Geography of South Dakota facts for kids
South Dakota is a state in the north-central United States. It's often seen as part of the Midwest. The state has three main areas: eastern South Dakota, western South Dakota, and the Black Hills. Eastern South Dakota is lower and gets more rain. The Black Hills are a group of mountains in the southwest. Smaller areas include the Coteau des Prairies and the James River Valley. South Dakota's rocks are very old, some are two billion years old! It is the 17th largest state in the country.
South Dakota has a humid continental climate in the east and Black Hills, and a semi-arid climate in the west. This means it has four clear seasons. The plants and animals are typical of a North American temperate grassland area. Many places are protected, like Badlands National Park, Wind Cave National Park, and Custer State Park.
In 2011, about 824,082 people lived in South Dakota. It has one of the smallest populations and fewest people per square mile in the U.S. Sioux Falls is the biggest city, with over 200,000 people. Rapid City is the second largest, and Pierre is the state capital. South Dakota used to be mostly about farming, but now services and tourism are also very important to its economy.
Contents
Where is South Dakota?
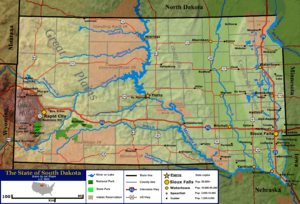
South Dakota is in the north-central part of the United States. The U.S. Census Bureau calls it part of the Midwest. But the Great Plains also cover the state. Western South Dakota feels more like the West in its culture and land. The state covers about 77,116 square miles (199,905 km²). This makes it the 17th largest state.
South Dakota shares borders with many states. To the north is North Dakota. To the south is Nebraska. To the east are Iowa and Minnesota. To the west are Wyoming and Montana. The western border is a special line called the Black Hills meridian. The northern border is the 46th parallel north. It was once marked by 720 stone monuments.
South Dakota uses two time zones. The state is split almost in half. The eastern part is in the Central Time Zone (UTC-6). The western part is in the Mountain Time Zone (UTC-7). The line between them follows the Missouri River for a while.
South Dakota's Unique Regions

South Dakota has three main areas: eastern South Dakota, western South Dakota, and the Black Hills. The Missouri River acts like a border. It separates the eastern and western parts. These two sides have different land, people, and ways of life. People sometimes call them West River and East River.
Eastern South Dakota gets more rain and has flatter land. This area includes the Coteau des Prairies, the Dissected Till Plains, and the James River Valley. The Coteau des Prairies is a higher area with many lakes. The Big Sioux River drains much of this land. The James River Basin is mostly flat and low. It follows the James River from north to south. The Dissected Till Plains have rolling hills and rich soil. This area reaches into the southeastern part of South Dakota.

The Missouri Coteau is between the James River Basin and the Missouri River. This is a southern part of a large plateau that goes into Canada.
The Great Plains cover most of western South Dakota. West of the Missouri River, the land becomes rougher. It has rolling hills, plains, and steep, flat-topped hills called buttes. These buttes can rise 400 to 600 feet (120 to 180 m) above the plains. In the south, near the Black Hills, you'll find the South Dakota Badlands.
The Black Hills are in the southwest and go into Wyoming. This low mountain range covers 6,000 square miles (15,500 km²). Mountains here rise 2,000 to 4,000 feet (600 to 1,200 m) from their bases. Black Elk Peak is the highest point in South Dakota. It is 7,242 feet (2,207 m) above sea level. This is the highest point in the U.S. east of the Rocky Mountains. The Black Hills have valuable minerals like gold and silver. The Homestake Mine was once North America's largest gold mine. It is now a science lab.
South Dakota's Ancient Geology
South Dakota's rocks and soil are very old. They range from billions to thousands of years old. The oldest rocks are in the Black Hills. They are over two billion years old. You can also find these old rocks in eastern South Dakota. Rocks from the Paleozoic Era (540 to 250 million years ago) form the outer ring of the Black Hills. These rocks, like limestone, formed when the area was an ancient sea.

