Czech Republic facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
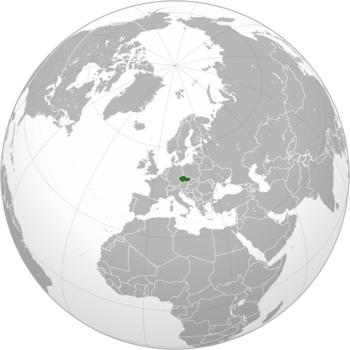
Czech Republic
Česká republika (Czech)
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Location of the Czech Republic (dark green)
– on the European continent (green & dark gray) |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Prague 50°05′N 14°28′E / 50.083°N 14.467°E |
| Official language | Czech |
| Ethnic groups
(2021)
|
|
| Religion
(2021)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Czech |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic |
| Petr Pavel | |
| Petr Fiala | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| Chamber of Deputies | |
| Establishment | |
|
• Duchy of Bohemia
|
c. 870 |
| 1198 | |
|
• Czechoslovakia
|
28 October 1918 |
|
• Czech Republic
|
1 January 1993 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
78,871 km2 (30,452 sq mi) (115th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
2.16 (as of 2022) |
| Population | |
|
• 2024 estimate
|
|
|
• 2021 census
|
|
|
• Density
|
133/km2 (344.5/sq mi) (91st) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2023) | ▼ 24.4 low |
| HDI (2022) | very high · 32nd |
| Currency | Czech koruna (CZK) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Date format | d. m. yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +420 |
| ISO 3166 code | CZ |
| Internet TLD | .cz |
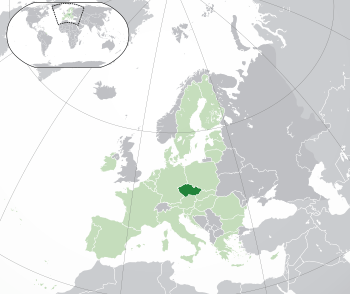
The Czech Republic, also called Czechia, is a country in Central Europe. It is a landlocked country, meaning it has no coastlines. It shares borders with Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast.
Historically, this area was known as Bohemia. The Czech Republic has many hills and covers about 78,871 square kilometers (30,452 sq mi). Its climate is mostly temperate, with warm summers and cold, snowy winters. The capital and largest city is Prague. Other important cities include Brno, Ostrava, and Plzeň.
The region's history dates back to the 9th century with the Duchy of Bohemia. It became a kingdom in 1198. Over time, it joined the Habsburg monarchy. After World War I, in 1918, it became part of Czechoslovakia. This country was one of the few democracies in Central Europe before World War II.
After being occupied by Nazi Germany, Czechoslovakia was restored in 1945. It then became a communist state in 1948. In 1989, the Velvet Revolution peacefully ended communist rule. On December 31, 1992, Czechoslovakia split into two independent countries: the Czech Republic and Slovakia.
Today, the Czech Republic is a parliamentary republic and a developed country. It has a strong economy and offers universal health care and free university education. It is considered one of the safest and most peaceful countries in the world. The Czech Republic is a member of the United Nations, NATO, and the European Union.
What's in a Name?
The name "Bohemia" comes from an old Latin word meaning "home of the Boii", an ancient tribe. The name "Czech" comes from the Slavic tribe called Češi. Legend says their leader, Čech, led them to the area. The word Čech means "member of the people" or "kinsman".
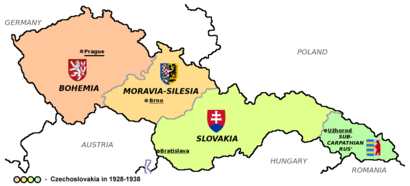
The country has three main historical parts: Bohemia in the west, Moravia in the east, and Czech Silesia in the northeast. These areas were known as the lands of the Bohemian Crown. Other names used were Czech lands or Czechia.
When the country became independent in 1918, it was called Czechoslovakia. This name showed the unity of the Czech and Slovak people. After Czechoslovakia peacefully split in 1992, the Czech short name Česko was adopted. The Czech government officially suggested using Czechia as the short English name in 2016. Organizations like the United Nations and the European Union now use it.
A Look at History
Early Times
Archaeologists have found signs of human settlements in the Czech Republic from the Paleolithic era, which was a very long time ago.
Around the 3rd century BC, a Celtic tribe called the Boii settled in the area. They built a fortified town near where Prague is today. Later, Germanic tribes like the Marcomanni and Quadi moved in.
Slavic people arrived in the 6th century. In the 7th century, a Frankish merchant named Samo became the ruler of the first known Slavic state in Central Europe, called Samo's Empire. The Great Moravia kingdom grew in the 8th century. It became very powerful in the 9th century. Christianity came to Great Moravia, helped by Cyril and Methodius. They created the first Slavic written language.
The Kingdom of Bohemia

