List of World Heritage in Danger facts for kids

The List of World Heritage in Danger is a special list made by UNESCO. UNESCO stands for the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. This list includes World Heritage Sites that are in danger. These are places that need a lot of help to be saved. The list helps people around the world know about the threats. It also encourages countries to take action.
Contents
Why Sites Get on the Danger List
Sites can be added to the danger list for different reasons. These can be threats that are happening now or dangers that might happen soon.
Dangers for Natural Sites
For natural places like national parks or forests, dangers can include:
- A big drop in the number of rare animals or plants.
- Damage to beautiful landscapes or important scientific areas.
- This damage can be caused by human activities.
- Examples are cutting down trees, pollution, building new towns, mining, farming, or big construction projects.
Dangers for Cultural Sites
For cultural places like old buildings or historical towns, dangers can include:
- Serious damage to materials, structures, or decorations.
- Losing the original look or historical meaning of the place.
Potential Dangers for All Sites
Some dangers might not be happening right now but could cause problems in the future. These include:
- New building projects.
- Armed conflicts or wars.
- Poor management of the site.
- Changes in laws that protect the sites.
- For cultural sites, slow changes from geology, climate, or the environment can also be a risk.
How Sites Get on and Off the List
Before a place is put on the danger list, experts check its condition. They also work with the country to create a plan to fix the problems. The World Heritage Committee makes the final decision. Sometimes, money from the World Heritage Fund is given to help these sites.
Reviewing the Sites
The committee checks on the sites every year. They might ask for more actions to be taken. If the dangers are gone, the site can be removed from the danger list. In some rare cases, a site might even be removed from the main World Heritage List entirely. For example, the Dresden Elbe Valley and the Liverpool Maritime Mercantile City were removed from the main list after being on the danger list.
Success Stories and Challenges
Being on the danger list can sometimes lead to good things. For example, the Galápagos Islands and Yellowstone National Park were once on the danger list. But they were later removed because of successful efforts to protect them.
However, some countries have criticized the danger list. They sometimes feel that UNESCO puts sites on the list without their full agreement. Some see it as a "black list" rather than a helpful tool. They believe it can be used for political reasons. Even so, the list often helps bring attention to sites that need urgent help.
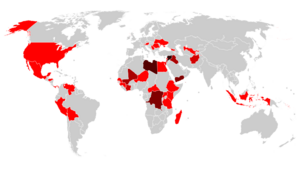
Current Sites in Danger
As of April 2024, there are 56 places on the List of World Heritage in Danger. This includes 16 natural sites and 40 cultural sites.
- Most of the sites (23) are in Arab countries.
- 14 are in Africa.
- 6 are in Latin America and the Caribbean.
- 6 are in Asia and the Pacific.
- 7 are in Europe and North America.
- Most of the natural sites in danger (11) are in Africa.
Many sites are facing threats from armed conflicts. For example, several sites in Syria, like the Ancient City of Aleppo, are in danger because of the Syrian Civil War. In the Democratic Republic of the Congo, national parks are threatened by military conflict and environmental damage.
Currently listed sites
- Table legend
- Name: The official name of the site.
- Location: Where the site is located, including the country.
- Criteria: The special reasons why the site was chosen as a World Heritage Site.
- Area: How big the site is (in hectares and acres).
- Year (WHS): The year the site became a World Heritage Site.
- Endangered: The year the site was added to the danger list.
- Reason: Why the site was put on the danger list.
- Refs: References (links to more information).
* This site crosses borders between countries.
