Portugal facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Portuguese Republic
República Portuguesa
|
|
|---|---|
![Location of Portugal (dark green)– on the European continent (green & dark grey)– in the European Union (green) — [Legend]](/images/thumb/a/a0/EU-Portugal_with_islands_circled.svg/350px-EU-Portugal_with_islands_circled.svg.png)
Location of Portugal (dark green)
– on the European continent (green & dark grey) |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Lisbon |
| Official languages | Portuguese |
| Recognised regional languages | Mirandese1 |
| Ethnic groups
(2007)
|
96.87% Portuguese and 3.13% other ethnicities (Cape Verdeans, Brazilians, Ukrainians, Goans, Angolans, etc.) |
| Demonym(s) | Portuguese |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic |
| Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa (PSD) | |
| António Costa (PS) | |
|
• Assembly President
|
Ferro Rodrigues (PS) |
| Formation
Conventional date for Independence is 1139
|
|
|
• Founding
|
868 |
|
• Re-founding
|
1095 |
| 24 June 1128 | |
|
• Kingdom
|
25 July 1139 |
| 5 October 1143 | |
|
• Papal Recognition
|
23 May 1179 |
| 1 December 1640 | |
| 13 February 1668 | |
|
• Republic
|
5 October 1910 |
|
• Democracy
|
25 April 1974 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
92,090 km2 (35,560 sq mi) (110th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
0.5 |
| Population | |
|
• 2011 estimate
|
10,647,763 (77th) |
|
• 2011 census
|
10,555,853 |
|
• Density
|
115/km2 (297.8/sq mi) (96th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2010 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$247.037 billion (48th) |
|
• Per capita
|
$23,222 (39th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2010 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$229.336 billion (37th) |
|
• Per capita
|
$21,558 (32nd) |
| Gini (2009) | 33.7 medium |
| HDI (2011) | very high · 41st |
| Currency | Euro (€)2 (EUR) |
| Time zone | UTC+0 (WET) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+1 (WEST) |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy, yyyy-mm-dd, yyyy/mm/dd |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | 351 |
| ISO 3166 code | PT |
| Internet TLD | .pt |
|
|
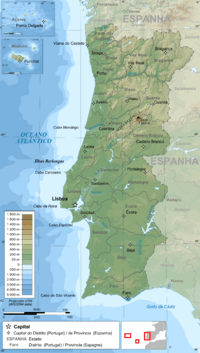
Portugal is a country in Southern Europe. It is located on the Iberian Peninsula, which is a large piece of land in the southwest of Europe. Portugal is the westernmost country in Europe.
To its west and south, Portugal has the Atlantic Ocean. To its north and east, it shares a border with Spain.
Portugal also includes three groups of islands in the Atlantic Ocean. These are the Azores (Açores), Madeira, and the Savage Isles (Ilhas Selvagens). The Savage Isles are small, uninhabited islands. They are managed by Madeira. Portugal also believes that Olivença is part of its land, but Spain controls it.
Contents
Exploring Portugal's Past
Portugal became its own kingdom in 1139. However, other countries did not officially recognize it until 1143. The border with Spain has stayed almost the same since the 13th century. For a long time, fishing and trade with other countries were very important.
The Age of Discovery
Portugal played a huge role in world exploration. This was especially true during the 15th century and 16th century. Prince Henry the Navigator, a Portuguese prince, was very interested in exploring. New inventions in navigation helped people learn more about geography.
This period of exploration led to the Portuguese Empire. Portugal was a powerful country around the world. But it lost a lot of money later on. The city of Lisbon was badly damaged by an earthquake in 1755. The country was also taken over during the Napoleonic Wars. Portugal lost its biggest colony, Brazil, in 1822.
Becoming a Republic and Democracy
In 1910, Portugal became a Republic. This meant it was no longer a kingdom. In 1926, a military group took control. This started a time of strict governments that lasted until 1974.
That year, a peaceful army takeover happened. It was called the Carnation Revolution. This event changed how the country was run. The next year, Portugal allowed its colonies in Africa to become independent. These included Mozambique, Angola, Guinea-Bissau, Cape Verde, and São Tomé and Príncipe.
East Timor in Asia declared its independence from Portugal in 1975. However, it was invaded by Indonesian forces soon after.
Portugal joined the European Union in 1986. Another Asian colony, Macau, later became part of China.
Famous Portuguese People
The main language spoken in Portugal is Portuguese.