The Duchy of Bohemia formed in the late 9th century. From 1002 to 1806, it was a state within the Holy Roman Empire. In 1212, Bohemia officially became a kingdom. German immigrants settled in the region during the 13th century.
In the late 14th century, people in Bohemia wanted to reform the church. Jan Hus led a movement that challenged the Catholic Church. This led to the Hussite Wars (1419–1434). The Hussites won against several crusades sent against them. For the next two centuries, most people in Bohemia and Moravia were Hussites.
A famous military leader, Jan Žižka, led the Hussites to victory in the Battle of Kutná Hora in 1421. He is still seen as a national hero.
After 1526, the Habsburgs took more control of Bohemia. From 1583 to 1611, Prague was the official home of the Holy Roman Emperor Rudolf II.
The Defenestration of Prague in 1618 started the Thirty Years' War. The rebellion in Bohemia was crushed in 1620 at the Battle of White Mountain. Many leaders of the rebellion were executed. Protestants had to become Catholic or leave the country.
The period from 1620 to the late 18th century is called the "Dark Age". The population decreased a lot due to war, disease, and people leaving. The Habsburgs only allowed Catholicism.
In the 18th and 19th centuries, the Czech National Revival began. This movement aimed to bring back the Czech language, culture, and national identity. The Revolution of 1848 in Prague, which sought reforms and more freedom for Bohemia, was stopped.
Bohemia became part of the Austrian Empire. Later, it was part of Austria-Hungary. Czech politicians fought for the right to vote for everyone. The first elections with universal male voting were held in 1907.
The Time of Czechoslovakia
In 1918, after World War I, the independent country of Czechoslovakia was formed. It included the lands of the Bohemian Crown. Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk was its first leader.
Czechoslovakia had only 27% of the population of the old Austria-Hungary, but it had almost 80% of its industry. This made it a strong industrial country. It was the only country in Central and Eastern Europe to remain a democracy during the time between the two World Wars.
In 1938, Nazi Germany took control of the Czech lands. This area became the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia. Many Jewish people from this area were killed in Nazi concentration camps. There was resistance against the Nazis. The German occupation ended in May 1945.
After World War II, Czechoslovakia was restored. In 1948, the Communist Party took control. For the next 41 years, Czechoslovakia was a communist state. In 1968, attempts to make the government more open, known as the Prague Spring, were stopped by an invasion led by the Soviet Union.
The Czech Republic Today