| Name | Image | Location | Criteria | Area ha (acre) |
Year (WHS) | Endangered | Reason | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abu Mena |  |
Abusir, 30°50′30″N 29°39′50″E / 30.84167°N 29.66389°E |
Cultural: (iv) |
182 (450) | 1979 | 2001– | The ground is collapsing because of too much water. | |
| Air and Ténéré Natural Reserves |  |
Arlit Department, 18°17′N 8°0′E / 18.283°N 8.000°E |
Natural: (vii), (ix), (x) |
7,736,000 (19,120,000) | 1991 | 1992– | Conflicts and unrest in the area. Also, fewer wild animals and damaged plant life. | |
| Ancient City of Aleppo |  |
Aleppo Governorate, 36°14′N 37°10′E / 36.233°N 37.167°E |
Cultural: (iii), (iv) |
350 (860) | 1986 | 2013– | Damaged by the Syrian Civil War. Bombings still threaten the site. | |
| Ancient City of Bosra |  |
Daraa Governorate, 32°31′5″N 36°28′54″E / 32.51806°N 36.48167°E |
Cultural: (i), (iii), (vi) |
— | 1980 | 2013– | Affected by the Syrian Civil War. | |
| Ancient City of Damascus |  |
Damascus Governorate, 33°30′41″N 36°18′23″E / 33.51139°N 36.30639°E |
Cultural: (i), (ii), (iii), (iv), (vi) |
86 (210) | 1979 | 2013– | Affected by the Syrian Civil War. Gunfire and shelling threaten its foundations. | |
| Ancient Villages of Northern Syria |  |
36°20′3″N 36°50′39″E / 36.33417°N 36.84417°E |
Cultural: (iii), (iv), (v) |
12,290 (30,400) | 2011 | 2013– | Affected by the Syrian Civil War. Reports of theft and destruction by armed groups. | |
| Archaeological Site of Cyrene |  |
Jebel Akhdar, 32°49′30″N 21°51′30″E / 32.82500°N 21.85833°E |
Cultural: (ii), (iii), (vi) |
— | 1982 | 2016– | Affected by the Libyan Civil War. Armed groups are present, causing damage. | |
| Archaeological Site of Leptis Magna |  |
Khoms, 32°38′18″N 14°17′35″E / 32.63833°N 14.29306°E |
Cultural: (i), (ii), (iii) |
— | 1982 | 2016– | Affected by the Libyan Civil War. Armed groups are present, causing damage. | |
| Archaeological Site of Sabratha |  |
Sabratha, 32°48′19″N 12°29′6″E / 32.80528°N 12.48500°E |
Cultural: (iii) |
— | 1982 | 2016– | Affected by the Libyan Civil War. Armed groups are present, causing damage. | |
| Ashur (Qal'at Sherqat) |  |
Salah ad Din, 35°27′24″N 43°15′45″E / 35.45667°N 43.26250°E |
Cultural: (iii), (iv) |
70 (170) | 2003 | 2003– | A planned water reservoir was stopped after the Iraq War. The site lacks proper protection. | |
| Chan Chan Archaeological Zone |  |
La Libertad, 8°6′40″S 79°4′30″W / 8.11111°S 79.07500°W |
Cultural: (i), (iii) |
600 (1,500) | 1986 | 1986– | Damaged by natural erosion. | |
| City of Potosí |  |
Potosí, 19°35′1″S 65°45′11″W / 19.58361°S 65.75306°W |
Cultural: (ii), (iv), (vi) |
11,810 (29,200) | 1987 | 2014– | Mining has made the mountain unstable, causing parts to collapse. Recommendations to protect the site have not been followed. | |
| Coro and its Port |  |
Falcón, 11°25′N 69°40′W / 11.417°N 69.667°W |
Cultural: (iv), (v) |
107 (260) | 1993 | 2005– | Heavy rain damaged many buildings. New construction nearby could also harm the site. | |
| Crac des Chevaliers and Qal’at Salah El-Din |  |
Homs and Latakia Governorates, 34°46′54″N 36°15′47″E / 34.78167°N 36.26306°E |
Cultural: (ii), (iv) |
9 (22) | 2006 | 2013– | Affected by the Syrian Civil War. Reports of damage and theft by armed groups. | |
| Cultural Landscape and Archaeological Remains of the Bamiyan Valley |