Many famous people come from Portugal. Some well-known figures include:
- D. Afonso Henriques (the first King of Portugal)
- Prince Henry the Navigator (who helped start the Age of Discovery)
- Explorers like Bartolomeu Dias, Vasco da Gama, Pedro Álvares Cabral, and Ferdinand Magellan
- Writers such as Luís de Camões and Fernando Pessoa
- The famous singer Amália Rodrigues
- Architects Álvaro Siza Vieira and Eduardo Souto de Moura
Luís de Camões wrote Portugal's national poem. It is called Os Lusíadas and was written in 1572.
Portugal's Geography
Portugal's land includes a part of the Iberian Peninsula. Most Portuguese people call this "the continent." It also includes two island groups in the Atlantic: Madeira and the Azores. Portugal is located between 33° and 43° North latitude, and 32° and 6° West longitude.
Mainland Features
Mainland Portugal is divided by its main river, the Tagus. This river flows from Spain and empties into the Atlantic Ocean near Lisbon. The northern part of Portugal has mountains and plateaus with river valleys. The south, including the Algarve and Alentejo regions, has flat plains.
Portugal's highest point is Mount Pico. It is on Pico Island in the Azores. This old volcano is 2,351 meters (7,713 feet) high. On the mainland, the Serra da Estrela mountains reach 1,991 meters (6,532 feet). This area is popular for skiing and winter sports.
Atlantic Islands
The Madeira and Azores islands are spread out in the Atlantic Ocean. The Azores sit on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, where Earth's plates meet. Madeira was formed by hotspots in the Earth's crust. These islands were created by volcanoes and earthquakes. The last volcanic eruption on land was in 1957–58. Small earthquakes still happen sometimes, but they are usually not strong.
Portugal has a very large exclusive economic zone (EEZ). This is a sea area where Portugal has special rights to explore and use ocean resources. It covers 1,727,408 square kilometers (666,956 square miles). This is the 3rd largest EEZ in the European Union and the 11th largest in the world.
Portugal's Climate
Portugal has a Mediterranean climate. This means it has hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. It is one of the warmest countries in Europe. The average yearly temperature on the mainland ranges from 8-12°C (46-54°F) in the northern mountains. It can be 16-20°C (61-68°F) in the south.

The Algarve region has a climate similar to southern Spain. Portugal gets a lot of sunshine each year, about 2,500 to 3,200 hours. This means 4–6 hours in winter and 10–12 hours in summer. The south-east gets more sun, and the north-west gets less.
Plants and Animals of Portugal
Even though people have lived in Portugal for thousands of years, some original plants still remain. In Gerês, you can find old forests with both deciduous and coniferous trees. A very rare Mediterranean forest still exists in parts of the Arrábida mountain. A subtropical laurissilva forest, which is very old, covers a large area on the main island of Madeira.
Wild animals like boars, Iberian red deer, roe deer, and Iberian wild goats have increased in number recently. Boars have even been seen in large cities at night.
Portugal has many protected areas. These include one national park, 12 natural parks, and many reserves. The Parque Nacional da Peneda-Gerês is the only national park.
The country's plant life includes many types of pine trees, oak trees, and chestnut trees. Some Eucalyptus trees were brought to Portugal for their economic value. They are now common, but they can affect the environment.
Laurisilva is a special type of subtropical rainforest. In Europe, it is now only found in the Azores and Madeira. The Madeira forest is protected as a natural heritage site.
Portugal is home to many different mammals. These include foxes, badgers, Iberian lynx, Iberian wolves, wild goats, wild cats, and hares. It is also an important stop for migratory birds. Thousands of birds fly between Europe and Africa over places like Cape St. Vincent.
About 600 bird species have been seen in Portugal. The Azores and Madeira islands are resting spots for birds from America, Europe, and Africa. Mainland Portugal mostly sees European and African birds.
There are over 100 types of freshwater fish. Some are very large, like the European catfish. Others are small and rare, found only in tiny lakes. The sea off Portugal's west coast is rich in nutrients. This means it has many different kinds of marine fish. These include sardines, tuna, and Atlantic mackerel.
Portugal also has many unique insects. Some are only found in certain areas. The stag beetle and the cicada are more common. The Macaronesian islands (Azores and Madeira) have many species that are found nowhere else. This includes birds, reptiles, bats, insects, and snails.
How Portugal is Organized
Portugal is divided into 308 municipalities. These are called municípios or concelhos. After a change in 2013, these are split into 3,092 civil parishes (freguesia). The municipality and civil parish are the main local government units.