In November 1989, the Velvet Revolution peacefully brought democracy back to Czechoslovakia. However, the Slovak people wanted more independence. On December 31, 1992, Czechoslovakia peacefully split into the Czech Republic and Slovakia.
Both countries started economic reforms to create a market economy. This was very successful. In 2006, the World Bank called the Czech Republic a "developed country".
The Czech Republic joined NATO in 1999 and the European Union in 2004. In 2007, it joined the Schengen Area, which means people can travel freely across its borders with other member countries.
In recent years, new political parties have gained power. In 2023, Petr Pavel became the new Czech president.
Geography of Czechia
The Czech Republic is located in Central Europe. It has a varied landscape.
Bohemia, in the west, has a large basin with the Elbe and Vltava rivers. This basin is surrounded by low mountains, like the Krkonoše range. The highest point in the country, Sněžka, is here at 1,603 meters (5,259 ft).
Moravia, in the east, is also hilly. The main river here is the Morava River. The Oder River also starts in this region.
Water from the Czech Republic flows to three different seas: the North Sea, Baltic Sea, and Black Sea. The country even has a special area in the Hamburg Docks in Germany, called the Moldauhafen, which was given to Czechoslovakia by a treaty. This allows the landlocked country to transfer goods to sea-going ships.
The Czech Republic has four national parks: Krkonoše National Park, Šumava National Park, Podyjí National Park, and Bohemian Switzerland. These parks protect the country's beautiful nature.
Climate in Czechia
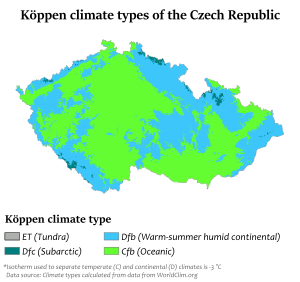
The Czech Republic has a temperate climate. This means it has warm summers and cold, cloudy, and snowy winters. Because it's a landlocked country, there are big temperature differences between summer and winter.
Temperatures change with elevation. Higher places are colder and get more rain or snow. The wettest area is in the Jizera Mountains. The driest area is near Louny District, northwest of Prague.
January is usually the coldest month. Snow falls in the mountains and sometimes in cities. Temperatures rise in spring, especially in April, when the weather can change quickly. Rivers also have higher water levels in spring due to melting snow.
July is the warmest month. Summer temperatures are usually between 20°C and 30°C (68°F and 86°F). Summers also have rain and thunderstorms.
Autumn starts in September, which is often warm and dry. By November, temperatures are usually around freezing.
The coldest temperature ever recorded was -42.2°C (-44°F) in 1929. The hottest was 40.4°C (104.7°F) in 2012. Most rain falls in the summer.
Protecting the Environment
The Czech Republic is very focused on protecting its environment. It ranks high among countries for its environmental efforts. The country has four National Parks and 25 Protected Landscape Areas. These areas help keep the country's nature safe and healthy.
How Czechia is Governed
The Czech Republic is a parliamentary democracy. This means people elect representatives to make laws. The country has a two-part Parliament. It includes the Chamber of Deputies (200 members) and the Senate (81 members).
Members of the Chamber of Deputies are elected for four-year terms. The Senate members are elected for six-year terms. One-third of the Senate is elected every two years.
The President is the head of state. They appoint the prime minister and other government members. Since 2013, the president has been directly elected by the people. The Prime Minister is the head of government. They set the agenda for most policies and choose government ministers.
Laws and Justice

The Czech Republic uses a civil law system. This system is based on written laws and codes. The main law is the Constitution of the Czech Republic, adopted in 1993.
The court system has different levels, including district, county, and supreme courts. There are three main supreme courts. The Constitutional Court checks if laws follow the Constitution. The Supreme Court handles most appeals. The Supreme Administrative Court deals with government and political matters.
International Relations
The Czech Republic is known as one of the safest and most peaceful countries. It is a member of the United Nations, the European Union, and NATO. Most countries have their embassies in Prague.
The Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs lead the country's foreign policy. The President also plays a role in representing the country abroad. Being part of the European Union and NATO is very important for Czech foreign policy.
The Czech Republic has strong ties with its neighbors, Slovakia, Poland, and Hungary, as part of the Visegrád Group. It also has good relationships with Germany, Israel, and the United States.
Military Forces

The Czech armed forces include the land forces and air force. The President is the Commander-in-chief. Since 2004, the army has been fully professional, meaning there is no compulsory military service. The country joined NATO in 1999.
The military's job is to protect the Czech Republic and its allies. It also helps with global security. Czech soldiers take part in NATO operations in places like Afghanistan and Kosovo. The Czech Air Force also helps protect the airspace of other countries.
Czech Economy
The Czech Republic has a strong, developed economy. It focuses on services, manufacturing, and innovation. It is part of the European Single Market within the European Union. However, it uses its own currency, the Czech koruna, not the euro.
The country's economy is considered one of Europe's most successful. In 2017, its economy grew by 4.5%. In 2016, the unemployment rate was the lowest in the EU. The poverty rate was also very low among developed countries.
Germany and the EU are the Czech Republic's biggest trading partners. The country has been part of the Schengen Area since 2004. This means there are no border controls with its neighbors.
Key Industries