 |
Bamyan, 34°49′55″N 67°49′36″E / 34.83194°N 67.82667°E |
Cultural: (i), (ii), (iii), (iv), (vi) |
159 (390) | 2003 | 2003– | In poor condition due to neglect, military action, and explosions. This causes risks like collapsing structures and theft. | |
| East Rennell |  |
Rennell and Bellona Province, 11°40′59″S 160°10′59″E / 11.68306°S 160.18306°E |
Natural: (ix) |
37,000 (91,000) | 1998 | 2013– | Damaged by logging, which harms the local environment. | |
| Everglades National Park |  |
Florida, 25°19′N 80°56′W / 25.317°N 80.933°W |
Natural: (viii), (ix), (x) |
592,920 (1,465,100) | 1979 | 1993–2007, 2010– | Damaged by Hurricane Andrew and by pollution from farms and cities. This has harmed marine life. | |
| Fortifications on the Caribbean Side of Panama: Portobelo-San Lorenzo |  |
Colón Province, 9°33′14″N 79°39′21″W / 9.55389°N 79.65583°W |
Cultural: (i), (iv) |
— | 1980 | 2012– | Affected by weather, lack of care, and new city buildings. | |
| Garamba National Park |  |
Orientale, 4°0′N 29°15′E / 4.000°N 29.250°E |
Natural: (vii), (x) |
500,000 (1,200,000) | 1980 | 1984–1992, 1996– | The number of Northern White Rhinoceros has dropped. There is also illegal hunting and a lack of protection plans. | |
| Hatra |  |
Nineveh Governorate, 35°35′17″N 42°43′6″E / 35.58806°N 42.71833°E |
Cultural: (ii), (iii), (iv), (vi) |
324 (800) | 1985 | 2015– | Damaged by armed groups. | |
| Hebron |  |
Hebron Governorate, 31°31′27″N 35°6′32″E / 31.52417°N 35.10889°E |
Cultural: (ii), (iv), (vi) |
20.6 (51) | 2017 | 2017– | ||
| Historic Centre of Odesa |  |
Odesa, 46°29′11.22″N 30°44′29.81″E / 46.4864500°N 30.7416139°E |
Cultural: (ii), (iv) |
— | 2023 | 2023– | Threatened by the Russo-Ukrainian War. | |
| Kyiv: Saint-Sophia Cathedral and Related Monastic Buildings, Kyiv Pechersk Lavra |  |
Kyiv, |
Cultural: (i), (ii), (iii), (iv) |
— | 1990 | 2023– | Threatened by the Russo-Ukrainian War. | |
| L'viv – the Ensemble of the Historic Centre |  |
Lviv, |
Cultural: (ii), (v) |
— | 1998 | 2023– | Threatened by the Russo-Ukrainian War. | |
| Historic Centre of Shakhrisyabz |  |
Qashqadaryo Region, 39°3′0″N 66°50′0″E / 39.05000°N 66.83333°E |
Cultural: (iii), (iv) |
240 (590) | 2000 | 2016– | Old buildings are being destroyed, and new city development continues. | |
| Historic Centre of Vienna |  |
Vienna, 48°12′N 16°22′E / 48.200°N 16.367°E |
Cultural: (ii), (iv), (vi) |
371 (920) | 2001 | 2017– | New tall buildings are being planned, which could harm the site. | |
| Historic Town of Zabīd |
 |
Al Hudaydah, 14°12′N 43°19′E / 14.200°N 43.317°E |
Cultural: (ii), (iv), (vi) |
— | 1993 | 2000– | Old buildings are falling apart. The country asked for it to be listed. | |
| Islands and Protected Areas of the Gulf of California |
 |
Baja California, Baja California Sur, Sonora, Sinaloa and Nayarit, 27°38′N 112°33′W / 27.633°N 112.550°W |
Natural: (vii), (ix), (x) |
688,558 (1,701,460) | 2005 | 2019– | The vaquita, a type of porpoise, is almost extinct. | |
| Kahuzi-Biega National Park |
 |
South Kivu and Maniema, 2°30′S 28°45′E / 2.500°S 28.750°E |
Natural: (x) |
600,000 (1,500,000) | 1980 | 1997– | Trees are being cut down, animals are being hunted, and there is war and conflict. | |
| Lake Turkana National Parks |
 |
3°3′8″N 36°30′13″E / 3.05222°N 36.50361°E |
