen Burroughs |
 | Michelle Alexander |