Much of western South Dakota has rocks from the Mesozoic Era (250 to 66 million years ago). Back then, a shallow sea covered this area. Skeletons from sea creatures settled and formed the rocks we see today. During this time, the Black Hills were very tall. They lost many layers of rock due to erosion. These eroded bits mixed with the sea deposits. This created the geology of western South Dakota. You can see these colorful rock layers in Badlands National Park.
The youngest layers are in eastern South Dakota. They formed about two million years ago. These layers are from several ice ages. Glaciers left behind a lot of rocks and soil called till. This till is 100 to 900 feet (30 to 270 m) thick. It makes the soil very fertile, which is why farming is big in eastern South Dakota.
South Dakota's history was shaped by its geology. Gold seekers started many cities around the Black Hills. Mining and quarrying (cutting stone) were important jobs. Today, South Dakota produces gold, Sioux quartzite, Milbank granite, sand, gravel, and limestone.
Rivers and Lakes of South Dakota
The Missouri River is the biggest and longest river in South Dakota. Other important rivers are the Cheyenne, the James, the Big Sioux, and the White. Almost all of South Dakota's rivers flow into the Missouri River. Dams on the Missouri River create four large lakes. These are Lake Oahe, Lake Sharpe, Lake Francis Case, and Lewis and Clark Lake. Power plants at these dams make about half of South Dakota's electricity.
Most of South Dakota's natural lakes are in the eastern part of the state. They were formed by the last ice age. The largest natural lake is debated. Lake Thompson is bigger than Lake Poinsett. But Lake Poinsett has been its current size for longer. Other big natural lakes include Lake Kampeska and Waubay Lake. Two large lakes, Big Stone Lake and Lake Traverse, form part of the border with Minnesota.
South Dakota's Wildlife and Plants
Most of South Dakota, except the Black Hills, is covered by grasslands. Even though grasses and crops are everywhere, you can find deciduous trees like cottonwoods and willows near rivers. In open areas, grasses like buffalograss and western wheatgrass grow well.
Animals here include bison, deer, pronghorn, coyotes, and prairie dogs. Reptiles like snapping turtles and different snakes live here. The prairie rattlesnake is the only venomous snake in South Dakota. Rivers and lakes have fish like walleye and bass. The Missouri River also has the ancient paddlefish. Chinook salmon have been added to Lake Oahe.
Tall Grass Prairies
Southeastern South Dakota gets the most rain. It once had grasses 3 to 6 feet tall. This area has lots of groundwater. Before modern farming, tall grasses like big bluestem and Indian grass were common. Along the Missouri and Big Sioux Rivers, you find wild rye. Shrubs like wild rose and herbs like goldenrod grow here. Birds like marsh hawks and bobolinks live in this prairie. Animals include jackrabbits and deer.
Mid and Tall Grass Prairies
Plants here grow 1 to 3 feet tall. This area gets 18 to 22 inches of rain each year. It's a mix between the tall grass areas and the shorter grass areas. Common grasses are needlegrass and needle-and-thread grass.
Mid and Short Grass Prairies
Plants in these prairies are about 6 inches tall, up to 1 foot. Short grasses grow in dry areas, and mid grasses in lowlands. Common grasses include western wheatgrass. The pasque flower is the South Dakota state flower. While antelope and bison used to be common, now you'll see deer, jackrabbits, and skunks. Pheasants, ducks, and sparrows are common birds. Bull snakes are now more common than rattlesnakes.
Short and Mid Grass Prairies
These steppe grasslands cover the western two-thirds of South Dakota. Rain is irregular, about 13 to 18 inches per year. Storms like hailstorms and blizzards happen often. Many animals live here, including wolves, coyotes, antelope, and bison. Rattlesnakes and bull snakes live here. Many birds like geese, ducks, and hawks make their homes here. Common plants include evening primroses and sunflowers.
The Coniferous Black Hills
The Black Hills have different plants and animals because they are higher and get more rain. The mountains are covered with evergreen trees. These include different types of ponderosa pine (which covers 80% of the forest), lodgepole, and spruces. The South Dakota state tree is the Black Hills spruce. Shrubs like wild plum and chokecherry grow here. Violets and thistles are common herbs. Vines like wild grape also grow here.
Black Hills mammals include deer, elk, bighorn sheep, and mountain lions. Streams and lakes have different kinds of trout. Cottontail rabbits, squirrels, and porcupines live throughout the Hills. You can also find wild burros and bobcats. Birds like woodpeckers, robins, and jays are common.
Birds of South Dakota
South Dakota has many types of birds. The state bird is the ring-necked pheasant. It came from China and has done very well here. More and more bald eagles live throughout the state, especially near the Missouri River. The wild turkey is another large bird found in many areas.
The many lakes and wet areas in eastern South Dakota are home to migrating birds. These include Canada geese, snow geese, mallards, and pelicans. The prairie is home to songbirds like meadowlarks and goldfinches. The open plains also suit many meat-eating birds, such as hawks, falcons, and owls.
South Dakota's Climate