Natural: (viii), (x) |
161,485 (399,040) | 1997 | 2018– | A dam in Ethiopia is changing the lake's water flow and harming its environment. | |
| Landmarks of Ancient Kingdom of Saba |
 |
Marib, 15°25′36.76″N 45°20′6.82″E / 15.4268778°N 45.3352278°E |
Cultural: (iii), (iv) |
375.29 (927.4) | 2023 | 2023– | Threatened by the Yemeni Civil War. | |
| Manovo-Gounda St Floris National Park | Bamingui-Bangoran, 9°0′N 21°30′E / 9.000°N 21.500°E |
Natural: (ix), (x) |
1,740,000 (4,300,000) | 1988 | 1997– | Illegal grazing and hunting. The area is also unsafe. | ||
| Minaret and Archaeological Remains of Jam |  |
Ghōr, 34°23′48″N 64°30′58″E / 34.39667°N 64.51611°E |
Cultural: (ii), (iii), (iv) |
70 (170) | 2002 | 2002– | No proper laws to protect it, no management plan, and the site is in bad condition. | |
| Medieval Monuments in Kosovo |  |
42°39′40″N 20°15′56″E / 42.66111°N 20.26556°E |
Cultural: (ii), (iii), (iv) |
2.88 (7.1) | 2004 | 2006– | Affected by violence and lacks proper protection and management. The area is politically unstable. | |
| Mount Nimba Strict Nature Reserve |  |
Lola Prefecture, 7°36′N 8°23′W / 7.600°N 8.383°W |
Natural: (ix), (x) |
18,000 (44,000) | 1981 | 1992– | Iron mining is allowed in part of the site. Many refugees have also moved into the area. | |
| Nan Madol: Ceremonial Centre of Eastern Micronesia |  |
Temwen Island, 6°50′23″N 158°19′51″E / 6.83972°N 158.33083°E |
Cultural: (i), (iii), (iv), (vi) |
76.7 (190) | 2016 | 2016– | Waterways are filling with dirt, causing plants to grow too much and damaging old structures. | |
| Niokolo-Koba National Park |  |
Tambacounda Region and Kédougou Region, 13°0′N 12°40′W / 13.000°N 12.667°W |
Natural: (x) |
913,000 (2,260,000) | 1981 | 2007– | The park is degrading, there are fewer mammals, and management problems exist. A planned dam could also affect it. | |
| Okapi Wildlife Reserve |  |
Orientale, 2°0′N 28°30′E / 2.000°N 28.500°E |
Natural: (x) |
1,372,625 (3,391,830) | 1996 | 1997– | Park facilities have been looted, and elephants killed due to conflict in the area. | |
| Old City of Jerusalem and its Walls |  |
Jerusalem District, 31°46′36″N 35°14′03″E / 31.77667°N 35.23417°E |
Cultural: (ii), (iii), (vi) |
— | 1981 | 1982– | Uncontrolled city growth, general decay due to tourism, and lack of care. | |
| Old City of Sana'a |
 |
Sana'a Governorate, 15°21′20″N 44°12′29″E / 15.35556°N 44.20806°E |
Cultural: (iv), (v), (vi) |
— | 1986 | 2015– | Affected by the Yemeni Civil War. | |
| Old Town of Ghadamès |  |
Ghadames, 30°08′00″N 9°30′00″E / 30.13333°N 9.50000°E |
Cultural: (v) |
— | 1986 | 2016– | Affected by the Libyan Civil War. Armed groups are present, causing damage. | |
| Old Towns of Djenné |  |
Djenné, 13°54′23″N 4°33′18″W / 13.90639°N 4.55500°W |
Cultural: (iii), (iv) |
— | 1988 | 2016– | Unsafe conditions in the region, the town is decaying, and city growth and erosion are problems. | |
| Palestine: Land of Olives and Vines – Cultural Landscape of Southern Jerusalem, Battir |  |
Battir, 31°43′11″N 35°7′50″E / 31.71972°N 35.13056°E |
Cultural: (iv)(v) |
349 (860) | 2014 | 2014– | A barrier might separate farmers from their fields, which they have worked for centuries. | |
| Old Walled City of Shibam |
 |
Hadhramaut Governorate, 15°55′37″N 48°37′36″E / 15.92694°N 48.62667°E |