Some of the largest companies in the Czech Republic include the car maker Škoda Auto, the utility company ČEZ Group, and the energy trading company EPH.
The Czech Republic is a major producer of transportation vehicles. Škoda Transportation is the fourth largest tram producer in the world. Nearly one-third of all trams globally come from Czech factories. Other companies make heavy trucks, military aircraft, tractors, and motorcycles.
The country is also the world's largest maker of vinyl records. GZ Media produces about 6 million records each year. Česká zbrojovka is one of the top ten firearms producers globally.
Energy Production
The Czech Republic produces more electricity than it uses, so it exports the extra. About 30% of its electricity comes from nuclear power plants. This share is expected to grow to 40%. Most of the rest comes from steam and coal power plants. A small amount comes from renewable sources.
The largest Czech power plants are Temelín Nuclear Power Station and Dukovany Nuclear Power Station. The country is trying to use less coal, which causes pollution. Natural gas is imported from Russia and Norway.
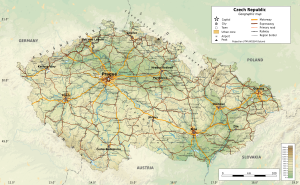
Getting Around: Transportation
The Czech Republic has a good road network. It includes over 1,200 km (745 mi) of motorways. The speed limit is 50 km/h (31 mph) in towns, 90 km/h (56 mph) outside towns, and 130 km/h (81 mph) on motorways.
The country also has one of the densest rail networks in the world. České dráhy (Czech Railways) is the main train operator. It carries about 180 million passengers each year.
Václav Havel Airport Prague is the main international airport. In 2019, it handled 17.8 million passengers. The Czech Republic has 91 airports in total, with six offering international flights.
Communication and Technology

The Czech Republic has some of the fastest internet speeds in the world. Many people use wireless internet providers. All three major mobile phone companies offer internet plans.
Two big computer security companies, Avast and AVG, were founded in the Czech Republic. In 2016, Avast bought AVG. Together, these companies protect hundreds of millions of users worldwide. Avast is a leading provider of antivirus software.
Tourism in Czechia
Prague is one of the most visited cities in Europe. Tourism brings a lot of money to the Czech economy. It also provides jobs for over 110,000 people.
The Czech Republic has 16 UNESCO World Heritage Sites. These are places recognized for their special cultural or natural importance.
Visitors enjoy the country's amazing architecture. There are many castles and châteaux from different historical periods, like Karlštejn Castle and Český Krumlov. There are also beautiful cathedrals and monasteries.
Outside the cities, areas like Bohemian Paradise and the Giant Mountains are popular for outdoor activities. The country also hosts many beer festivals.
The Czech Republic has many museums. Puppetry and marionette shows are a big part of the culture. There are also puppet theater festivals. Aquapalace Prague is the largest water park in the country.
Science and Innovation

The Czech Republic has a long history of scientific discoveries. Today, it has a very advanced and innovative scientific community. Czech scientists work with colleagues around the world and publish in many international journals. The Czech Republic ranks high in the Global Innovation Index.
Historically, Prague was a center for science. Famous scientists like Tycho Brahe, Nicolaus Copernicus, and Johannes Kepler worked there. The Czech Academy of Sciences is a major scientific organization today.
Many important scientists were born in the Czech lands. These include Nobel Prize winners like biochemists Gerty and Carl Ferdinand Cori, and chemist Jaroslav Heyrovský. Sigmund Freud, who founded psychoanalysis, was born in Příbor. Gregor Mendel, who founded genetics, spent most of his life in Brno.
Today, important scientific centers include the CEITEC in Brno and the HiLASE and Eli Beamlines centers, which have the world's most powerful laser. Prague is also home to the GSA Agency, which operates the European navigation system Galileo.
People of Czechia
Population and Diversity
The Czech Republic has a population of about 10.9 million people. The average age is 43.3 years. Most people in the Czech Republic are Czechs (57.3%). Other groups include Moravians (3.4%), Slovaks (0.9%), and Ukrainians (0.7%). Many people did not state their nationality in the 2021 census.
There are also many foreigners living in the country. In 2016, about 496,413 foreigners lived there. The largest groups were Ukrainian, Slovak, and Vietnamese. Most foreigners live in Prague and the Central Bohemia Region.
The Jewish population was almost completely destroyed during the Holocaust. Today, there are about 3,900 Jews in the Czech Republic.
Religion in Czechia