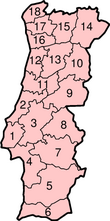
Continental Portugal is grouped into 18 districts. The Azores and Madeira islands are special autonomous regions. These larger units were set up in 1976.
The 18 districts of mainland Portugal are: Aveiro, Beja, Braga, Bragança, Castelo Branco, Coimbra, Évora, Faro, Guarda, Leiria, Lisbon, Portalegre, Porto, Santarém, Setúbal, Viana do Castelo, Vila Real and Viseu. Each district is named after its main city.
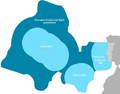
Portugal is also divided into nine regions for the European Union's NUTS system. These are the Azores, Alentejo, Algarve, Centro, Lisboa, Madeira, Norte, Oeste e Vale do Tejo and Península de Setúbal.
| Region | Capital | Area | Population | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | North Region | Porto | 21,278 km2 (8,215 sq mi) | 3,673,861 | |
| 2 | Central Region | Coimbra | 22,636 km2 (8,740 sq mi) | 1,695,635 | |
| 3 | West and Tagus Valley | Santarém | 9,839 km2 (3,799 sq mi) | 852,583 | |
| 4 | Greater Lisbon | Lisbon | 1,580 km2 (610 sq mi) | 2,126,578 | |
| 5 | Setúbal Peninsula | Setúbal | 1,421 km2 (549 sq mi) | 834,599 | |
| 6 | Alentejo Region | Évora | 27,329 km2 (10,552 sq mi) | 474,701 | |
| 7 | Algarve Region | Faro | 4,997 km2 (1,929 sq mi) | 484,122 | |
| 8 | Madeira Autonomous Region | Funchal | 801 km2 (309 sq mi) | 256,622 | |
| 9 | Azores Autonomous Region | Ponta Delgada | 2,351 km2 (908 sq mi) | 241,025 |
Portugal's Culture
Portugal has a unique culture. It has been shaped by many different civilizations. These include groups from the Mediterranean and Europe. Its culture was also influenced when Portugal played a big role in the Age of Discovery.
In recent years, Portugal has improved its public cultural places. These include the Belém Cultural Centre in Lisbon. There is also the Serralves Foundation and the Casa da Música in Porto. Many cities across the country have built or updated libraries and concert halls.
Portugal is home to 17 UNESCO World Heritage Sites. This means it ranks 9th in Europe and 18th in the world for these special sites.
Images for kids
-
Roman Temple of Évora, in the Alentejo, is one of the best preserved Roman-built structures in the country.
-
Suebi King Miro and St. Martin of Braga; c. 1145
-
Statue of Ibn Qasi outside the Castle of Mértola, in the Alentejo
-
A statue of Count Vímara Peres, first Count of Portugal
-
Alfonso VI of León investing Henry, Count of Portugal, in 1093
-
Afonso Henriques was the last Count of Portugal and the first King of Portugal after winning the Battle of Ourique in 1139.
-
Areas across the world that were, at one point in their history, part of the Portuguese Empire
-
The 1st Marquis of Pombal effectively ruled Portugal as an enlightened despot during the reign of King Joseph I.
-
Left to right: President Bernardino Machado, President Teófilo Braga, President António José de Almeida, and Prime Minister Afonso Costa; 1911
-
António de Oliveira Salazar ruled Portugal from 1932 to 1968, within the Estado Novo regime.
-
Mário Soares became Portugal's first democratically elected Prime-Minister in 1976.
-
The Treaty of Lisbon was signed in 2007, when Portugal held the presidency for the European Council.
-
Chameleo from Algarve
-
November 2011 protests against austerity measures outside the Assembly of the Republic
-
A Portucel Soporcel pulp and paper factory in Setúbal
-
Vasco da Gama Bridge is the longest bridge in the EU.
-
King Diniz statue at the University of Coimbra: the first university in Portugal (now the University of Coimbra), then called the Estudo Geral (General Study), was founded in Lisbon with his signing of the document Scientiae thesaurus mirabilis in Leiria on 3 March 1290.
-
Amália Rodrigues, known as the Queen of Fado, performing in 1969
-
Domingos Sequeira was one of the most prolific neoclassical painters. (Adoration of the Magi; 1828)
-
Cristiano Ronaldo is consistently ranked as one of the best football players in the world and considered to be one of the greatest players of all time.
See also
 In Spanish: Portugal para niños
In Spanish: Portugal para niños