Cultural: (iii), (iv), (v) |
— | 1982 | 2015– | Threatened by armed conflict, which makes it harder to protect and manage the site. | |
| Rainforests of the Atsinanana |
 |
Eastern Madagascar, 14°28′S 49°42′E / 14.467°S 49.700°E |
Natural: (ix), (x) |
479,660 (1,185,300) | 2007 | 2010– | Illegal logging and hunting of endangered lemurs. | |
| Rachid Karami International Fair |
 |
Tripoli, 34°26′22″N 35°49′33″E / 34.4395°N 35.8259°E |
Cultural: (ii)(iv) |
72 (180) | 2023 | 2023– | Threatened by lack of money for upkeep, city development, and its very poor condition. | |
| Río Plátano Biosphere Reserve |  |
La Mosquitia, 15°44′40″N 84°40′30″W / 15.74444°N 84.67500°W |
Natural: (vii), (viii), (ix), (x) |
— | 1982 | 1996–2007, 2011– | Logging, fishing, and people building on the land. Also, illegal hunting and the government's reduced ability to manage the site. | |
| Rock-Art Sites of Tadrart Acacus |  |
Fezzan, 24°50′N 10°20′E / 24.833°N 10.333°E |
Cultural: (iii) |
— | 1985 | 2016– | Affected by the Libyan Civil War. Armed groups are present, causing damage. | |
| Samarra Archaeological City |  |
Salah ad Din, 34°12′N 43°52′E / 34.200°N 43.867°E |
Cultural: (ii), (iii), (iv) |
15,058 (37,210) | 2007 | 2007– | Unsafe conditions after the Iraq War and a lack of government control to protect the site. | |
| Selous Game Reserve |  |
Coast, Morogoro, Lindi, Mtwara and Ruvuma Regions,
|
Natural: (ix), (x) |
5,120,000 (12,700,000) | 1982 | 2014– | Mining for minerals and large construction projects. | |
| Site of Palmyra |  |
Homs Governorate, 34°33′15″N 38°16′0″E / 34.55417°N 38.26667°E |
Cultural: (i), (ii), (iv) |
0.36 (0.89) | 1980 | 2013– | Affected by the Syrian Civil War. It was captured by a terrorist group that destroyed parts of it. | |
| Timbuktu |  |
Timbuktu, Timbuktu Region, 16°46′24″N 2°59′58″W / 16.77333°N 2.99944°W |
Cultural: (ii), (iv), (v) |
— | 1988 | 2012– | Threatened by armed groups. Some monuments have been looted and destroyed. | |
| Tomb of Askia |  |
Gao, Gao Region, 16°17′23″N 0°02′40″W / 16.28972°N 0.04444°W |
Cultural: (ii), (iii), (iv) |
4.24 (10.5) | 2004 | 2012– | Damaged by armed groups. | |
| Tropical Rainforest Heritage of Sumatra |  |
Sumatra, 02°30′S 101°30′E / 2.500°S 101.500°E |
Natural: (vii), (ix), (x) |
2,595,124 (6,412,690) | 2004 | 2011– | Illegal hunting, illegal logging, farms expanding into the area, and plans to build roads through the site. | |
| Virunga National Park |  |
North Kivu and Orientale, 0°55′N 29°10′E / 0.917°N 29.167°E |
Natural: (vii), (viii), (x) |
800,000 (2,000,000) | 1979 | 1994– | Trees are being cut down and animals are being hunted because many refugees have moved into the area due to conflict. | |
| Roșia Montană Mining Landscape |
 |
Alba County, 46°18′22″N 23°7′50″E / 46.30611°N 23.13056°E |
Cultural: (ii), (iii), (iv) |
314.42 (776.9) | 2021 | 2021– | Plans to restart mining would damage a large part of this historic mining area. |
Previously Listed Sites
Some sites were once on the danger list but are now safe. This happened because of better management and conservation efforts. The Everglades National Park and the Río Plátano Biosphere Reserve were listed, removed, and then listed again. So, they are also in the "Currently listed sites" section above.