Most people in the Czech Republic do not say they have a religion. About 75% to 79% of residents do not declare any religion in surveys. The Czech people are often described as "tolerant and even indifferent towards religion."
Christianity came to the region in the 9th and 10th centuries. After the Bohemian Reformation, many Czechs became followers of Jan Hus. Later, the Habsburgs forced people to convert to Catholicism.
Today, only about 10% of the population is Catholic. Protestantism is very small. The Jewish community is also small after the Holocaust. The proportion of religious believers changes across the country.
Education and Healthcare

Education in the Czech Republic is required for nine years. Citizens can get free university education. Charles University, founded in 1348, was the first university in Central Europe. Other major universities include Masaryk University and Czech Technical University.
The Czech education system is ranked very high globally. It is considered one of the most successful in the world.
Healthcare in the Czech Republic is good, similar to other developed countries. It has a universal health care system. This means that healthcare is funded by mandatory insurance plans. The Czech healthcare system is ranked highly in Europe.
Czech Culture
Art and Design
The Czech lands have a rich history of art. The Venus of Dolní Věstonice is a very old piece of prehistoric art. In the Gothic era, Theodoric of Prague was a famous painter. The Baroque era saw artists like Wenceslaus Hollar and sculptors like Matthias Braun.
In the 19th century, artists like Josef Mánes were part of the romantic movement. Later, the "National Theatre generation" included sculptors like Josef Václav Myslbek and painters like Mikoláš Aleš. At the turn of the 20th century, Art Nouveau became popular. Alfons Mucha was a main artist of this style. He is famous for his posters and his large paintings called the Slav Epic.
The 20th century brought new art styles like Cubism and Surrealism. František Kupka was a pioneer of abstract painting. Famous illustrators include Josef Lada and Zdeněk Burian. The Czech Republic is also known for its beautiful, handmade Bohemian glass.
Architecture Styles
The oldest stone buildings in Bohemia and Moravia date back to the 9th and 10th centuries. The Czech lands have used the same architectural styles as other parts of Europe. Early churches were built in the Romanesque style. Later, the Gothic style became popular. Emperor Charles IV brought architects from France and Germany to Prague in the 14th century.
The Renaissance style arrived in the late 15th century. An example is the Queen Anne's Summer Palace in Prague. This style brought large chateaus with courtyards and gardens.
In the 17th century, the Baroque style spread. The 18th century saw a unique "Baroque Gothic style," which mixed Gothic and Baroque elements.
The 19th century brought back older styles like Neo-Romanesque and Neo-Gothic. At the turn of the 20th century, Art Nouveau appeared.
The Czech Republic also contributed a unique style called Cubism in architecture. This style tried to bring the ideas of Cubist painting into buildings.
Between World War I and II, Functionalism became the main style. After World War II, Soviet influence was seen in art. Later, the "Brussels style" emerged in the 1960s, combining theater, dance, and film.
Modern architecture is also present, like the Dancing House in Prague.
Literature and Stories
Literature from the Czech Republic was mostly written in Czech. But it was also written in Latin, German, and even Old Church Slavonic. Franz Kafka, a famous writer, wrote his works like The Trial in German.
Bible translations were very important for the development of Czech literature. The first complete Czech Bible was printed in 1488. The Codex Gigas from the 12th century is the largest medieval manuscript in the world.
Czech literature has gone through many periods. It includes medieval times, the Hussite period, the Renaissance, and the Baroque. Modern literature developed in the 19th and 20th centuries.
The anti-war comedy novel The Good Soldier Švejk is the most translated Czech book ever. The Franz Kafka Prize is an international literary award given in the Czech Republic. The Czech Republic has the most libraries per person in Europe.
Czech literature has often helped the nation fight for freedom when it was under difficult political times.
Music and Sounds
Czech music began with church hymns in the 10th and 11th centuries. Two important hymns are "Lord, Have Mercy on Us" and "Saint Wenceslaus Chorale".
Czech music has a rich tradition of classical music. This includes Baroque, Classical, Romantic, and modern classical music. Folk music from Bohemia, Moravia, and Silesia has also influenced composers.
Czech music has been very important in Europe and worldwide. Famous works include The Bartered Bride, New World Symphony, and Jenůfa.
The Prague Spring International Music Festival is a famous classical music festival in the country. It showcases talented musicians and orchestras.
Theatre and Puppets
Czech theatre has roots in the Middle Ages. In the 19th century, theatre helped the national awakening movement. In the 20th century, it became part of modern European theatre.
A unique Czech cultural project from the 1950s is Laterna magika. It combines theatre, dance, and film in a poetic way. This is considered one of the first multimedia art projects.
Karel Čapek's play R.U.R. introduced the word "robot" to the world.
The country has a strong tradition of puppet theater. In 2016, Czech and Slovak Puppetry was added to the UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists.
Film and Cinema