South Dakota has a continental climate. This means it has four clear seasons. Winters are very cold, and summers are hot. In summer, the average high temperature is often near 90°F (32°C). It often cools down to about 60°F (16°C) at night. Temperatures can go above 100°F (38°C) several times each summer.
Winters are cold. January high temperatures are usually below freezing. Low temperatures are often below 10°F (-12°C). But in the west, warm chinook winds can raise temperatures above 50°F (10°C) in winter. The highest temperature ever was 120°F (49°C) in Gann Valley in 1936. The lowest was -58°F (-50°C) in McIntosh in 1936.
Average yearly rainfall changes across the state. The northwest gets about 15 inches (381 mm). The southeast gets about 25 inches (635 mm). A small area in the Black Hills, near Lead, gets the most rain, almost 30 inches (762 mm) per year.
South Dakota summers have many thunderstorms. These can be strong with high winds and hail. The eastern part of the state is in tornado alley. South Dakota has about 29 tornadoes each year. Winters are more stable, but blizzards and ice storms can happen. Bad weather can sometimes be deadly. The 1972 Black Hills flood killed 238 people in Rapid City.
Protected Natural Areas

South Dakota has several places protected by the National Park Service. Two national parks are in the southwest. Badlands National Park was created in 1978. It has colorful, eroded landscapes and dry grasslands. Wind Cave National Park, started in 1903, has a huge cave system. It also has a large herd of bison. Mount Rushmore National Memorial is in the Black Hills. It has a mountain carved with the faces of four U.S. presidents.
Other protected areas include Jewel Cave National Monument and the Minuteman Missile National Historic Site. This site has a old nuclear missile silo. The Missouri National Recreational River is also protected. The United States Forest Service manages other areas. South Dakota has two national forests: Black Hills National Forest and a small part of Custer National Forest. It also has three national grasslands.
South Dakota also has many state parks. They are managed by the South Dakota Department of Game, Fish, and Parks. Custer State Park in the Black Hills is very large. It has over 71,000 acres. It includes Sylvan Lake and a wildlife loop with a big bison herd. Other parks are Bear Butte State Park and Lewis and Clark State Recreation Area.
South Dakota's People and Cities
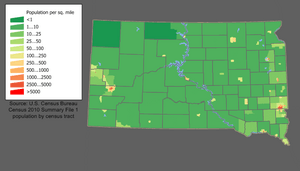
In 2010, South Dakota had 814,180 people. It ranks as one of the states with the fewest people. It also has one of the lowest population densities. This means there are not many people per square mile.
The largest groups of people in South Dakota are: German (40.7%), Norwegian (15.3%), and Irish (10.4%). Native Americans make up 8.3% of the population. They are mostly Lakota, Dakota, and Nakota (Sioux) people. South Dakota has the third-highest percentage of Native Americans of any state.
Many rural areas in South Dakota are losing people. But the areas around Sioux Falls and the Black Hills are growing. For example, Lincoln County, near Sioux Falls, is one of the fastest-growing counties in the U.S. This growth helps the state's total population keep increasing.
Cities and Counties

South Dakota does not have many very large cities. Sioux Falls is the biggest city. Its population was about 184,000 in 2019. It is located in the southeast. Sioux Falls started with farming and quarrying. Now, its economy is mostly about shopping and financial services.
Rapid City is the second-largest city. Its population was about 64,000 in 2007. It is on the edge of the Black Hills. Rapid City's economy relies on tourism and military spending. This is because of nearby tourist spots and Ellsworth Air Force Base.
Other larger cities include Aberdeen, Watertown, and Brookings. Pierre is the state capital. Brookings and Vermillion have the state's two biggest universities. Rapid City is the only one of the ten largest cities west of the Missouri River.
South Dakota's Economy
South Dakota's first economy depended on its land. Early settlers were farmers, miners, or trappers. Even though other jobs have grown, farming is still very important. Especially in rural areas. The most valuable farm products are cattle, corn, soybeans, wheat, and hogs. Industries related to farming, like meat packing and ethanol production, are also important. South Dakota makes a lot of ethanol.
Tourism is another big part of South Dakota's economy. Many people visit the national parks and monuments. Especially those in the Black Hills. South Dakota's location between western national parks and eastern cities helps its tourism. In 2006, tourism created about 33,000 jobs. It also brought over two billion U.S. dollars to the state.
Getting Around South Dakota
South Dakota has many roads and highways. It has about 83,609 miles (134,556 km) of roads. Two main interstate highways cross the state. Interstate 90 goes east and west. Interstate 29 goes north and south in the east. There are also shorter interstates, 190 and 229. Several major U.S. highways also run through the state.
Railroads have been important for transportation since the mid-1800s. A lot of railroad track was built in the past. Now, about 1,839 miles (2,959 km) of track are still used. South Dakota's biggest airports are in Sioux Falls and Rapid City.
 | Calvin Brent |
 | Walter T. Bailey |
 | Martha Cassell Thompson |
 | Alberta Jeannette Cassell |