River facts for kids

A river is a natural flow of water that moves through a channel on the ground. The path where the river flows is called the river bed. The land on each side is called a river bank. Rivers usually start on high ground, like hills or mountains. They flow downhill to lower ground because of gravity. A river often begins as a small stream and gets wider and deeper as it travels.
Contents
How Rivers Change as They Flow
Where a River Starts
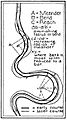
The very beginning of a river is called its source or headwater. The part of the river near its source is often called a 'young' river. A young river usually flows quickly downhill. Its path is often V-shaped, and it rushes over stones and around big rocks. You might see many small waterfalls and rapids in a young river. As it flows, it slowly wears away the ground, picking up small bits of rock and soil.
- A river's source can be a spring, which is water flowing out from under the ground. Springs are often found on hills or mountains.
- Sometimes, a river starts from a lake where many small streams gather water from rain or melting snow.
- Rivers can also begin in mountains where snow melts. The melting snow forms tiny streams that join together, growing bigger until they become a river.
- Some rivers flow from hills that get a lot of rain, even without snow.
- Certain rivers only flow after heavy rain near their source.
-
The Soča River begins in the mountains of Slovenia.
-
This river in Northern Australia only runs after heavy rain.
The Middle Part of a River
The middle part of a river is called a 'mature' river. A mature river carves out a U-shaped path. It can be very deep and still flow quite fast. It moves over smaller rocks and makes big turns around hills. It is much wider than a young river but not as wide as an 'old' river. People often build bridges to cross mature rivers. Many towns and cities are built along their banks. Farms with animals like dairy cows, horses, and sheep are also common along mature rivers, as the animals can drink from them.
-
The city of Florence was built beside the Arno River.
Where a River Ends
A river usually finishes its journey by flowing into an ocean, a lake, or a bigger river. The spot where a river meets a larger body of water is called its mouth.
As a river gets closer to its mouth, the land around it often becomes flat instead of hilly. Over this flat land, the river becomes wider and slower. A wide, slow river is called an 'old river'. Old rivers often flood the land after heavy rains at their source. They slowly build up high banks on either side, called levees. An old river often twists and turns (this is called a meander). Sometimes, after a flood, it leaves behind curved lakes called ox-bows or billabongs. Old rivers are very good for growing crops like corn, rice, fruit, and sugar.
The shape of a river's mouth depends on the sea conditions. If there is a strong tide where the river meets the sea, it forms an estuary. An estuary is a wide, funnel-shaped mouth where the river's fresh water slowly mixes with salty sea water, creating brackish (somewhat salty) water. Many kinds of fish, clams, and other sea creatures live in estuaries. Many of the world's largest cities and harbors are located at estuaries.
Sometimes, where a river flows into the sea, it moves very slowly through sandy or muddy land. It breaks into many smaller streams, forming a triangle shape, like the Greek letter delta. This area is called a river delta. Deltas are often not ideal for towns or farms, but they are excellent places for birds, other wildlife, and fishing. Many deltas are protected as wildlife reserves. Not all rivers have deltas. Famous deltas include those of the Nile River, the Amazon River, and the Mississippi River.
-
The grassy islands of the Okavango delta are home to elephants, lions and flamingos.
Rivers That Flow Underground
Some rivers flow completely underground through caves. Underground rivers form where there are many cracks in the rocks above. Rainwater seeps down and collects in small underground streams. Sometimes, this underground water trickles or gushes out of the ground, forming a small spring. In other places, these small streams join together in caves to form a river. These rivers can flow through large underground caverns. While many underground rivers flow gently, some can have rapids, especially after heavy rain. Many underground rivers eventually flow out of a cave mouth to become a regular river above ground.
-
Underground water flowing out of the Katafygi Vatsinidi Caves, Peloponnese, Greece
-
Exploring the Ouysse River which flows from the Vitarelles Cave, France
-
Rapids on the Kyzyl-Koba underground river in Crimea
-
The River Styx runs out of the Mammoth Cave in Kentucky, US
How People Use Rivers
The water in rivers is "fresh water" that comes from rain, snow, and underground streams. It can usually be drunk safely by people, unless it's too muddy or polluted. People and animals need fresh water, so they often live near rivers.