This site was completely removed from the World Heritage List. Only part of this site was removed from the World Heritage List.
| Name | Image | Location | Criteria | Area ha (acre) |
Year (WHS) | Endangered | Reason | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angkor |  |
Siem Reap Province, 13°26′N 103°50′E / 13.433°N 103.833°E |
Cultural: (i), (ii), (iii), (iv) |
|
1992 | 1992–2004 | It was listed to ensure proper protection and management after a civil war. | |
| Bagrati Cathedral and Gelati Monastery |  |
Imereti, 42°15′44″N 42°42′59″E / 42.26222°N 42.71639°E |
Cultural: (iv) |
7.87 (19.4) | 1994 | 2010–2017 | A large rebuilding project changed the site too much. Bagrati Cathedral was removed from the World Heritage List after its reconstruction, but Gelati Monastery remained. | |
| Bahla Fort |  |
Bahla, 22°58′N 57°18′E / 22.967°N 57.300°E |
Cultural: (iv) |
|
1987 | 1988–2004 | The fort's mud structures and the nearby oasis were falling apart. | |
| Bam and its Cultural Landscape |  |
Kerman, 29°07′01″N 58°22′07″E / 29.11694°N 58.36861°E |
Cultural: (ii), (iii), (iv), (v) |
— | 2004 | 2004–2013 | Listed after being damaged by a big earthquake in 2003. | |
| Belize Barrier Reef Reserve System |  |
Belize, Stann Creek and Toledo 17°19′N 87°32′W / 17.317°N 87.533°W |
Natural: (vii), (ix), (x) |
96,300 (238,000) | 1996 | 2009–2018 | Mangrove trees were being cut down, and there was too much development. | |
| Birthplace of Jesus: Church of the Nativity and the Pilgrimage Route, Bethlehem |  |
Bethlehem, 31°42′16″N 35°12′27″E / 31.70444°N 35.20750°E |
Cultural: (iv), (vi) |
2.98 (7.4) | 2012 | 2012–2019 | Damaged by water leaks. | |
| Butrint |  |
Sarandë District, 39°45′N 20°1′E / 39.750°N 20.017°E |
Cultural: (iii) |
3,980 (9,800) | 1992 | 1997–2005 | Damaged due to poor management and conservation. | |
| Cologne Cathedral |
 |
North Rhine-Westphalia, 50°56′29″N 6°57′29″E / 50.94139°N 6.95806°E |
Cultural: (i), (ii), (iv) |
|
1996 | 2004–2006 | Plans for a tall building nearby threatened the site. It was removed from the list after the building plan was stopped. | |
| Comoé National Park |  |
Zanzan, 9°10′N 3°40′W / 9.167°N 3.667°W |
Natural: (ix), (x) |
1,150,000 (2,800,000) | 1983 | 2003–2017 | Civil unrest, illegal hunting, and a lack of effective management. | |
| Djoudj National Bird Sanctuary |  |
Biffeche, 16°30′N 16°10′W / 16.500°N 16.167°W |
Natural: (vii), (x) |
16,000 (40,000) | 1981 | 1984–1988, 2000–2006 | A planned dam threatened the water supply. Later, invasive plants and water management issues caused problems. | |
| Dresden Elbe Valley |  |
Saxony, 51°3′N 13°49′E / 51.050°N 13.817°E |
Cultural: (ii), (iii), (iv), (v) |
1,930 (4,800) | 2004 | 2006–2009 | Plans to build a bridge in the area. It was removed from the World Heritage List in 2009 after construction started. | |
| Dubrovnik |  |
Dubrovnik-Neretva County, 42°38′25″N 18°06′30″E / 42.64028°N 18.10833°E |
Cultural: (i), (iii), (iv) |
97 (240) | 1979 | 1991–1998 | Affected by the Croatian War of Independence. | |
| Fort and Shalamar Gardens in Lahore |  |
Punjab, 31°35′25″N 74°18′35″E / 31.59028°N 74.30972°E |
Cultural: (i), (ii), (iii) |
— | 1981 | 2000–2012 | Historic water tanks were destroyed to widen a road, and the garden walls were decaying. Pakistan asked for it to be listed. | |
| Galápagos Islands |  |
Galápagos Province, 0°40′S 90°30′W / 0.667°S 90.500°W |
Natural: (vii), (viii), (ix), (x) |
14,066,514 (34,759,110) | 1978 | 2007–2010 | Many threats, including new species being introduced, not enough money for conservation, illegal immigrants, too much tourism, and overfishing. | |
| Group of Monuments at Hampi |
 |
Bellary district, 15°20′6″N 76°27′43″E / 15.33500°N 76.46194°E |
Cultural: (i), (iii), (iv) |
|
1986 | 1999–2006 | Parts of two bridges were built within the protected area, threatening the site's original look. | |
| Historical Monuments of Mtskheta |  |
Mtskheta-Mtianeti, 41°50′32″N 44°43′16″E / 41.84222°N 44.72111°E |
Cultural: (iii), (iv) |
— | 1994 | 2009–2016 | Stone work and paintings were decaying, and there was poor management and new city development. | |
| Humberstone and Santa Laura Saltpeter Works |  |
Tarapacá, 20°12′30″S 69°47′40″W / 20.20833°S 69.79444°W |
Cultural: (ii), (iii), (iv) |
— | 2005 | 2005–2019 | Structures were fragile due to 40 years of no maintenance. There was also damage, vandalism, and theft. | |
| Ichkeul National Park |  |
Bizerta, 37°10′N 9°40′E / 37.167°N 9.667°E |
Natural: (x) |
12,600 (31,000) | 1980 | 1996–2006 | Dams were built, reducing fresh water flow. This made the lake saltier and reduced bird populations. | |
| Iguaçu National Park |  |
Paraná State, 25°41′S 54°26′W / 25.683°S 54.433°W |
Natural: (vii), (x) |
170,086 (420,290) | 1986 | 1999–2001 | An illegally opened road, dams on the Iguazu River, and helicopter flights caused problems. | |
| Kathmandu Valley |  |
Kathmandu Valley, 27°42′14″N 85°18′31″E / 27.70389°N 85.30861°E |
Cultural: (iii), (iv), (vi) |
167 (410) | 1979 | 2003–2007 | Traditional parts of the monument zones were lost, affecting the site's original look. | |
| Liverpool – Maritime Mercantile City |
 |
Liverpool England, 53°24′24″N 2°50′40″W / 53.40667°N 2.84444°W |
Cultural: (ii), (iii), (iv) |
136 (340) | 2004 | 2012–2021 | Plans to redevelop historic docklands. It was removed from World Heritage status in 2021 because of these developments. | |
| Los Katíos National Park |  |
Antioquia and Chocó, 7°40′0″N 77°0′0″W / 7.66667°N 77.00000°W |
Natural: (ix), (x) |
72,000 (180,000) | 1994 | 2009–2015 | Trees were being cut down, and there was illegal fishing and hunting. It was removed after park management improved. | |
| Manas Wildlife Sanctuary |
 |
Assam, 26°30′N 91°51′E / 26.500°N 91.850°E |
Natural: (vii), (ix), (x) |
39,100 (97,000) | 1985 | 1992–2011 | Illegal hunting, damage to park buildings, and a drop in animal populations after militants invaded in 1992. | |
| Natural and Culturo-Historical Region of Kotor |  |
Bay of Kotor, Kotor and surrounding territory, 42°29′N 18°42′E / 42.483°N 18.700°E |
Cultural: (i), (ii), (iii), (iv) |
|
1979 | 1979–2003 | Damaged by an earthquake in 1979. | |
| Ngorongoro Conservation Area |  |
Arusha Region, 3°11′S 35°32′E / 3.183°S 35.533°E |
Natural: (iv), (vii), (viii), (ix), (x) |
|
1978 | 1984–1989 | Its conservation status was getting worse. | |
| Plitvice Lakes National Park |  |
Lika-Senj County, 44°53′N 15°37′E / 44.883°N 15.617°E |
Natural: (vii), (viii), (ix) |
19,200 (47,000) | 1979 | 1992–1997 | Threatened by the Croatian War of Independence. | |
| Rice Terraces of the Philippine Cordilleras |  |
Ifugao, 16°55′N 121°3′E / 16.917°N 121.050°E |
Cultural: (iii), (iv), (v) |
