Classification of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas facts for kids
The classification of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas helps us understand the many different groups of people who lived in North and South America before Europeans and Africans arrived. Scientists called anthropologists started sorting these groups based on where they lived and the languages they spoke. This work began around the 15th century. Some groups now live in different areas because they were forced to move from their original homes long ago.
Contents
- Indigenous Peoples of North America
- Indigenous Peoples of Mexico and Central America
- Indigenous Peoples of the Circum-Caribbean
- Indigenous Peoples of the Guianas
- Indigenous Peoples of Eastern Brazil
- Indigenous Peoples of the Andes
- Indigenous Peoples of the Amazon
- Indigenous Peoples of Gran Chaco
- Indigenous Peoples of the Southern Cone
- Indigenous Languages of the Americas
- Genetic History of Indigenous Peoples
- Interesting Facts About Indigenous Peoples
- See also
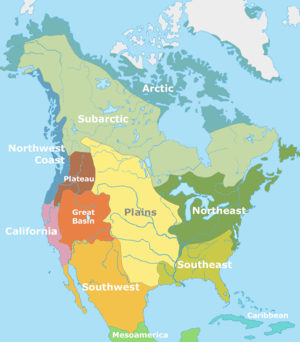
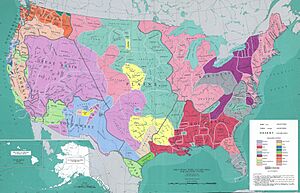
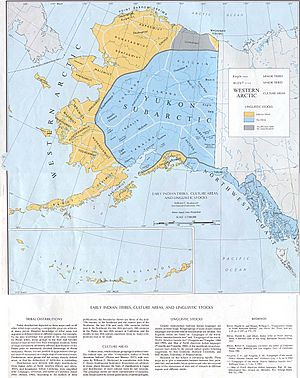
Indigenous Peoples of North America
In the United States and Canada, experts usually divide Indigenous peoples into ten main cultural regions. These regions share similar ways of life and traditions.
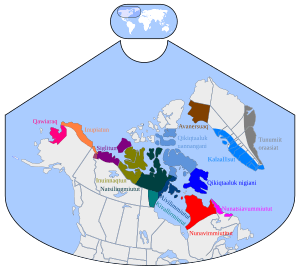
Arctic Peoples
The Arctic region is a very cold place, including parts of Russia, Alaska, Canada, and Greenland. People here adapted to life in the snow and ice.
- Paleo-Eskimo: These were very old cultures that lived in the Arctic from about 2500 BC to AD 1500.
- Aleut (Unangan): They live on the Aleutian Islands of Alaska and in Russia.
- Inuit: These people live across Russia, Alaska, Canada, and Greenland.
- Thule: These were the ancestors of today's Inuit, living from AD 900 to 1500.
- Greenlandic Inuit: They live in Greenland.
- Inuvialuit: Found in the western Canadian Arctic.
- Iñupiat: Live in northern Alaska.
- Yupik peoples (Yup'ik): They live in Alaska and Russia.
- Alutiiq (Sugpiaq): Found in south-central Alaska.
- Central Alaskan Yup'ik people: Live in west-central Alaska.
- Siberian Yupik: Live in the Russian Far East and on St. Lawrence Island, Alaska.
Subarctic Peoples
The Subarctic region covers a huge area of forests and tundra in Alaska and Canada. People here often hunted and fished for survival.
- Ahtna (Ahtena)
- Anishinaabe: A large group including the Ojibwa and Oji-Cree.
- Atikamekw: From Quebec.
- Chipewyan: Live in Alaska and Western Canada.
- Cree: A very large group found across Central and Eastern Canada and North Dakota.
- Dakelh (Carrier): From British Columbia.
- Dena’ina (Tanaina): From Alaska.
- Gwich'in (Kutchin): Live in Alaska and Yukon.
- Innu (Montagnais): From Labrador and Quebec.
- Koyukon: From Alaska.
- Slavey: Live in Alberta and British Columbia.
- Inland Tlingit
- Yellowknives
Pacific Northwest Coast Peoples
This region stretches along the coast from Alaska to Oregon. It's known for its rich resources, like salmon, and unique art, such as totem poles.
- Haida: From British Columbia and Alaska.
- Heiltsuk: From the BC Central Coast.
- Kwakwaka'wakw: From British Columbia.
- Lummi: From Washington.
- Makah: From Washington.
- Nisga'a: From British Columbia.
- Nuu-chah-nulth: From the West Coast of Vancouver Island.
- Quileute: From Washington.
- Saanich: From Southern Vancouver Island.
- Squamish: From British Columbia.
- Tlingit: From Alaska.
- Tsimshian: From British Columbia.
- Yurok: From northwestern California.
Northwest Plateau Peoples
The Plateau region is inland, between the Cascade Mountains and the Rocky Mountains. People here often relied on salmon fishing and gathering plants.
- Chinook peoples: Including Wasco-Wishram, from Oregon and Washington.
- Interior Salish peoples: Such as Coeur d'Alene Tribe (Idaho, Montana, Washington) and Flathead (Idaho, Montana).
- Sahaptin peoples: Including Nez Perce (Idaho) and Yakama (Washington).
- Kutenai (Kootenai): From British Columbia, Idaho, and Montana.
- Modoc: From California and Oregon.
Great Plains Peoples
The Great Plains stretch across the middle of North America. Many tribes here were known for hunting bison and living a nomadic lifestyle.
- Apache: Including Lipan Apache and Plains Apache.
- Arapaho: From Colorado, Oklahoma, and Wyoming.
- Arikara: From North Dakota.
- Blackfoot: A group of tribes from Alberta and Montana.
- Cheyenne: From Montana and Oklahoma.
- Comanche: From Oklahoma and Texas.
- Crow (Absaroka): From Montana.
- Kiowa: From Oklahoma.
- Mandan: From North Dakota.
- Osage: From Oklahoma.
- Pawnee: From Oklahoma.
- Sioux: A large group including the Dakota, Lakota, and Nakoda (Stoney, Assiniboine).
- Wichita and Affiliated Tribes: From Oklahoma.
Eastern Woodlands Peoples
This large region covers the eastern part of North America, from the Great Lakes to the Atlantic coast. People here often lived in settled villages and farmed.
Northeastern Woodlands
This area includes parts of Canada and the northeastern United States.
- Abenaki: From Quebec, Maine, and New Hampshire.
- Anishinaabeg: A large group including the Algonquin and Ojibwe.
- Iroquois Confederacy (Haudenosaunee): A powerful group of nations like the Mohawk, Oneida, and Seneca, from Ontario, Quebec, and New York.
- Lenni Lenape (Delaware): From Pennsylvania, Delaware, and New Jersey.
- Mi'kmaq (Micmac): From Eastern Canada and Maine.
- Mohegan: From Connecticut.
- Narragansett: From Rhode Island.
- Penobscot: From Maine.
- Pequot: From Connecticut.
- Powhatan Confederacy: A group of tribes from Virginia.
- Shawnee: From Ohio, Virginia, and Pennsylvania.
- Wampanoag: From Massachusetts.
- Wyandot (Huron): From Ontario.
Southeastern Woodlands
This region covers the southeastern United States. Many tribes here were skilled farmers.
- Apalachee: From northwestern Florida.
- Caddo Confederacy: From Arkansas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, and Texas.
- Catawba: From North and South Carolina.
- Cherokee: A large and well-known nation from North Carolina, Tennessee, and Georgia.
- Chickasaw: From Alabama and Mississippi.
- Choctaw: From Mississippi, Alabama, and Louisiana.
- Muscogee (Creek): A large confederacy from the southeastern states, including the Alabama and Seminole.
- Natchez: From Louisiana and Mississippi.
- Timucua: From Florida and Georgia.
- Yuchi (Euchee): From Tennessee and Georgia.
Great Basin Peoples
This dry region includes parts of California, Nevada, Utah, and Idaho. People here often gathered food and hunted small animals.
California Peoples
California was home to many diverse groups, often living in smaller communities and relying on local resources.
- Cahuilla: From southern California.
- Chumash: From coastal southern California.
- Hupa: From northwestern California.
- Karok: From northwestern California.
- Kumeyaay: From southern California and northwestern Mexico.
- Maidu: From northeastern California.
- Miwok: From central California.
- Ohlone (Costanoan): From west-central California.
- Pomo: From northwestern and central-western California.
- Yuki: From northwestern California.
- Yurok: From northwestern California.
Southwest Peoples
This region, also called "Oasisamerica," includes parts of Arizona, New Mexico, and northern Mexico. It's known for its desert landscapes and ancient Pueblo cultures.
- Akimel O'odham (Pima): From Arizona.
- Southern Athabaskan peoples: Including the Navajo (Diné) from Arizona and New Mexico, and various Apache groups.
- Havasupai: From Arizona.
- Mojave: From Arizona, California, and Nevada.
- Pueblo peoples: Famous for their multi-story homes, including the Hopi (Arizona), Zuni people (New Mexico), and many others in New Mexico like Acoma Pueblo and Taos Pueblo.
- Quechan (Yuma): From Arizona and California.
- Tohono O'odham: From Arizona and Mexico.
- Yaqui (Yoreme): From Arizona and Sonora, Mexico.
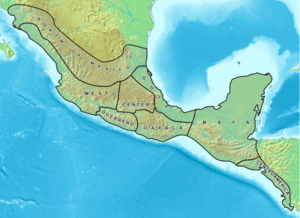
Indigenous Peoples of Mexico and Central America
These regions include parts of Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama.
Aridoamerica Peoples
This dry region covers parts of northern Mexico and the southwestern United States.
- Chichimeca: A general term for several groups in central Mexico, including the Guachichil and Zacatec.
- Cochimí: From Baja California.
- Huichol (Wixáritari): From Nayarit and Jalisco in Mexico, known for their vibrant art.
- Mayo: From Sonora and Sinaloa, Mexico.
- Seri: From Sonora, Mexico.
- Tarahumara: From Chihuahua, Mexico, known for their long-distance running.
- Yaqui: From Sonora, Mexico.
Mesoamerica Peoples
This region includes central and southern Mexico and parts of Central America. It was home to advanced ancient civilizations.
- Nahua: A large group in Mexico and Guatemala, including the Aztec (who built a great empire).
- Huastec: From eastern Mexico.
- Maya: A major civilization with many different groups across Belize, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Mexico. They were known for their writing, math, and astronomy.
- Mazatec: From Oaxaca, Mexico.
- Mixtec: From Oaxaca, Mexico.
- Olmec: An ancient civilization in southern Mexico, known for giant stone heads.
- Purépecha (Tarascan): From Michoacán, Mexico.
- Zapotec: From Oaxaca, Mexico.
- Toltec: An important ancient civilization in central Mexico (AD 900–1168).
Indigenous Peoples of the Circum-Caribbean
This area includes the Caribbean islands and parts of Central and South America near the Caribbean Sea.
Caribbean Islands Peoples
Central America Mainland Peoples
This area covers most of Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama.
Colombia and Venezuela Peoples
This region covers most of Colombia and Venezuela.
- Achagua: From eastern Colombia and western Venezuela.
- Guahibo: From eastern Colombia and southern Venezuela.
- Kogi: From northern Colombia, known for their traditional way of life.
- Muisca: An ancient culture from the Colombian highlands, known for their gold work.
- Pijao: From Colombia.
- Quimbaya: An ancient culture from central Colombia, famous for their gold art.
- Tairona: An ancient culture from northern Colombia.
- Wayuu (Guajiro): From northeastern Colombia and northwestern Venezuela.
- Zenú: An ancient culture from northwestern Colombia, known for their metalwork and hydraulic engineering.
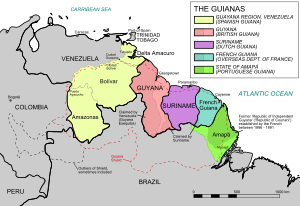
Indigenous Peoples of the Guianas
This region includes parts of Colombia, French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname, Venezuela, and northern Brazil.
- Akawaio: From Brazil, Guyana, and Venezuela.
- Apalaí: From Amapá, Brazil.
- Carib (Kalinago): From Venezuela.
- Lokono (Arawak): From Guyana, Trinidad, and Venezuela.
- Macushi: From Brazil and Guyana.
- Pemon (Arecuna): From Brazil, Guyana, and Venezuela.
- Wai-Wai: From Brazil and Guyana.
- Wapishana: From Brazil and Guyana.
- Warao: From Guyana and Venezuela.
- Ya̧nomamö (Yanomami): From Venezuela and Brazil, one of the largest isolated tribes in South America.
Indigenous Peoples of Eastern Brazil
This region covers various states in eastern Brazil.
- Apinajé: From Rio Araguiaia.
- Bororo: From Mato Grosso, Brazil.
- Guató: From Mato Grosso, Brazil.
- Kaingang: From southern Brazil.
- Karajá: From Goiás, Mato Grosso, Pará, and Tocantins, Brazil.
- Kayapo: From Mato Grosso and Pará, Brazil, known for their strong cultural identity.
- Pataxó: From Bahia, Brazil.
- Terena: From Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil.
- Xavánte: From Mato Grosso, Brazil.
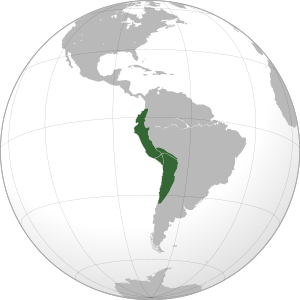
Indigenous Peoples of the Andes
The Andes Mountains stretch along the western side of South America. This region was home to the powerful Inca Empire.
- Aymara: From Bolivia, Chile, and Peru.
- Chachapoyas: An ancient culture from Amazonas, Peru.
- Diaguita: From Argentina.
- Inca Empire (Inka): A vast empire based in Peru, known for its advanced engineering and social structure.
- Muisca: From the Colombian highlands.
- Quechua (Kichua): The language of the Inca, spoken by many people in Bolivia, Chile, and Peru.
- Tiwanaku culture (Tiahuanaco): An ancient culture from Bolivia (AD 400–1000).
- Uru: From Bolivia and Peru, known for living on floating islands.
- Wari culture: An ancient culture from central Peru (AD 500–1000).
Pacific Lowlands Peoples
This region includes the coastal areas along the Pacific Ocean in South America.
- Chimú: An ancient culture from north coastal Peru (AD 1000–1450).
- Moche (Mochica): An ancient culture from north coastal Peru (AD 1–750), known for their pottery.
- Nazca culture (Nasca): An ancient culture from south coastal Peru (AD 1–700), famous for the Nazca Lines.
- Norte Chico civilization: One of the oldest civilizations in the Americas, from coastal Peru.
- Valdivia culture: An ancient culture from Ecuador (3500–1800 BC), known for early pottery.
Indigenous Peoples of the Amazon
The Amazon rainforest is a huge area in South America, home to many diverse Indigenous groups.
Northwestern Amazon Peoples
This part of the Amazon includes areas in Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru.
- Baniwa: From Brazil, Colombia, and Venezuela.
- Bora: From Peru.
- Cofán: From Colombia and Ecuador.
- Huaorani: From Ecuador, known for living deep in the rainforest.
- Jivaroan peoples: A group including the Achuar and Shuar from Ecuador and Peru.
- Kichua (Quichua): Various groups speaking Kichua dialects in Ecuador and Peru.
- Mura: From Amazonas, Brazil, including the Pirahã.
- Nukak: From eastern Colombia, one of the last nomadic groups.
- Ticuna: From Brazil, Colombia, and Peru, one of the largest Amazonian tribes.
- Witoto: From Peru.
- Yagua: From Peru.
- Záparo: From Ecuador.
Eastern Amazon Peoples
This part of the Amazon is mainly in Brazil.
- Awá (Guajá): From Brazil, one of the most endangered tribes.
- Guajajára: From Maranhão, Brazil.
- Guaraní: A large group found in Paraguay and parts of Brazil.
- Kayapo: From Mato Grosso and Pará, Brazil.
- Zo'é people: From Pará, Brazil, known for their long wooden lip plugs.
Southern Amazon Peoples
This region includes southern Brazil and eastern Bolivia.
- Apiacá: From Mato Grosso and Pará, Brazil.
- Bororo: From Mato Grosso, Brazil.
- Chiquitano: From Brazil and Bolivia.
- Kayapo: From Mato Grosso, Brazil.
- Moxo (Mojo): From Bolivia.
- Sateré-Mawé: From Brazil, known for their traditional guarana cultivation.
- Wari': From Rondônia, Brazil.
- Wuy jugu (Mundurucu): From Brazil.
Southwestern Amazon Peoples
This area covers eastern Peru, parts of Brazil, and Bolivia.
- Amahuaca: From Brazil and Peru.
- Asháninka: From Brazil and Peru, one of the largest Indigenous groups in the Peruvian Amazon.
- Harakmbut: From Madre de Dios, Peru.
- Kaxinawá: From Peru and Brazil.
- Mashco-Piro: An uncontacted tribe in Peru.
- Shipibo: From Peru, known for their intricate geometric designs.
- Yine: From Peru.
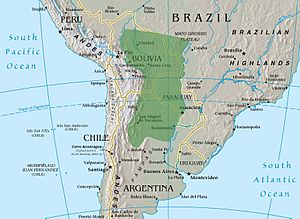
Indigenous Peoples of Gran Chaco
The Gran Chaco is a hot, dry plain in South America, covering parts of Argentina, Bolivia, Paraguay, and Brazil.
- Ayoreo: From Bolivia and Paraguay.
- Chamacoco: From Paraguay.
- Guaraní: Various groups from Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, and Paraguay.
- Guaycuru peoples: A group including the Mocoví and Toba from Argentina, Bolivia, and Paraguay.
- Nivaclé: From Argentina and Paraguay.
- Wichí (Mataco): From Argentina and Bolivia.
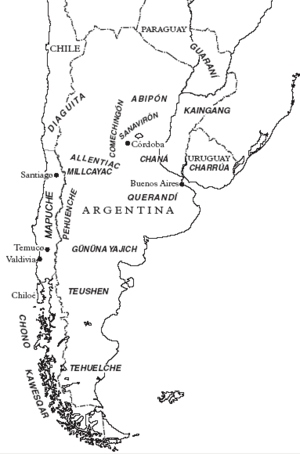
Indigenous Peoples of the Southern Cone
This region includes Argentina, Chile, Paraguay, and Uruguay.
- Aché: From southeastern Paraguay.
- Charrúa: From southern Brazil and Uruguay.
- Mapuche (Araucanian): A large and important group from southwestern Argentina and Chile, known for their resistance to colonization.
- Tehuelche: From Patagonia, Argentina.
- Selk'nam (Ona): From Tierra del Fuego, known for their body painting.
Fjords and Channels of Patagonia
This very southern part of Chile has many islands and channels.
- Alacaluf (Kaweshkar): From Chile.
- Yaghan (Yamana): From Tierra del Fuego, known as the southernmost people in the world.
Indigenous Languages of the Americas
The Indigenous languages of the Americas are made up of many different language families. Some are "language isolates," meaning they are not related to any other known language. Sadly, many of these languages are now endangered or have become extinct. This means they are no longer spoken.
Genetic History of Indigenous Peoples
Scientists believe that the Indigenous peoples of the Americas have a unique genetic history. This history was shaped by the first people who came to the Americas a very long time ago. It was also affected by the arrival of Europeans in the 15th century. A specific type of DNA, called Haplogroup Q1a3a (Y-DNA), is often found in Indigenous American populations.
Interesting Facts About Indigenous Peoples
- The United States has over 1,000 different Native American tribes.
- There are about 476 million Indigenous people around the world, living in more than 90 countries. Most of them live in Asia.
- Experts estimate that one Indigenous language dies every two weeks. This is a big loss of culture and knowledge.
- Many Indigenous peoples do not fully control their traditional lands.
- Eight Indigenous North American tribes have at least 100,000 members.
- Many Indigenous people speak more than one language, often their native language and another common language.
See also
 In Spanish: Clasificación de los pueblos indígenas de América para niños
In Spanish: Clasificación de los pueblos indígenas de América para niños
- Classification of indigenous languages of the Americas
- Indigenous languages of the Americas
- List of pre-Columbian cultures
- List of traditional territories of the indigenous peoples of North America
- Population history of Indigenous peoples of the Americas
|