- Rivers provide water for drinking, bathing, and washing clothes.
- Rivers supply water for farm animals and for growing plants.
- Rivers offer useful products like fish for food, clay for bricks, and reeds for making roofs.
- Rivers can be used to transport people, crops, and goods by boat.
- Rivers can power machinery, such as water mills.
- Rivers provide water for factories that make things like cloth and steel.
- Sometimes, dams are built across rivers to store water for drinking or to make electricity.
- Rivers are great for leisure and sports like swimming, boating, fishing, or just walking along the banks.
- Rivers often have beautiful scenery, inspiring artists, writers, and poets.
- Some rivers are changed into canals for easier transport.
Water for Daily Life
Water for Work and Factories
-
Cargo containers waiting for transport from North River Port, Moscow.
Water for Fun
Rivers in Art and Stories
Rivers have inspired many famous works:
- Mark Twain wrote The Adventures of Tom Sawyer, a novel set near the Mississippi River.
- Kenneth Grahame wrote The Wind in the Willows, a novel featuring river animals.
Rivers in Photography
-
Narewka River runs through a nature reserve in Poland.
-
A forest reflected in a river in Sweden
-
Evening on the Brahmaputra River, India
-
Sunset in Coquitlam, Canada
-
Hong Kong river reflections
-
Taieri River, Otago
Famous Rivers Around the World
Here are some of the world's most important rivers:
- The Amazon River in South America is a very wide tropical river. It flows through the Amazon Jungle and into the Atlantic Ocean through a large delta. Many types of fish live in it. It is the largest river in the world by the amount of water it carries.
- The Nile River in Africa. For thousands of years, this river has provided water for people in Egypt to grow food. Cairo, the biggest city in Egypt and Africa, is built near the Nile's delta on the Mediterranean Sea. It is often called the longest river in the world.
- The Mississippi River in the United States. Many crops are grown along its banks. It was also very important for transport. The Mississippi flows through ten different states.
- The Yangtze River in China is the third longest river in the world and the longest in Asia.
- The Rhine River
- The Tigris and Euphrates rivers
- The Ganges River
- The Mekong River
- The Danube River
- The Volga River
- The St. Lawrence River
- The Murray River in Australia, which is 1609 miles long.
- The Congo River
- The Niger River
- The River Thames
- The Tiber River
River Words to Know
- A meander is a bend or curve in a river's path.
- The mouth of a river is where it flows into the sea, ocean, or a lake.
- An oxbow lake is a curved lake found beside a river, shaped like a meander that has been cut off.
- A braided river is a river that usually flows slowly and splits into many smaller channels that join back together repeatedly.
Other Kinds of Rivers
- A submarine river is a stream of water that flows under the surface of an ocean. One such river, called the Cromwell current, was discovered in 1952. ("Submarine" comes from Latin and means "under sea.")
- A subterranean river is a river that flows under the surface of the earth. One was found in August 1958 under the Nile River. ("Subterranean" also comes from Latin and means "under ground.")
Longest Rivers in the World
| Rank | River | Length (km) | Length (miles) | Outflow | Main Countries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nile | 6,650 | 4,130 | Mediterranean | Egypt, Sudan, Ethiopia, Uganda, and others |
| 2. | Amazon | 6,400 | 3,976 | Atlantic Ocean | Brazil, Peru, Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Venezuela, Guyana |
| 3. | Yangtze | 6,300 | 3,917 | East China Sea | China |
| 4. | Mississippi–Missouri | 6,275 | 3,902 | Gulf of Mexico | United States, Canada |
| 5. | Yenisey–Angara | 5,539 | 3,445 | Kara Sea | Russia, Mongolia |
Related topics
Images for kids
-
Melting toe of Athabasca Glacier, Jasper National Park, Alberta, Canada
-
The Colorado River at Horseshoe Bend, Arizona
-
Nile River delta, as seen from Earth orbit. The Nile is an example of a wave-dominated delta that has the classic Greek letter delta (Δ) shape after which river deltas were named.
-
Flash flooding caused by a large amount of rain falling in a short amount of time
-
Leisure activities on the River Avon at Avon Valley Country Park, Keynsham, United Kingdom. A boat giving trips to the public passes a moored private boat.
See also
 In Spanish: Río para niños
In Spanish: Río para niños
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |