Geography of California facts for kids
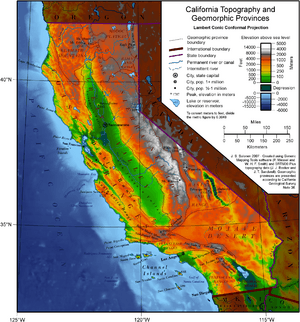
California is a large state on the western coast of North America. It shares borders with Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and Mexico to the south. The Pacific Ocean forms its entire western edge. California is known for its amazing variety of landscapes, covering about 163,696 square miles (423,970 km²). It is home to some incredible natural wonders. You can find the world's tallest trees (coast redwoods), the most massive trees (Giant Sequoias), and the oldest trees (bristlecone pines) here. California also has both the highest point (Mount Whitney) and the lowest point (Death Valley) in the connected United States.
Contents
Exploring Northern California's Geography
Northern California usually includes the 48 northernmost counties of the state. Big cities in this area are San Francisco, Oakland, San Jose, and Sacramento, which is the state capital.
Klamath Mountains: A Rugged Region
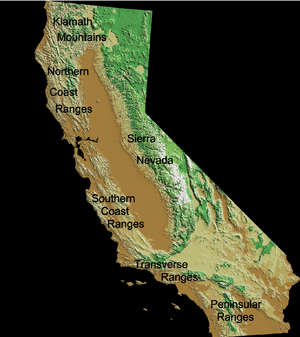
The Klamath Mountains are a mountain range found in northwest California and southwest Oregon. Their highest point is Mount Eddy in Trinity County, California, reaching 9,037 feet (2,755 m). This area has cold winters with lots of snow and warm, dry summers with little rain.
Cascade Range: Home to Volcanoes
The Cascade Range is a chain of mountains that stretches from British Columbia, Canada, all the way south to Lassen Peak in California. These mountains are often called the Cascades. They are part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, which is a circle of volcanoes around the Pacific Ocean. Mount Shasta, the second-highest peak in the Cascades, is located here.
Modoc Plateau: High and Wild
The Modoc Plateau is in the northeast corner of California. It sits between the Cascade Range to the west and the Warner Mountains to the east. About nine percent of this plateau is protected as wildlife areas, like the Modoc National Wildlife Refuge.
Sierra Nevada: Majestic Mountains
To the east of the state lies the Sierra Nevada mountain range, which runs north to south for about 400 miles (640 km). Mount Whitney, the highest peak in the connected United States at 14,505 feet (4,421 m), is found in the Sierra Nevada. The famous Yosemite Valley is also located in the central part of the Sierra. Lake Tahoe, a large, deep freshwater lake, is north of Yosemite.
The Sierra Nevada is also home to the Giant Sequoia trees, which are the most massive trees on Earth. A well-known hiking trail here is the John Muir Trail. It goes from the top of Mount Whitney to Yosemite Valley and is part of the longer Pacific Crest Trail that stretches from Mexico to Canada. Famous national parks like Yosemite National Park, Kings Canyon National Park, and Sequoia National Park are all in this region.
Basin and Range: Ancient Lakes and Old Trees
The Basin and Range area extends east into Nevada. Mono Lake, which is the oldest lake in North America, is located here. The salt from many old lake beds in the Basin and Range has been mined for many years. This is especially true for Owens Lake and Death Valley. The White Mountains are also in this area. They are home to the oldest living organisms in the world, the bristlecone pine trees.
Central Valley: California's Farmland
California's main feature is the Central Valley. This is a huge, very fertile valley located between the coastal mountains and the Sierra Nevada. Rivers flowing from the mountains water the entire Central Valley. These rivers are large and deep enough to allow ships to reach seaports in several cities far from the coast.
California Coast Ranges: Home of Tall Trees
The Coast Ranges are located west of the Central Valley. North of San Francisco, these mountains become increasingly foggy and rainy. These mountains are where you can find coast redwood trees, the tallest trees on Earth. They thrive in the cool, moist air from the coastal fog.
Discovering Southern California's Wonders
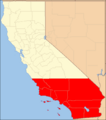
Southern California usually refers to the ten southernmost counties of the state. Another way to define Southern California is by using the Tehachapi Mountains as its northern border. This region has a more urban feel and is home to some of the state's largest cities. These include Los Angeles, Orange County, San Diego, and the Riverside-San Bernardino area. About 60% of California's population lives in Southern California. This area is famous for industries like the film industry, building homes, entertainment, and military aerospace. It's even possible to surf in the Pacific Ocean and ski on a mountain during the same winter day in Southern California!