Czech cinematography started in the late 1890s. Early Czech sound films included comedies and dramas.
Hermína Týrlová was a famous Czech animator and film director. She made over 60 animated children's short films using puppets and stop motion. Irena Dodalová also established the first Czech animation studio in 1933.
After World War II, Czech film became known for animated films. The Fabulous World of Jules Verne (1958) combined live action with animation. Jiří Trnka was a pioneer of modern puppet film. This started a tradition of animated films, like the popular Mole.

In the 1960s, the Czechoslovak New Wave films used improvised dialogues and dark humor. Directors like František Vláčil and Jan Švankmajer created unique and psychological films.
The Barrandov Studios in Prague are the largest film studios in the country. Many filmmakers come to Prague to shoot movies because of its beautiful scenery. The city of Karlovy Vary was used for the James Bond film Casino Royale.
The Czech Lion is the highest Czech award for film. The Karlovy Vary International Film Festival is a major film festival.
Media and News

Czech journalists and media have a good degree of freedom. The Czech press was ranked as the 40th most free in the world in 2021. Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty has its main office in Prague.
The national public television service is Czech Television. It has a 24-hour news channel, ČT24. Czech Television is the most watched TV channel in the country. Other public services include Czech Radio and the Czech News Agency.
Many Czechs read their news online. Popular news websites include Seznam.cz and iDNES.cz.
Delicious Czech Cuisine

Czech cuisine often features meat dishes like pork, beef, and chicken. Goose, duck, and venison are also served. Fish is less common, except for fresh trout and carp at Christmas.
There are many local sausages, pâtés, and smoked meats. Czech desserts include pastries, tarts, and traditional cakes like buchty and koláče.
Czech beer has a history of over a thousand years. The Czech Republic has the highest beer consumption per capita in the world. The pilsner style beer started in Plzeň. The world's first blond lager, Pilsner Urquell, is still made there. It has inspired most of the beer produced globally today.
The South Moravian region has been making wine since the Middle Ages. Besides beer and wine, the Czech Republic also makes slivovitz and two liquors, Fernet Stock and Becherovka. Kofola is a popular Czech soft drink.
Sports and Recreation

The two most popular sports in the Czech Republic are football (soccer) and ice hockey. The most watched events are the Olympic and World Championships for ice hockey. Other popular sports include tennis, volleyball, and golf.
The Czech Republic has won many medals in the Summer and Winter Olympics. The Czech ice hockey team won the gold medal at the 1998 Winter Olympics. They have also won twelve gold medals at the World Championships.
Škoda Motorsport has been involved in car racing since 1901 and has won many titles.
Hiking is a very popular activity. The Czech Republic has a special Czech Hiking Markers System with around 40,000 km (25,000 mi) of marked trails. These trails cross the entire country and its mountains.
Images for kids
-
Köppen climate classification types of the Czech Republic using the 0 °C isotherm
Error: no page names specified (help).
See also
 In Spanish: República Checa para niños
In Spanish: República Checa para niños