Asia–Pacific facts for kids
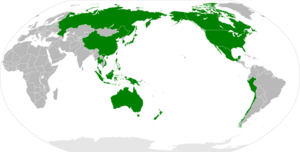
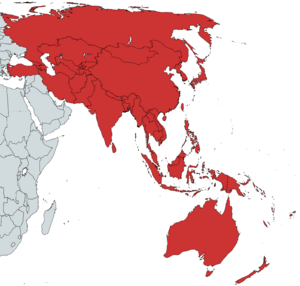
The Asia–Pacific (often called APAC) is a huge part of the world. It includes countries and territories that are close to the western side of the Pacific Ocean.
The exact borders of the Asia-Pacific region can change depending on who is talking about it. But usually, it includes places in Australasia (like Australia and New Zealand), East Asia (like China and Japan), and Southeast Asia (like Indonesia and Vietnam).
Sometimes, the term is used even more widely. It can include parts of Central Asia, North Asia, and many Pacific Islands. It might even include countries in the Americas that are on the Pacific coast, like Canada, Chile, Mexico, Peru, and the United States. For example, the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) group includes these American countries.
The name "Asia–Pacific" became very popular in the late 1980s. People use it a lot when talking about business, money, and politics. Even though the economies in this region are very different, many of the countries are "emerging markets." This means their economies are growing very quickly. Sometimes, people talk about "Asia–Pacific excluding Japan" (APEJ) to focus on the other fast-growing economies.
Contents
What Countries Are in Asia-Pacific?
The United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) says the Asia-Pacific region has 51 countries and seven territories. They are grouped into five main areas:
East and North East Asia
 People's Republic of China
People's Republic of China
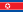 Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea)
Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea) Japan
Japan Mongolia
Mongolia South Korea
South Korea Taiwan
Taiwan
North and Central Asia
 Armenia
Armenia Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan Georgia
Georgia Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan Russian Federation
Russian Federation Tajikistan
Tajikistan Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
South and South West Asia
 Afghanistan
Afghanistan Bangladesh
Bangladesh Bhutan
Bhutan India
India Iran (Islamic Republic of)
Iran (Islamic Republic of) Maldives
Maldives Nepal
Nepal Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Turkey (Türkiye)
Turkey (Türkiye)
South East Asia (ASEAN)
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam Cambodia
Cambodia Indonesia
Indonesia Lao People's Democratic Republic (Laos)
Lao People's Democratic Republic (Laos) Malaysia
Malaysia Myanmar (Burma)
Myanmar (Burma) Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Thailand
Thailand Timor-Leste (East Timor)
Timor-Leste (East Timor) Viet Nam (Vietnam)
Viet Nam (Vietnam)
The Pacific (Oceania)
 American Samoa (United States)
American Samoa (United States) Australia
Australia Cook Islands
Cook Islands Fiji
Fiji French Polynesia (France)
French Polynesia (France) Guam (United States)
Guam (United States) Kiribati
Kiribati Marshall Islands
Marshall Islands Micronesia (Federated States of)
Micronesia (Federated States of) Nauru
Nauru New Caledonia (France)
New Caledonia (France) New Zealand
New Zealand Niue
Niue Northern Mariana Islands (United States)
Northern Mariana Islands (United States) Palau
Palau Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea Samoa
Samoa Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands Tonga
Tonga Tuvalu
Tuvalu Vanuatu
Vanuatu
Other Countries Sometimes Included
In a broader sense, some other countries and territories are also sometimes considered part of the Asia–Pacific region:
In Asia
 Bahrain
Bahrain British Indian Ocean Territory (United Kingdom)
British Indian Ocean Territory (United Kingdom) Cyprus
Cyprus Iraq
Iraq Israel
Israel Jordan
Jordan Kuwait
Kuwait Lebanon
Lebanon Oman
Oman Palestine
Palestine Qatar
Qatar Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Syria
Syria United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates Yemen
Yemen
In North America
In Oceania
 Baker Island (United States)
Baker Island (United States) Clipperton Island (France)
Clipperton Island (France) Coral Sea Islands (Australia)
Coral Sea Islands (Australia) Howland Island (United States)
Howland Island (United States) Jarvis Island (United States)
Jarvis Island (United States) Johnston Atoll (United States)
Johnston Atoll (United States) Kingman Reef (United States)
Kingman Reef (United States) Midway Atoll (United States)
Midway Atoll (United States) Norfolk Island (Australia)
Norfolk Island (Australia) Palmyra Atoll (United States)
Palmyra Atoll (United States) Pitcairn Islands (United Kingdom)
Pitcairn Islands (United Kingdom) Tokelau (New Zealand)
Tokelau (New Zealand) Wake Island (United States)
Wake Island (United States) Wallis and Futuna (France)
Wallis and Futuna (France) Chuuk State (Micronesia)
Chuuk State (Micronesia)
In South America
Economy of the Asia-Pacific Region
The Asia-Pacific region is very important for the world's economy. In 2024, experts from the World Bank expect the economies in this region (not including China) to grow a bit faster than before. This shows that the region is strong, even with challenges around the world.
Global trade, which means countries buying and selling goods to each other, is also expected to get better. This is good news for Asia-Pacific countries, as many of them rely on selling their products to other nations.
However, there are still some challenges. Businesses are not investing as much money as they did before the COVID-19 pandemic. This is partly because countries have more debt and interest rates are higher. This means it costs more to borrow money.
The region also faces problems like rising prices (inflation) and political uncertainties. These things can make it harder for economies to grow. Also, if big economies like the US or China slow down, it can affect the growth of other countries in Asia-Pacific.
Some countries, especially G-20 nations, have been putting in place more rules to protect their own industries. This is called "protective industrial policies." While this trend has grown, most other East Asia-Pacific countries have not been as involved in these measures, except for China and Indonesia.
See Also
 In Spanish: Asia-Pacífico para niños
In Spanish: Asia-Pacífico para niños
- Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
- Asia Pacific Forum
- Asia Pacific Foundation of Canada
- Asia-Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC)
- Asia Society
- Asian Century
- China Rim
- East Asia Summit
- East-West dichotomy
- Free and Open Indo-Pacific
- Indo-Pacific
- List of country groupings (including AMEA and AMER)
- Oceania
- Pivot to Asia
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)
- Valeriepieris circle