500,000 (1,200,000) | 1995 | 2001–2012 | No regular checks or a full management plan were in place. | |
| Royal Palaces of Abomey |  |
Zou Department, 7°11′26″N 1°59′36″E / 7.19056°N 1.99333°E |
Cultural: (iii), (iv) |
48 (120) | 1985 | 1985–2007 | The palaces were decaying due to weather and improper restoration, which changed their original look. | |
| Ruins of Kilwa Kisiwani and Ruins of Songo Mnara |
 |
Kilwa District, 8°57′28″S 39°31′22″E / 8.95778°S 39.52278°E |
Cultural: (iii) |
— | 1981 | 2004–2014 | The site continued to decay due to things like erosion and plants growing on it. | |
| Rwenzori Mountains National Park |  |
Bundibugyo, Kabarole and Kasese District, 0°13′N 29°55′E / 0.217°N 29.917°E |
Natural: (vii), (ix) |
99,600 (246,000) | 1994 | 1999–2004 | Safety issues and a lack of monitoring in a large part of the park. | |
| Salonga National Park |  |
Équateur and Bandundu Province, 2°S 21°E / 2°S 21°E |
Natural: (vii), (ix) |
3,600,000 (8,900,000) | 1984 | 1999–2021 | Illegal hunting and new housing construction. It was removed from the danger list because its condition improved. | |
| Sangay National Park |  |
Chimborazo, Morona-Santiago and Tungurahua Province, 1°50′S 78°20′W / 1.833°S 78.333°W |
Natural: (vii), (viii), (ix), (x) |
271,925 (671,940) | 1983 | 1992–2005 | Heavy illegal hunting, illegal animal grazing, people moving into the area, and a potential threat from a road construction project. | |
| Simien National Park |  |
Amhara Region, 13°11′N 38°4′E / 13.183°N 38.067°E |
Natural: (vii), (x) |
22,000 (54,000) | 1978 | 1996–2017 | The population of the Walia ibex was decreasing. | |
| Srebarna Nature Reserve |  |
Srebarna, Silistra Province, 44°06′50″N 27°04′40″E / 44.11389°N 27.07778°E |
Natural: (x) |
638 (1,580) | 1983 | 1992–2003 | Preventing seasonal floods and using land for farming caused a drop in water birds. | |
| Timbuktu |  |
Circle and Region of Tombouctou, 16°46′24″N 2°59′58″W / 16.77333°N 2.99944°W |
Cultural: (ii), (iv), (v) |
|
1988 | 1990–2005 | Threatened by sand covering the area. | |
| Tipasa |  |
Tipaza Province, 36°35′39″N 2°26′36″E / 36.59417°N 2.44333°E |
Cultural: (iii), (iv) |
52 (130) | 1982 | 2002–2006 | Not enough maintenance was harming the site and its surrounding area. | |
| Tombs of Buganda Kings at Kasubi |  |
Kampala District, 0°19′45″N 32°33′12″E / 0.32917°N 32.55333°E |
Cultural: (i), (iii), (iv), (vi) |
27 (67) | 2001 | 2010–2023 | The main building was destroyed by fire in 2010. It was removed from the danger list in 2023 after being rebuilt. | |
| Walled City of Baku with Shirvanshah's Palace and Maiden Tower |  |
Baku, 40°21′59″N 49°50′7″E / 40.36639°N 49.83528°E |
Cultural: (iv) |
|
2000 | 2003–2009 | Damaged by an earthquake in 2000. Also, new city development and not enough conservation efforts. | |
| Wieliczka Salt Mine |  |
Wieliczka, Wieliczka County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, 49°58′45″N 20°03′50″E / 49.97917°N 20.06389°E |
Cultural: (iv) |
969 (2,390) | 1978 | 1989–1998 | Problems with humidity (too much moisture). | |
| Yellowstone National Park |
 |
Wyoming, Montana, and Idaho, 44°30′N 110°50′W / 44.500°N 110.833°W |
Natural: (vii), (viii), (ix), (x) |
898,349 (2,219,870) | 1978 | 1995–2003 | Dangers to a type of trout, sewage leaks, and waste. Also, potential threats to water and past or planned mining activities. |