Transverse Ranges: East-West Mountains
Southern California is separated from the rest of the state by mountains that run from east to west. These are called the Transverse Ranges. They stretch eastward from the Pacific coast and go about halfway across the state.
Mojave Desert: A Hot, Dry Place
The Mojave Desert is in southeast California and extends east into Nevada and Arizona. The Mojave Desert gets less than 6 inches (150 mm) of rain each year. It is generally between 3,000 and 6,000 feet (1,000 and 2,000 m) high. It also contains the lowest and hottest place in the Americas: Death Valley.
Peninsular Ranges: Southernmost Mountains
The southernmost mountains of California are the Peninsular Ranges. They run east of San Diego and continue into Baja California in Mexico.
Colorado and Sonoran Deserts: Low-Lying Lands
The Colorado and Sonoran Deserts are east of the Peninsular Ranges. They extend into Arizona and Mexico. Calipatria, California, which is the lowest community in California, is 160 feet (49 m) below sea level.
Channel Islands: Islands Off the Coast
The Channel Islands are a group of islands off the coast of Southern California. They are divided into two groups: the Northern Channel Islands and the Southern Channel Islands. There are eight islands in total:
| Northern islands | Southern islands |
| Anacapa Island | San Clemente Island |
| San Miguel Island | San Nicolas Island |
| Santa Cruz Island | Santa Barbara Island |
| Santa Rosa Island | Santa Catalina Island |
The Pacific Ocean: California's Western Border
The Pacific Ocean lies to the west of California. The ocean water here is usually cool, even in summer, rarely getting warmer than 65 °F (18 °C). The sea off California is green and full of fish.
California's Geology: Earthquakes and Volcanoes
Faults, Tsunamis, and Volcanoes: Natural Forces
Earthquakes happen in California because of cracks in the Earth's crust called faults. These faults run along the Pacific coast. The biggest and most famous fault is the San Andreas Fault. Here are some major historical earthquakes that have happened in California:
- The 1906 San Francisco earthquake (magnitude 7.8–8.2)
- The 1971 San Fernando earthquake (magnitude 6.6)
- The 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake (magnitude 6.9–7.1)
- The 1994 Northridge earthquake (magnitude 6.7)
Cities along California's coast could be affected by a tsunami. These giant, fast-moving waves are caused by earthquakes that move the sea floor, either nearby or in other parts of the Pacific Ring of Fire.
California also has several volcanoes, including Lassen Peak, which erupted in 1914 and 1921, and Mount Shasta.
California's Climate: A Mix of Weather
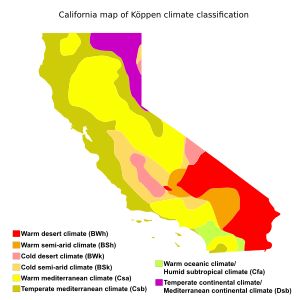
California is one of the few U.S. states where you can find snow and warm summer weather at the same time. Southern parts of the state at lower elevations have a desert climate. The northern part can be very cold, almost like a subarctic region. Coastal and Southern areas have a Mediterranean climate, which means they have somewhat rainy winters and dry summers. The ocean helps keep areas near the coast warmer in winter and cooler in summer.
Heavy rain, storms, and melting snow can sometimes cause floods. Also, steep slopes and unstable soil make some places likely to have landslides during wet weather or earthquakes.
Fun Facts About California's Geography
- Both the highest and lowest points in the connected United States are in California, and they are only about 80 miles apart! The tallest mountain peak is Mount Whitney at 14,496 feet (4,418 m). The lowest point in California and North America is in Death Valley at 282 feet (86 m) below sea level.
- California faces natural dangers like earthquake shaking, fault movement, tsunamis, landslides, volcanic eruptions, floods, and exposure to certain hazardous minerals.
- The longest fault system in California is the San Andreas Fault.
- There are over 700 named faults in California that have been active recently. Many other active faults are still unnamed.
- About 100 earthquakes happen in California every day, but most are too small to feel.
- Fossils of large animals like mammoths, bears, cats, horses, camels, and bison have been found in rocks near Barstow in Southern California. Fossils of turtles, shellfish, flamingos, and even palm trees have also been discovered.
- Tsunamis that affect California are usually caused by earthquakes and fault movement that happen under the ocean, both off California's coast and in other parts of the world.
- Fumaroles (vents that release volcanic gas and steam) found near Lassen Peak show that there is still volcanic activity happening there.
- Pillow basalts, like those found in the Coast Ranges, are rocks that formed when hot lava cooled under the ocean, creating shapes that look like pillows.
- California's state mineral is gold. The Gold Rush of 1849 brought many settlers to the state and led to California becoming the 31st state in 1850.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Geografía de California para niños
In Spanish: Geografía de California para niños